Abstract
In the title compound, C15H12F3N3, the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine system ring is essentially planar with a maximum deviation from the mean plane of 0.014 (1) Å. The 4-tolyl group makes a dihedral angle of 14.1 (1)° with the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine ring system. The crystal packing is stabilized mainly by van der Waals forces.
Related literature
For related pyrazolopyrimidine compounds, see: Wen et al. (2004 ▶, 2005 ▶); Oliveira-Campos et al. (2006 ▶). For related literature and the synthetic procedure, see: Martins et al. (2004 ▶, 2006 ▶). For the pharmacological activity, see: Almanza et al. (2001 ▶); Novinson et al. (1977 ▶); George (2001 ▶).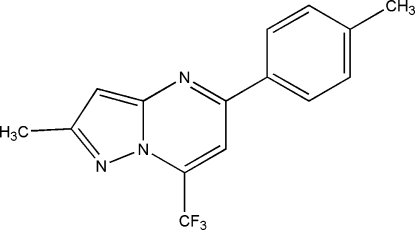
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H12F3N3
M r = 291.28
Triclinic,
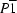
a = 4.8715 (2) Å
b = 11.2655 (5) Å
c = 13.5584 (6) Å
α = 110.225 (3)°
β = 96.808 (3)°
γ = 99.835 (3)°
V = 675.13 (5) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.12 mm−1
T = 293 (2) K
0.98 × 0.21 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker X8 APEXII diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (XPREP; Bruker, 2006 ▶) T min = 0.874, T max = 0.977
16787 measured reflections
3757 independent reflections
2200 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.040
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.057
wR(F 2) = 0.227
S = 1.05
3757 reflections
190 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2006 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2006 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807064318/xu2373sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807064318/xu2373Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq/PRONEX) and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS) for financial support. The fellowships from CNPq and CAPES are also acknowledged. The diffractometer was funded by a CT-INFRA grant from the Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos (FINEP), Brazil.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Pyrazolopyrimidine derivatives are important biologically active compounds obtained to showed anti-inflammatory (PGHS-2 inhibitors) (Almanza et al., 2001) and antifungal activities (cAMP phosphodiasterase and xanthine oxidase inhibitors) (Novinson et al., 1977). In addition, this scaffold have been found to be integral parts of potent nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic agents (George, 2001). Zaleplon is one example of a pyrazolopyrimidine derivative in clinical use (George, 2001). In a continuation of our study about synthesis and reactivity of pyrazolopyrimidine (Martins et al., 2006) as well as trihalomethylated compounds (Martins et al., 2004) we reported, in this communication, the crystal structure of the title compound, 2-methyl-5-(4-tolyl)-7-(trifluoromethyl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine.
The analysis showed that the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine ring is essentially planar with maximum deviation from mean plane of 0.014 (1) Å. The 4-tolyl group makes a dihedral angle of 14.1 (1)° with respect to the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine ring system. In addition, the dihedral angle between the five-membered ring and the fused six-membered ring is 0.84 (1)° in accordance with previous reports (Wen et al., 2004; Wen et al., 2005; Oliveira-Campos et al., 2006). The crystal packing is stabilized mainly by van der Waals forces.
Experimental
To a stirred solution of 1,1,1-trifluoro-4-methoxy-4-(4-tolyl)-but-3-en-2-one (0.244 g, 1.0 mmol) in acetic acid (5 ml) a solution containing the 5-methyl-3-amino-1H-pyrazole (0.097 g, 1.0 mmol) in acetic acid (5 ml) was added dropwise. The mixture was stirred under reflux for 16 h. After this time, the resultant solution was extracted with chloroform (3 × 10 ml), washed with distilled water (3 × 10 ml) and dried over magnesium sulfate. Finally, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and a solid was obtained in good yield (79%). The product was purified by recrystallization from hexane, the slow evaporation of this solution at room temperature furnished the crystal used for the data collection.
Refinement
All H atoms were refined using a riding model, with C—H distances set to 0.93 or 0.96 Å. Uiso(H) = xUeq(C), with x = 1.5 for methyl groups and x = 1.2 otherwise.
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the asymmetric unit of the title compound, showing the atom labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are represented by circles of arbitrary radii.
