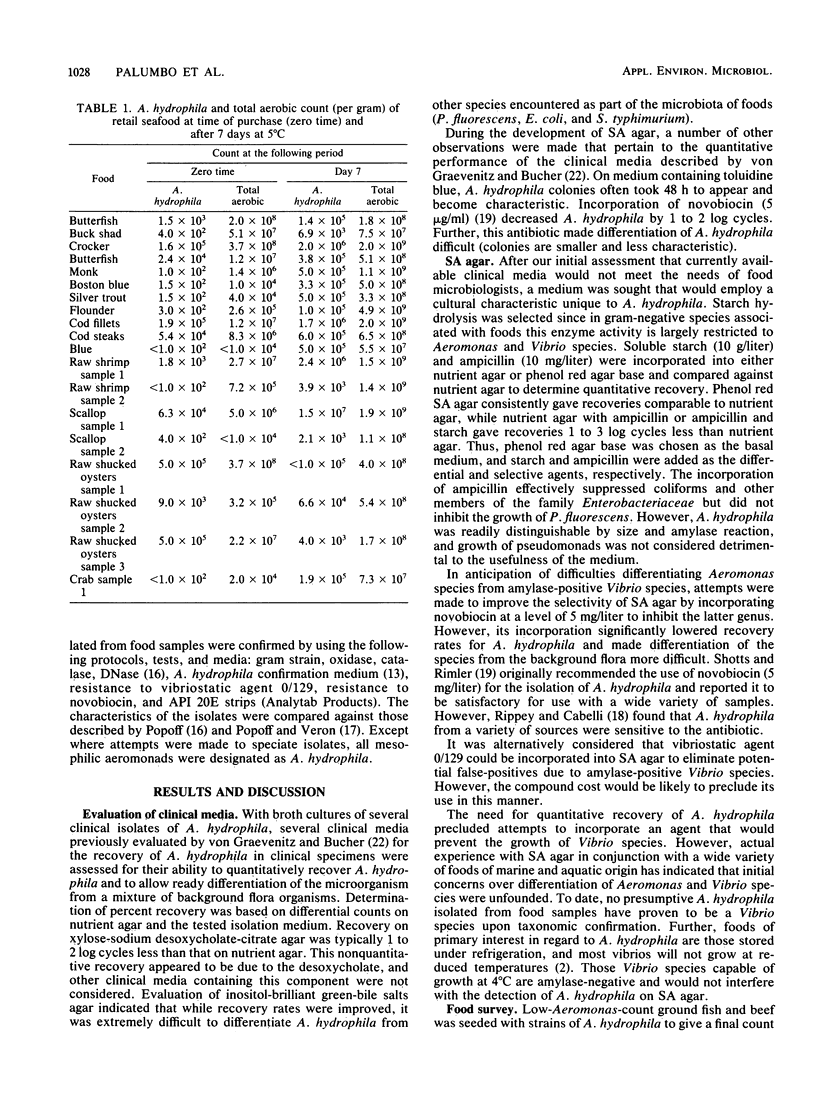
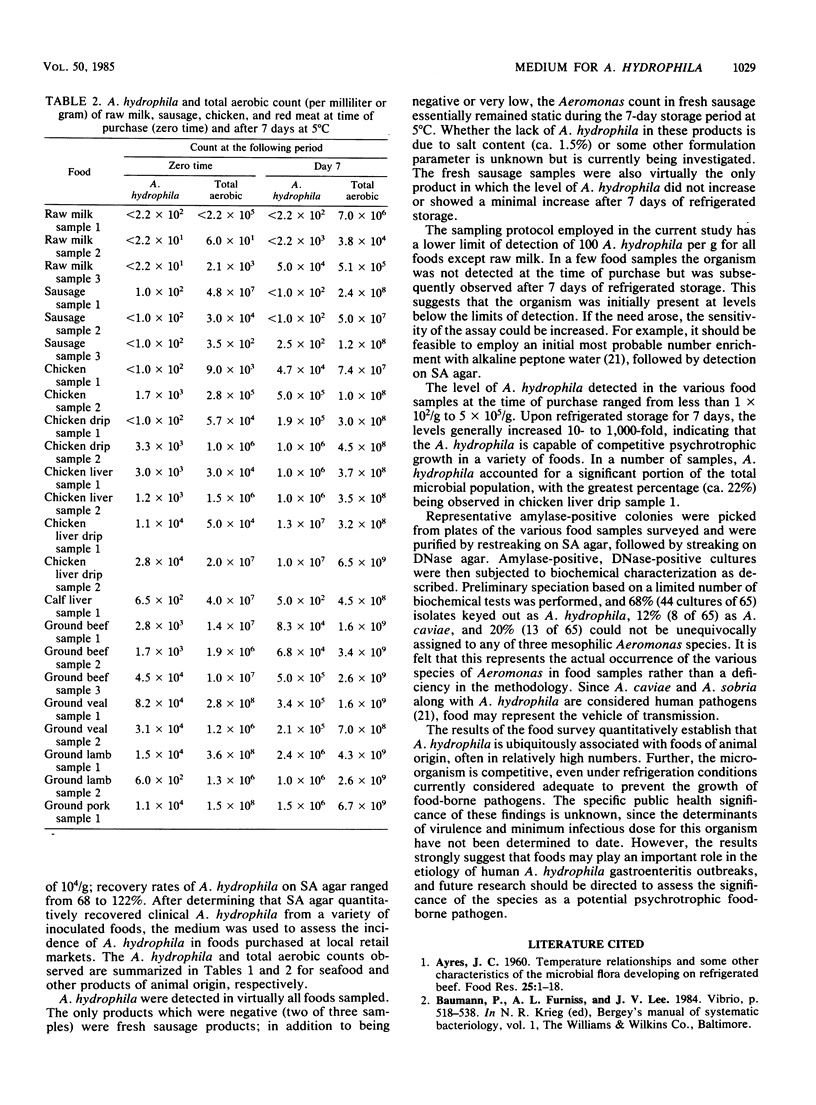
Abstract
Interest in Aeromonas hydrophila as a food-borne and human pathogen is increasing. Isolation media from the clinical laboratory were evaluated for food use and either did not give quantitative recovery of A. hydrophila or did not permit ready differentiation of A. hydrophila from the background microflora. A new medium was developed which permitted quantitative recovery of A. hydrophila from foods. The medium consisted of phenol red agar base (Difco Laboratories), soluble starch (10 g/liter), and ampicillin (10 mg/liter). All foods surveyed contained A. hydrophila. Foods sampled included red meats, chicken, raw milk, and seafood (fish, shrimp, scallops, crab, and oysters). The count of A. hydrophila at the time of purchase ranged from 1 × 102/g (lower limit of detection) to 5 × 105/g. In most instances, the count of A. hydrophila increased during 1 week of storage at 5°C. The starch-ampicillin agar developed permitted rapid quantitative recovery of A. hydrophila from foods in the presence of very large numbers of competing microflora.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke V., Gracey M., Robinson J., Peck D., Beaman J., Bundell C. The microbiology of childhood gastroenteritis: Aeromonas species and other infective agents. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):68–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enfors S. O., Molin G., Ternström A. Effect of packaging under carbon dioxide, nitrogen or air on the microbial flora of pork stored at 4 degrees C. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;47(2):197–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb01746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faghri M. A., Pennington C. L., Cronholm L. S., Atlas R. M. Bacteria associated with crabs from cold waters with emphasis on the occurrence of potential human pathogens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1054–1061. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1054-1061.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Robinson J. Aeromonas-associated gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1982 Dec 11;2(8311):1304–1306. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91510-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen T. C., Fliermans C. B., Hirsch R. P., Esch G. W. Prevalence and distribution of Aeromonas hydrophila in the United States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):731–738. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.731-738.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay J. M. Nature, characteristics, and proteolytic properties of beef spoilage bacteria at low and high temperatures. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jul;15(4):943–944. doi: 10.1128/am.15.4.943-944.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J., Seidler R. J., Lockman H., Colwell R. R. Medium for the presumptive identification of Aeromonas hydrophila and Enterobacteriaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):1023–1026. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.1023-1026.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M., Véron M. A taxonomic study of the Aeromonas hydrophila-Aeromonas punctata group. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):11–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippey S. R., Cabelli V. J. Membrane filter procedure for enumeration of Aeromonas hydrophila in fresh waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):108–113. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.108-113.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotts E. B., Jr, Rimler R. Medium for the isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):550–553. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.550-553.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Lee J. V., Miliotis M. D., Van de Walle S., Koornhof H. J., Jeffery L., Bryant T. N. Enterotoxin production in relation to taxonomic grouping and source of isolation of Aeromonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.175-180.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Graevenitz A., Bucher C. Evaluation of differential and selective media for isolation of Aeromonas and Plesiomonas spp. from human feces. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.16-21.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


