Abstract
The title compound, C10H11N3O4, is a condensation product of 4-nitrophenylhydrazine and methyl pyruvate. The complete molecule except for the methyl groups can be considered as a conjugated π system. All non-H atoms are approximately coplanar (r.m.s. deviation 0.117 Å). The crystal packing involves an N—H⋯O hydrogen bond and a π–π interaction between the aromatic rings, with a centroid–centroid distance of 3.617 Å.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Humphrey & Kuethe (2006 ▶); Tietze et al. (2003 ▶); Van Order & Lindwall (1942 ▶).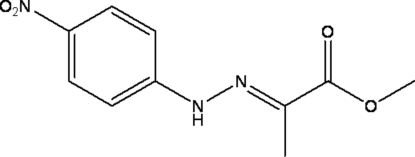
Experimental
Crystal data
C10H11N3O4
M r = 237.22
Monoclinic,
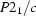
a = 12.836 (3) Å
b = 6.9260 (14) Å
c = 11.915 (2) Å
β = 90.11 (3)°
V = 1059.3 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.12 mm−1
T = 173 (2) K
0.60 × 0.54 × 0.16 mm
Data collection
Rigaku R-AXIS SPIDER diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
9730 measured reflections
2416 independent reflections
1997 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.021
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.126
S = 1.09
2416 reflections
176 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3
Data collection: RAPID-AUTO (Rigaku, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: RAPID-AUTO; data reduction: RAPID-AUTO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 1990 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEX (McArdle, 1995 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067268/bt2665sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067268/bt2665Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H5⋯O3i | 0.853 (18) | 2.200 (18) | 2.9928 (17) | 154.6 (16) |
Symmetry code: (i) 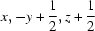 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Foundations of Fujian Province (No. 2006F5058) and Fuzhou University (No. XRC0527).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound, a phenylhydrazone derivative, is an important intermediate for the synthesis of indoles by the Fischer indole reaction (Van Order & Lindwall, 1942; Humphrey & Kuethe, 2006).
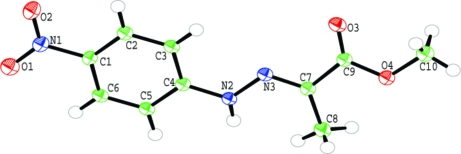
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1. The complete molecule except the methyl groups can be considered as a conjugated π-system. All non-H atoms lie in a common plane (r.m.s. deviation 0.117 Å). The crystal packing shows an N—H···O hydrogen bond (Table 1) and a π-π interaction between the aromatic rings with a centroid-centroid distance of 3.617Å (symmetry operator: 1 - x, -y, 1 - z).
Experimental
A suspension of 4-nitrophenylhydrazine (7.65 g, 50 mmol) in concd. HCl (20 ml) and H2O (20 ml) was heated to reflux untill the suspension solved. The solution was cooled to room temperature. Then the precipitate was filtrated off and dried. The solid was dissolved in methanol (100 ml) and treated with NaOAc (4.92 g, 60 mmol) and methyl pyruvate (5.10 g, 50 mmol). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 18 h. Then the yellow precipitate was filtered off, washed with methanol and dried to afford 11.13 g of the title compound (47 mmol, 94%) (Tietze et al., 2003). mp: 209.6–211.1°C. IR: (KBr, ν, cm-1): 3301 (N—H), 2962 (C—H), 1716 (C—O), 1611 (C—N), 1578, 1504, 1486, 1438, 1338, 1399, 1253, 1177, 1130, 1113, 847, 751.
Refinement
H atoms of the two methyl groups were refined using a riding model with C—H = 0.96Å and U(H)=1.5Ueq(C). These methyl groups were allowed to rotate but not to tip. All other H atoms were freely refined.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms.
