Abstract
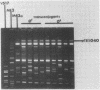
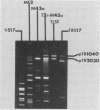
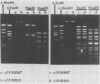
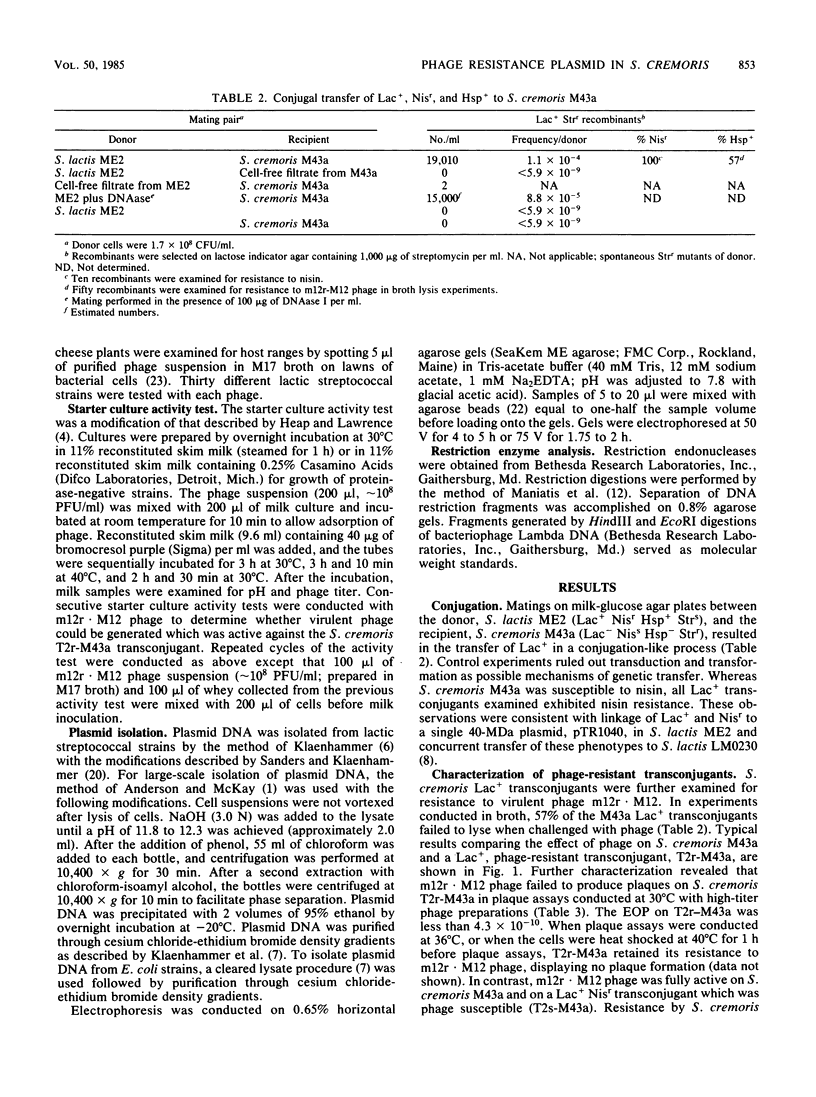
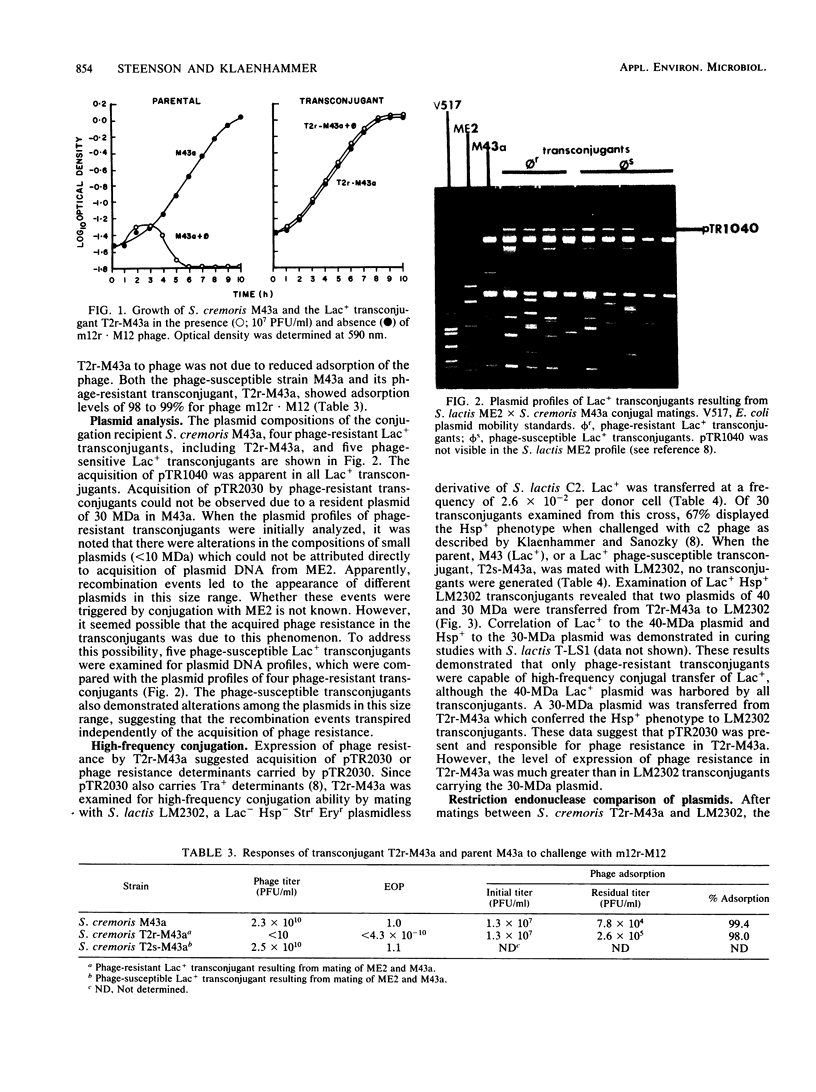
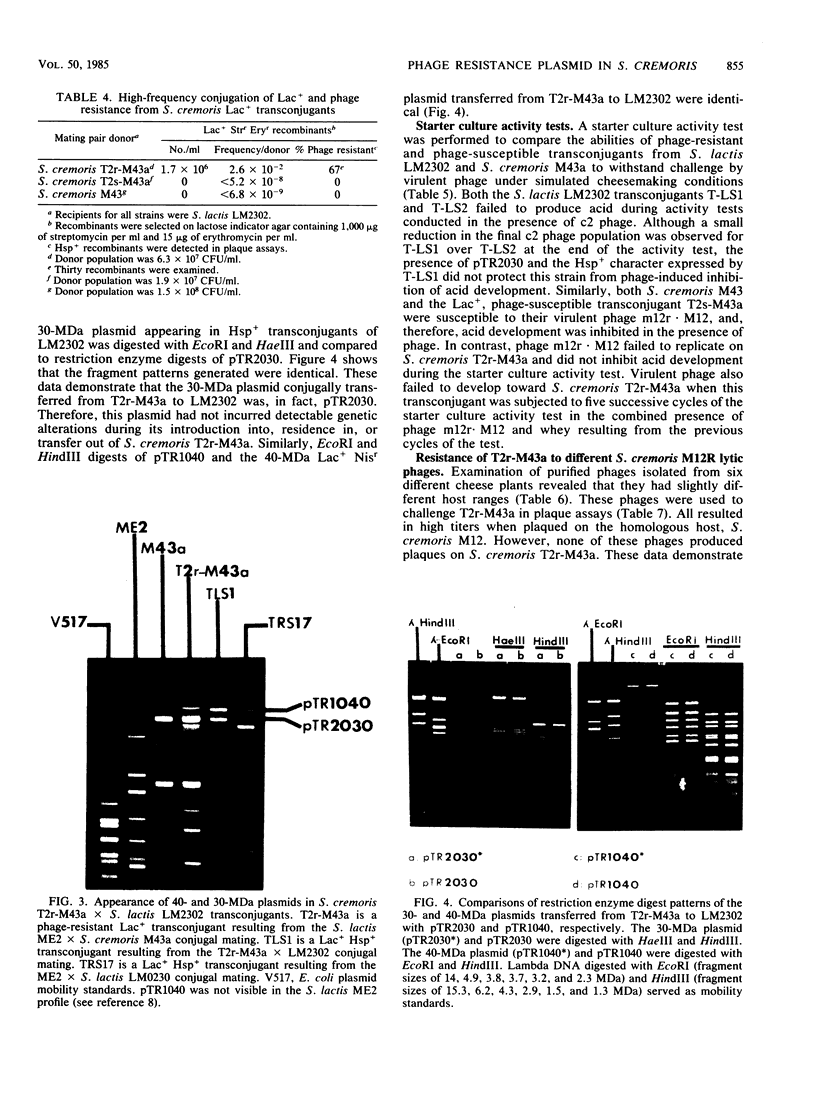
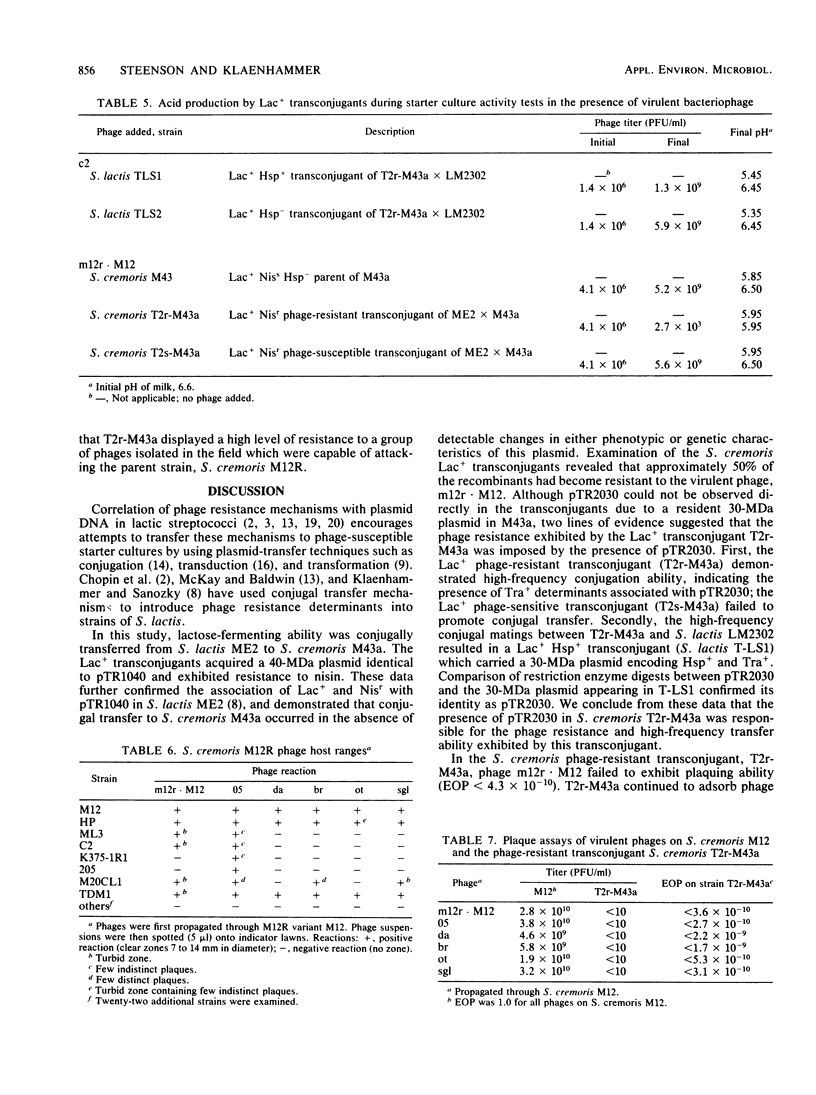
Conjugal transfer of lactose-fermenting ability (Lac+), nisin resistance (Nisr), and phage resistance (Hsp+) was demonstrated in matings between Streptococcus lactis ME2 (donor) and Streptococcus cremoris M43a (recipient), a derivative of M12R. Transconjugants were detected by transfer of Lac+ and were found to exhibit Nisr and harbor a 40-megadalton plasmid (pTR1040). Fifty-six percent of Lac+ transconjugants were resistant to the S. cremoris M12R lytic phage. Efficiency of plaquing for phage m12r . M12 on a phage-resistant transconjugant, T2r-M43a, was less than 4.3 X 10(-10). Five additional phages which were virulent for S. cremoris M12R and isolated from industrial sources failed to plaque on S. cremoris T2r-M43a. Mating experiments with T2r-M43a revealed that phage resistance was accompanied by high-frequency conjugation ability (Tra+) and the appearance of both pTR1040 and pTR2030 encoding Lac+ Nisr and Tra+ Hsp+, respectively, in transconjugants of S. lactis LM2302. Phage-sensitive Lac+ transconjugants of S. cremoris M43a (T2s-M43a) showed no conjugal ability. These observations confirmed that pTR2030 was present and responsible for the phage resistance and conjugal ability exhibited by the S. cremoris transconjugant T2r-M43a. Unlike