Abstract
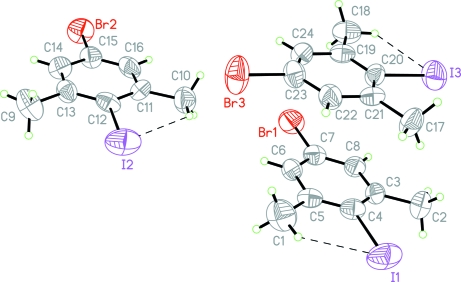
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, C8H8BrI, contains three independent molecules. In each molecule, the Br, I and C atoms of the methyl groups lie in the benzene ring plane. Intramolecular C—H⋯I hydrogen bonds result in the formation of three planar five-membered rings, which are nearly coplanar with the adjacent rings.
Related literature
For general background, see: Hu et al. (2001 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C8H8BrI
M r = 310.94
Triclinic,

a = 10.282 (2) Å
b = 11.314 (2) Å
c = 12.951 (3) Å
α = 69.27 (3)°
β = 89.11 (3)°
γ = 83.70 (3)°
V = 1400.1 (6) Å3
Z = 6
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 7.64 mm−1
T = 294 (2) K
0.10 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer
Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968 ▶) T min = 0.466, T max = 0.466
5802 measured reflections
5481 independent reflections
2809 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.042
3 standard reflections frequency: 120 min intensity decay: none
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.059
wR(F 2) = 0.133
S = 1.06
5481 reflections
271 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.76 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.72 e Å−3
Data collection: CAD-4 Software (Enraf–Nonius, 1985 ▶); cell refinement: CAD-4 Software; data reduction: XCAD4 (Harms & Wocadlo, 1995 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL (Bruker, 2000 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807064537/hk2404sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807064537/hk2404Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1—H1A⋯I1 | 0.96 | 2.70 | 3.316 (11) | 122 |
| C10—H10A⋯I2 | 0.96 | 2.70 | 3.303 (10) | 122 |
| C18—H18A⋯I3 | 0.96 | 2.63 | 3.252 (10) | 123 |
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Center of Testing and Analysis, Nanjing University, for support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound, (I), contains two different halogen groups, which can react with different groups to prepare various function organic compounds by the different reaction activity of Br and I. It is a kind of aromatic organic intermediate that can be used for many fields such as aromatic conductive polymer, organometallic chemistry (Hu et al., 2001). We herein report its crystal structure.
The asymmetric unit of (I) contains three independent molecules (Fig. 1), in which the bond lengths and angles (Table 1) are within normal ranges (Allen et al., 1987). The Br, I and C atoms of the methyl groups lie in the benzene ring planes. The intramolecular C—H···I hydrogen bonds (Table 2) result in the formations of three planar five-membered rings; B (I1/H1A/C1/C4/C5), D (I2/H10A/C10—C12) and F (I3/H18A/C18—C20). Rings A (C3—C8), C (C11—C16) and E (C19—C24) are, of course, planar and the dihedral angles between them are A/B = 1.29 (3)°, C/D = 1.73 (3)° and E/F = 1.77 (2)°. So, the adjacent rings are also nearly co-planar.
As can be seen from the packing diagram, (Fig. 2), the molecules are stacked along the b axis. The π-π interactions of benzene rings with a face-to-face stacking distance of 3.636 Å are also found.
Experimental
For the preparation of the title compound, a mixture of 4-bromo-2,6-dimethyl- aniline (4.0 g, 20 mmol), concentrated sulfuric acid (40 mmol, 2.24 ml) and water (100 ml) was stirred in an ice bath. When the mixture was below 278 K, the solution of sodium nitrite (1.75 g, 25 mmol) and water (100 ml) was added dropwise. Then, the mixture was added to a solution of KI (3.3 g, 20 mmol) and water (50 ml) with stirring. The solid residue was extracted with boiling hexane (40 ml) and hexane was distilled off. The product was recrystallized from ethanol. The crystals were obtained by dissolving (I) in ethanol (20 ml) and evaporating ethanol slowly at room temperature for about 10 d.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically, with C—H = 0.93 and 0.96 Å for aromatic and methyl H, respectively, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = xUeq(C), where x = 1.5 for methyl H, and x = 1.2 for aromatic H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Fig. 2.
