Abstract
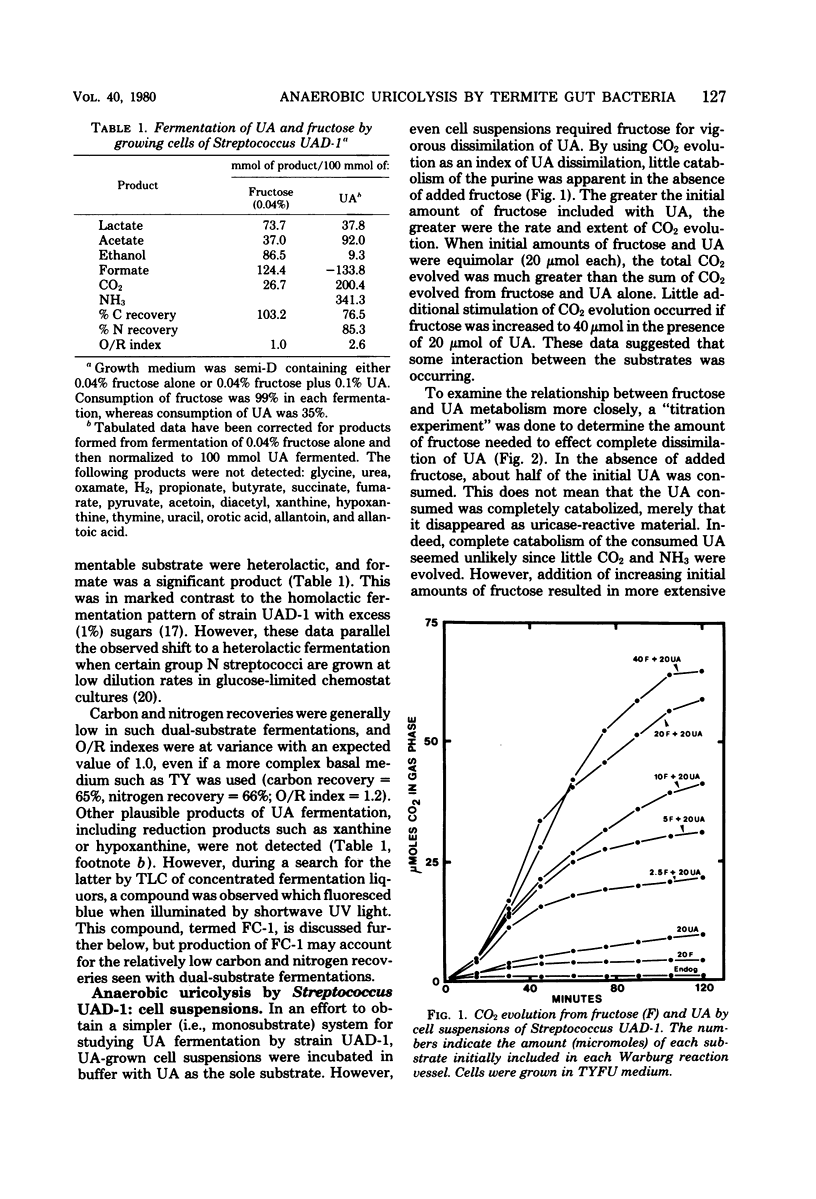
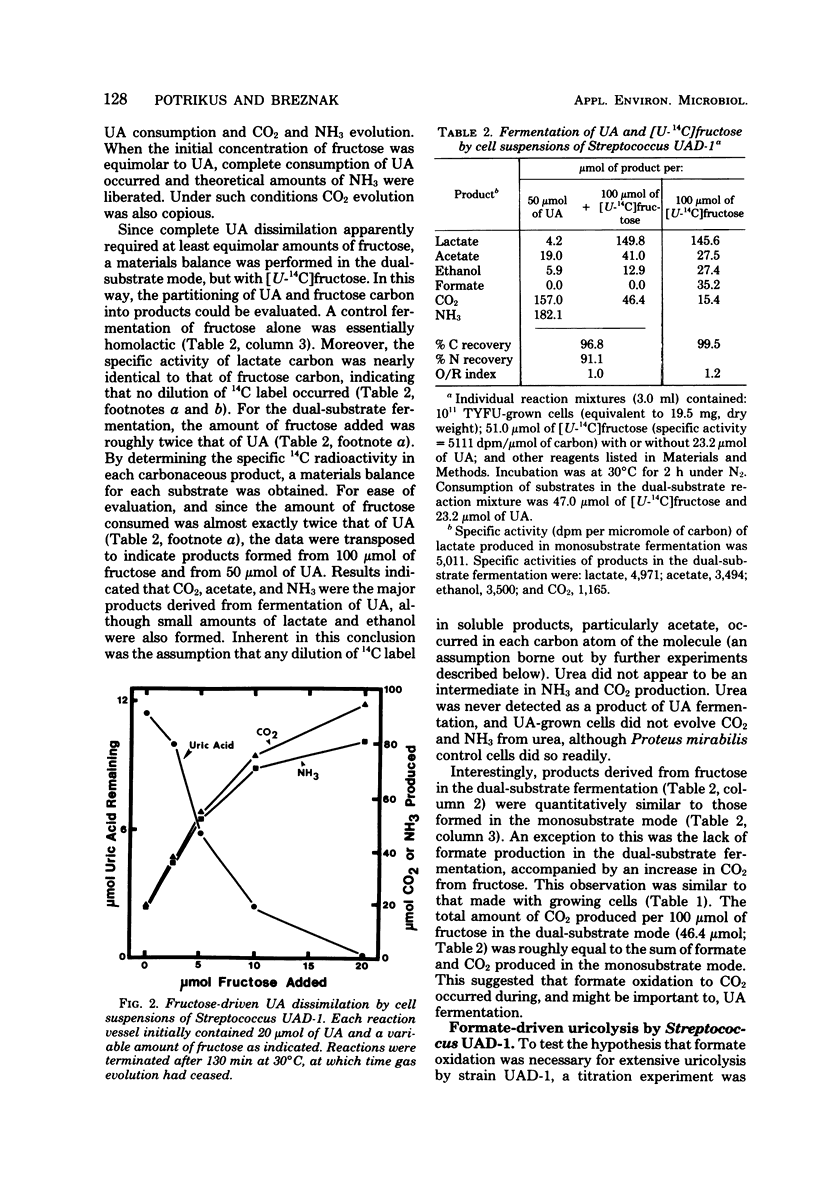
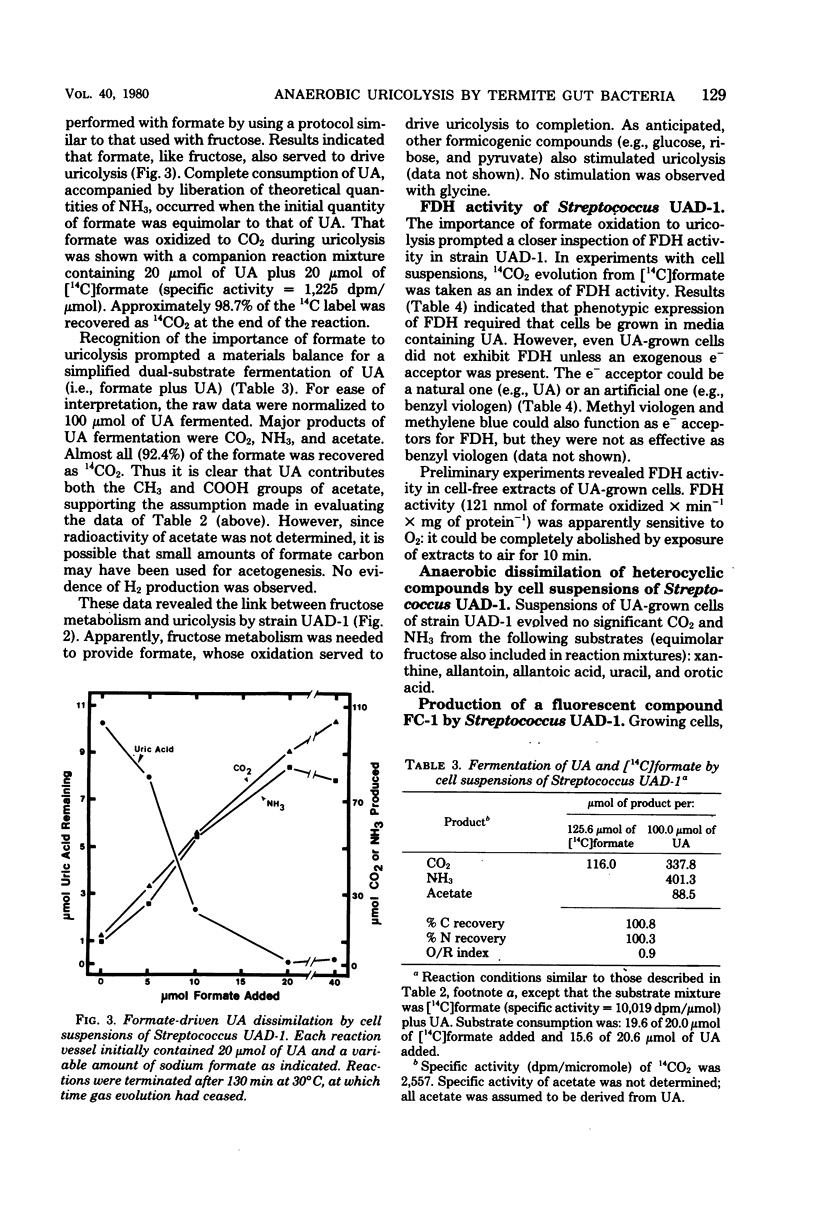
A study was done of anaerobic degradation of uric acid (UA) by representative strains of uricolytic bacteria isolated from guts of Reticulitermes flavipes termites. Streptococcus strain UAD-1 degraded UA incompletely, secreting a fluorescent compound into the medium, unless formate (or a formicogenic compound) was present as a cosubstrate. Formate functioned as a reductant, and its oxidation to CO2 by formate dehydrogenase provided 2H+ + 2e− needed to drive uricolysis to completion. Uricolysis by Streptococcus UAD-1 thus corresponded to the following equation: 1UA + 1formate → 4CO2 + 1acetate + 4NH3. Urea did not appear to be an intermediate in CO2 and NH3 formation during uricolysis by strain UAD-1. Formate dehydrogenase and uricolytic activities of strain UAD-1 were inducible by growth of cells on UA. Bacteroides termitidis strain UAD-50 degraded UA as follows: 1UA → 3.5 CO2 + 0.75acetate + 4NH3. Exogenous formate was neither required for nor stimulatory to uricolysis by strain UAD-50. Studies of UA catabolism by Citrobacter strains were limited, because only small amounts of UA were metabolized by cells in liquid medium. Uricolytic activity of such bacteria in situ could be important to the carbon, nitrogen, and energy economy of R. flavipes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreesen J. R., Ljungdahl L. G. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dependent formate dehydrogenase from Clostridium thermoaceticum: purification and properties. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):6–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.6-14.