Abstract
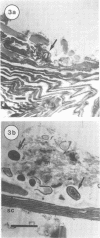
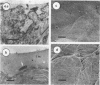
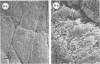
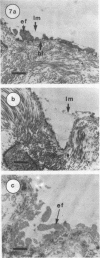
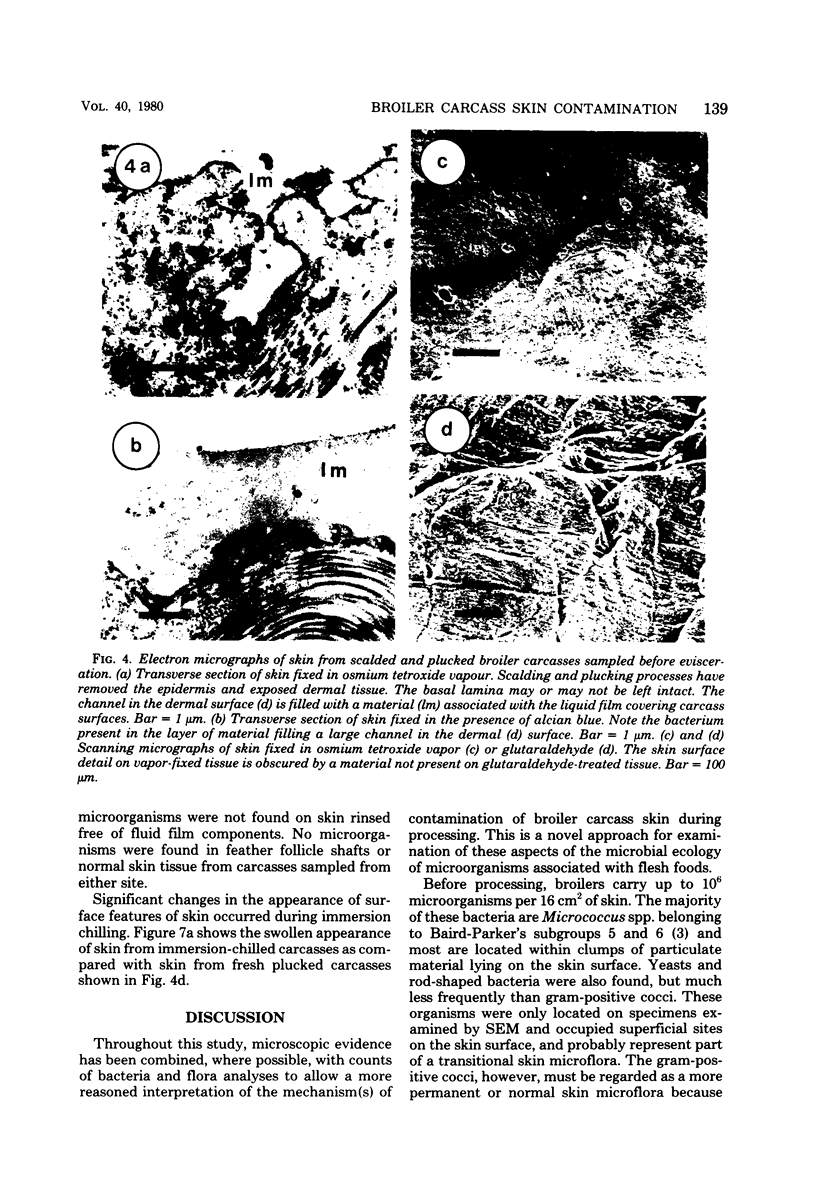
Scanning and transmission electron microscopy were used in conjunction with normal microbiological cultural techniques to examine some aspects of contamination of broiler carcass skin by bacteria during processing. The autochthonous skin microflora of poultry, before processing, was mainly Micrococcus spp. which were located in accumulations of sebum-like substances on the surface of the stratum corneum. During scalding and plucking, the skin epidermis was removed, and exposed dermal tissue was contaminated by microorganisms from the mechanical plucker and subsequent stages of processing. Major sources of psychrotrophic contamination were the immersion washer and chiller water. Microbial contaminants were found within a fluid film on the skin surface and inside deep skin channels. Skin microtopography and the presence of the liquid film were implicated as major factors controlling contamination during processing.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
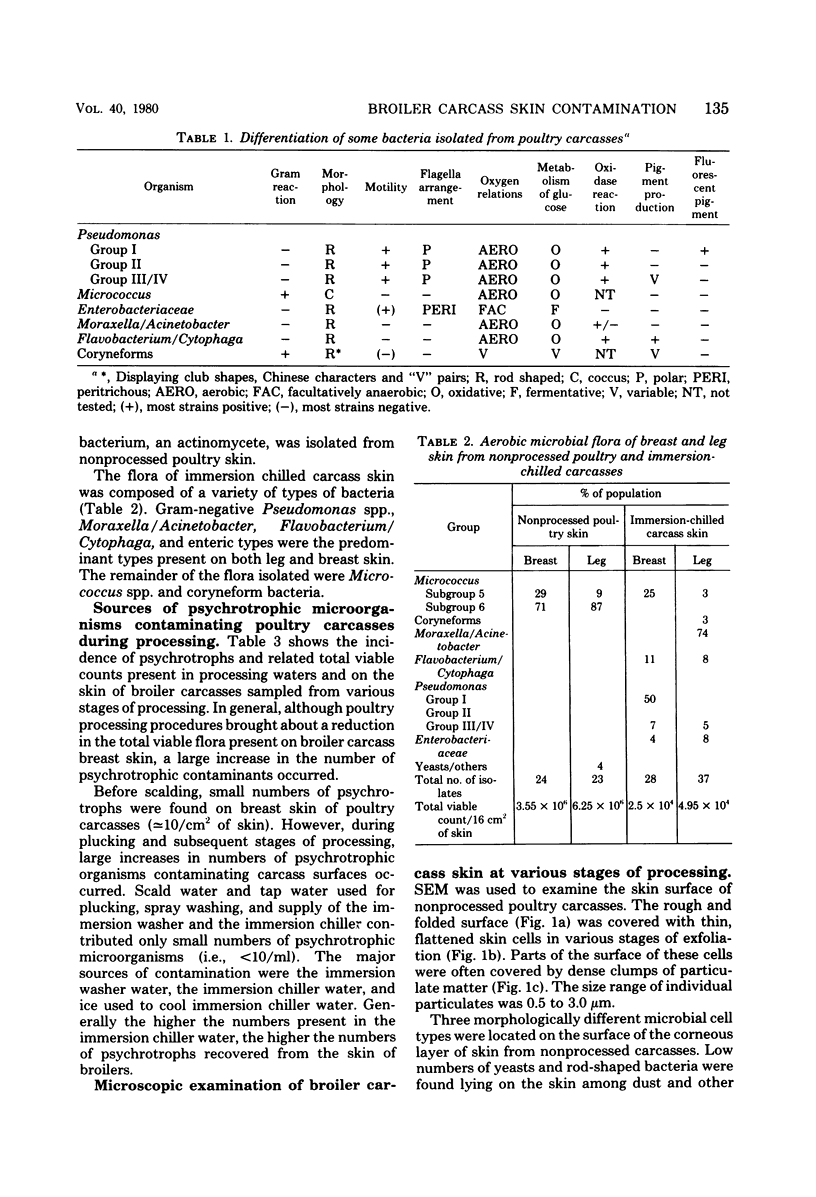
- Avens J. S., Miller B. F. Quantifying bacteria on poultry carcass skin. Poult Sci. 1970 Sep;49(5):1309–1315. doi: 10.3382/ps.0491309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIRD-PARKER A. C. A classification of micrococci and staphylococci based on physiological and biochemical tests. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:409–427. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNES E. M. Bacteriological problems in broiler preparation and storage. R Soc Health J. 1960 May-Jun;80:145–148. doi: 10.1177/146642406008000314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes E. M. Microbiological problems of poultry at refrigerator temperatures--a review. J Sci Food Agric. 1976 Aug;27(8):777–782. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740270813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. S. Growth of psychrotolerant psudomonads and achromobacter on chicken skin. Poult Sci. 1968 Sep;47(5):1575–1578. doi: 10.3382/ps.0471575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daud H. B., McMeekin T. A., Thomas C. J. Spoilage association of chicken skin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):399–401. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.399-401.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLAUERT A. M., GLAUERT R. H. Araldite as an embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Mar 25;4(2):191–194. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGH R., LEIFSON E. The taxonomic significance of fermentative versus oxidative metabolism of carbohydrates by various gram negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):24–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.1.24-26.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVACS N. Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction. Nature. 