Abstract
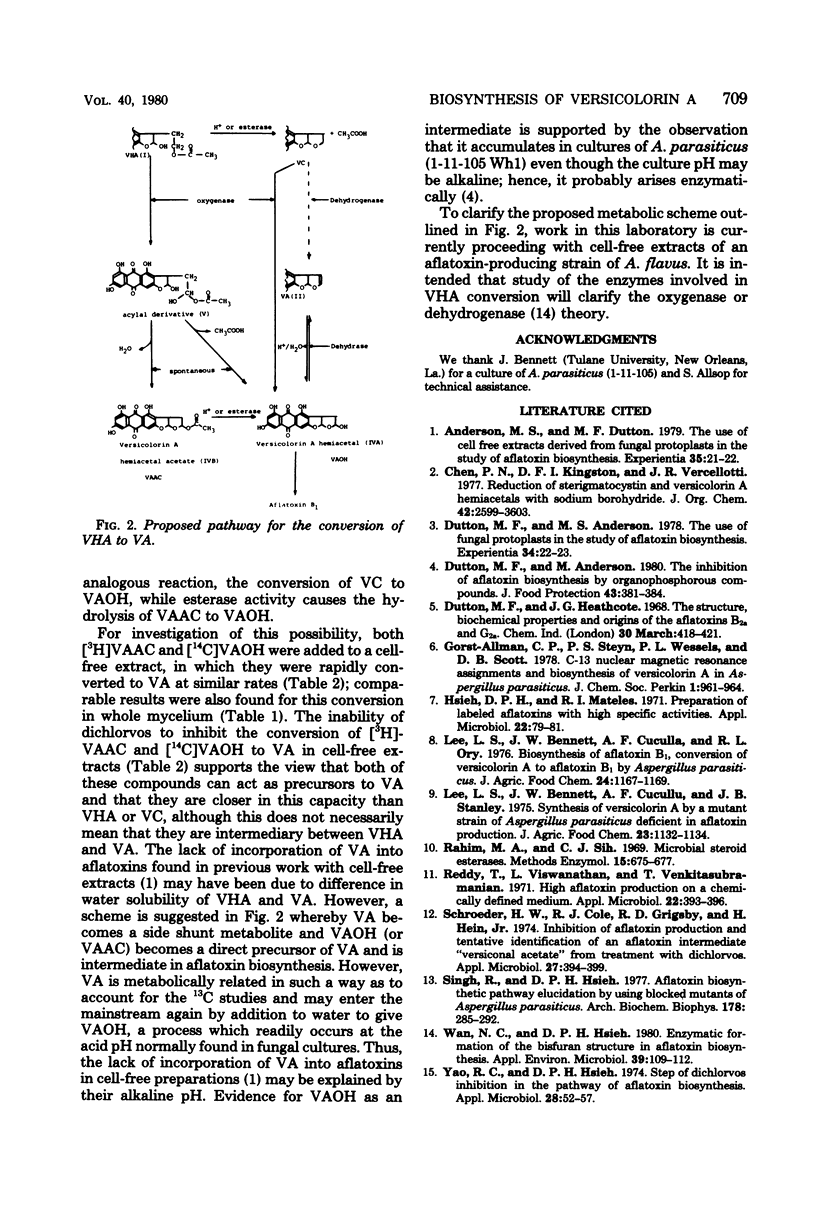
The incorporation of various potential intermediates into versicolorin A by a versicolorin A-accumulating mutant of Aspergillus parasiticus was studied. Both whole mycelium and cell-free extracts of this mutant were able to convert 14C-labeled versiconal hemiacetal acetate to versicolorin A. By the use of a labeled double substrate technique it was shown that two other compounds, versicolorin A hemiacetal and its acetate derivative, were also converted to versicolorin A. It is concluded that one or both of these compounds are intermediates in the biosynthesis of versicolorin A and therefore may possibly be involved in the biogenesis of the aflatoxins.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. S., Dutton M. F. The use of cell free extracts derived from fungal protoplasts in the study of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Experientia. 1979 Jan 15;35(1):21–22. doi: 10.1007/BF01917850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton M. F., Heathcote J. G. The structure, biochemical properties and origin of the aflatoxins B2a and G2a. Chem Ind. 1968 Mar 30;13:418–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P., Mateles R. I. Preparation of labeled aflatoxins with high specific activities. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jul;22(1):79–83. doi: 10.1128/am.22.1.79-83.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Bennett J. W., Cucullu A. F., Ory R. L. Biosynthesis of aflatoxin B1. Conversion of versicolorin A to aflatoxin B1 by Aspergillus parasiticus. J Agric Food Chem. 1976 Nov-Dec;24(6):1167–1170. doi: 10.1021/jf60208a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Bennett J. W., Cucullu A. F., Stanley J. B. Synthesis of versicolorin A by a mutant strain of Aspergillus parasiticus deficient in aflatoxin production. J Agric Food Chem. 1975 Nov-Dec;23(6):1132–1134. doi: 10.1021/jf60202a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy T. V., Viswanathan L., Venkitasubramanian T. A. High aflatoxin production on a chemically defined medium. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Sep;22(3):393–396. doi: 10.1128/am.22.3.393-396.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Cole R. J., Grigsby R. D., Hein H., Jr Inhibition of aflatoxin production and tentative identification of an aflatoxin intermediate "versiconal acetate" from treatment with dichlorvos. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):394–399. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.394-399.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R., Hsieh D. P. Aflatoxin biosynthetic pathway: elucidation by using blocked mutants of Aspergillus parasiticus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 15;178(1):285–292. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90193-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan N. C., Hsieh D. P. Enzymatic formation of the bisfuran structure in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):109–112. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.109-112.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao R. C., Hsieh D. P. Step of dichlorvos inhibition in the pathway of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jul;28(1):52–57. doi: 10.1128/am.28.1.52-57.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