Crystal data
| C10H11N3O4 | F000 = 496 |
| Mr = 237.22 | Dx = 1.487 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71069 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P2ybc | Cell parameters from 7757 reflections |
| a = 12.836 (3) Å | θ = 6.4–55.0º |
| b = 6.9260 (14) Å | µ = 0.12 mm−1 |
| c = 11.915 (2) Å | T = 173 (2) K |
| β = 90.11 (3)º | Chip, yellow |
| V = 1059.3 (4) Å3 | 0.60 × 0.54 × 0.16 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS Spider diffractometer | 2416 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Rotating Anode | 1997 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.021 |
| Detector resolution: 10 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5º |
| T = 173(2) K | θmin = 3.2º |
| ω oscillation scans | h = −16→16 |
| Absorption correction: none | k = −8→7 |
| 9730 measured reflections | l = −15→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.126 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0696P)2 + 0.336P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.09 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2416 reflections | Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3 |
| 176 parameters | Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.23523 (9) | 0.09076 (17) | 0.62405 (10) | 0.0249 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.65298 (8) | 0.28388 (17) | 0.55245 (9) | 0.0217 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.6937 (13) | 0.255 (3) | 0.6065 (15) | 0.028 (4)* | |
| N3 | 0.68657 (8) | 0.33719 (16) | 0.44935 (9) | 0.0202 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.21019 (8) | 0.03458 (18) | 0.71835 (9) | 0.0362 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.17278 (8) | 0.10441 (19) | 0.54620 (10) | 0.0381 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.75514 (8) | 0.43209 (18) | 0.24033 (8) | 0.0339 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.90897 (7) | 0.50736 (15) | 0.31757 (8) | 0.0256 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.34331 (10) | 0.14249 (18) | 0.60429 (11) | 0.0200 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.37287 (10) | 0.2085 (2) | 0.49903 (11) | 0.0219 (3) | |
| H1 | 0.3235 (14) | 0.217 (3) | 0.4375 (16) | 0.040 (5)* | |
| C3 | 0.47596 (10) | 0.25744 (19) | 0.48098 (11) | 0.0207 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.4965 (13) | 0.309 (2) | 0.4086 (15) | 0.029 (4)* | |
| C4 | 0.54879 (9) | 0.23761 (19) | 0.56748 (10) | 0.0188 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.51738 (10) | 0.1701 (2) | 0.67302 (11) | 0.0225 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.5685 (14) | 0.158 (3) | 0.7310 (16) | 0.035 (5)* | |
| C6 | 0.41453 (10) | 0.1227 (2) | 0.69133 (11) | 0.0225 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.3938 (13) | 0.072 (3) | 0.7635 (15) | 0.031 (4)* | |
| C7 | 0.78391 (10) | 0.37883 (19) | 0.43797 (11) | 0.0204 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.86529 (11) | 0.3763 (3) | 0.52797 (12) | 0.0333 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.8767 | 0.5053 | 0.5548 | 0.050* | |
| H7 | 0.9291 | 0.3258 | 0.4980 | 0.050* | |
| H8 | 0.8423 | 0.2962 | 0.5888 | 0.050* | |
| C9 | 0.81181 (10) | 0.44003 (19) | 0.32127 (11) | 0.0204 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.94452 (11) | 0.5806 (2) | 0.21009 (12) | 0.0303 (3) | |
| H9 | 1.0130 | 0.6345 | 0.2185 | 0.045* | |
| H10 | 0.8975 | 0.6788 | 0.1841 | 0.045* | |
| H11 | 0.9466 | 0.4770 | 0.1566 | 0.045* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0205 (6) | 0.0267 (6) | 0.0276 (6) | −0.0007 (5) | 0.0051 (4) | −0.0034 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0181 (5) | 0.0302 (6) | 0.0169 (5) | −0.0020 (5) | 0.0008 (4) | 0.0016 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0202 (5) | 0.0217 (6) | 0.0188 (5) | −0.0005 (4) | 0.0040 (4) | −0.0011 (4) |
