Abstract
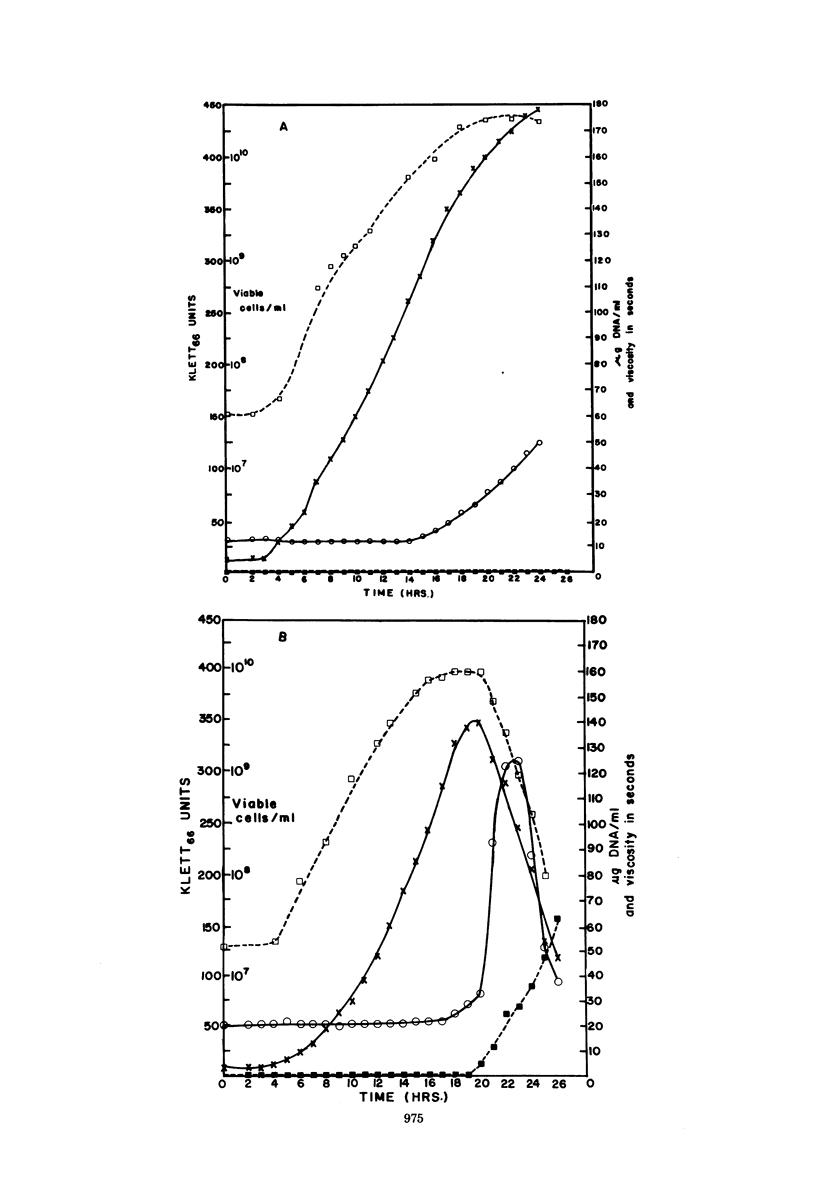
The growth of Enterobacter cloacae in 25% sodium dodecyl sulfate is described. The bacteria appeared to tolerate sodium dodecyl sulfate rather than metabolize it. The process was energy dependent, and cell lysis occurred during stationary phase. Extreme detergent resistance may be characteristic of the genus Enterobacter.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair F. W., Geftic S. G., Heymann H. Lytic effect of di- or tricarboxylic acids plus sodium dodecyl sulfate against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):417–420. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsell D. C., Cota-Robles E. H. Lysis of spheroplasts of Escherichia coli by a non-ionic detergent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 May 10;31(3):438–446. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90496-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornett J. B., Shockman G. D. Cellular lysis of Streptococcus faecalis induced with triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):153–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.153-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gledhill W. E. Linear alkylbenzene sulfonate: biodegradation and aquatic interactions. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1974;17(0):265–293. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70561-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabara J. J., Vrable R. Antimicrobial lipids: natural and synthetic fatty acids and monoglycerides. Lipids. 1977 Sep;12(9):753–759. doi: 10.1007/BF02570908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller J. K., Bak A. L., Christiansen C., Christiansen G., Stenderup A. Extrachromosomal deoxyribonucleic acid in R factor-harboring Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):398–403. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.398-403.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotmistrov M. N., Stavskaia S. S., Krivets I. A., Samoilenko L. S. Mikroorganizmy, razrushaiushchie alkilsul'faty. Mikrobiologiia. 1978 Mar-Apr;47(2):338–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomoeda M., Inuzuka M., Anto S., Konishi M. Curing action of sodium dodecyl sulfate on a Proteus mirabilis R+ strain. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1158–1163. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1158-1163.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Host-dependent, thermosensitive replication of an R plasmid, pJY5, isolated from Enterobacter cloacae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):923–930. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.923-930.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



