The Neural Architecture of Music-Evoked Autobiographical Memories
doi:10.1093/cercor/bhp008
Cerebral Cortex 19(11), 2579–2594; 2009
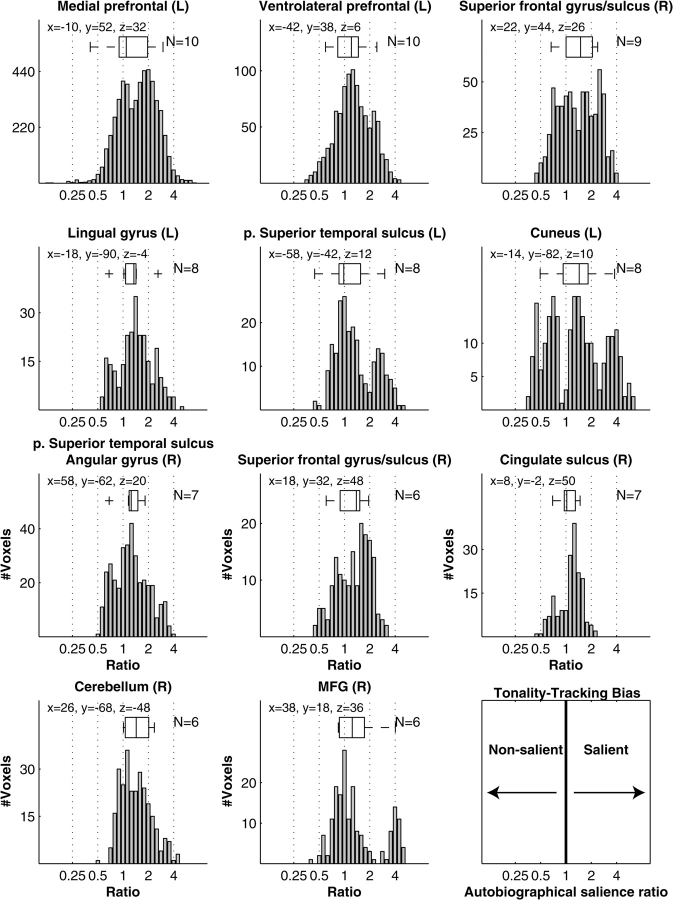
The formula for tonality tracking bias on pg. 2585 was implemented incorrectly. Rather than being normalized by the number of non-autobiographical songs, Fnonauto was normalized by the total number of songs, resulting in inflated estimates of tonality-tracking bias toward autobiographically salient songs. This error primarily affected Figure 6 and Table 5, which are presented in corrected form below.
Figure 6.
Table 5.
Summary of tonality-tracking activation clusters
| Location (mm) |
|||||||
| Anatomical Location | Brodmann Area | #voxels in cluster | x | y | z | #subjects at peak | #subjects in cluster |
| Cluster 1 | 1197 | 10 | |||||
| superior frontal gyrus | 9 | −10 | 52 | 32 | 7 | ||
| anterior cingulate cortex | 32 | −4 | 28 | 34 | 6 | ||
| anterior cingulate cortex | 32 | −8 | 42 | 8 | 5 | ||
| superior frontal gyrus | 10 | −16 | 62 | 22 | 5 | ||
| superior frontal gyrus | 8 | −4 | 42 | 50 | 5 | ||
| superior frontal gyrus | 9 | 2 | 40 | 32 | 5 | ||
| Cluster 2 | 230 | 10 | |||||
| inferior frontal gyrus | 45 | −42 | 38 | 6 | 6 | ||
| inferior frontal sulcus | 46 | −40 | 32 | 14 | 6 | ||
| middle frontal gyrus | 46 | −42 | 42 | 18 | 6 | ||
| lateral orbital gyrus | 47 | −46 | 42 | −2 | 5 | ||
| Cluster 3 | 148 | 9 | |||||
| superior frontal gyrus | 9/10 | 22 | 44 | 26 | 5 | ||
| Cluster 4 | 65 | 8 | |||||
| lingual gyrus | 18 | −18 | −90 | −4 | 5 | ||
| Cluster 5 | 58 | 8 | |||||
| cuneus | 17 | −14 | −82 | 10 | 5 | ||
| Cluster 6 | 55 | 8 | |||||
| posterior superior temporal sulcus | 22 | −58 | −42 | 12 | 5 | ||
| Cluster 7 | 88 | 7 | |||||
| posterior superior temporal sulcus, angular gyrus | 39 | 58 | −62 | 20 | 5 | ||
| Cluster 8 | 43 | 7 | |||||
| cingulate sulcus | 24 | 8 | −2 | 50 | 5 | ||
| Cluster 9 | 41 | 6 | |||||
| superior frontal sulcus | 8 | 18 | 32 | 48 | 5 | ||
| Cluster 10 | 42 | 6 | |||||
| middle frontal gyrus | 9 | 38 | 18 | 36 | 5 | ||
| Cluster 11 | 67 | 6 | |||||
| cerebellum | 26 | −68 | −48 | 5 | |||