Crystal data
| C15H12F3N3 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 291.28 | F000 = 300 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.433 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Melting point = 415–416 K |
| a = 4.8715 (2) Å | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 11.2655 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 150 reflections |
| c = 13.5584 (6) Å | θ = 3.0–24.6º |
| α = 110.225 (3)º | µ = 0.12 mm−1 |
| β = 96.808 (3)º | T = 293 (2) K |
| γ = 99.835 (3)º | Block, yellow |
| V = 675.13 (5) Å3 | 0.98 × 0.21 × 0.20 mm |
Data collection
| X8 APEXII diffractometer | 2200 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.040 |
| T = 293(2) K | θmax = 29.7º |
| φ and ω scans | θmin = 1.6º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(XPREP; Bruker, 2006) | h = −6→6 |
| Tmin = 0.874, Tmax = 0.977 | k = −15→15 |
| 16787 measured reflections | l = −18→18 |
| 3757 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.057 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.227 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1373P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3757 reflections | Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3 |
| 190 parameters | Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N4 | −0.1395 (3) | 0.64063 (13) | 0.15766 (10) | 0.0437 (4) | |
| C51 | 0.2301 (3) | 0.60519 (16) | 0.27094 (13) | 0.0434 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.0595 (3) | 0.69036 (16) | 0.24463 (12) | 0.0427 (4) | |
| N1A | −0.2415 (3) | 0.85107 (14) | 0.19699 (11) | 0.0475 (4) | |
| C3A | −0.2918 (3) | 0.71919 (16) | 0.13244 (13) | 0.0443 (4) | |
| C7 | −0.0385 (4) | 0.90322 (17) | 0.28737 (15) | 0.0517 (4) | |
| N1 | −0.4126 (3) | 0.91420 (15) | 0.15720 (13) | 0.0560 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.1130 (4) | 0.82475 (17) | 0.31325 (14) | 0.0501 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.2514 | 0.8577 | 0.3753 | 0.06* | |
| C56 | 0.2277 (4) | 0.48484 (18) | 0.19505 (14) | 0.0526 (5) | |
| H56 | 0.1165 | 0.4575 | 0.1271 | 0.063* | |
| C55 | 0.3880 (4) | 0.40510 (18) | 0.21898 (15) | 0.0571 (5) | |
| H55 | 0.381 | 0.3245 | 0.1668 | 0.069* | |
| C52 | 0.4029 (4) | 0.64261 (19) | 0.37085 (15) | 0.0584 (5) | |
| H52 | 0.4097 | 0.723 | 0.4233 | 0.07* | |
| C54 | 0.5592 (4) | 0.44182 (19) | 0.31862 (15) | 0.0539 (5) | |
| C3 | −0.5081 (4) | 0.69986 (19) | 0.04969 (15) | 0.0514 (4) | |
| H3 | −0.5939 | 0.622 | −0.0068 | 0.062* | |
| C2 | −0.5725 (4) | 0.81980 (18) | 0.06756 (15) | 0.0522 (5) | |
| C53 | 0.5645 (5) | 0.5626 (2) | 0.39352 (16) | 0.0631 (5) | |
| H53 | 0.6796 | 0.5906 | 0.4608 | 0.076* | |
| C8 | 0.7329 (5) | 0.3537 (2) | 0.34284 (18) | 0.0700 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.7031 | 0.2754 | 0.2807 | 0.105* | |
| H8B | 0.6763 | 0.3327 | 0.4014 | 0.105* | |
| H8C | 0.9303 | 0.3967 | 0.3619 | 0.105* | |
| C71 | 0.0064 (5) | 1.0448 (2) | 0.3532 (2) | 0.0714 (6) | |
| C21 | −0.7881 (4) | 0.8562 (2) | 0.00171 (18) | 0.0689 (6) | |
| H21A | −0.7828 | 0.9471 | 0.0353 | 0.103* | |
| H21B | −0.9738 | 0.8064 | −0.0036 | 0.103* | |
| H21C | −0.7457 | 0.8385 | −0.0686 | 0.103* | |
| F3 | −0.2264 (3) | 1.07474 (12) | 0.38784 (11) | 0.0893 (5) | |
| F1 | 0.2076 (3) | 1.07989 (12) | 0.43939 (12) | 0.1008 (6) | |
