Abstract
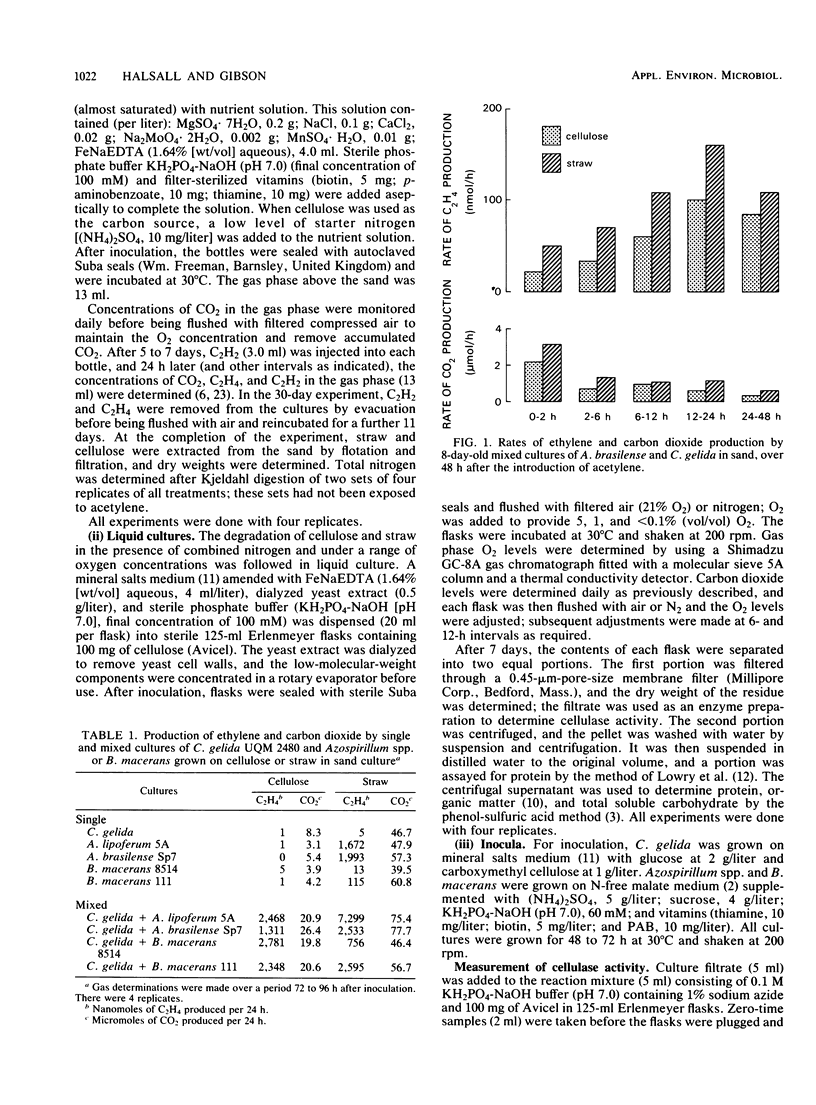
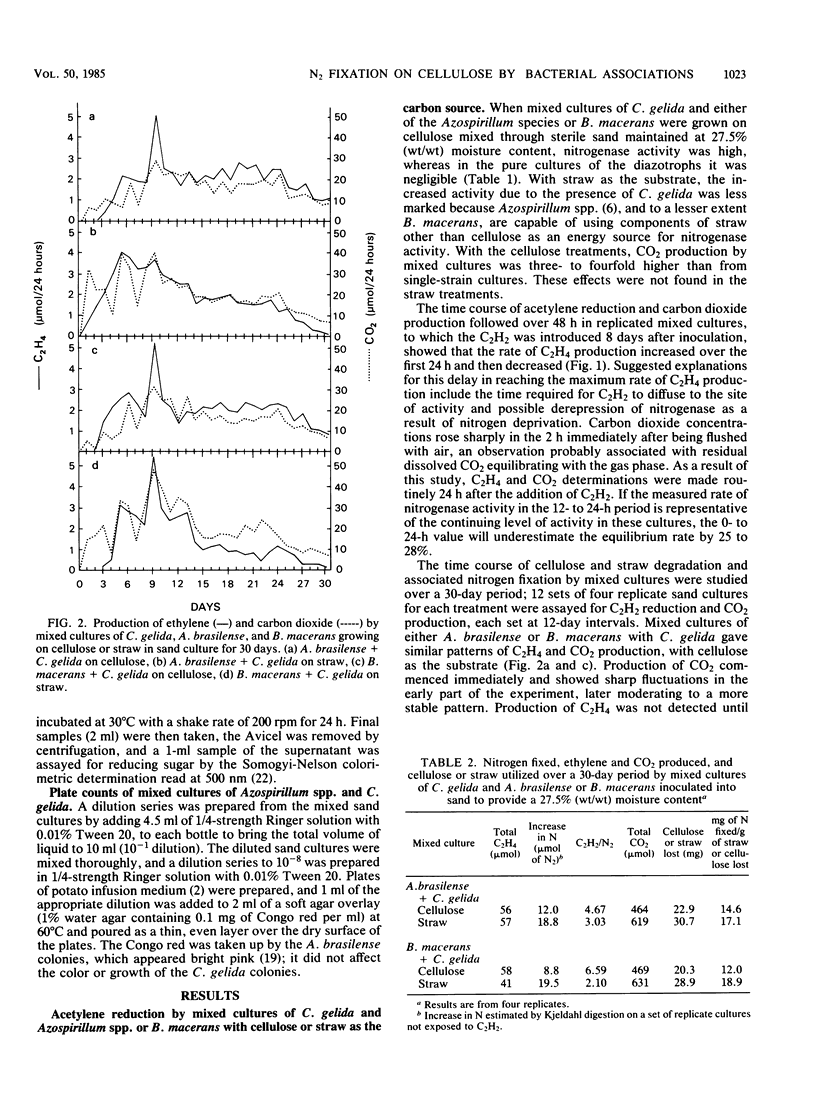
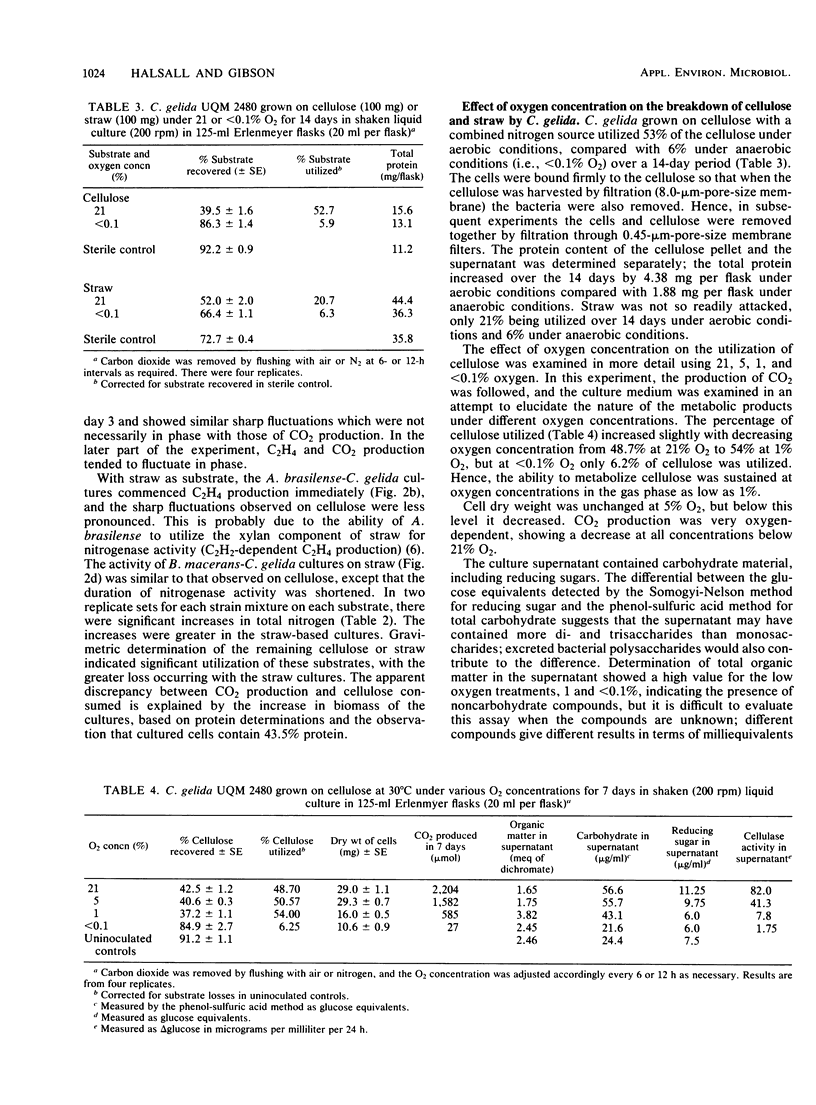
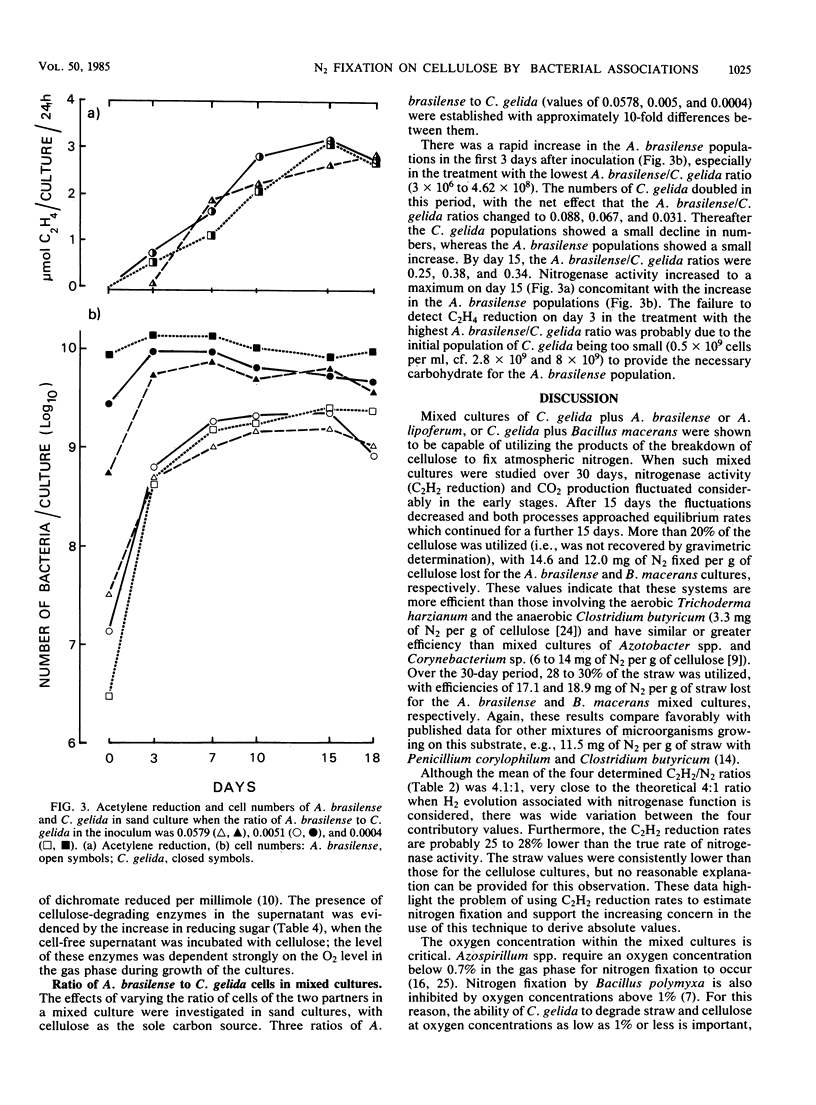
Mixed cultures of Cellulomonas gelida plus Azospirillum lipoferum or Azospirillum brasilense and C. gelida plus Bacillus macerans were shown to degrade cellulose and straw and to utilize the energy-yielding products to fix atmospheric nitrogen. This cooperative process was followed over 30 days in sand-based cultures in which the breakdown of 20% of the cellulose and 28 to 30% of the straw resulted in the fixation of 12 to 14.6 mg of N per g of cellulose and 17 to 19 mg of N per g of g straw consumed. Cellulomonas species have certain advantages over aerobic cellulose-degrading fungi in being able to degrade cellulose at oxygen concentrations as low as 1% O2 (vol/vol) which would allow a close association between cellulose-degrading and microaerobic diazotrophic microorganisms. Cultures inoculated with initially different proportions of A. brasilense and C. gelida