1956 Sep 29;178(4535):703–703. doi: 10.1038/178703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matoltsy A. G. Keratinization of the avian epidermis: an ultrastructural study of the newborn chick skin. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Dec;29(5):438–458. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMeekin T. A., Thomas C. J., McCall D. Scanning electron microscopy of microorganisms on chicken skin. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;46(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb02600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMeekin T. A., Thomas C. J. Retention of bacteria on chicken skin after immersion in bacterial suspensions. J Appl Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;45(3):383–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1978.tb04239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead G. C., Adams B. W., Parry R. T. The effectiveness of in-plant chlorination in poultry processing. Br Poult Sci. 1975 Sep;16(5):517–526. doi: 10.1080/00071667508416220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead G. C., Impey C. S. The distribution of clostridia in poultry processing plants. Br Poult Sci. 1970 Jul;11(3):407–414. doi: 10.1080/00071667008415831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead G. C. Microbiology of the poultry carcass and processing plant. R Soc Health J. 1976 Aug;96(4):164-7, 192. doi: 10.1177/146642407609600410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead G. C., Thomas N. L. The bacteriological condition of eviscerated chickens processed under controlled conditions in a spin-chilling system and sampled by two different methods. Br Poult Sci. 1973 Jul;14(4):413–419. doi: 10.1080/00071667308416045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Kampelmacher E. H. Attachment of some bacterial strains to the skin of broiler chickens. Br Poult Sci. 1974 Nov;15(6):573–585. doi: 10.1080/00071667408416148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Kampelmacher E. H. Further studies on the attachment of bacteria to skin. Br Poult Sci. 1975 Sep;16(5):487–496. doi: 10.1080/00071667508416217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Kampelmacher E. H. Heat destruction of some bacterial strains attached to broiler skin. Br Poult Sci. 1975 Jul;16(4):351–361. doi: 10.1080/00071667508416199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Van Leusden F. M., Van Schothorst M. Suitability of different bacterial groups for determining faecal contamination during post scalding stages in the processing of broiler chickens. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;43(3):383–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00764.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson J. T. Microbiological aspects of poultry processing. Br Poult Sci. 1971 Apr;12(2):197–203. doi: 10.1080/00071667108415870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson J. T. Microbiological sampling of poultry carcasses. J Appl Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;35(4):569–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1972.tb03738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]