| O1 | 0.0273 (5) | 0.0512 (7) | 0.0302 (6) | −0.0087 (5) | 0.0102 (4) | 0.0038 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0202 (5) | 0.0564 (8) | 0.0376 (6) | −0.0041 (5) | −0.0033 (4) | 0.0014 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0255 (5) | 0.0559 (7) | 0.0202 (5) | −0.0093 (5) | −0.0011 (4) | 0.0031 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0199 (5) | 0.0350 (6) | 0.0220 (5) | −0.0066 (4) | 0.0039 (3) | 0.0013 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0174 (6) | 0.0199 (6) | 0.0227 (6) | −0.0011 (5) | 0.0036 (5) | −0.0039 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0204 (6) | 0.0246 (7) | 0.0208 (6) | 0.0013 (5) | −0.0005 (5) | −0.0005 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0216 (6) | 0.0234 (6) | 0.0172 (6) | 0.0006 (5) | 0.0026 (5) | 0.0017 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0186 (6) | 0.0184 (6) | 0.0193 (6) | 0.0000 (5) | 0.0031 (4) | −0.0022 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0210 (6) | 0.0293 (7) | 0.0173 (6) | −0.0004 (5) | 0.0001 (5) | −0.0010 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0235 (6) | 0.0266 (7) | 0.0173 (6) | −0.0014 (5) | 0.0045 (5) | −0.0006 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0195 (6) | 0.0217 (6) | 0.0199 (6) | −0.0017 (5) | 0.0019 (5) | −0.0024 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0234 (6) | 0.0543 (10) | 0.0223 (7) | −0.0100 (7) | −0.0005 (5) | 0.0040 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0191 (6) | 0.0216 (6) | 0.0207 (6) | −0.0007 (5) | 0.0028 (5) | −0.0022 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0256 (7) | 0.0384 (8) | 0.0270 (7) | −0.0052 (6) | 0.0085 (5) | 0.0057 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| N1—O2 | 1.2284 (17) | C3—C4 | 1.3970 (18) |
| N1—O1 | 1.2323 (16) | C3—H2 | 0.970 (18) |
| N1—C1 | 1.4525 (16) | C4—C5 | 1.4016 (18) |
| N2—N3 | 1.3540 (15) | C5—C6 | 1.3783 (18) |
| N2—C4 | 1.3872 (16) | C5—H3 | 0.956 (18) |
| N2—H5 | 0.853 (18) | C6—H4 | 0.966 (18) |
| N3—C7 | 1.2897 (16) | C7—C8 | 1.4958 (19) |
| O3—C9 | 1.2080 (17) | C7—C9 | 1.4977 (18) |
| O4—C9 | 1.3323 (15) | C8—H6 | 0.9600 |
| O4—C10 | 1.4518 (16) | C8—H7 | 0.9600 |
| C1—C6 | 1.3880 (19) | C8—H8 | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.3885 (19) | C10—H9 | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3831 (17) | C10—H10 | 0.9600 |
| C2—H1 | 0.970 (19) | C10—H11 | 0.9600 |
| O2—N1—O1 | 122.81 (12) | C4—C5—H3 | 118.7 (11) |
| O2—N1—C1 | 118.73 (11) | C5—C6—C1 | 119.20 (12) |
| O1—N1—C1 | 118.46 (12) | C5—C6—H4 | 119.5 (10) |
| N3—N2—C4 | 119.27 (11) | C1—C6—H4 | 121.3 (10) |
| N3—N2—H5 | 123.6 (11) | N3—C7—C8 | 126.68 (12) |
| C4—N2—H5 | 116.0 (11) | N3—C7—C9 | 113.23 (11) |
| C7—N3—N2 | 117.81 (11) | C8—C7—C9 | 120.07 (11) |
| C9—O4—C10 | 116.57 (11) | C7—C8—H6 | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 121.79 (12) | C7—C8—H7 | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—N1 | 118.84 (12) | H6—C8—H7 | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—N1 | 119.37 (12) | C7—C8—H8 | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 118.97 (12) | H6—C8—H8 | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H1 | 119.4 (11) | H7—C8—H8 | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H1 | 121.6 (11) | O3—C9—O4 | 123.49 (12) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.02 (12) | O3—C9—C7 | 125.70 (12) |
| C2—C3—H2 | 119.3 (10) | O4—C9—C7 | 110.81 (11) |
| C4—C3—H2 | 120.6 (10) | O4—C10—H9 | 109.5 |
| N2—C4—C3 | 121.74 (12) | O4—C10—H10 | 109.5 |
| N2—C4—C5 | 118.16 (12) | H9—C10—H10 | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.10 (12) | O4—C10—H11 | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.92 (12) | H9—C10—H11 | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H3 | 121.4 (11) | H10—C10—H11 | 109.5 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H5···O3i | 0.853 (18) | 2.200 (18) | 2.9928 (17) | 154.6 (16) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT2665).
References
- Humphrey, G. R. & Kuethe, J. T. (2006). Chem. Rev.106, 2875–2911. [DOI] [PubMed]
- McArdle, P. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst.28, 65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rigaku (2004). RAPID-AUTO Version 3.0. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1990). Acta Cryst. A46, 467–473.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97. University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Tietze, L. F., Haunert, F., Feuerstein, T. & Herzig, T. (2003). Eur. J. Org. Chem. pp. 562–566.
- Van Order, R. B. & Lindwall, H. G. (1942). Chem. Rev.30, 69–96.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067268/bt2665sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067268/bt2665Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report