Abstract
The inducible water-soluble bioemulsifier liposan (M. C. Cirigliano and G. M. Carman, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 48:747-750, 1984) was purified from the yeast Candida lipolytica. The purification procedure included repeated solvent extractions of a concentrated culture filtrate and Affi-Gel concanavalin A affinity chromatography. The procedure yielded a preparation containing a major band (Mr = 27,600) which stained for protein and carbohydrate upon polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. Liposan is composed of approximately 83% carbohydrate and 17% protein. Acid and enzymatic digestions of the emulsifier revealed that the carbohydrate portion is a heteropolysaccharide consisting of glucose, galactose, galactosamine, and galacturonic acid. Liposan effected and stabilized oil-in-water emulsions with a variety of commercial vegetable oils. Emulsification and stabilization properties of liposan were compared to those of a number of commercial emulsifiers and stabilizers.
Full text
PDF
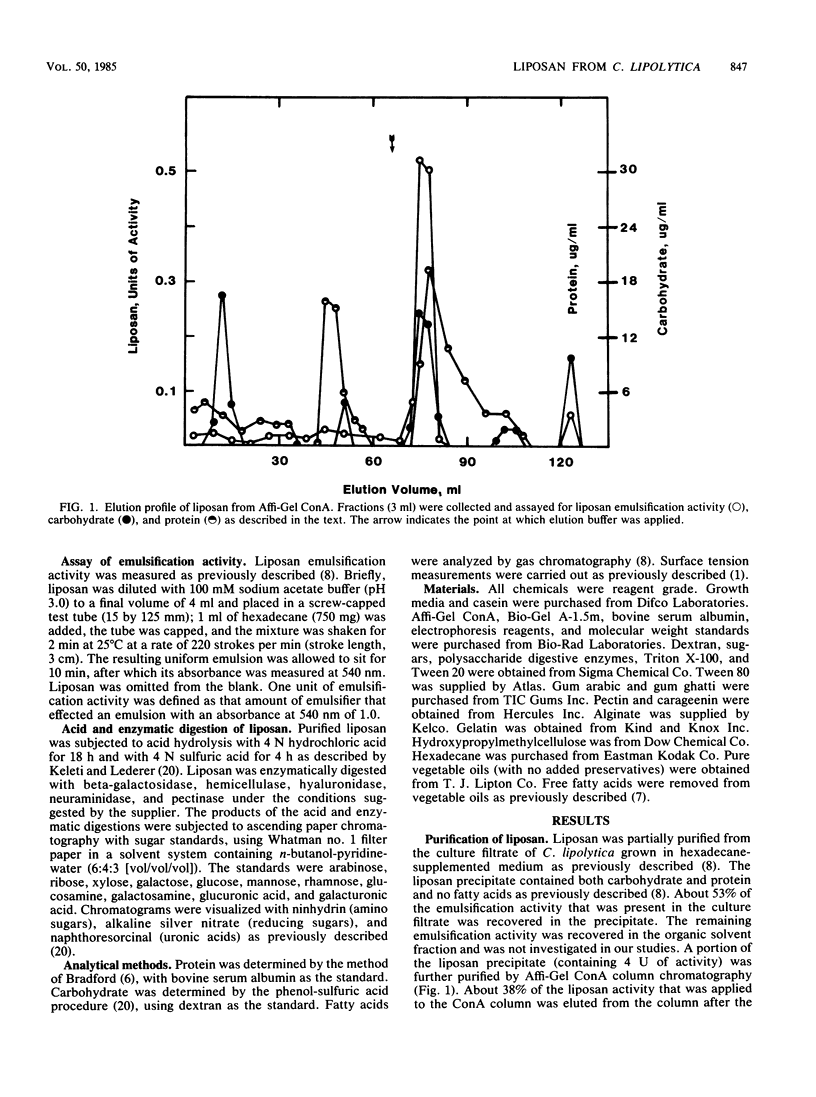
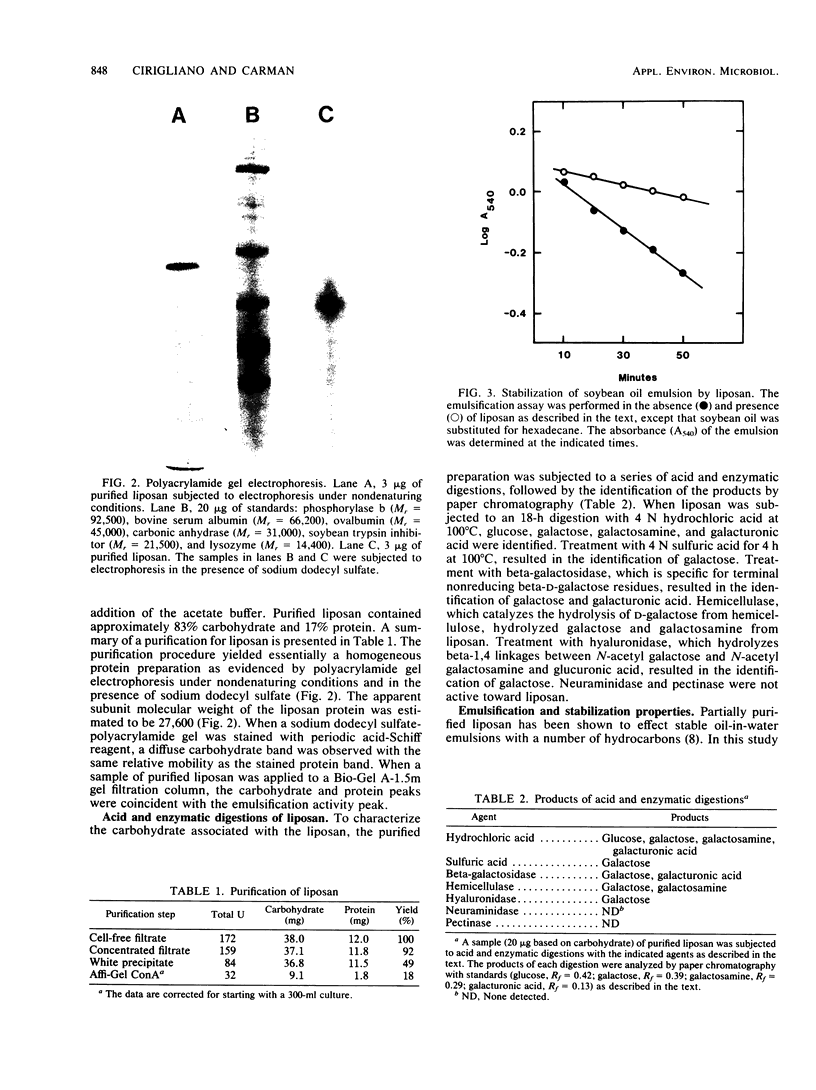
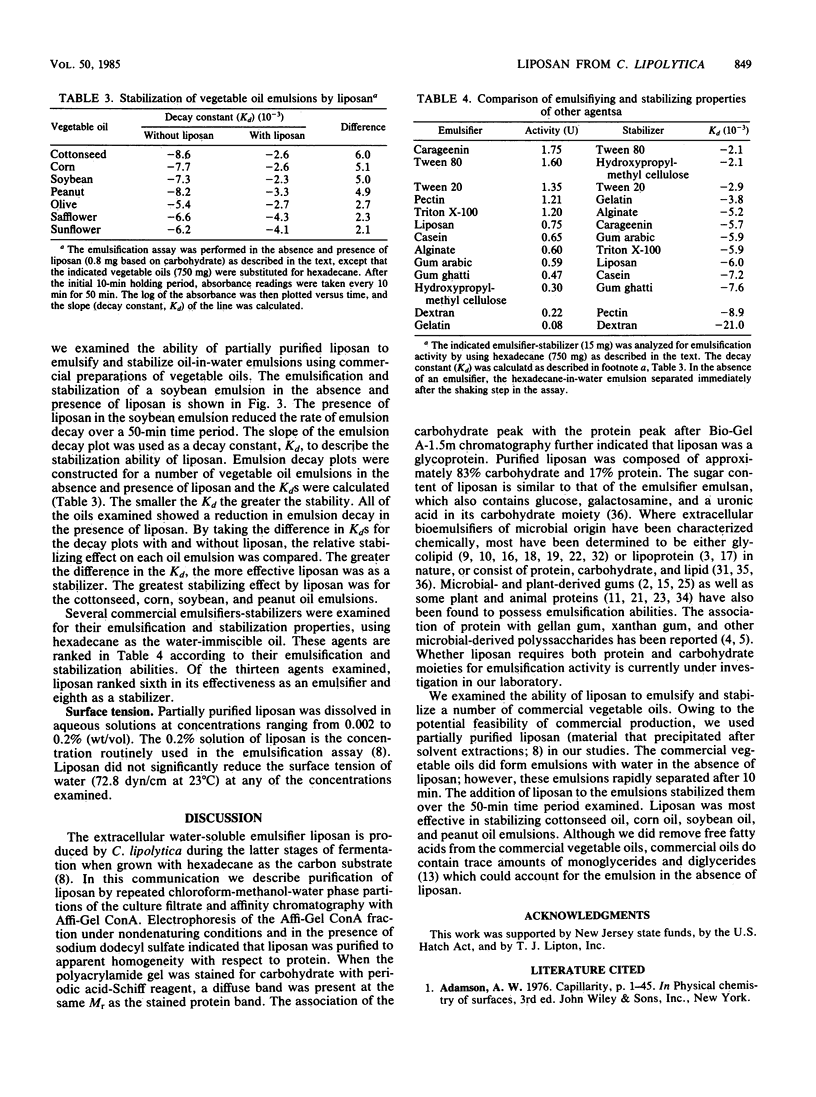

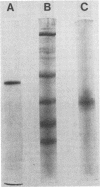
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo O. E. Emulsifying properties of a new polysaccharide gum. J Pharm Sci. 1967 Sep;56(9):1141–1145. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600560919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arima K., Kakinuma A., Tamura G. Surfactin, a crystalline peptidelipid surfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis: isolation, characterization and its inhibition of fibrin clot formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 May 10;31(3):488–494. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90503-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle C. D., Reade A. E. Characterization of two extracellular polysaccharides from marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):392–399. