Abstract
Localized involutional lipoatrophy (LIL) is a rare distinctive idiopathic form of localized lipoatrophy. The characteristic features in histopathology of LIL are diminutive fat lobules composed of small adipocyte resembling fetal fat tissue. LIL is not a well-known disorder, there have been only a few reports on LIL in the English literature. We herein report 2 cases of LIL and review the previously published cases.
Keywords: Idiopathic, Involutional, Lipoatrophy, Localized
INTRODUCTION
Localized involutional lipoatrophy (LIL) is a rare distinctive idiopathic form of localized lipoatrophy. It is characterized by loss of adipose tissue without antecedent inflammation and was first described by Peters and Winkelmann1 in 1986. LIL is not a well-known disorder; indeed, there have been only a few reports on LIL in the English literature. We herein report 2 cases of LIL and review the previously published reports.
CASE REPORT
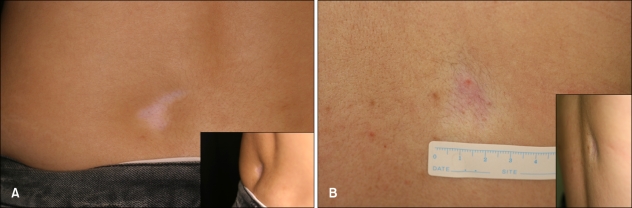
The first case was that of a 25-year-old woman, who presented with a history of an asymptomatic lesion on her lower back that had slowly become depressed over the past 4 months. She denied any history of injury or injection at the site. She had no associated medical problems or history of drug intake. On physical examination, she had a well-demarcated, 3×4 cm sized, hypopigmented, atrophic, depressed lesion on her lower back (Fig. 1A). Laboratory examination showed no abnormal findings in her complete blood count, blood chemistry, or autoantibody profile. The biopsy specimen showed epidermal atrophy (Fig. 2A), dermal fibrosis, and diminutive fat lobules composed of small adipocytes and vessels without inflammation (Fig. 2B).
Fig. 1.
(A) Well-demarcated, 3×4 cm, hypopigmented, atrophic, depressed lesion on the lower back was seen on the lower back of the first patient (inlet, lateral aspect view). (B) Well-demarcated, 3×4 cm, hypopigmented, atrophic, pinkish, depressed lesion was seen on the upper back of the second patient (inlet, lateral aspect view).
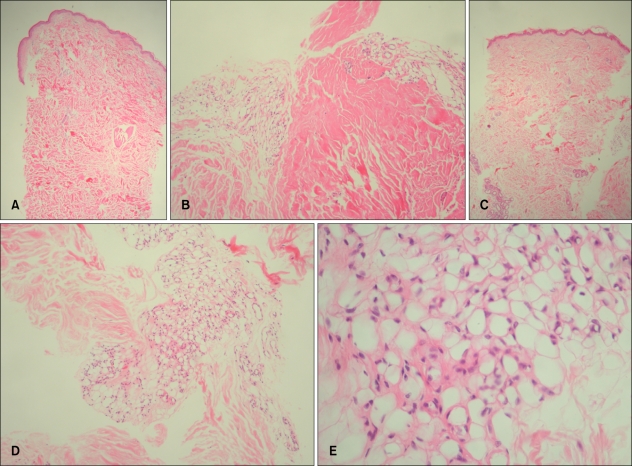
Fig. 2.
(A) Histopathologic examination of a sample taken from the first patient showed atrophic epidermis and prominent collagen bundles in the dermis without inflammation (H&E stain, ×40). (B) A view at higher magnification revealed that the homogenized collagen bundles entrapped characteristic diminutive fat lobules resembling fetal adipose tissue (H&E stain, ×100). (C) The biopsy specimen from the second patient showed atrophic epidermis and increased collagen bundles in the dermis (H&E stain, ×40). (D) Diminutive fat lobules were seen in the subcutaneous layer (H&E stain, ×100). (E) A view at higher magnification revealed that the immature adipocytes were variable in size and embedded in well-vascularized stroma (H&E stain, ×400).