all reached a stable ratio of approximately 1 Azospirillum/3 Cellulomonas cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cáceres E. A. Improved Medium for Isolation of Azospirillum spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):990–991. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.990-991.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAU F. H., WILSON P. W. Physiology of nitrogen fixation by Bacillus polymyxa. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:490–496. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.490-496.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINO S., WILSON P. W. Nitrogen fixation by a facultative bacillus. J Bacteriol. 1958 Apr;75(4):403–408. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.4.403-408.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsall D. M., Turner G. L., Gibson A. H. Straw and Xylan Utilization by Pure Cultures of Nitrogen-Fixing Azospirillum spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):423–428. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.423-428.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON M. J. A rapid micromethod for estimation of non-volatile organic matter. J Biol Chem. 1949 Dec;181(2):707–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. M. Phytotoxicity of acetic acid produced in the anaerobic decomposition of wheat straw. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;42(1):81–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okon Y., Houchins J. P., Albrecht S. L., Burris R. H. Growth of Spirillum lipoferum at constant partial pressures of oxygen, and the properties of its nitrogenase in cell-free extracts. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jan;98(1):87–93. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie R. J. Dinitrogen-fixing bacteria: computer-assisted identification of soil isolates. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Nov;26(11):1275–1283. doi: 10.1139/m80-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOGYI M. Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


