Abstract
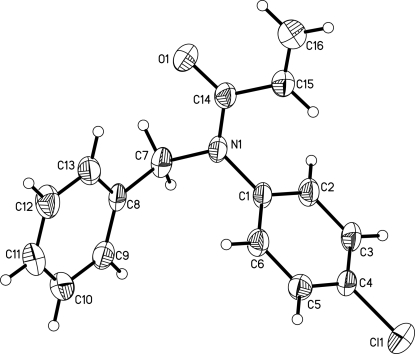
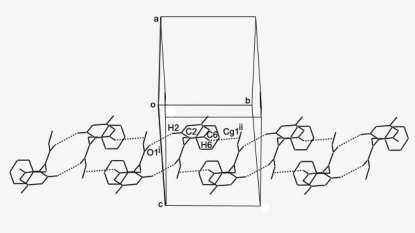
In the molecular structure of the title compound, C16H14ClNO, the acrylamide unit is essentially planar and makes dihedral angles of 80.06 (12) and 68.91 (13)°, respectively, with the benzene and phenyl rings. The dihedral angle between the two rings is 49.79 (11)°. In the crystal structure, molecules are connected via weak C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π interactions, forming a molecular tape running along the b axis.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Fairlamb (2004 ▶); Hu et al. (2003 ▶); Park & Hoffmann (1990 ▶); Otero & Cantero (1995 ▶); Riggi et al. (1992 ▶).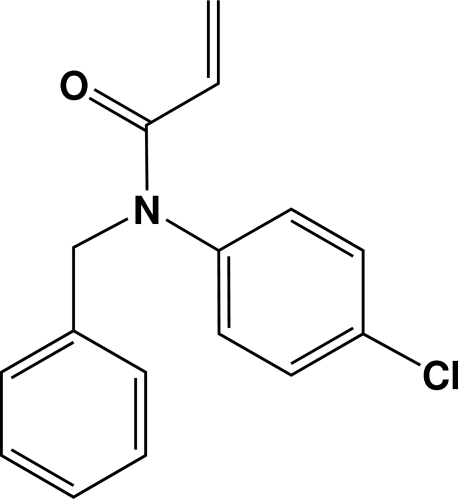
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H14ClNO
M r = 271.73
Monoclinic,
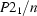
a = 9.215 (4) Å
b = 9.210 (4) Å
c = 17.090 (8) Å
β = 102.842 (6)°
V = 1414.2 (12) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.26 mm−1
T = 291 (2) K
0.30 × 0.26 × 0.24 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000 ▶) T min = 0.93, T max = 0.94
11395 measured reflections
3172 independent reflections
1666 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.057
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.064
wR(F 2) = 0.158
S = 1.06
3172 reflections
173 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.30 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT-Plus (Bruker, 2000 ▶); data reduction: SAINT-Plus; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Bruker, 2000 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680706432X/is2254sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680706432X/is2254Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the mid-point of atoms C15 and C16.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.405 (4) | 157 |
| C6—H6⋯Cg1ii | 0.93 | 3.02 | 3.75 (2) | 136 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 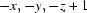 ; (ii)
; (ii) 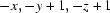 . Cg1 is the mid-point of atoms C15 and C16.
. Cg1 is the mid-point of atoms C15 and C16.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Science Foundation of Anhui Province (project No. 2004kj164zd), the Education Department of Anhui Province Program (grant Nos. 2006K J006TD and TD200707) and the National Science Foundation of China (project No. 20572001) for financial support of this work.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Many active molecules in nature contain highly functionalized heterocyclic rings (Fairlamb, 2004). In recent research, we report a novel palladium catalyzed Heck intermolecular reactions of aryl halides with the nitron-containing olefins (Hu et al., 2003). We found that polyene amide was prepared by two steps (Riggi et al., 1992). The substrate of N-benzyl-N-(4-chlorophenyl)acrylamide is used to obtain this pyrrole skeleton (Park & Hoffmann, 1990; Otero & Cantero, 1995).
In this paper, we report the crystal structure of the title compound, C16H14ClNO (Fig. 1). The crystal data show that all bond lengths and angles in the title compound have normal values. The bond length of C15=C16 is 1.288 (4) Å, belonging to typical Csp2—Csp2 double bonds. The molecule contains two six-membered rings, A (C1—C6) and B (C8—C13). Rings A and B are not coplanar, the dihedral angle between ring A and ring B being 49.79 (11)°. In the structure there are a weak intermolecular C—H···O interaction [C2—H2···O1i, symmetry code: (i) -x, -y, 1 - z] and a C—H···π interaction [C6—H6···Cg1ii, Cg1 is the centroid of atoms C15 and C16; symmetry code: (ii) -x,1 - y,1 - z]. These weak intermolecular interactions extended the title compound molecules into a one-dimensional chain structure (Fig. 2) along the b axis.