The second case involved a 27-year-old woman who presented with a 1-month history of an asymptomatic lesion on her upper back. She denied any history of injury or injection at the site. She had no associated medical problems or history of drug intake. Physical examination revealed a well-demarcated, 3×4 cm sized, hypopigmented, atrophic, pinkish, depressed lesion on her upper back (Fig. 1B). Laboratory tests, including complete blood count, chemistry, and autoantibody screening, were all normal. Histopathological examination of the biopsy specimen revealed atrophic epidermis and increased collagen bundles in the dermis (Fig. 2C), as well as characteristic diminutive fat lobules (Fig. 2D) resembling fetal adipose tissue in the subcutaneous layer. There were small, attenuated fat lobules of variable size composed of small adipocytes embedded in well-vascularized and hyalinized tissue (Fig. 2E). There was no evidence of dermal or subcutaneous inflammation.
DISCUSSION
Clinically, LIL presents as an asymptomatic, noninflamed, well demarcated, localized, atrophic depression. The differential diagnoses of LIL include lupus erythematosus profundus2, morphea3, lichen sclerosus et atrophicus3, and other types of lipoatrophy associated with triggers. These disorders can be differentiated from LIL based on the latter's characteristic histopathological feature, which is the presence of diminutive fat lobules composed of small adipocytes that resemble fetal fat tissue3.
There are 6 reports on LIL in the medical literature. Since Peters and Winkelmann1 first described LIL, Dahl et al.4 reported on 16 patients with LIL in 1996. Ten of the 16 patients, however, had histories of local injections of either corticosteroids or antibiotics at the affected sites, which often involved the lateral aspect of the arms or buttocks. Yamamoto et al.5 described 6 cases of LIL in 2002, and 4 of the 6 cases had local injections at the sites of the subsequent development of LIL. Hisamichi et al.6 reported 2 Japanese cases of LIL in 2002. One of the 2 was preceded by an intramuscular injection of a corticosteroid. The above previous reports4-6 have confused LIL with lipoatrophy after drug injection or traumatic injury. Originally, LIL has been defined as a focal loss of subcutaneous tissue on one or several sites, occurring without any significant trigger or autoimmune disease (hence their idiopathic nature). Injections of several drugs, including triamcinolone, are known to cause lipoatrophy and should be considered as triggers. The pathophysiology of idiopathic LIL, however, is unknown. Patients with reported idiopathic LIL have all been young women, except for a 5-year-old boy who was the one exception1. Due to lack of report on and interest in idiopathic LIL, the pathogenesis of idiopathic LIL remains unclear, and the female predominance is difficult to explain. Therefore, herein, we suggest that dermatologists should pay attention to LIL and differentiate idiopathic LIL from other types of lipoatrophy after drug administration or injury. The precise diagnosis would pave a way for further study.
Footnotes
This work was supported by the SRC/ERC program of MOST/KOSEF (R11-2005-017-05003-0) and Basic research program through the NRF funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2010-0002431).
References
- 1.Peters MS, Winkelmann RK. The histopathology of localized lipoatrophy. Br J Dermatol. 1986;114:27–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1986.tb02776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cendras J, Durand L, Dereure O. Idiopathic localized involutional lipoatrophy: a lupus profunds-like condition. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007;87:546–547. doi: 10.2340/00015555-0300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Abbas O, Salman S, Kibbi AG, Chedraoui A, Ghosn S. Localized involutional lipoatrophy with epidermal and dermal changes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:490–493. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.06.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dahl PR, Zalla MJ, Winkelmann RK. Localized involutional lipoatrophy: a clinicopathologic study of 16 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:523–528. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(96)90673-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yamamoto T, Yokozeki H, Nishioka K. Localized involutional lipoatrophy: report of six cases. J Dermatol. 2002;29:638–643. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2002.tb00194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hisamichi K, Suga Y, Hashimoto Y, Matsuba S, Mizoguchi M, Ogawa H. Two Japanese cases of localized involutional lipoatrophy. Int J Dermatol. 2002;41:176–177. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-4362.2002.01395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]