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes E. M., Impey C. S. The occurence and properties of uric acid decomposing anaerobic bacteria in the avian caecum. J Appl Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;37(3):393–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1974.tb00455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion A. B., Rabinowitz J. C. Ferredoxin and formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase: comparative studies with Clostridium acidiurici, Clostridium cylindrosporum, and newly isolated anaerobic uric acid-fermenting strains. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):1003–1020. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.1003-1020.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch H. G., Lester R. L. The purification and properties of formate dehydrogenase and nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6693–6705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead G. C. Anaerobic utilization of uric acid by some group D streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jun;82(2):421–423. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-2-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen A., Tindall A. Uric acid metabolism in the caeca of grouse (Lagopus lagopus) [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:159P–160P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potrikus C. J., Breznak J. A. Nitrogen-fixing Enterobacter agglomerans isolated from guts of wood-eating termites. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):392–399. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.392-399.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potrikus C. J., Breznak J. A. Uric Acid-Degrading Bacteria in Guts of Termites [Reticulitermes flavipes (Kollar)]. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):117–124. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.117-124.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D., Ellwood D. C., Longyear V. M. Change from homo- to heterolactic fermentation by Streptococcus lactis resulting from glucose limitation in anaerobic chemostat cultures. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):109–117. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.109-117.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C., WOLFE R. S. Phosphorolysis of carbamyl oxamic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Dec 4;45:389–391. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91467-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogels G. D., Van der Drift C. Degradation of purines and pyrimidines by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Jun;40(2):403–468. doi: 10.1128/br.40.2.403-468.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITELEY H. R., DOUGLAS H. C. The fermentation of purines by Micrococcus lactilyticus. J Bacteriol. 1951 May;61(5):605–616. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.5.605-616.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R., Andreesen J. R. Differentiation between Clostridium acidiurici and Clostridium cylindrosporum on the basis of specific metal requirements for formate dehydrogenase formation. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Sep 28;114(3):219–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00446865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