Experimental
The solution of 4-chlorobenzenamine (12.75 g, 0.1 mol) and triethylamine (14 ml, 0.1 mol) in CCl4 (20 ml) was placed in a three-necked flask equipped with reflux condenser, dropping funnel and mechanical stirrer. The 1-chloromethylbenzene (13.91 g, 0.11 mol) in CCl4 (20 ml) was added at a rate such as to produce gentle reflux at room temperature. The crude product was recrystallized from C2H5OH; yield (21.54 g, 90%). N-benzyl-4-chlorobenzenamine (10.89 g, 0.05 mol) was stirred at ice-water in the presence of 2-propenoyl chloride (4.9 ml, 0.06 mol) and triethylamine (8.4 ml, 0.06 mol) in CCl4 (20 ml). The mixture was washed with water and the organic layer was dried by MgSO4. The crude product was purified by flash column chromatography on silica gel (light petroleum/EtOAc, 8:1) to obtain the product (8.23 g, 61%). Colorless crystals of the N-benzyl-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-propanamide suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained from an ethyl acetate solution over one week.
Refinement
H atoms were placed in calculated positions with C—H distances 0.93–0.97 Å and treated as riding, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I), showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids with numbering scheme.
Fig. 2.
View of the chain packing of (I) approximately down the a axis. H atoms have been omitted except H2 and H6 for clarity [symmetry codes: (i) -x, -y, 1 - z; (ii) -x, 1 - y, 1 - z].
Crystal data
| C16H14ClNO | F000 = 568 |
| Mr = 271.73 | Dx = 1.276 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 3741 reflections |
| a = 9.215 (4) Å | θ = 2.1–25.4º |
| b = 9.210 (4) Å | µ = 0.26 mm−1 |
| c = 17.090 (8) Å | T = 291 (2) K |
| β = 102.842 (6)º | Block, colourless |
| V = 1414.2 (12) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.26 × 0.24 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3172 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: sealed tube | 1666 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.057 |
| T = 291(2) K | θmax = 27.5º |
| φ and ω scans | θmin = 2.3º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Bruker, 2000) | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.93, Tmax = 0.94 | k = −11→11 |
| 11395 measured reflections | l = −20→22 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.064 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.05P)2 + 0.55P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.158 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.06 | Δρmax = 0.30 e Å−3 |
| 3172 reflections | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
| 173 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL, Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.008 (2) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes.Least-squares planes (x,y,z in crystal coordinates) and deviations from them (* indicates atom used to define plane)9.0764 (0.0047) x - 0.6878 (0.0111) y - 1.1393 (0.0196) z = 0.3034 (0.0082)* -0.0078 (0.0020) C1 * 0.0033 (0.0020) C2 * 0.0052 (0.0021) C3 * -0.0091 (0.0020) C4 * 0.0045 (0.0020) C5 * 0.0039 (0.0020) C6Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.00604.7161 (0.0105) x - 5.4299 (0.0094) y + 8.4686 (0.0192) z = 4.7812 (0.0131)Angle to previous plane (with approximate e.s.d.) = 49.79 (0.11)* 0.0026 (0.0019) C8 * 0.0023 (0.0020) C9 * -0.0059 (0.0022) C10 * 0.0046 (0.0023) C11 * 0.0004 (0.0023) C12 * -0.0040 (0.0021) C13Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0037 |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.1090 (3) | 0.2996 (3) | 0.42821 (14) | 0.0487 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.0953 (3) | 0.2145 (3) | 0.36048 (15) | 0.0586 (8) | |
| H2 | 0.0888 | 0.1141 | 0.3641 | 0.070* | |
| C3 | 0.0913 (3) | 0.2801 (3) | 0.28706 (15) | 0.0623 (8) | |
| H3 | 0.0824 | 0.2240 | 0.2410 | 0.075* | |
| C4 | 0.1004 (3) | 0.4277 (3) | 0.28296 (15) | 0.0561 (7) | |
