Abstract
We have previously established that the anti-cancer lysophospholipid edelfosine (1-O-octadecyl-2-O-methyl-rac-glycero-3-phosphocholine, Et-18-OCH3) induces cell death in yeast by selective modification of lipid raft composition at the plasma membrane. In this study we determined that α-tocopherol protects cells from the edelfosine cytotoxic effect, preventing the internalization of sterols and the plasma membrane proton pump ATPase, Pma1p. Two non-mutually exclusive hypotheses were considered to explain the protective effect of α-tocopherol: (i) its classical antioxidant activity is necessary to break progression of lipid peroxidation, despite the fact Saccharomyces cerevisiae does not possess polyunsaturated fatty acids and (ii) due to its complementary cone shape, insertion of α-tocopherol could correct membrane curvature stress imposed by edelfosine (inverted cone shape). We then developed tools to distinguish between these two hypotheses and dissect the structural requirements that confer α-tocopherol its protective effect. Our results indicated its lipophilic nature and the H donating hydroxyl group from the chromanol ring are both required to counteract the cytotoxic effect of edelfosine, suggesting edelfosine induces oxidation of membrane components. To further support this finding and learn more about the early cellular response to edelfosine we investigated the role that known oxidative stress signaling pathways play in modulating sensitivity to the lipid drug. Our results indicate the transcription factors Yap1 and Skn7 as well as the major peroxiredoxin, Tsa1, mediate a response to edelfosine. Interestingly, the pathway differed from the one triggered by hydrogen peroxide and its activation (measured as Yap1 translocation to the nucleus) was abolished by co-treatment of the cells with α-tocopherol.
Keywords: α-Tocopherol, Lipid Ether, Lipid Oxidation, Lipid Raft, Yeast, oxidative Stress Response
Introduction
Targeting of cellular membranes as a therapeutic strategy is a relatively novel approach that recognizes the importance of lipids in cellular function as well as the relevance of alterations in membrane lipid composition and structure associated with specific pathologies (1). The lipid components of cellular membranes both maintain the required physical properties of the membrane and store and release many bioactive lipids that act as signaling molecules. In addition to their role as docks for proteins, bioactive lipids could change membrane fluidity, curvature, and domain architecture, which also have an impact on activation and/or localization of signaling components. This provides a degree of versatility in the regulation and coordination of signaling pathways that we have just begun to appreciate. Cancer, for example, is characterized by a broad diversity of alterations in signaling pathways. The nature of the alteration depends on the type of cancer but one common aspect of pathways that regulate cell proliferation and survival is the association of several of their proteins with specific lipid components or domains in membranes (1). Therefore, a lipid drug that upon insertion in cellular membranes has the ability to induce structural changes in those domains would be expected to affect a plethora of signaling pathways, eventually leaning the balance toward cell death. We have proposed this is the case for the class of drugs known as synthetic antitumor lipids (ATLs)2 (2). ATLs specifically insert in membranes of tumoral cells and induce apoptosis. Edelfosine (1-O-octadecyl-2-O-methyl-rac-glycero-3-phosphocholine; ET-18-OCH3) has become the effective prototype of ATLs, selectively inducing apoptosis in cancer cells (3, 4). In the last two decades research efforts toward identification of the molecular target of this family of drugs have produced a complex picture. Several membrane-associated proteins have been proposed to be the target of the drug, but which one is affected seems to depend on the type of cells studied (5, 6). Thus, it has become clear that the reductionist view of only one protein/pathway target does not fit the mode of action of this class of drugs.
