Abstract
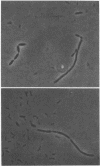
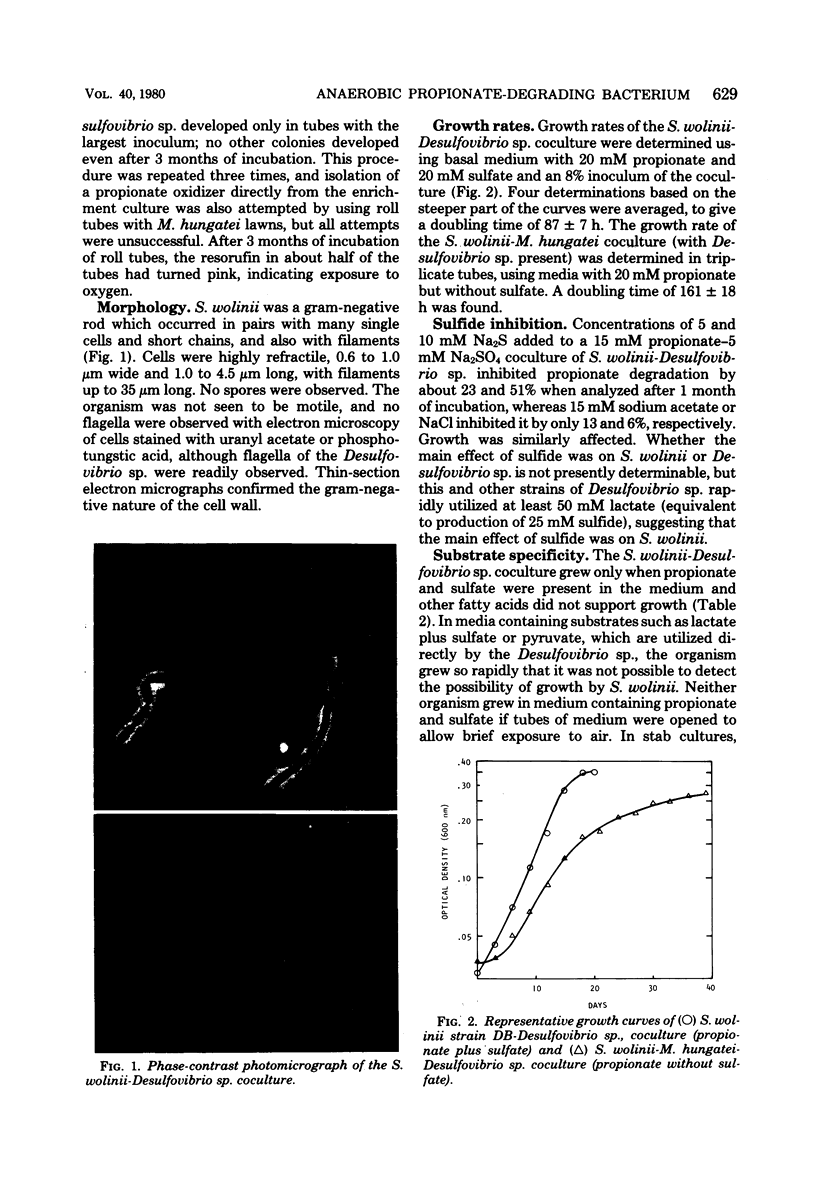
A new genus and species of a nonmotile gram-negative rod, Syntrophobacter wolinii, is the first bacterium described which degrades propionate only in coculture with an H2-using organism and in the absence of light or exogenous electron acceptors such as O2, sulfate, or nitrate. It was isolated from methanogenic enrichments from an anaerobic municipal sewage digestor, using anaerobic roll tubes containing a medium with propionate as the energy source in association with an H2-using, sulfate-reducing Desulfovibrio sp. which cannot utilize fatty acids other than formate. S. wolinii produced acetate and, presumably, CO2 and H2 (or formate) from propionate. In media without sulfate and with Methanospirillum hungatei, a methanogen that uses only H2-CO2 or formate as an energy source, acetate, methane, and, presumably, CO2 were produced from propionate and only small amounts of Desulfovibrio sp. were present. Isolation in coculture with the methanogen was not successful. S. wolinii does not use other saturated fatty acids as energy sources.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. New approach to the cultivation of methanogenic bacteria: 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM)-dependent growth of Methanobacterium ruminantium in a pressureized atmosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Dec;32(6):781–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.6.781-791.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P. Commentary on the Hungate technique for culture of anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1324–1328. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., Wolin E. A., Wolin M. J., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacillus omelianskii, a symbiotic association of two species of bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):20–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00406313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry J. G., Wolfe R. S. Anaerobic degradation of benzoate to methane by a microbial consortium. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Feb;107(1):33–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00427864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar H. F., Wuhrmann K. Kinetic parameters and relative turnovers of some important catabolic reactions in digesting sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.1-7.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN T. C., BARKER H. A. Studies on the methane fermentation. VIII. Tracer experiments of fatty acid oxidation by methane bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1951 Jan;61(1):67–80. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.1.67-80.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salanitro J. P., Muirhead P. A. Quantitative method for the gas chromatographic analysis of short-chain monocarboxylic and dicarboxylic acids in fermentation media. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Mar;29(3):374–381. doi: 10.1128/am.29.3.374-381.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUEPER H. G., SCHLEGEL H. G. SULPHUR METABOLISM IN THIORHODACEAE. I. QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENTS ON GROWING CELLS OF CHROMATIUM OKENII. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1964;30:225–238. doi: 10.1007/BF02046728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Jungermann K., Decker K. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):100–180. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.100-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]