Abstract
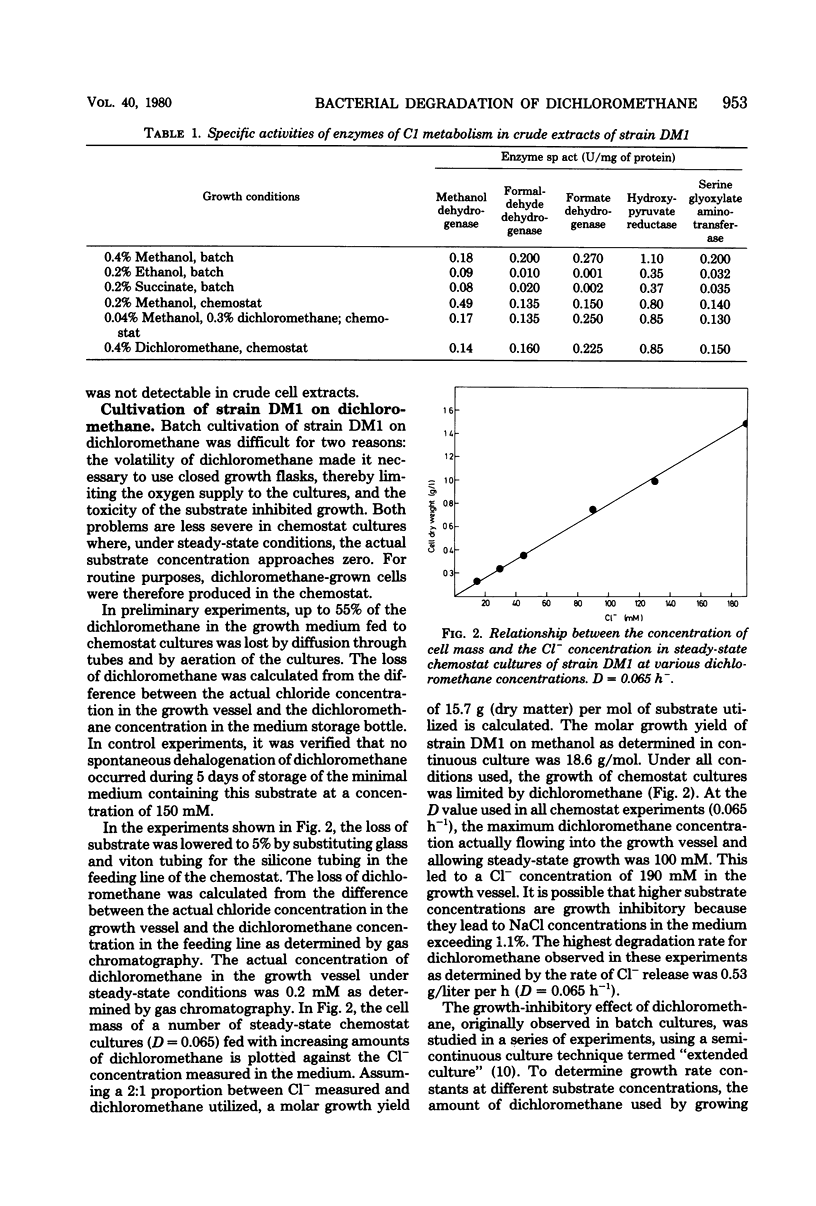
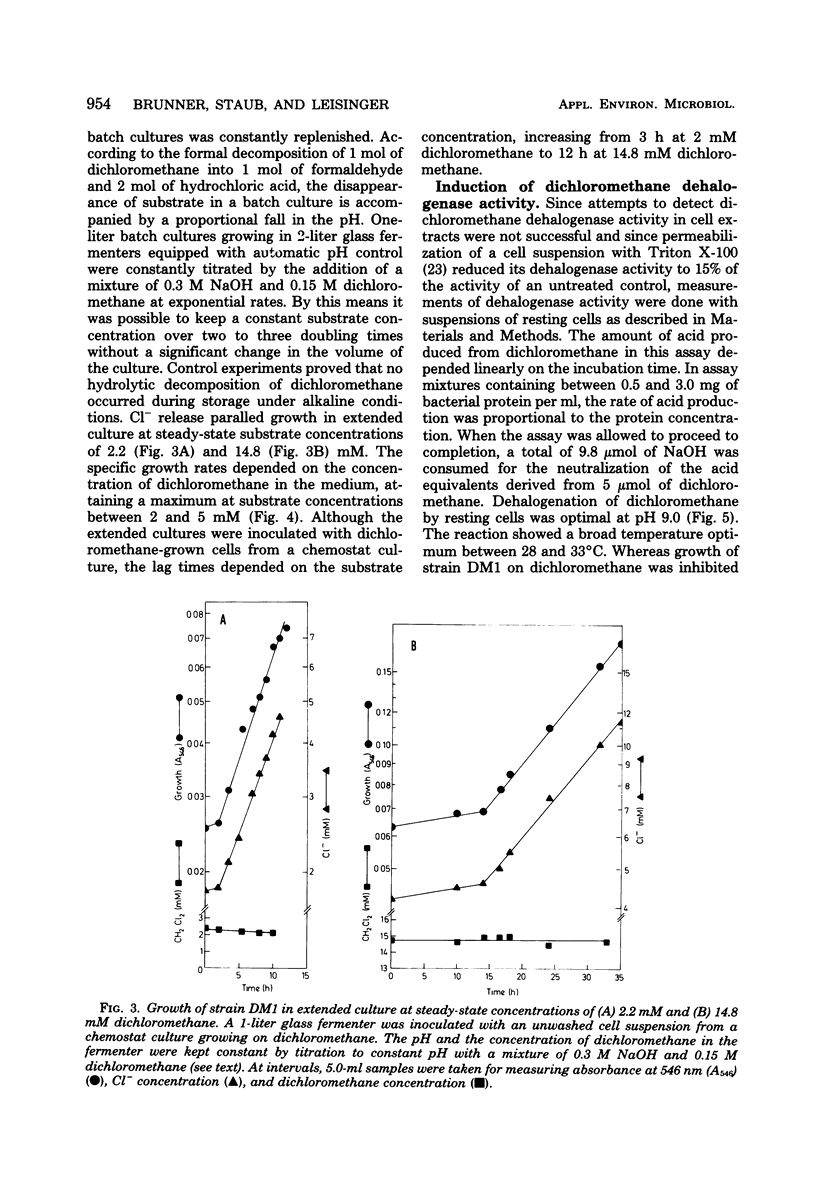
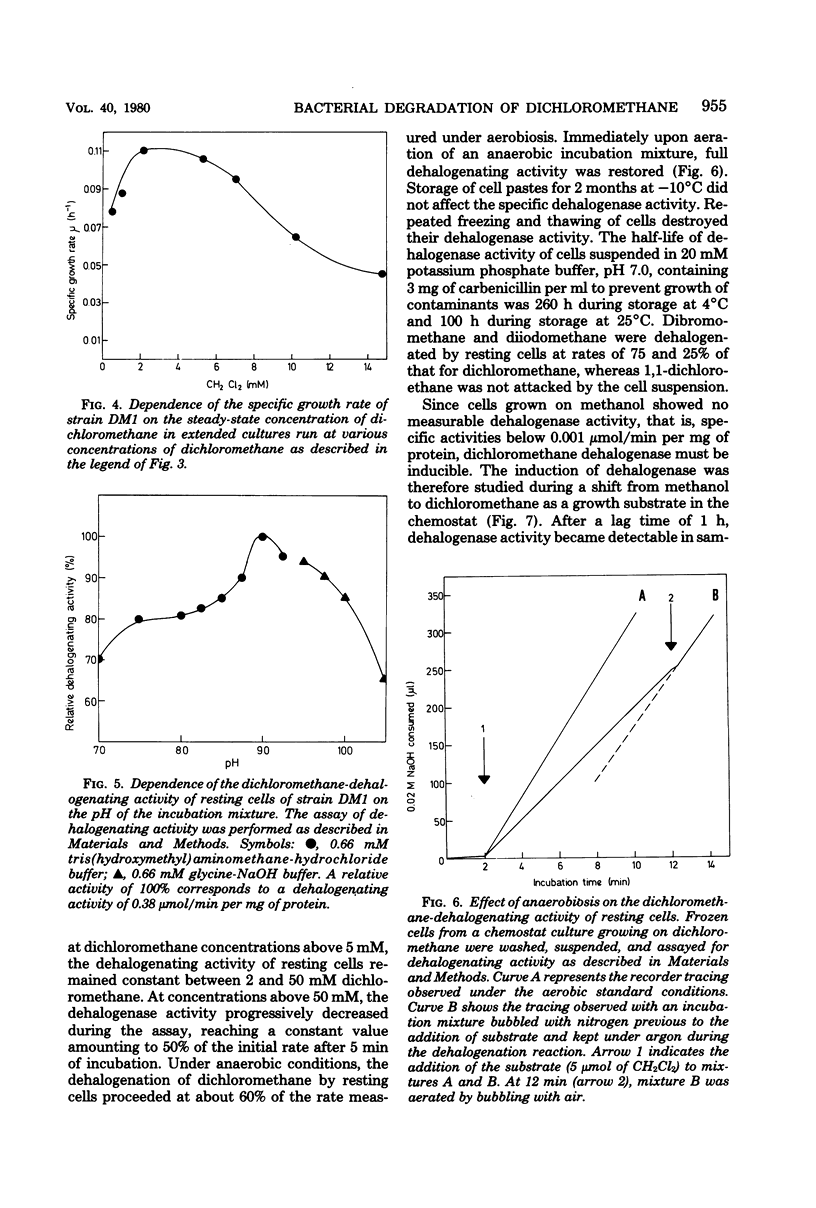
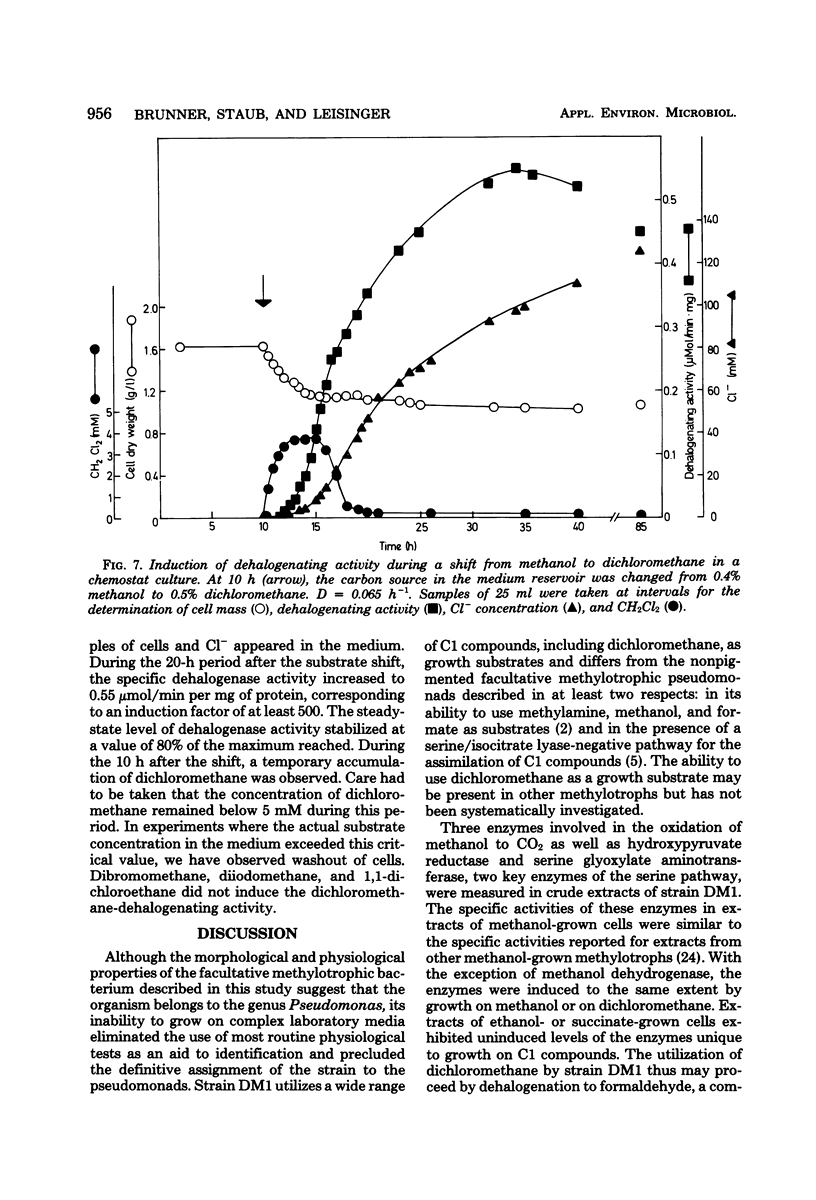
Strain DM1, a facultative methylotrophic bacterium utilizing methanol, formate, mono-, di-, and trimethylamine, as well as dichloromethane as C1 substrates was isolated as an airborne contaminant. The organism is a strictly aerobic, gram-negative, oxidase-positive short rod, motile by a single lateral flagellum. Enzyme assays in crude extracts suggested that it assimilates C1 compounds by the serine/isocitrate lyase-negative pathway. Experiments with extended cultures demonstrated that dichloromethane is a growth-inhibitory substrate. The maximum specific growth rate of 0.11 h−1 was reached between 2 and 5 mM dichloromethane. The release of Cl−1 from dichloromethane paralleled growth in extended and continuous cultures. Molar growth yields on methanol and on dichloromethane were 18.6 and 15.7 g/mol, respectively. Since attempts to demonstrate dehalogenation of dichloromethane by crude extracts failed, a dehalogenation assay with resting cells was developed. Maximum dehalogenating activity of cell suspensions was at pH 9.0. The reaction was partially and reversibly inhibited by anaerobiosis. During a shift of a chemostat culture from methanol to dichloromethane as the carbon source, the dehalogenating activity of resting cells was increased at least 500-fold.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Mccann J., Yamasaki E. Methods for detecting carcinogens and mutagens with the Salmonella/mammalian-microsome mutagenicity test. Mutat Res. 1975 Dec;31(6):347–364. