Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title salt, C4H12N2 2+·2C7H4NO4 − or pipzH2 2+·2(py-2,3-dcH−), prepared by a reaction between pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid (py-2,3-dcH2) and piperazine (pipz), contains a monoanion and half of a centrosymmetric dication. The anionic fragment individually has two intramolecular hydrogen bonds, an almost linear O—H⋯O bond between two carboxylate groups and a C—H⋯O bond between the aromatic ring and carboxylate group. Other O—H⋯O, N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are responsible for three-dimensional expansion of the structure.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Aghabozorg et al. (2006 ▶); Aghabozorg, Daneshvar et al. (2007 ▶); Aghabozorg, Sadr-khanlou et al. (2007 ▶); Khalil & Attia (1999 ▶); Manteghi et al. (2007 ▶).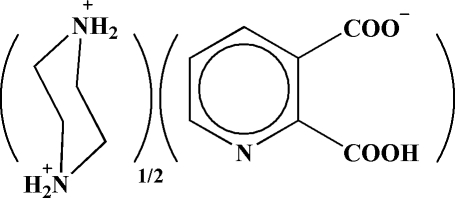
Experimental
Crystal data
C4H12N2 2+·2C7H4NO4 −
M r = 420.38
Monoclinic,
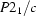
a = 8.0116 (6) Å
b = 11.0588 (9) Å
c = 10.4621 (7) Å
β = 106.574 (2)°
V = 888.42 (11) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.13 mm−1
T = 100 (2) K
0.20 × 0.15 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
6962 measured reflections
2341 independent reflections
2104 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.015
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.034
wR(F 2) = 0.084
S = 1.03
2341 reflections
136 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2; data reduction: APEX2; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 1998 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL and Mercury (Version 1.4.2; Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807065002/om2187sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807065002/om2187Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3—H3O⋯O1 | 0.85 | 1.57 | 2.4219 (11) | 175 |
| N2—H2A⋯O2i | 0.90 | 1.94 | 2.7778 (12) | 154 |
| N2—H2B⋯O1 | 0.90 | 1.97 | 2.7571 (11) | 146 |
| C3—H3A⋯O4 | 0.95 | 2.31 | 2.6773 (13) | 102 |
| C8—H8A⋯O2ii | 0.99 | 2.58 | 3.2982 (13) | 130 |
| C9—H9A⋯O4iii | 0.99 | 2.39 | 3.3491 (14) | 163 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 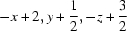 ; (ii)
; (ii) 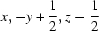 ; (iii)
; (iii) 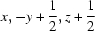 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
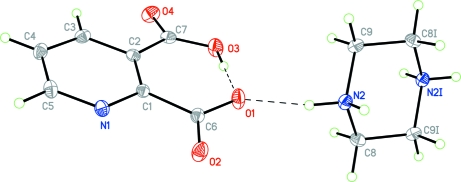
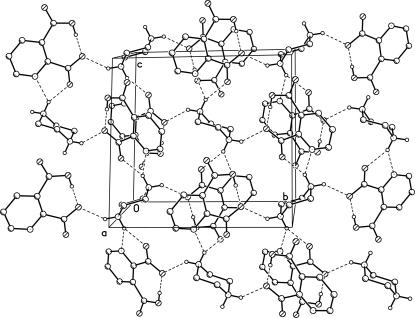
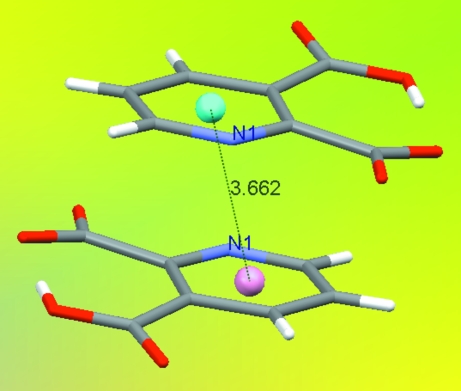
Pyridinedicarboxylic acids are of great interest in medicinal chemistry because of the wide variety of their physiological properties displayed by natural as well as synthetic acids. These acids are present in many natural products, such as alkaloids, vitamins and coenzymes. Pyridinedicarboxylic acid metal complexes are therefore, especially interesting model systems (Khalil & Attia, 1999). Pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid (py-2,3-dcH2) and piperazine (pipz) with other acids and bases are found in many ion pairs, such as (pipzH2)2(pydc) (Aghabozorg et al., 2006) and (pnH2)(py-2,3-dc).H2O (Manteghi et al., 2007). Moreover, a polymeric complex {(pipzH2)[Zn(py-2,3-dc)2].4H2O}n including fragments of the title zwitterion has been synthesized (Aghabozorg, Daneshvar et al., 2007). In all mentioned compounds, piperazine is biprotonated and pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid is doubly deprotonated. But in the title ion pair and a complex formulated as [Zn(py-2,3-dcH)2(H2O)2] (Aghabozorg, Sadr-khanlou et