| F2 | 0.0852 (3) | 1.11914 (12) | 0.29935 (14) | 0.1004 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N4 | 0.0444 (8) | 0.0425 (8) | 0.0452 (7) | 0.0121 (6) | 0.0056 (6) | 0.0175 (6) |
| C51 | 0.0427 (9) | 0.0434 (9) | 0.0449 (9) | 0.0114 (7) | 0.0059 (6) | 0.0177 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0430 (9) | 0.0401 (9) | 0.0447 (9) | 0.0100 (6) | 0.0078 (6) | 0.0155 (7) |
| N1A | 0.0449 (8) | 0.0430 (8) | 0.0557 (8) | 0.0131 (6) | 0.0048 (6) | 0.0197 (7) |
| C3A | 0.0449 (9) | 0.0425 (9) | 0.0476 (9) | 0.0113 (7) | 0.0081 (7) | 0.0191 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0478 (10) | 0.0399 (9) | 0.0606 (11) | 0.0105 (7) | 0.0043 (8) | 0.0121 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0507 (9) | 0.0533 (10) | 0.0723 (10) | 0.0189 (7) | 0.0068 (7) | 0.0318 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0472 (10) | 0.0425 (9) | 0.0522 (10) | 0.0106 (7) | −0.0016 (7) | 0.0109 (8) |
| C56 | 0.0583 (11) | 0.0473 (10) | 0.0510 (10) | 0.0183 (8) | 0.0021 (8) | 0.0168 (8) |
| C55 | 0.0628 (12) | 0.0511 (11) | 0.0613 (11) | 0.0257 (9) | 0.0107 (9) | 0.0201 (9) |
| C52 | 0.0654 (12) | 0.0500 (11) | 0.0530 (10) | 0.0179 (9) | −0.0029 (9) | 0.0133 (8) |
| C54 | 0.0471 (10) | 0.0617 (12) | 0.0653 (11) | 0.0200 (8) | 0.0125 (8) | 0.0346 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0495 (10) | 0.0514 (10) | 0.0526 (9) | 0.0108 (7) | 0.0018 (7) | 0.0213 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0453 (9) | 0.0570 (11) | 0.0617 (11) | 0.0134 (8) | 0.0080 (8) | 0.0310 (9) |
| C53 | 0.0654 (12) | 0.0637 (13) | 0.0580 (11) | 0.0204 (9) | −0.0065 (9) | 0.0233 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0662 (13) | 0.0779 (14) | 0.0844 (15) | 0.0355 (11) | 0.0151 (11) | 0.0438 (12) |
| C71 | 0.0619 (13) | 0.0448 (11) | 0.0919 (16) | 0.0169 (9) | −0.0039 (11) | 0.0104 (11) |
| C21 | 0.0577 (12) | 0.0765 (15) | 0.0826 (14) | 0.0196 (10) | 0.0006 (10) | 0.0442 (12) |
| F3 | 0.0826 (10) | 0.0650 (9) | 0.1014 (10) | 0.0344 (7) | 0.0122 (8) | 0.0017 (7) |
| F1 | 0.0906 (11) | 0.0543 (8) | 0.1095 (11) | 0.0197 (7) | −0.0302 (9) | −0.0132 (7) |
| F2 | 0.0970 (11) | 0.0468 (8) | 0.1534 (14) | 0.0113 (7) | 0.0153 (10) | 0.0378 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| N4—C5 | 1.316 (2) | C52—C53 | 1.379 (3) |
| N4—C3A | 1.351 (2) | C52—H52 | 0.93 |
| C51—C56 | 1.387 (2) | C54—C53 | 1.382 (3) |
| C51—C52 | 1.391 (2) | C54—C8 | 1.502 (3) |
| C51—C5 | 1.475 (2) | C3—C2 | 1.385 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.435 (2) | C3—H3 | 0.93 |
| N1A—C7 | 1.357 (2) | C2—C21 | 1.499 (3) |
| N1A—N1 | 1.3609 (19) | C53—H53 | 0.93 |
| N1A—C3A | 1.400 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.96 |
| C3A—C3 | 1.375 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.96 |
| C7—C6 | 1.351 (2) | C8—H8C | 0.96 |
| C7—C71 | 1.496 (3) | C71—F1 | 1.326 (2) |
| N1—C2 | 1.347 (2) | C71—F2 | 1.328 (3) |
| C6—H6 | 0.93 | C71—F3 | 1.330 (3) |
| C56—C55 | 1.380 (2) | C21—H21A | 0.96 |
| C56—H56 | 0.93 | C21—H21B | 0.96 |
| C55—C54 | 1.386 (3) | C21—H21C | 0.96 |
| C55—H55 | 0.93 | ||
| C5—N4—C3A | 118.71 (14) | C53—C54—C8 | 121.90 (18) |
| C56—C51—C52 | 117.46 (16) | C55—C54—C8 | 120.90 (18) |
| C56—C51—C5 | 120.61 (15) | C3A—C3—C2 | 106.06 (16) |
| C52—C51—C5 | 121.91 (15) | C3A—C3—H3 | 127 |
| N4—C5—C6 | 121.31 (15) | C2—C3—H3 | 127 |
| N4—C5—C51 | 118.72 (14) | N1—C2—C3 | 113.05 (16) |