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(75)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony C. The biochemistry of methylotrophic micro-organisms. Sci Prog. 1975 Summer;62(246):167–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony C., Zatman L. J. The microbial oxidation of methanol. 1. Isolation and properties of Pseudomonas sp. M27. Biochem J. 1964 Sep;92(3):609–614. doi: 10.1042/bj0920609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellion E., Spain J. C. The distribution of the isocitrate lyase serine pathway amongst one-carbon utilizing organisms. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Mar;22(3):404–408. doi: 10.1139/m76-061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore M. A., Quayle J. R. Microbial growth on oxalate by a route not involving glyoxylate carboligase. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):53–59. doi: 10.1042/bj1180053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby J., Stirling D. I., Dalton H. The soluble methane mono-oxygenase of Methylococcus capsulatus (Bath). Its ability to oxygenate n-alkanes, n-alkenes, ethers, and alicyclic, aromatic and heterocyclic compounds. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):395–402. doi: 10.1042/bj1650395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby J., Zatman L. J. Trimethylamine metabolism in obligate and facultative methylotrophs. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;132(1):101–112. doi: 10.1042/bj1320101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkhuizen L., Harder W. Substrate inhibition in Pseudomonas oxalaticus OX1: a kinetic study of growth inhibition by oxalate and formate using extended cultures. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1975;41(2):135–146. doi: 10.1007/BF02565045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards V. H. The influence of high substrate concentrations on microbial kinetics. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1970 Sep;12(5):679–712. doi: 10.1002/bit.260120504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein L. Industrial mutagens and potential mutagens I. Halogenated aliphatic derivatives. Mutat Res. 1976;32(3-4):267–307. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(76)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh R., Quayle J. R. Phenazine ethosulfate as a preferred electron acceptor to phenazine methosulfate in dye-linked enzyme assays. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;99(1):112–117. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman P., Milne G. W., Keister D. B. Carbon-halogen bond cleavage. 3. Studies on bacterial halidohrolases. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 25;243(2):428–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heptinstall J., Quayle J. R. Pathways leading to and from serine during growth of Pseudomonas AM1 on C1 compounds or succinate. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(3):563–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1170563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B. Malate adenosine triphosphate lyase. Separation of the reaction into a malate thiokinase and malyl coenzyme A lyase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 10;248(21):7295–7303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongen W. M., Alink G. M., Koeman J. H. Mutagenic effect of dichloromethane on Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1978 Jan;56(3):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(78)90191-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. I., Fewson C. A. Enzymes of the mandelate pathway in Bacterium N.C.I.B. 8250. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(4):497–506. doi: 10.1042/bj1070497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubic V. L., Anders M. W. Metabolism of dihalomethanes to carbon monoxide--III. Studies on the mechanism of the reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(19):2349–2355. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little M., Williams P. A. A bacterial halidohydrolase. Its purification, some properties and its modification by specific amino acid reagents. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jul 15;21(1):99–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01445.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miozzari G. F., Niederberger P., Hütter R. Permeabilization of microorganisms by Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):220–233. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omori T., Alexander M. Bacterial dehalogenation of halogenated alkanes and fatty acids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 May;35(5):867–871. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.5.867-871.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson C. R., McConnell G. Chlorinated C1 and C2 hydrocarbons in the marine environment. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 May 20;189(1096):305–332. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1975.0059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahm H., Cox R. B., Quayle J. R. Metabolism of methanol by Rhodopseudomonas acidophila. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jun;94(2):313–322. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]