| C5 | 0.1168 (3) | 0.5138 (3) | 0.35022 (16) | 0.0586 (7) | |
| H5 | 0.1250 | 0.6141 | 0.3466 | 0.070* | |
| C6 | 0.1209 (3) | 0.4476 (3) | 0.42326 (16) | 0.0565 (7) | |
| H6 | 0.1318 | 0.5039 | 0.4694 | 0.068* | |
| C7 | 0.2646 (3) | 0.2115 (3) | 0.55720 (15) | 0.0607 (8) | |
| H7A | 0.3338 | 0.1858 | 0.5242 | 0.073* | |
| H7B | 0.2612 | 0.1311 | 0.5934 | 0.073* | |
| C8 | 0.3224 (3) | 0.3442 (3) | 0.60604 (15) | 0.0524 (7) | |
| C9 | 0.4397 (3) | 0.4235 (3) | 0.59152 (16) | 0.0606 (8) | |
| H9 | 0.4840 | 0.3961 | 0.5499 | 0.073* | |
| C10 | 0.4933 (4) | 0.5435 (4) | 0.63763 (19) | 0.0716 (9) | |
| H10 | 0.5720 | 0.5966 | 0.6264 | 0.086* | |
| C11 | 0.4310 (4) | 0.5840 (4) | 0.69955 (19) | 0.0747 (9) | |
| H11 | 0.4680 | 0.6637 | 0.7312 | 0.090* | |
| C12 | 0.3137 (4) | 0.5065 (4) | 0.71468 (19) | 0.0776 (10) | |
| H12 | 0.2704 | 0.5342 | 0.7566 | 0.093* | |
| C13 | 0.2590 (3) | 0.3874 (3) | 0.66831 (16) | 0.0641 (8) | |
| H13 | 0.1788 | 0.3360 | 0.6791 | 0.077* | |
| C14 | −0.0055 (3) | 0.1827 (3) | 0.52919 (16) | 0.0569 (7) | |
| C15 | −0.1547 (4) | 0.2031 (3) | 0.47419 (17) | 0.0622 (8) | |
| H15 | −0.1607 | 0.2433 | 0.4237 | 0.075* | |
| C16 | −0.2751 (4) | 0.1660 (4) | 0.4955 (2) | 0.0807 (10) | |
| H16A | −0.2702 | 0.1258 | 0.5459 | 0.097* | |
| H16B | −0.3669 | 0.1796 | 0.4604 | 0.097* | |
| Cl1 | 0.09117 (12) | 0.51004 (11) | 0.18992 (5) | 0.0938 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.1152 (3) | 0.2311 (2) | 0.50484 (12) | 0.0537 (6) | |
| O1 | 0.0044 (3) | 0.1269 (2) | 0.59589 (12) | 0.0769 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0522 (16) | 0.0546 (17) | 0.0341 (13) | −0.0008 (13) | −0.0014 (12) | −0.0025 (11) |
| C2 | 0.074 (2) | 0.0544 (17) | 0.0410 (15) | −0.0033 (15) | −0.0019 (14) | −0.0061 (12) |
| C3 | 0.073 (2) | 0.073 (2) | 0.0352 (15) | −0.0065 (16) | 0.0005 (14) | −0.0101 (13) |
| C4 | 0.0506 (17) | 0.074 (2) | 0.0385 (15) | −0.0049 (14) | −0.0020 (13) | 0.0064 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0630 (19) | 0.0550 (17) | 0.0540 (17) | −0.0017 (14) | 0.0053 (14) | 0.0020 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0683 (19) | 0.0553 (18) | 0.0420 (15) | 0.0004 (14) | 0.0036 (14) | −0.0072 (13) |
| C7 | 0.0650 (19) | 0.0652 (19) | 0.0442 (15) | 0.0101 (15) | −0.0045 (14) | 0.0000 (13) |
| C8 | 0.0536 (17) | 0.0630 (18) | 0.0326 (13) | 0.0028 (14) | −0.0074 (12) | 0.0008 (12) |
| C9 | 0.0597 (19) | 0.077 (2) | 0.0411 (15) | 0.0046 (17) | 0.0035 (14) | 0.0050 (14) |
| C10 | 0.060 (2) | 0.081 (2) | 0.066 (2) | −0.0098 (17) | −0.0038 (17) | 0.0063 (17) |
| C11 | 0.069 (2) | 0.085 (2) | 0.060 (2) | −0.0075 (19) | −0.0065 (17) | −0.0151 (17) |
| C12 | 0.079 (2) | 0.099 (3) | 0.0520 (18) | −0.004 (2) | 0.0088 (17) | −0.0219 (17) |
| C13 | 0.0554 (18) | 0.085 (2) | 0.0488 (17) | −0.0074 (16) | 0.0057 (14) | −0.0068 (15) |
| C14 | 0.074 (2) | 0.0511 (17) | 0.0410 (15) | −0.0084 (15) | 0.0031 (15) | −0.0050 (12) |
| C15 | 0.068 (2) | 0.0663 (19) | 0.0489 (17) | −0.0113 (16) | 0.0054 (15) | −0.0012 (14) |
| C16 | 0.061 (2) | 0.0653 (2) | 0.053 (2) | −0.009 (2) | 0.0097 (19) | −0.0015 (18) |
| Cl1 | 0.1158 (8) | 0.1115 (8) | 0.0498 (5) | −0.0131 (6) | 0.0093 (5) | 0.0202 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0605 (15) | 0.0593 (15) | 0.0345 (11) | −0.0032 (12) | −0.0044 (11) | −0.0001 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0958 (17) | 0.0819 (15) | 0.0480 (12) | −0.0129 (12) | 0.0052 (11) | 0.0133 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C6 | 1.372 (4) | C8—C13 | 1.382 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.380 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.383 (4) |
| C1—N1 | 1.443 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.386 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.363 (4) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.365 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.367 (5) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.376 (4) | C12—C13 | 1.381 (4) |
