Abstract
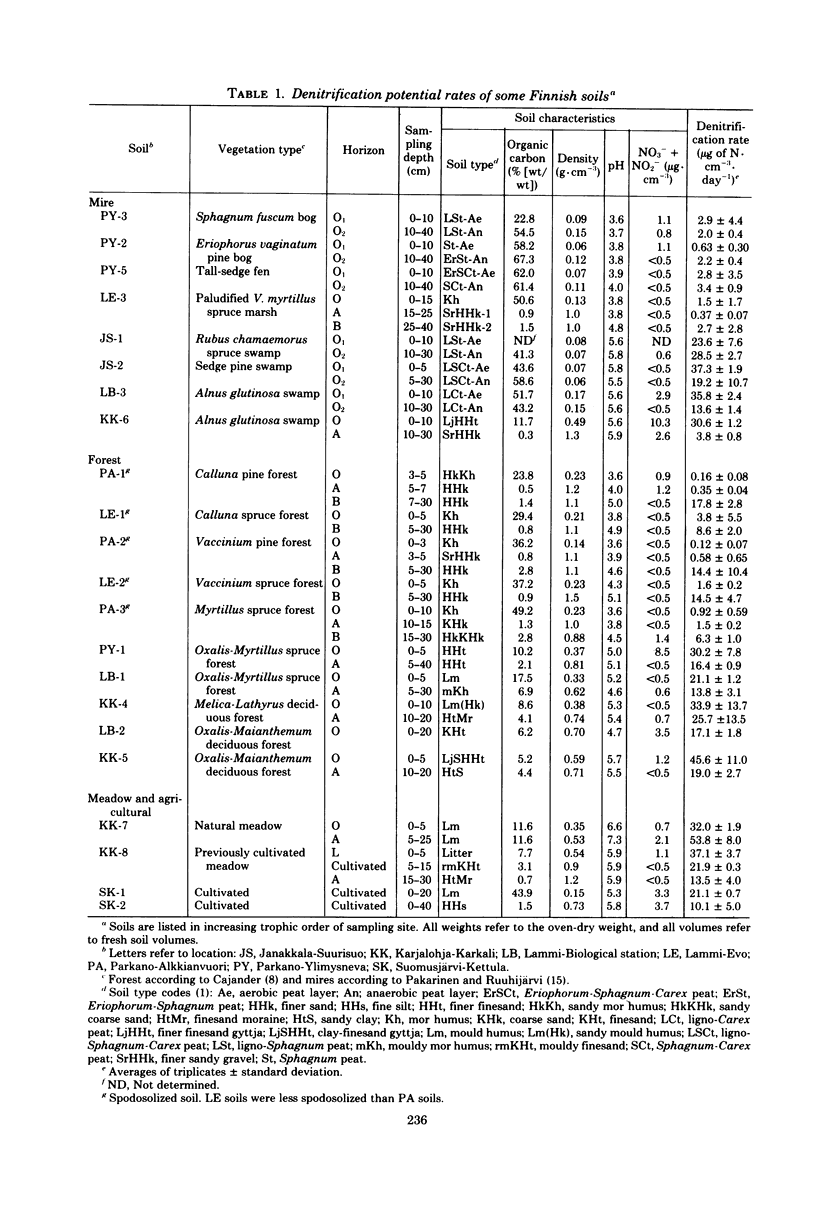
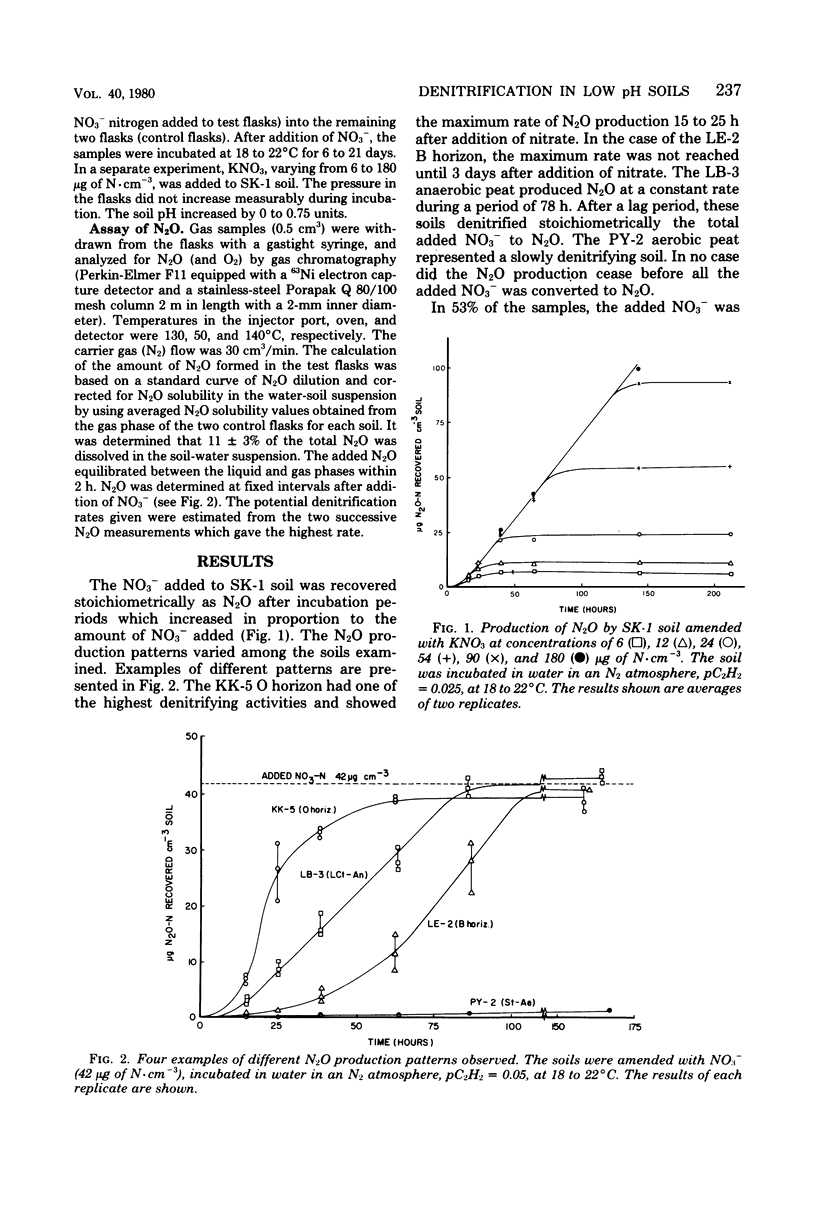
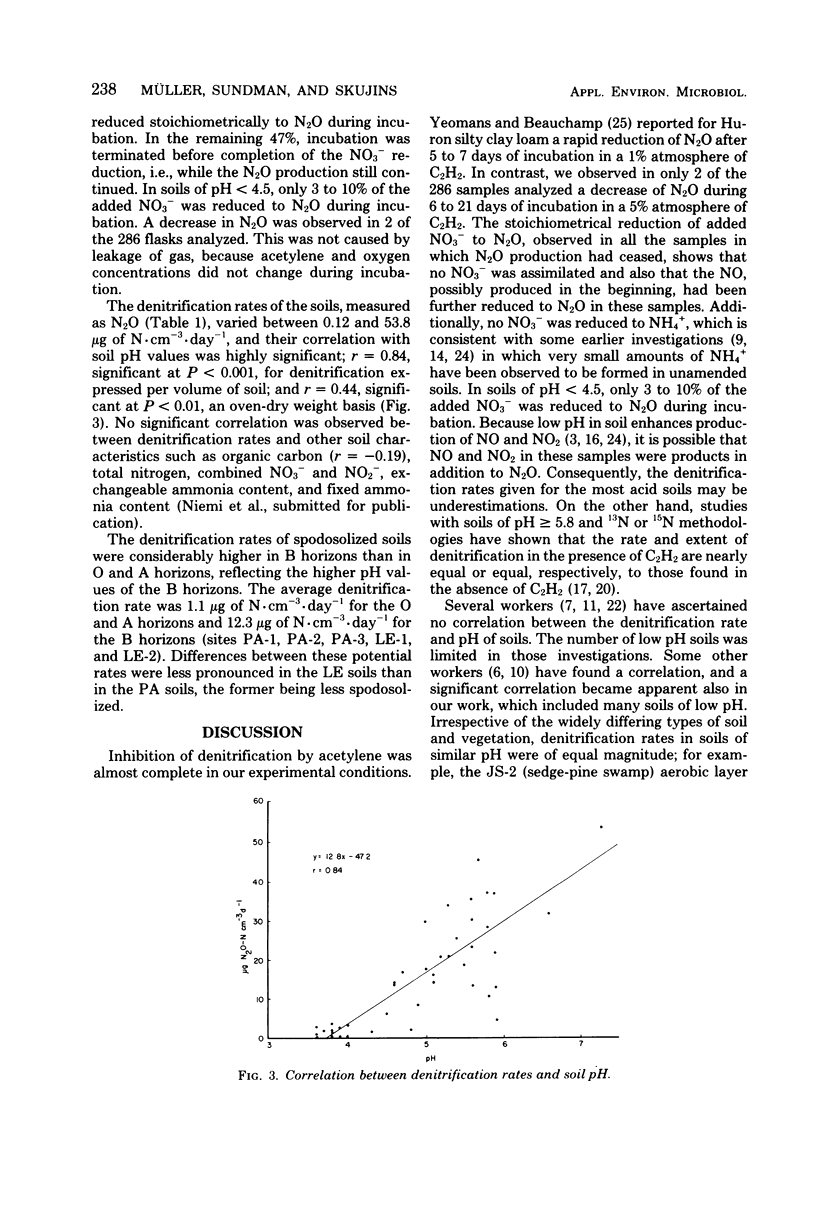
Potential denitrification rates were determined for predominantly acid (pH ≥ 3.6) horizons of forestal, miry, and agricultural soils from 22 locations in southern Finland. The acetylene inhibition method was used with nitrate-amended water-logged soils incubated in an N2 atmosphere containing 2.5 or 5% C2H2. Complete inhibition of the reduction of N2O to N2 was observed in 99.3% of the samples. The denitrification rates varied from 0.12 to 53.8 μg of N·cm-3·day-1. Correlation between denitrification rate and soil pH was highly significant: r = 0.84 on a volume basis, and r = 0.44 on a weight basis. Vegetation type and amount of soil organic matter had a minor or no effect, respectively. In spodosolized soils the rates were significantly higher for B horizons than for A horizons. These results show that denitrification can occur in acid soils.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balderston W. L., Sherr B., Payne W. J. Blockage by acetylene of nitrous oxide reduction in Pseudomonas perfectomarinus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):504–508. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.504-508.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinari T., Knowles R. Acetylene inhibition of nitrous oxide reduction by denitrifying bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Apr 5;69(3):705–710. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90932-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


