Abstract
Lichen sclerosus is a chronic inflammatory mucocutaneous disorder predominately affecting prepubertal girls and postmenopausal women. Isolated lichen sclerosus affecting the oral mucosa is exceedingly rare, and only 13 patients with biopsy-proved isolated oral disease have been reported in the literature. We report on a 7-year-old Korean girl with a well-demarcated 1.2×1.2 cm atrophic white plaque with an erythematous border and focal telangiectasia on the left vermillion lip, extending to the labial mucosa. No other cutaneous surfaces, including genitalia, were involved. An incisional biopsy of the plaque on the lip revealed a patchy lichenoid infiltrate of lymphocytes associated with sclerosis of the papillary dermis and a thinned epidermis consistent with a diagnosis of linear orofacial lichen sclerosus. Treatment with a short course of 1% pimecrolimus cream effectively prevented the progression of this lesion.
Keywords: Childhood, Lichen sclerosus, Oral, Pimecrolimus
INTRODUCTION
Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus (LSA) is a relatively uncommon chronic inflammatory disease of the skin and mucous membranes. Although LSA may affect all parts of the body, LSA confined to the oral mucosa is extremely rare, according to the few reported cases of histopathologically verified oral LSA1,2. Herein, we report the case of a 7-year-old girl with LSA that developed on the oral mucosa. This report adds a new case to the limited number of histologically proven oral LSA cases, and 1% pimecrolimus cream (Elidel™; Novartis Korea, Korea) seems to be a safe and effective treatment modality for steroid-resistant oral mucosal LSA.
CASE REPORT
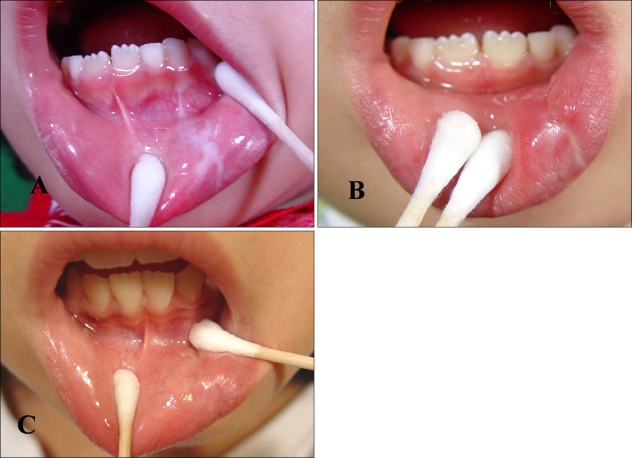
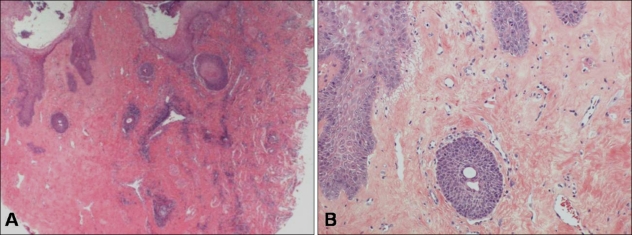
We report the case of a 7-year-old Korean girl who presented with a 2-year history of a white patch on her left lower lip, extending intraorally. Although asymptomatic, a gradual spreading of the whitish atrophic patch was noted. The patient did not have a history of trauma such as lip or cheek biting. Skin and anogenital lesions were not reported, and there was no family history of similar lesions. On physical examination, we found a macular, white lesion affecting the left lower lip and extending intraorally to the left buccal mucosa. The lesion was a 2.5×1.5 cm in size, creamy-white atrophic plaque with sclerosis and telangiectasia (Fig. 1A). An incision biopsy of the lesion revealed a patchy lichenoid infiltrate of lymphocytes associated with hyalinization of the papillary dermis and a thinned epidermis consistent with a diagnosis of linear orofacial lichen sclerosus (Fig. 2). Immunofluorescent staining of the section was negative for immunoglobulin G, M, A, and C3. Her mother's main concern was its cosmetic appearance and the possibility of further spreading, so she asked for relief of tightening at the left buccal mucosa. Although previous treatments including topical antibiotics, emollients, and topical steroids up to the strength of 0.05% clobetasol propionate ointment were tried, the results were unsatisfactory, and her mother complained that the lower lip lesion showed more atrophic features than before topical steroid treatment. After application of 1% pimecrolimus cream twice daily, the condition improved within 4 weeks, and the patient felt less tightening at the buccal mucosa. Moreover, the sclerotic and telangiectatic features of the lesion had improved better than before (Fig. 1B). At the 2-month follow up, the mucosal lesion of her lip appeared almost normal. In contrast to the buccal mucosal lesions, the atrophic lower lip lesion was resistant to treatment and tended to be chronic with little tendency for spontaneous resolution. The patient stopped using the 1% pimecrolimus cream. Review after a further 4 weeks showed that the lesions had undergone resolution with some residual lip atrophy, and no relapse has occurred since then for 30 months (Fig. 1C).