A packing diagram of (I). Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C8H8BrI | Z = 6 |
| Mr = 310.94 | F000 = 864 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 2.213 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Melting point: 307 K |
| a = 10.282 (2) Å | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 11.314 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 25 reflections |
| c = 12.951 (3) Å | θ = 10–13º |
| α = 69.27 (3)º | µ = 7.64 mm−1 |
| β = 89.11 (3)º | T = 294 (2) K |
| γ = 83.70 (3)º | Block, colorless |
| V = 1400.1 (6) Å3 | 0.10 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer | Rint = 0.042 |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | θmax = 26.0º |
| Monochromator: graphite | θmin = 1.7º |
| T = 294(2) K | h = −12→12 |
| ω/2θ scans | k = −12→13 |
| Absorption correction: ψ scan(North et al., 1968) | l = 0→15 |
| Tmin = 0.466, Tmax = 0.466 | 3 standard reflections |
| 5802 measured reflections | every 120 min |
| 5481 independent reflections | intensity decay: none |
| 2809 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.059 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.133 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.050P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 5481 reflections | Δρmax = 0.76 e Å−3 |
| 271 parameters | Δρmin = −0.72 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| I1 | 0.26694 (7) | 0.30503 (8) | 0.13847 (7) | 0.0898 (3) | |
| I2 | 0.77050 (7) | 0.30518 (8) | 0.67167 (8) | 0.0901 (3) | |
| I3 | 0.74437 (8) | −0.00666 (8) | 0.03475 (6) | 0.0798 (3) | |
| Br1 | 0.90853 (10) | 0.36368 (12) | 0.15368 (10) | 0.0785 (4) | |
| Br2 | 1.40828 (10) | 0.38917 (12) | 0.62860 (10) | 0.0782 (4) | |
| Br3 | 0.75298 (12) | 0.00304 (14) | 0.54991 (9) | 0.0891 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.4494 (11) | 0.3088 (11) | 0.3459 (8) | 0.086 (4) | |
| H1A | 0.3588 | 0.3038 | 0.3332 | 0.129* | |
| H1B | 0.4573 | 0.3817 | 0.3661 | 0.129* | |
| H1C | 0.4847 | 0.2332 | 0.4046 | 0.129* | |
| C2 | 0.4834 (10) | 0.3314 (10) | −0.0588 (8) | 0.075 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.5506 | 0.3421 | −0.1127 | 0.113* | |
| H2B | 0.4144 | 0.3999 | −0.0856 | 0.113* | |
| H2C | 0.4491 | 0.2520 | −0.0459 | 0.113* | |
| C3 | 0.5415 (9) | 0.3319 (8) | 0.0497 (7) | 0.050 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.4687 (8) | 0.3180 (8) | 0.1459 (8) | 0.051 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.5241 (9) | 0.3211 (8) | 0.2418 (8) | 0.051 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.6560 (9) | 0.3308 (8) | 0.2456 (7) | 0.048 (2) | |
| H6A | 0.6955 | 0.3292 | 0.3103 | 0.058* | |
| C7 | 0.7295 (9) | 0.3430 (8) | 0.1529 (8) | 0.051 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.6722 (9) | 0.3438 (8) | 0.0557 (7) | 0.054 (2) | |
| H8A | 0.7234 | 0.3525 | −0.0059 | 0.064* | |
| C9 | 0.9707 (9) | 0.3346 (9) | 0.8546 (8) | 0.073 (3) | |
| H9A | 1.0325 | 0.3445 | 0.9050 | 0.109* | |
| H9B | 0.9362 | 0.2545 | 0.8875 | 0.109* | |
| H9C | 0.9006 | 0.4024 | 0.8382 | 0.109* | |
| C10 | 0.9673 (10) | 0.3129 (10) | 0.4659 (8) | 0.070 (3) | |
| H10A | 0.8774 | 0.2996 | 0.4818 | 0.105* | |
| H10B | 1.0117 | 0.2411 | 0.4518 | 0.105* | |
| H10C | 0.9714 | 0.3883 | 0.4020 | 0.105* | |
| C11 | 1.0326 (9) | 0.3283 (8) | 0.5637 (7) | 0.048 (2) | |
| C12 | 0.9713 (9) | 0.3258 (8) | 0.6616 (8) | 0.053 (2) | |
| C13 | 1.0378 (10) | 0.3385 (8) | 0.7501 (7) | 0.053 (2) | |
| C14 | 1.1692 (9) | 0.3532 (8) | 0.7396 (7) | 0.055 (3) | |
| H14A | 1.2160 | 0.3591 | 0.7982 | 0.066* | |
| C15 | 1.2316 (9) | 0.3594 (9) | 0.6444 (8) | 0.055 (2) | |
| C16 | 1.1665 (9) | 0.3466 (8) | 0.5572 (8) | 0.058 (3) | |
| H16A | 1.2113 | 0.3502 | 0.4934 | 0.070* | |