al., 2007), pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid is singly deprotonated. Fig. 1 shows the monoanion and the dication and the strong intramolecular hydrogen bond (see table of hydrogen-bond geometry). Fig. 2 illustrates the hydrogen bonded layers parallel to bc plane. The title ion pair has three C—H···O hydrogen bonds amongst them the C3—H3A···O4 has a short distance (H···O, 2.31 Å) compared with common C—H···O bonds, although its angle is far from linearity. Additionally, as shown in Fig. 3, the ion pair has a π-π stacking at the distance of 3.6623 (7) Å between the π-rings (symmetry code: 1 - x, -y, 1 - z).
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized via reaction of 1.67 g (10 mmol) of pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid with 0.86 g (20 mmol) piperazine in a teterahydrofuran (THF) solution (50 ml). After a while, the obtained white precipitate was filtered out and dissolved in water to recrystallize. Colorless crystals of the title compound were obtained after 1 week.
Refinement
The H(N) and H(O) atoms were found from difference Fourier map. The H(C) atom positions were calculated. All the hydrogen atoms were refined in isotropic approximatiom within riding model with the Uiso(H) parameters equal to 1.2Ueq(Ci), 1.2Ueq(Nj) and 1.5Ueq(O) where U(Ci), U(Cj) and U(O) are the equivalent thermal parameters of the carbon, nitrogen and oxygen atoms correspondingly to which corresponding H atoms are bonded.
Figures
Fig. 1.
A view of the ion pair drawn at 50% probability level. Symmetry related atoms are labeled "i" and are generated by 2 - x, 1 - y, 1 - z. Some of the hydrogen bonds are shown and are depicted by dashed lines.
Fig. 2.
Hydrogen bonded layers parallel to bc plane. Hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity except those involved in hydrogen bonding.
Fig. 3.
The π-π stacking at the distance of 3.6623 (7) Å (symmetry code: 1 - x, -y, 1 - z).
Crystal data
| C4H12N22+·2C7H4NO4− | F(000) = 440 |
| Mr = 420.38 | Dx = 1.571 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2095 reflections |
| a = 8.0116 (6) Å | θ = 2.7–28.6° |
| b = 11.0588 (9) Å | µ = 0.13 mm−1 |
| c = 10.4621 (7) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 106.574 (2)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 888.42 (11) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.15 × 0.15 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII diffractometer | 2104 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.015 |
| graphite | θmax = 29.0°, θmin = 2.7° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −10→10 |
| 6962 measured reflections | k = −15→15 |
| 2341 independent reflections | l = −14→12 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.034 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.084 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.035P)2 + 0.450P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2341 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 136 parameters | Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.88615 (11) | 0.17340 (7) | 0.51531 (8) | 0.02036 (18) | |
| O2 | 0.98274 (10) | 0.08122 (7) | 0.70930 (8) | 0.02041 (18) | |
| O3 | 0.72179 (11) | 0.13267 (7) | 0.28657 (8) | 0.02033 (18) | |
| H3O | 0.7842 | 0.1467 | 0.3657 | 0.030* | |
| O4 | 0.54664 (10) | −0.00934 (8) | 0.17740 (8) | 0.02126 (18) | |
| N1 | 0.77161 (11) | −0.10247 (8) | 0.63974 (9) | 0.01409 (18) | |
| N2 | 0.98062 (11) | 0.40793 (8) | 0.59237 (8) | 0.01352 (17) | |
| H2A | 1.0047 | 0.4441 | 0.6726 | 0.016* | |
| H2B | 0.9555 | 0.3300 | 0.6036 | 0.016* | |