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.392-399.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirigliano M. C., Carman G. M. Isolation of a bioemulsifier from Candida lipolytica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):747–750. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.747-750.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. G., Paddock D. A. Production of a Biosurfactant from Torulopsis bombicola. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):173–176. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.173-176.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Inoue S. Sophorolipids from Torulopsis bombicola: possible relation to alkane uptake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1278–1283. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1278-1283.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer A., Bock H., Wagner F. Chemical and Physical Characterization of Interfacial-Active Lipids from Rhodococcus erythropolis Grown on n-Alkanes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):864–870. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.864-870.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. Y., Lang S., Wagner F., Witte L., Wray V. Formation and identification of interfacial-active glycolipids from resting microbial cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):610–617. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.610-617.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahara T., Erickson L. E., Gutierrez J. R. Characteristics of hydrocarbon uptake in cultures with two liquid phases. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1977 Jan;19(1):9–25. doi: 10.1002/bit.260190103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines O., Bayer E. A., Gutnick D. L. Localization of emulsan-like polymers associated with the cell surface of acinetobacter calcoaceticus. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):893–905. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.893-905.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokop A., Ludvik M., Erickson L. E. Growth models of cultures with two liquid phases. 8. Experimental observations on droplet size and interfacial area. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1972 Jul;14(4):587–608. doi: 10.1002/bit.260140405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E., Perry A., Gibson D. T., Gutnick D. L. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: specificity of hydrocarbon substrate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):409–413. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.409-413.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E., Zuckerberg A., Rubinovitz C., Gutnick D. L. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: isolation and emulsifying properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):402–408. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.402-408.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajic J. E., Guignard H., Gerson D. F. Properties and biodegradation of a bioemulsifier from Corynebacterium hydrocarboclastus. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1977 Sep;19(9):1303–1320. doi: 10.1002/bit.260190905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerberg A., Diver A., Peeri Z., Gutnick D. L., Rosenberg E. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: chemical and physical properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):414–420. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.414-420.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]