| C17 | 0.5044 (9) | −0.0355 (10) | 0.2075 (8) | 0.068 (3) | |
| H17A | 0.4380 | −0.0454 | 0.2619 | 0.102* | |
| H17B | 0.5147 | −0.1090 | 0.1861 | 0.102* | |
| H17C | 0.4790 | 0.0389 | 0.1440 | 0.102* | |
| C18 | 0.9888 (9) | 0.0237 (10) | 0.1763 (8) | 0.072 (3) | |
| H18A | 0.9751 | 0.0152 | 0.1062 | 0.108* | |
| H18B | 1.0562 | −0.0406 | 0.2178 | 0.108* | |
| H18C | 1.0150 | 0.1062 | 0.1647 | 0.108* | |
| C19 | 0.8630 (9) | 0.0082 (7) | 0.2397 (7) | 0.047 (2) | |
| C20 | 0.7480 (9) | −0.0034 (8) | 0.1963 (7) | 0.048 (2) | |
| C21 | 0.6322 (8) | −0.0216 (8) | 0.2552 (7) | 0.049 (2) | |
| C22 | 0.6335 (9) | −0.0184 (9) | 0.3618 (8) | 0.058 (3) | |
| H22A | 0.5577 | −0.0273 | 0.4028 | 0.070* | |
| C23 | 0.7527 (10) | −0.0012 (9) | 0.4076 (7) | 0.056 (3) | |
| C24 | 0.8632 (8) | 0.0125 (8) | 0.3466 (7) | 0.047 (2) | |
| H24A | 0.9400 | 0.0249 | 0.3765 | 0.056* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I1 | 0.0426 (4) | 0.0927 (6) | 0.1290 (8) | −0.0114 (4) | 0.0064 (4) | −0.0322 (5) |
| I2 | 0.0441 (4) | 0.0918 (6) | 0.1307 (7) | −0.0115 (4) | 0.0106 (4) | −0.0342 (5) |
| I3 | 0.0972 (6) | 0.0946 (6) | 0.0534 (4) | −0.0077 (5) | 0.0096 (4) | −0.0345 (4) |
| Br1 | 0.0446 (6) | 0.0942 (9) | 0.1125 (10) | −0.0111 (6) | 0.0070 (6) | −0.0554 (7) |
| Br2 | 0.0446 (6) | 0.0999 (9) | 0.0907 (9) | −0.0137 (6) | 0.0124 (6) | −0.0333 (7) |
| Br3 | 0.0792 (8) | 0.1468 (12) | 0.0609 (7) | −0.0395 (8) | 0.0175 (6) | −0.0538 (8) |
| C1 | 0.085 (9) | 0.101 (9) | 0.076 (8) | −0.019 (7) | 0.026 (7) | −0.034 (7) |
| C2 | 0.077 (8) | 0.089 (8) | 0.066 (7) | −0.011 (6) | −0.015 (6) | −0.034 (6) |
| C3 | 0.051 (6) | 0.045 (6) | 0.058 (6) | −0.006 (4) | −0.005 (5) | −0.023 (5) |
| C4 | 0.041 (6) | 0.048 (6) | 0.061 (6) | −0.005 (4) | 0.009 (5) | −0.014 (5) |
| C5 | 0.043 (5) | 0.048 (6) | 0.057 (6) | 0.002 (4) | 0.008 (5) | −0.014 (5) |
| C6 | 0.049 (6) | 0.055 (6) | 0.041 (5) | −0.004 (5) | 0.007 (4) | −0.019 (5) |
| C7 | 0.045 (6) | 0.038 (5) | 0.069 (7) | −0.010 (4) | 0.003 (5) | −0.018 (5) |
| C8 | 0.042 (6) | 0.069 (7) | 0.053 (6) | 0.000 (5) | 0.005 (5) | −0.028 (5) |
| C9 | 0.070 (7) | 0.084 (8) | 0.078 (7) | −0.039 (6) | 0.047 (6) | −0.040 (6) |
| C10 | 0.070 (7) | 0.081 (8) | 0.072 (7) | −0.014 (6) | −0.002 (6) | −0.039 (6) |
| C11 | 0.042 (5) | 0.053 (6) | 0.043 (5) | −0.005 (4) | −0.007 (4) | −0.010 (4) |
| C12 | 0.043 (6) | 0.047 (6) | 0.071 (7) | −0.006 (4) | 0.016 (5) | −0.026 (5) |
| C13 | 0.067 (7) | 0.048 (6) | 0.043 (6) | −0.008 (5) | 0.010 (5) | −0.017 (5) |
| C14 | 0.045 (6) | 0.062 (6) | 0.051 (6) | −0.011 (5) | 0.014 (5) | −0.012 (5) |
| C15 | 0.036 (5) | 0.071 (7) | 0.062 (6) | −0.010 (5) | 0.013 (5) | −0.029 (5) |
| C16 | 0.064 (7) | 0.059 (6) | 0.054 (6) | −0.002 (5) | 0.020 (5) | −0.024 (5) |
| C17 | 0.049 (6) | 0.093 (8) | 0.068 (7) | −0.014 (6) | −0.009 (5) | −0.033 (6) |
| C18 | 0.047 (6) | 0.082 (8) | 0.084 (8) | 0.001 (5) | 0.018 (6) | −0.030 (6) |
| C19 | 0.045 (6) | 0.034 (5) | 0.050 (6) | −0.002 (4) | 0.009 (4) | −0.002 (4) |
| C20 | 0.050 (6) | 0.056 (6) | 0.037 (5) | −0.003 (5) | −0.003 (4) | −0.017 (4) |
| C21 | 0.038 (5) | 0.048 (6) | 0.058 (6) | 0.005 (4) | 0.000 (5) | −0.015 (5) |
| C22 | 0.056 (6) | 0.068 (7) | 0.058 (6) | −0.004 (5) | 0.005 (5) | −0.032 (5) |
| C23 | 0.067 (7) | 0.061 (6) | 0.043 (6) | −0.017 (5) | 0.012 (5) | −0.021 (5) |
| C24 | 0.039 (5) | 0.061 (6) | 0.038 (5) | −0.007 (4) | 0.009 (4) | −0.015 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| I1—C4 | 2.102 (9) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| Br1—C7 | 1.881 (9) | C11—C12 | 1.399 (12) |
| C1—C5 | 1.513 (13) | C11—C16 | 1.412 (12) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9600 | C12—C13 | 1.401 (12) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9600 | C13—C14 | 1.378 (12) |
