Abstract
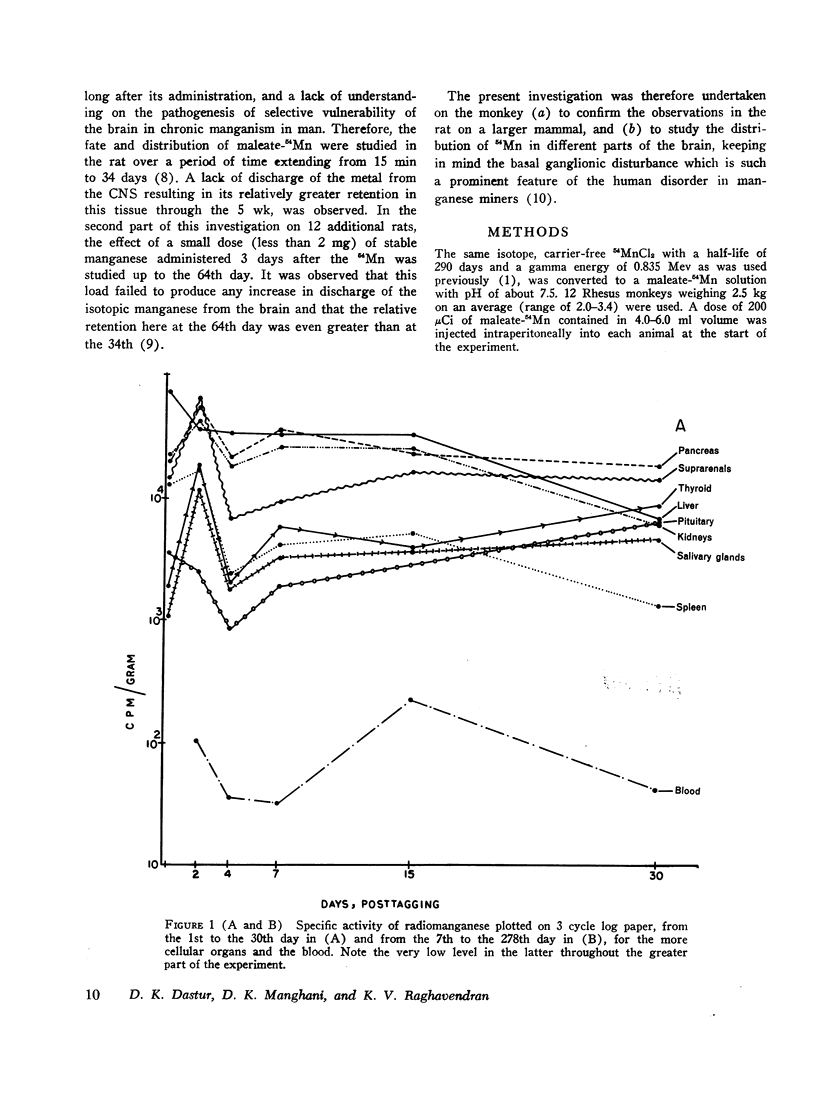
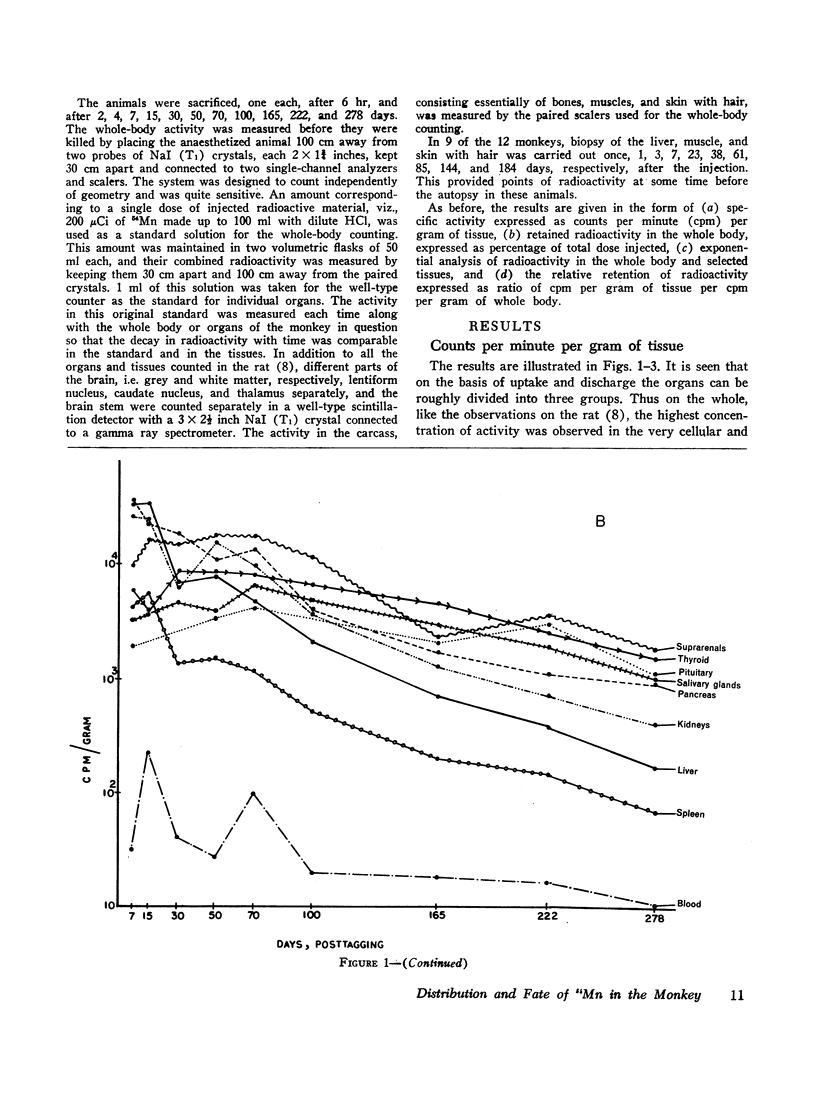
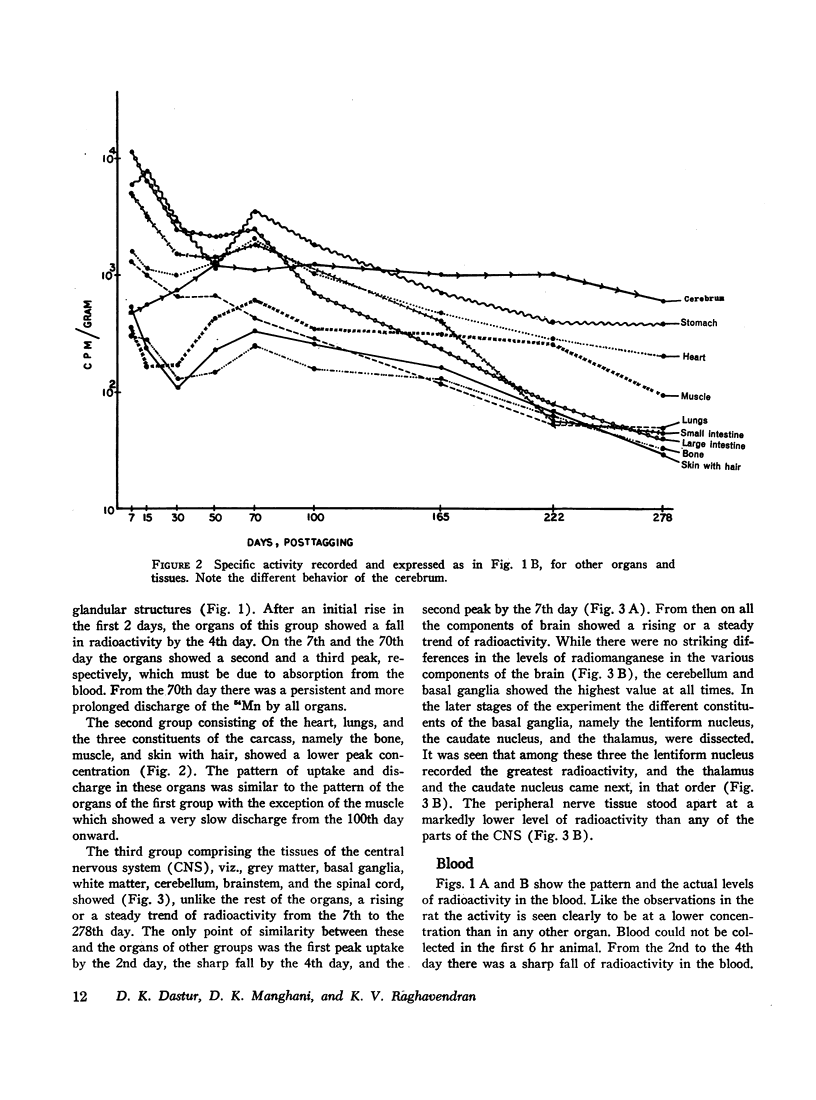
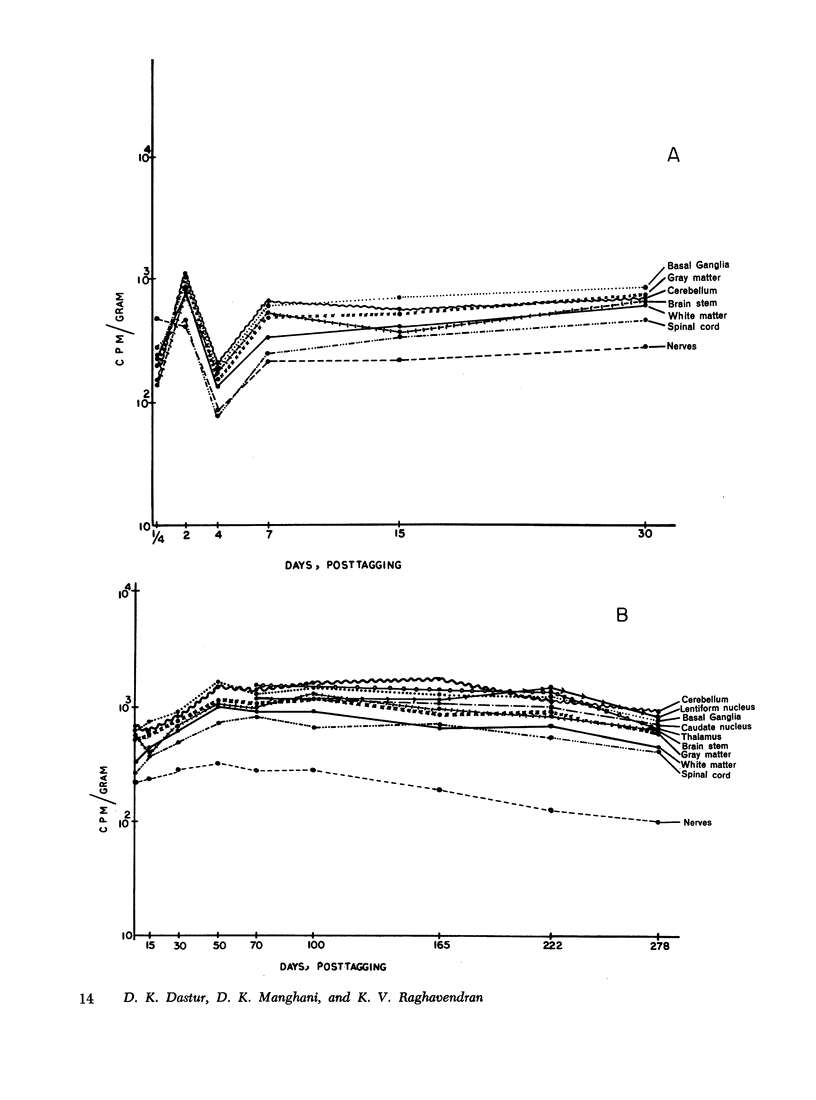
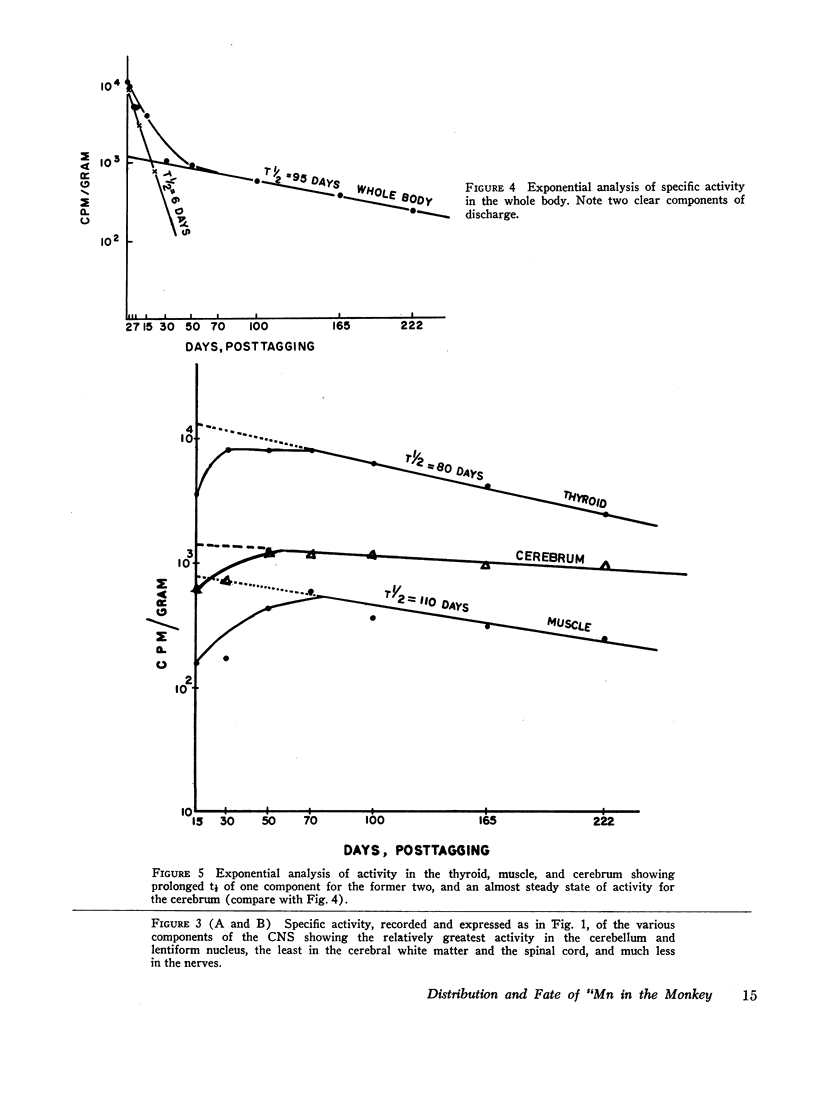
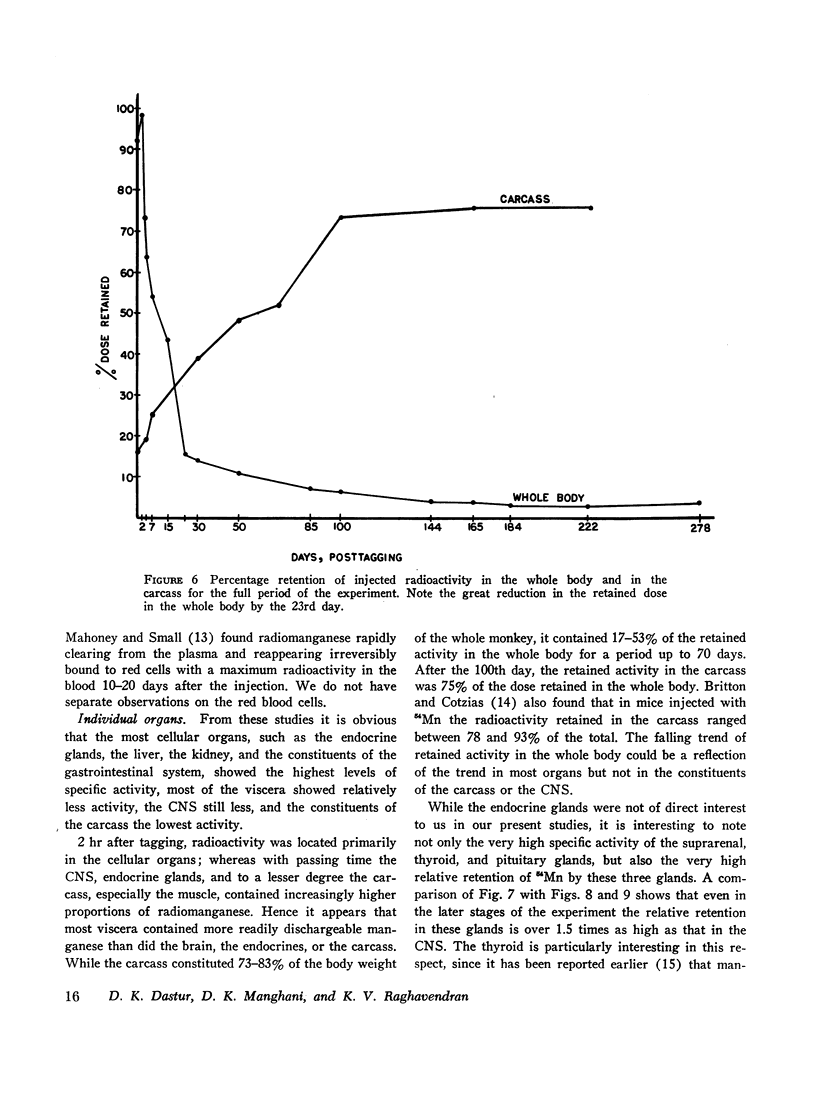
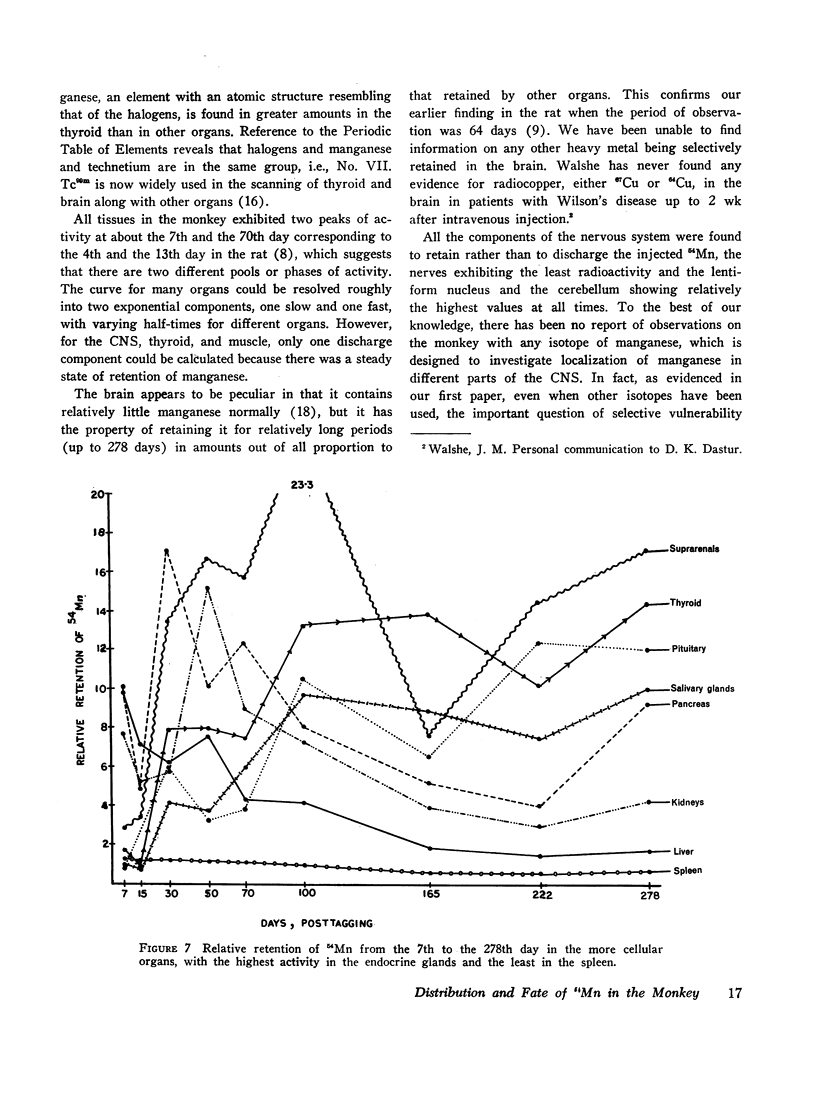
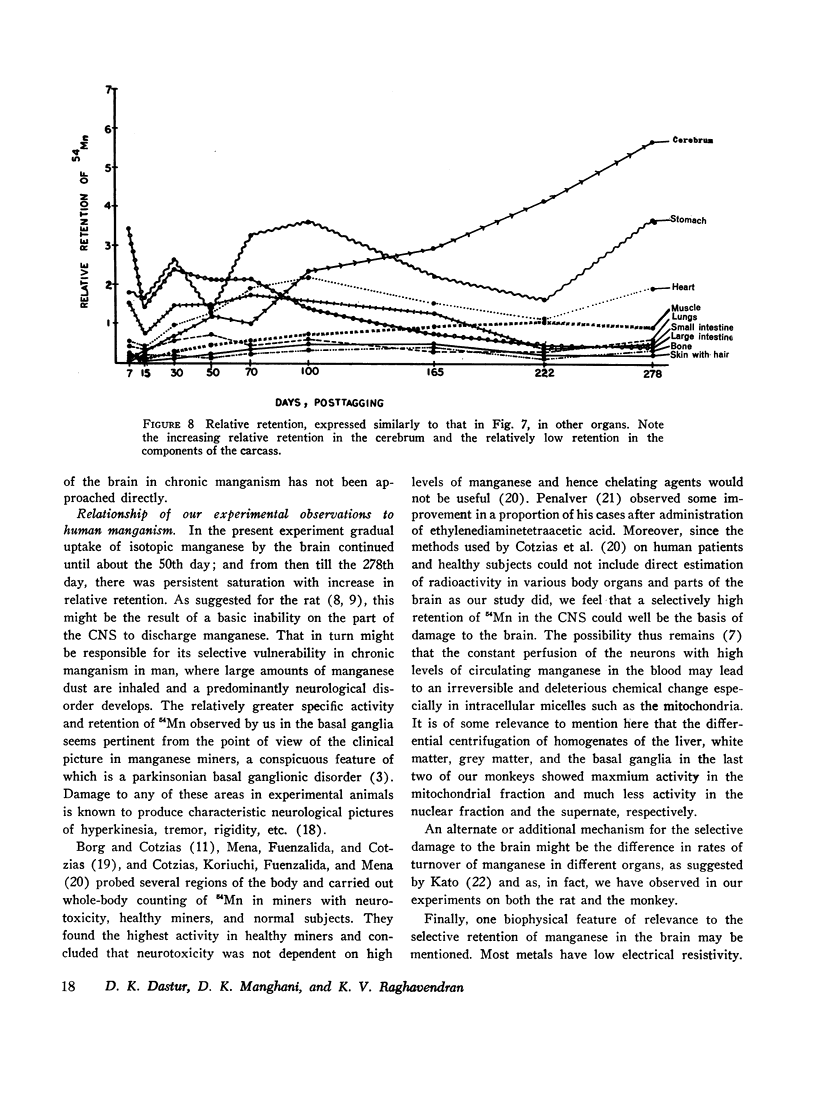
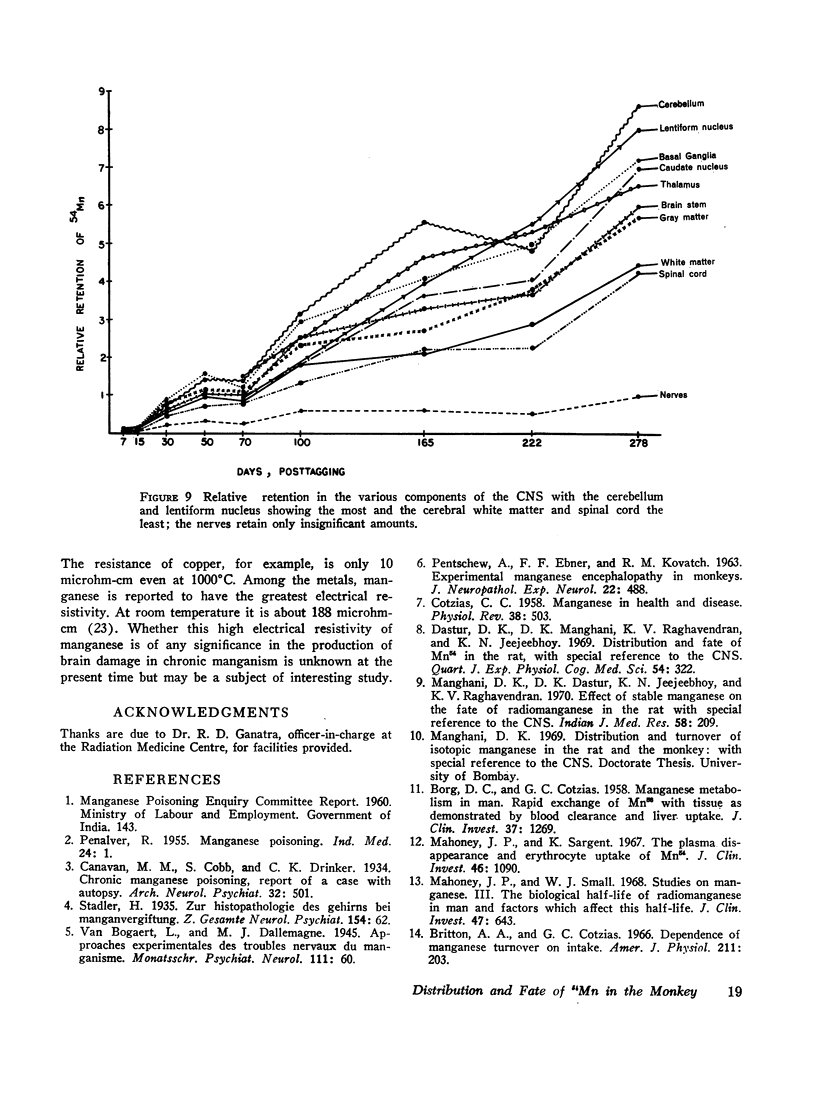
The fate and distribution of isotopic manganese administered as a single carrier-free dose of 200 μCi of maleate-54Mn to 12 rhesus monkeys was studied at different time periods from the 6th hr to the 278th day. Whole-body activity was measured, and all body organs and tissues and different parts of the