the S. lactis LM2302 transconjugant carrying pTR2030, resistance of T2r-M43a to phage was not affected at high temperatures (35 to 40 degrees C) or destabilized in repeated transfers through a starter culture activity test. These results demonstrated that phage resistance conferred by pTR2030 in the S. cremoris transconjugant was effective against industrially significant phages under fermentation conditions normally encountered during cheese manufacture.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopin A., Chopin M. C., Moillo-Batt A., Langella P. Two plasmid-determined restriction and modification systems in Streptococcus lactis. Plasmid. 1984 May;11(3):260–263. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R., McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A. Improved lysis of group N streptococci for isolation and rapid characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Mar;35(3):592–600. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.3.592-600.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R., Sanozky R. B. Conjugal transfer from Streptococcus lactis ME2 of plasmids encoding phage resistance, nisin resistance and lactose-fermenting ability: evidence for a high-frequency conjugative plasmid responsible for abortive infection of virulent bacteriophage. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jun;131(6):1531–1541. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-6-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J. K., McKay L. L. Plasmid transformation of Streptococcus lactis protoplasts: optimization and use in molecular cloning. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):252–259. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.252-259.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A. Conjugative 40-megadalton plasmid in Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis DRC3 is associated with resistance to nisin and bacteriophage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):68–74. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.68-74.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Walsh P. M. Conjugal transfer of genetic information in group N streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.84-91.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Zottola E. A. Loss of lactose metabolism in lactic streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jun;23(6):1090–1096. doi: 10.1128/am.23.6.1090-1096.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Cords B. R., Baldwin K. A. Transduction of lactose metabolism in Streptococcus lactis C2. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):810–815. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.810-815.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Klaenhammer T. R. Characterization of Phage-Sensitive Mutants from a Phage-Insensitive Strain of Streptococcus lactis: Evidence for a Plasmid Determinant that Prevents Phage Adsorption. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1125–1133. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1125-1133.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Klaenhammer T. R. Evidence for Plasmid Linkage of Restriction and Modification in Streptococcus cremoris KH. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Dec;42(6):944–950. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.6.944-950.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Klaenhammer T. R. Phage Resistance in a Phage-Insensitive Strain of Streptococcus lactis: Temperature-Dependent Phage Development and Host-Controlled Phage Replication. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):979–985. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.979-985.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Klaenhammer T. R. Restriction and modification in group N streptococci: effect of heat on development of modified lytic bacteriophage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):500–506. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.500-506.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer H. E., Sederoff R. R. Improved estimation of DNA fragment lengths from Agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jul 15;115(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90533-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. M., McKay L. L. Recombinant plasmid associated cell aggregation and high-frequency conjugation of Streptococcus lactis ML3. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):937–944. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.937-944.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]