| C1—H1C | 0.9600 | C14—C15 | 1.364 (12) |
| C2—C3 | 1.537 (11) | C14—H14A | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9600 | C15—C16 | 1.380 (12) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9600 | C16—H16A | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2C | 0.9600 | I3—C20 | 2.106 (8) |
| C3—C8 | 1.372 (11) | Br3—C23 | 1.861 (9) |
| C3—C4 | 1.413 (12) | C17—C21 | 1.508 (11) |
| C4—C5 | 1.387 (12) | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.376 (12) | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.382 (11) | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9300 | C18—C19 | 1.515 (11) |
| C7—C8 | 1.395 (12) | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9300 | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| I2—C12 | 2.100 (9) | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| Br2—C15 | 1.879 (9) | C19—C20 | 1.356 (11) |
| C9—C13 | 1.498 (12) | C19—C24 | 1.402 (11) |
| C9—H9A | 0.9600 | C20—C21 | 1.399 (11) |
| C9—H9B | 0.9600 | C21—C22 | 1.394 (12) |
| C9—H9C | 0.9600 | C22—C23 | 1.431 (12) |
| C10—C11 | 1.515 (12) | C22—H22A | 0.9300 |
| C10—H10A | 0.9600 | C23—C24 | 1.365 (11) |
| C10—H10B | 0.9600 | C24—H24A | 0.9300 |
| C5—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C11—C12—C13 | 122.8 (9) |
| C5—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C11—C12—I2 | 117.3 (7) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C13—C12—I2 | 119.9 (7) |
| C5—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C14—C13—C12 | 118.1 (8) |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C14—C13—C9 | 119.9 (9) |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C12—C13—C9 | 122.0 (9) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.5 | C15—C14—C13 | 120.8 (9) |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C15—C14—H14A | 119.6 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C13—C14—H14A | 119.6 |
| C3—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C14—C15—C16 | 121.2 (9) |
| H2A—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C14—C15—Br2 | 120.2 (7) |
| H2B—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C16—C15—Br2 | 118.6 (7) |
| C8—C3—C4 | 117.2 (8) | C15—C16—C11 | 120.7 (8) |
| C8—C3—C2 | 118.9 (9) | C15—C16—H16A | 119.6 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 123.9 (9) | C11—C16—H16A | 119.6 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 122.3 (8) | C21—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—I1 | 119.4 (7) | C21—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—I1 | 118.2 (7) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.0 (9) | C21—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C1 | 116.9 (9) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C1 | 124.0 (9) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.7 (9) | C19—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 120.2 | C19—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 120.2 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 120.9 (8) | C19—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—Br1 | 120.6 (7) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—Br1 | 118.4 (7) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C3—C8—C7 | 120.9 (9) | C20—C19—C24 | 118.0 (8) |
| C3—C8—H8A | 119.5 | C20—C19—C18 | 123.2 (9) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 119.5 | C24—C19—C18 | 118.7 (8) |
| C13—C9—H9A | 109.5 | C19—C20—C21 | 123.6 (8) |
| C13—C9—H9B | 109.5 | C19—C20—I3 | 118.8 (7) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 | C21—C20—I3 | 117.5 (6) |
| C13—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C22—C21—C20 | 117.8 (8) |
| H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C22—C21—C17 | 118.3 (8) |