| C1 | 0.76624 (12) | −0.02324 (8) | 0.54104 (10) | 0.01174 (18) | |
| C2 | 0.65530 (12) | −0.04141 (9) | 0.41030 (10) | 0.01209 (19) | |
| C3 | 0.54476 (13) | −0.14260 (9) | 0.39063 (10) | 0.0147 (2) | |
| H3A | 0.4655 | −0.1565 | 0.3052 | 0.018* | |
| C4 | 0.54919 (13) | −0.22223 (9) | 0.49329 (11) | 0.0161 (2) | |
| H4A | 0.4736 | −0.2902 | 0.4802 | 0.019* | |
| C5 | 0.66802 (14) | −0.19939 (9) | 0.61616 (10) | 0.0160 (2) | |
| H5A | 0.6760 | −0.2552 | 0.6867 | 0.019* | |
| C6 | 0.88903 (13) | 0.08412 (9) | 0.59330 (10) | 0.01317 (19) | |
| C7 | 0.63871 (13) | 0.03075 (9) | 0.28268 (10) | 0.01448 (19) | |
| C8 | 1.13286 (13) | 0.40868 (9) | 0.53727 (10) | 0.0146 (2) | |
| H8A | 1.1067 | 0.3580 | 0.4560 | 0.018* | |
| H8B | 1.2353 | 0.3736 | 0.6036 | 0.018* | |
| C9 | 0.82508 (13) | 0.46401 (9) | 0.49653 (10) | 0.0147 (2) | |
| H9A | 0.7270 | 0.4659 | 0.5365 | 0.018* | |
| H9B | 0.7892 | 0.4149 | 0.4141 | 0.018* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0283 (4) | 0.0139 (3) | 0.0167 (4) | −0.0056 (3) | 0.0029 (3) | 0.0024 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0234 (4) | 0.0200 (4) | 0.0146 (4) | −0.0074 (3) | 0.0003 (3) | 0.0013 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0268 (4) | 0.0184 (4) | 0.0135 (3) | −0.0025 (3) | 0.0021 (3) | 0.0034 (3) |
| O4 | 0.0197 (4) | 0.0294 (4) | 0.0129 (4) | −0.0027 (3) | 0.0019 (3) | 0.0005 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0165 (4) | 0.0130 (4) | 0.0133 (4) | 0.0001 (3) | 0.0051 (3) | 0.0006 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0147 (4) | 0.0136 (4) | 0.0120 (4) | −0.0018 (3) | 0.0033 (3) | 0.0006 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0120 (4) | 0.0110 (4) | 0.0129 (4) | 0.0007 (3) | 0.0047 (3) | −0.0008 (3) |
| C2 | 0.0119 (4) | 0.0128 (4) | 0.0123 (4) | 0.0023 (3) | 0.0047 (3) | −0.0005 (3) |
| C3 | 0.0124 (4) | 0.0162 (4) | 0.0158 (5) | 0.0002 (3) | 0.0044 (4) | −0.0040 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0160 (4) | 0.0131 (4) | 0.0209 (5) | −0.0022 (3) | 0.0082 (4) | −0.0034 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0202 (5) | 0.0125 (4) | 0.0171 (5) | −0.0004 (4) | 0.0084 (4) | 0.0011 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0136 (4) | 0.0123 (4) | 0.0145 (4) | −0.0005 (3) | 0.0054 (3) | −0.0009 (3) |
| C7 | 0.0130 (4) | 0.0181 (5) | 0.0128 (4) | 0.0035 (3) | 0.0044 (3) | 0.0017 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0143 (4) | 0.0156 (4) | 0.0143 (4) | 0.0032 (3) | 0.0046 (4) | 0.0000 (3) |
| C9 | 0.0113 (4) | 0.0181 (5) | 0.0138 (4) | −0.0013 (3) | 0.0023 (3) | 0.0003 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C6 | 1.2769 (12) | C2—C3 | 1.4053 (14) |
| O2—C6 | 1.2319 (12) | C2—C7 | 1.5284 (14) |
| O3—C7 | 1.3036 (13) | C3—C4 | 1.3815 (15) |
| O3—H3O | 0.8501 | C3—H3A | 0.9500 |
| O4—C7 | 1.2209 (13) | C4—C5 | 1.3872 (15) |
| N1—C5 | 1.3348 (13) | C4—H4A | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.3456 (12) | C5—H5A | 0.9500 |
| N2—C8 | 1.4903 (13) | C8—C9i | 1.5129 (14) |
| N2—C9 | 1.4933 (13) | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| N2—H2A | 0.9000 | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| N2—H2B | 0.9000 | C9—C8i | 1.5129 (14) |
| C1—C2 | 1.4169 (13) | C9—H9A | 0.9900 |
| C1—C6 | 1.5394 (13) | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| C7—O3—H3O | 110.0 | N1—C5—H5A | 118.5 |
| C5—N1—C1 | 119.93 (9) | C4—C5—H5A | 118.5 |
| C8—N2—C9 | 110.87 (7) | O2—C6—O1 | 122.99 (9) |
| C8—N2—H2A | 112.1 | O2—C6—C1 | 118.55 (9) |
| C9—N2—H2A | 110.9 | O1—C6—C1 | 118.44 (9) |