Fig. 1.
(A) The 2.5×1.5 cm sized, creamy white atrophic, erythematous and telangiectatic bordered lichen sclerosus et atrophicus lesion is affecting the left lower lip and extending intraorally onto the left buccal mucosa. Clinical appearance after 4 weeks (B) and 30 months (C) of treatment with 1% pimecrolimus cream.
Fig. 2.
(A) Histopathological findings show a patchy lichenoid infiltrate of lymphocytes associated with degenerative changes and hyalinization of the papillary dermis (H&E stain, ×40). (B) Hydropic degeneration along the basement membrane is shown on high power magnification (H&E stain, ×100).
DISCUSSION
LSA is a relatively uncommon chronic inflammatory disease of the skin and mucous membranes that may affect all parts of the body1,2. Treatment of oral LSA is usually unnecessary because of its asymptomatic nature, but some patients complain of slight tightening and soreness at the adjacent buccal gingival that could be explained by sclerosis of the lesion3-5. Treatment strategies for oral LS are derived from therapeutic experience with extraoral mucosal presentations. At present, there is no effective, curative treatment for oral LSA. The efficacy of topical application or intralesional injection of corticosteroid has been used successfully in the few instances of oral LSA described previously in adults and adolescents5-7. Although ultrapotent topical corticosteroids have been the first-line treatment for LSA at any site, the outcomes are variable3,7,8. Moreover, there has been no randomized controlled trial comparing therapeutic experiences. In another case of oral LSA, the efficacy of topical corticosteroids was insufficient, so grafting treatment was performed to restore gingival health3. There have been several case reports of successfully treating anogenital LSA with topical tacrolimus9. Furthermore, in a report of vulval LSA, 1% pimecrolimus cream was applied twice daily for 3 months, resulting in complete remission within 6 weeks10. In our oral LSA patient, we tried a treatment plan to reduce possible complications by using a potent topical corticosteroid. We prescribed a twice daily application of 1% pimecrolimus cream, and the patient experienced improvement within 4 weeks. The improvement in oral soreness and lightening was dramatic, and the progression of this lesion likely prevented any discomfort such as atrophy and irritation.
Tacrolimus belongs to a new class of topical calcineurin inhibitors and has been licensed for atopic eczema. It reduces antigen presentation and T-cell activation by inhibiting the calcineurin pathway. Moreover, tacrolimus affects other cell types involved in pruritus and inflammation by preventing the cascade of immune and inflammatory signals9. Pimecrolimus has a similar mode of action to that of tacrolimus but is more selective and may be better tolerated than topical tacrolimus due to less local irritation. In contrast to topical steroid, there is no potential for pimecrolimus to induce skin atrophy and telangiectasia8.