| H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C20—C21—C17 | 123.8 (8) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 109.5 | C21—C22—C23 | 119.3 (8) |
| C11—C10—H10B | 109.5 | C21—C22—H22A | 120.4 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 | C23—C22—H22A | 120.4 |
| C11—C10—H10C | 109.5 | C24—C23—C22 | 119.9 (8) |
| H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 | C24—C23—Br3 | 121.3 (7) |
| H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 | C22—C23—Br3 | 118.8 (7) |
| C12—C11—C16 | 116.3 (8) | C23—C24—C19 | 121.2 (8) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 125.5 (9) | C23—C24—H24A | 119.4 |
| C16—C11—C10 | 118.1 (8) | C19—C24—H24A | 119.4 |
| C8—C3—C4—C5 | 2.5 (13) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 2.0 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −178.9 (9) | C9—C13—C14—C15 | −178.8 (8) |
| C8—C3—C4—I1 | 178.2 (7) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −2.3 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4—I1 | −3.1 (12) | C13—C14—C15—Br2 | 176.4 (7) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −3.7 (14) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.7 (15) |
| I1—C4—C5—C6 | −179.4 (6) | Br2—C15—C16—C11 | −177.9 (7) |
| C3—C4—C5—C1 | 179.0 (9) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 0.9 (13) |
| I1—C4—C5—C1 | 3.3 (13) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | −179.1 (9) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 2.9 (14) | C24—C19—C20—C21 | −5.4 (13) |
| C1—C5—C6—C7 | −179.6 (8) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 178.0 (9) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.9 (13) | C24—C19—C20—I3 | 178.9 (6) |
| C5—C6—C7—Br1 | 177.3 (7) | C18—C19—C20—I3 | 2.2 (12) |
| C4—C3—C8—C7 | −0.4 (13) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | 4.8 (14) |
| C2—C3—C8—C7 | −179.2 (8) | I3—C20—C21—C22 | −179.4 (6) |
| C6—C7—C8—C3 | −0.3 (14) | C19—C20—C21—C17 | −179.5 (9) |
| Br1—C7—C8—C3 | −178.6 (7) | I3—C20—C21—C17 | −3.7 (12) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | −1.1 (13) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | −2.1 (14) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 178.9 (9) | C17—C21—C22—C23 | −178.1 (8) |
| C16—C11—C12—I2 | 177.9 (6) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | 0.3 (14) |
| C10—C11—C12—I2 | −2.1 (12) | C21—C22—C23—Br3 | 179.9 (7) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.3 (14) | C22—C23—C24—C19 | −1.0 (14) |
| I2—C12—C13—C14 | −179.3 (7) | Br3—C23—C24—C19 | 179.5 (6) |
| C11—C12—C13—C9 | −179.5 (8) | C20—C19—C24—C23 | 3.4 (13) |
| I2—C12—C13—C9 | 1.5 (12) | C18—C19—C24—C23 | −179.8 (8) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C1—H1A···I1 | 0.96 | 2.70 | 3.316 (11) | 122 |
| C10—H10A···I2 | 0.96 | 2.70 | 3.303 (10) | 122 |
| C18—H18A···I3 | 0.96 | 2.63 | 3.252 (10) | 123 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HK2404).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bruker (2000). SHELXTL Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Enraf–Nonius (1985). CAD-4 Software. Version 5.0. Enraf–Nonius, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Harms, K. & Wocadlo, S. (1995). XCAD4 University of Marburg, Germany.
- Hu, Y., Ishikawa, Y., Hirai, K. & Tomioka, H. (2001). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 74, 2207–2218.
- North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C. & Mathews, F. S. (1968). Acta Cryst. A24, 351–359.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97 University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807064537/hk2404sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807064537/hk2404Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report