| C6—C5—C51 | 119.96 (15) | N1—C2—C21 | 117.78 (17) |
| C7—N1A—N1 | 127.00 (15) | C3—C2—C21 | 129.17 (17) |
| C7—N1A—C3A | 120.58 (14) | C52—C53—C54 | 121.53 (17) |
| N1—N1A—C3A | 112.42 (14) | C52—C53—H53 | 119.2 |
| N4—C3A—C3 | 133.62 (16) | C54—C53—H53 | 119.2 |
| N4—C3A—N1A | 121.23 (15) | C54—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| C3—C3A—N1A | 105.15 (15) | C54—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—N1A | 118.36 (16) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C71 | 123.34 (17) | C54—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| N1A—C7—C71 | 118.31 (16) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C2—N1—N1A | 103.32 (14) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.78 (16) | F1—C71—F2 | 107.13 (18) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.1 | F1—C71—F3 | 106.74 (19) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 | F2—C71—F3 | 107.32 (18) |
| C55—C56—C51 | 120.88 (17) | F1—C71—C7 | 110.86 (17) |
| C55—C56—H56 | 119.6 | F2—C71—C7 | 112.3 (2) |
| C51—C56—H56 | 119.6 | F3—C71—C7 | 112.17 (18) |
| C56—C55—C54 | 121.77 (17) | C2—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C56—C55—H55 | 119.1 | C2—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C54—C55—H55 | 119.1 | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C53—C52—C51 | 121.14 (17) | C2—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C53—C52—H52 | 119.4 | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C51—C52—H52 | 119.4 | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C53—C54—C55 | 117.20 (17) | ||
| N4—C51—C5—C56 | −14.5 (3) | N4—C51—C5—C52 | 166.90 (16) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: XU2373).
References
- Almanza, C., Arriba, F. A., Cavalcanti, F. L., Gómez, L. A., Miralle, A., Merlos, M., Rafanell, J. G. & Forn, J. (2001). J. Med. Chem.44, 350–361. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2006). APEX2 (Version 2.1), SAINT (Version 7.34A) and XPREP (Version 2005/4). Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- George, C. F. P. (2001). Lancet, 358, 1623–1626. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Martins, M. A. P., Cunico, W., Pereira, C. M. P., Sinhorin, A. P., Flores, A. F. C., Bonacorso, H. G. & Zanatta, N. (2004). Curr. Org. Synth.1, 391–403 and references therein.
- Martins, M. A. P., Cunico, W., Scapin, E., Emmerich, D. J., Fiss, G. F., Rosa, F. A., Bonacorso, H. B., Zanatta, N. & Flores, A. F. C. (2006). Lett. Org. Chem.3, 358–362.
- Novinson, T., Robins, R. K. & Matthews, T. R. (1977). J. Med. Chem.20, 296–299. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Campos, A. M. F., Rodrigues, L. M., Kaja, M., Guilardi, S., Franca, E. de F. & Ellena, J. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o5246–o5248.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXL97 and SHELXS97 University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Wen, L.-R., Wang, S.-W., Li, M. & Guo, W.-S. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o1459–o1460.
- Wen, L.-R., Wang, S.-W., Xu, H.-Z., Zhang, X.-L., Li, M. & Liu, J.-H. (2004). Acta Cryst. E60, o1294–o1295.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807064318/xu2373sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807064318/xu2373Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