central nervous system (CNS) were evaluated for specific activity, exponential analysis, and relative retention. Exponential analysis revealed a pattern of discharge with a fast and a slow component for the whole body and for many of the viscera. All parts of the CNS and, to a lesser degree, the thyroid and muscle showed an almost steady state of activity after the initial uptake. While the whole body and most organs and tissues appeared to discharge their radioactivity with the passage of time, first rapidly and then gradually, the CNS, endocrine glands, and muscle tissues showed persistent levels of specific activity. All components of the brain exhibited increasing relative retention, the lentiform nucleus and the cerebellum showing this more. It is suggested that the selective vulnerability of the brain in manganese miners might result from this inability on the part of the CNS to discharge the 54Mn with time. This investigation confirms and amplifies our earlier similar study on the rat.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORG D. C., COTZIAS G. C. Manganese metabolism in man: rapid exchange of MN56 with tissue as demonstrated by blood clearance and liver uptake. J Clin Invest. 1958 Sep;37(9):1269–1278. doi: 10.1172/JCI103714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton A. A., Cotzias G. C. Dependence of manganese turnover on intake. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):203–206. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTZIAS G. C. Manganese in health and disease. Physiol Rev. 1958 Jul;38(3):503–532. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.3.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotzias G. C., Horiuchi K., Fuenzalida S., Mena I. Chronic manganese poisoning. Clearance of tissue manganese concentrations with persistance of the neurological picture. Neurology. 1968 Apr;18(4):376–382. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.4.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dastur D. K., Manghani D. K., Raghavendran K. V., Jeejeebhoy K. N. Distribution and fate of Mn54 in the rat, with special reference to the C.N.S. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1969 Jul;54(3):322–331. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1969.sp002030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanig R. C., Aprison M. H. Determination of calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium, sodium, zinc, and chloride concentrations in several brain areas. Anal Biochem. 1967 Nov;21(2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATO M. DISTRIBUTION AND EXCRETION OF RADIOMANGANESE ADMINISTERED TO THE MOUSE. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1963 Oct;48:355–369. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1963.sp001678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney J. P., Small W. J. Studies on manganese. 3. The biological half-life of radiomanganese in man and factors which affect this half-life. J Clin Invest. 1968 Mar;47(3):643–653. doi: 10.1172/JCI105760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manghani D. K., Dastur D. K., Jeejeebhoy K. N., Raghavendran K. V. Effect of stable manganese on the fate of radiomanganese in the rat with special reference to the CNS. Indian J Med Res. 1970 Feb;58(2):209–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mena I., Marin O., Fuenzalida S., Cotzias G. C. Chronic manganese poisoning. Clinical picture and manganese turnover. Neurology. 1967 Feb;17(2):128–136. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.2.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENALVER R. Diagnosis and treatment of manganese intoxication; report of a case. AMA Arch Ind Health. 1957 Jul;16(1):64–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENTSCHEW A., EBNER F. F., KOVATCH R. M. EXPERIMENTAL MANGANESE ENCEPHALOPATHY IN MONKEYS. A PRELIMINARY REPORT. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1963 Jul;22:488–499. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196307000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