| C8—N2—H2B | 107.1 | O4—C7—O3 | 120.92 (9) |
| C9—N2—H2B | 108.1 | O4—C7—C2 | 118.56 (9) |
| H2A—N2—H2B | 107.5 | O3—C7—C2 | 120.51 (9) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 121.50 (9) | N2—C8—C9i | 110.92 (8) |
| N1—C1—C6 | 110.63 (8) | N2—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 127.85 (9) | C9i—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 116.74 (9) | N2—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C7 | 113.19 (8) | C9i—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C7 | 130.06 (9) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.0 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.22 (9) | N2—C9—C8i | 110.15 (8) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 119.4 | N2—C9—H9A | 109.6 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 119.4 | C8i—C9—H9A | 109.6 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 117.58 (9) | N2—C9—H9B | 109.6 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 121.2 | C8i—C9—H9B | 109.6 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 121.2 | H9A—C9—H9B | 108.1 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 122.94 (9) | ||
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | −1.52 (14) | N1—C1—C6—O2 | 5.34 (13) |
| C5—N1—C1—C6 | 176.91 (9) | C2—C1—C6—O2 | −176.36 (10) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 3.28 (14) | N1—C1—C6—O1 | −173.07 (9) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −174.85 (9) | C2—C1—C6—O1 | 5.23 (15) |
| N1—C1—C2—C7 | −174.82 (9) | C3—C2—C7—O4 | −6.01 (13) |
| C6—C1—C2—C7 | 7.04 (16) | C1—C2—C7—O4 | 172.15 (10) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −2.13 (14) | C3—C2—C7—O3 | 174.22 (9) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | 176.30 (9) | C1—C2—C7—O3 | −7.62 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.66 (15) | C9—N2—C8—C9i | 57.28 (11) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | −1.56 (15) | C8—N2—C9—C8i | −56.84 (11) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 2.64 (15) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3—H3O···O1 | 0.85 | 1.57 | 2.4219 (11) | 175 |
| N2—H2A···O2ii | 0.90 | 1.94 | 2.7778 (12) | 154 |
| N2—H2B···O1 | 0.90 | 1.97 | 2.7571 (11) | 146 |
| C3—H3A···O4 | 0.95 | 2.31 | 2.6773 (13) | 102 |
| C8—H8A···O2iii | 0.99 | 2.58 | 3.2982 (13) | 130 |
| C9—H9A···O4iv | 0.99 | 2.39 | 3.3491 (14) | 163 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (iii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iv) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: OM2187).
References
- Aghabozorg, H., Daneshvar, S., Motyeian, E., Ghadermazi, M. & Attar Gharamaleki, J. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, m2468–m2469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Aghabozorg, H., Ghadermazi, M., Manteghi, F. & Nakhjavan, B. (2006). Z Anorg. Allg. Chem.632, 2058–2064.
- Aghabozorg, H., Sadr-khanlou, E., Soleimannejad, J. & Adams, H. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, m1769.
- Bruker (2005). APEX2. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Khalil, M. M. & Attia, A. E. (1999). J Chem Eng Data, 44, 180.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst.39, 453–457.
- Manteghi, F., Ghadermazi, M. & Aghabozorg, H. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o2809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1998). SHELXTL. Version 5.10. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807065002/om2187sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807065002/om2187Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report