| C4—Cl1 | 1.747 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.382 (4) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C14—O1 | 1.235 (3) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C14—N1 | 1.347 (4) |
| C7—N1 | 1.476 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.495 (4) |
| C7—C8 | 1.509 (4) | C15—C16 | 1.288 (4) |
| C7—H7A | 0.9700 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7B | 0.9700 | C16—H16A | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.371 (4) | C16—H16B | 0.9300 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 120.4 (2) | C8—C9—C10 | 121.2 (3) |
| C6—C1—N1 | 120.2 (2) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.4 |
| C2—C1—N1 | 119.4 (2) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.4 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.4 (3) | C11—C10—C9 | 120.1 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.3 | C11—C10—H10 | 119.9 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.3 | C9—C10—H10 | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.4 (3) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.4 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.3 | C10—C11—H11 | 120.3 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.3 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.3 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.8 (3) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.6 (3) |
| C3—C4—Cl1 | 119.2 (2) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C5—C4—Cl1 | 119.0 (2) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 118.4 (3) | C12—C13—C8 | 120.5 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.8 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.8 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.8 | C8—C13—H13 | 119.8 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 120.5 (3) | O1—C14—N1 | 121.7 (3) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.8 | O1—C14—C15 | 120.1 (3) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.8 | N1—C14—C15 | 118.1 (2) |
| N1—C7—C8 | 113.8 (2) | C16—C15—C14 | 121.3 (3) |
| N1—C7—H7A | 108.8 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.4 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 108.8 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.4 |
| N1—C7—H7B | 108.8 | C15—C16—H16A | 120.0 |
| C8—C7—H7B | 108.8 | C15—C16—H16B | 120.0 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 107.7 | H16A—C16—H16B | 120.0 |
| C9—C8—C13 | 118.1 (3) | C14—N1—C1 | 123.8 (2) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 121.8 (3) | C14—N1—C7 | 119.7 (2) |
| C13—C8—C7 | 120.1 (3) | C1—N1—C7 | 116.6 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2···O1i | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.405 (4) | 157 |
| C6—H6···Cg1ii | 0.93 | 3.02 | 3.75 (2) | 136 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: IS2254).
References
- Bruker (2000). SMART (Version 5.0), SAINT-Plus (Version 6), SHELXTL (Version 6.1) and SADABS (Version 2.03). Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Fairlamb, I. J. S. (2004). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.43, 1048–1052. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-M., Zhou, J., Lian, H.-Z., Zhu, C.-J. & Pan, Y. (2003). Synthesis, pp. 1177–1180.
- Otero, T. F. & Cantero, I. (1995). J. Electroanal. Chem.395, 75–78.
- Park, T. G. & Hoffmann, A. S. (1990). Biotechnol. Bioeng.35, 152–154. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Riggi, I. D., Gastaldi, S., Surzur, J. M. & Bertrand, M. P. M. (1992). J. Org. Chem.50, 6118–6125.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97 University of Göttingen, Germany.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680706432X/is2254sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680706432X/is2254Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report