The prevalence of LSA affecting the oral mucosa is extremely rare, according to the few reported cases of histopathologically confirmed oral LSA, but, in some instances, it may be the only manifestation of the disease1,2. Oral LSA occurs on the palate, tongue, buccal mucosa, or labial mucosa with vermillion lip2. Oral mucosal lesions appear as well-demarcated, whitish, flat lesions with varying size and rare coexistence with telangiectasia. Oral lesions may occur without accompanying skin or genital lesions and are generally asymptomatic. The gender distribution of patients with oral LSA is almost equal with no racial preferences. Skin and mucosal lesions show almost identical histopathologic features characterized by a gradual epidermal atrophy and subepidermal homogenization and hyalinization of collagen fibers with an underlying band-like lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate3. Clinically, the differential diagnosis of oral LSA includes lichen planus, leukoplakia, oral submucous fibrosis, chronic hyperplastic candidial infections, and other white mucosal lesions that tend to be plaque-like in their presentation. It is sometimes difficult to differentiate oral LSA from oral lichen planus; the band of lymphocytes at the upper dermis usually found with lichen planus is not found with LSA4. Leukoplakia is defined as a white plaque that does not wipe off and is characterized by hyperkeratosis or hyperorthokeratosis with varying degrees of acanthosis and chronic inflammation. Sometimes, this lesion is accompanied by a loss of normal differentiation of epithelium, dyskeratosis, basal cell hyperplasia, and anaplasia. Oral submucosal fibrosis becomes progressively pallor, and fibrosis and ulcer of the tissues usually begins in the soft palate and then involves the buccal mucosa, lip, and tongue. Histologically, in our case, eosinophilic collagen bands were found in the submucosal fibrosis, but a hyalinized eosinophilic subepithelial band and basal cell degeneration were found in oral LSA.
This report adds a new case to the limited number of histologically proven oral LSA cases, and 1% pimecrolimus cream seems to be a safe and may be a valuable second-line treatment modality for patients with steroid-related side effects or steroid-resistant LSA. Further case-controlled studies on a larger number of patients are now warranted to substantiate our findings and to investigate the long-term efficacy and safety of 1% pimecrolimus cream for treating oral LSA.
References
- 1.Jensen T, Worsaae N, Melgaard B. Oral lichen sclerosus et atrophicus: a case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;94:702–706. doi: 10.1067/moe.2002.129185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ravits HG, Welsh AS. Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus of the mouth. AMA Arch Derm. 1957;76:56–58. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1957.01550190060011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Buajeeb W, Kraivaphan P, Punyasingh J, Laohapand P. Oral lichen sclerosus et atrophicus. A case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1999;88:702–706. doi: 10.1016/s1079-2104(99)70013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mendonça EF, Ribeiro-Rotta RF, Silva MA, Batista AC. Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus of the oral mucosa. J Oral Pathol Med. 2004;33:637–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2004.00193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kaur S, Thami GP, Kanwar AJ, Mohan H. Linear oro-facial lichen sclerosus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2002;27:467–470. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2230.2002.01068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kelly SC, Helm KF, Zaenglein AL. Lichen sclerosus of the lip. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006;23:500–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2006.00293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rajlawat BP, Triantafyllou A, Field EA, Parslew R. Lichen sclerosus of the lip and buccal mucosa. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2004;29:684–685. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2004.01653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Neill SM, Tatnall FM, Cox NH British Association of Dermatologists. Guidelines for the management of lichen sclerosus. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:640–649. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.05012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hengge UR, Krause W, Hofmann H, Stadler R, Gross G, Meurer M, et al. Multicentre, phase II trial on the safety and efficacy of topical tacrolimus ointment for the treatment of lichen sclerosus. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155:1021–1028. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Goldstein AT, Marinoff SC, Christopher K. Pimecrolimus for the treatment of vulvar lichen sclerosus in a premenarchal girl. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2004;17:35–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2003.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]