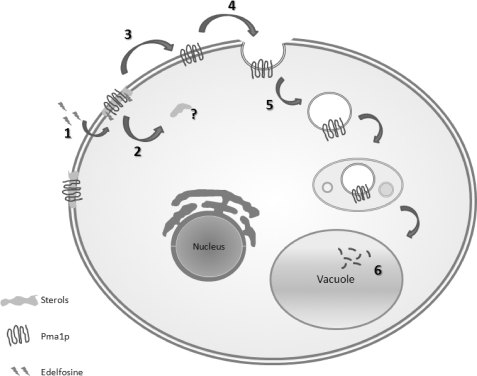
Our studies in yeast using unbiased genetic screens have implicated sphingolipid and sterol metabolism as important modulators of edelfosine cytotoxicity (2). Furthermore, our results pointed to a novel mode of action for an anti-cancer drug through modification of plasma membrane lipid composition resulting in the displacement of proteins and lipids from lipid microdomains in cellular membranes. Our current working model is depicted in Fig. 1. The drug first inserts in the plasma membrane and is flipped into the inner leaflet by a transporter from the P4-ATPase family, which is regulated by Lem3p (7). Early interaction of the drug with the plasma membrane induces sterol internalization and displacement of the essential proton pump, Pma1p, from lipid microdomains. This is followed by Pma1p endocytosis and degradation in the vacuole. Therefore, edelfosine interaction with the plasma membrane induces biophysical alterations in lipid domains resulting in displacement of proteins that use those domains as scaffolds (2). Interestingly, resistance to the drug has been observed in cells able to recycle internalized lipid/proteins back to the plasma membrane (2). Another way to overcome the edelfosine cytotoxic effect is through treatment with vitamin E (8, 9).
FIGURE 1.
Edelfosine mode of action: current model. 1, edelfosine inserts in the plasma membrane and is flipped by a Lem3p regulated flippase. 2, interaction of edelfosine with the plasma membrane induces sterol internalization. 3, displacement of the essential proton pump, Pma1p, from lipid rafts. 4, Pma1p is endocytosed followed by 5- degradation in the vacuole.
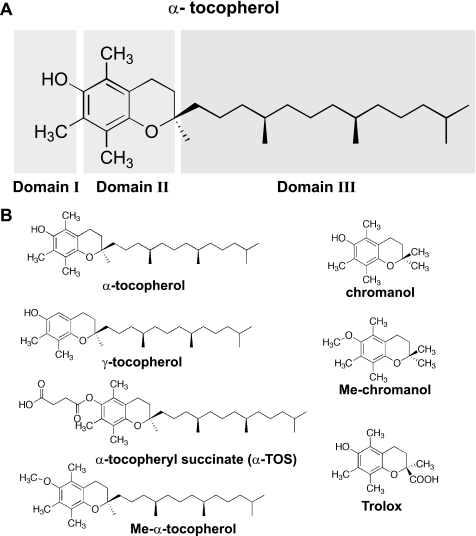
Vitamin E includes several lipophilic compounds also referred to as tocols, which comprise eight isomers, i.e. α, β, γ, and δ tocopherols and tocotrienols. Although vitamin E is well known to spontaneously associate with polyunsaturated fatty acids acting as a chain-breaking inhibitor of lipid peroxidation, new biological activities, apparently independent of its antioxidant attributes, have been described (10, 11). Three major domains characterize vitamin E analogues (Fig. 2A). Domain I is considered the functional domain, responsible for antioxidant and proapoptotic activities of vitamin E, domain II consists of the chroman nucleus and has been proposed to be responsible for “signaling” activity affecting PP2A and protein kinase C pathways (11, 12); last, domain III comprises the phytil tail responsible for docking in membranes and lipoproteins and is considered “passive” in relation to vitamin E activities (13).The redox-active hydroxyl group in all tocols can be modified to produce redox-silent derivatives, like α-tocopheryl succinate (α-TOS) (11) (Fig. 2B). It has been proposed that vitamin E prevents the edelfosine cytotoxic effect in mammalian cells due to its antioxidant activity against peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids, but as far as we are aware, in all cases reported in the literature redox-silent analogues like α-TOS were used (9, 14–16). Furthermore, it has been reported that α-TOS exerts a protective effect in edelfosine-treated yeast cells (8). This is particularly intriguing, because in addition, Saccharomyces cerevisiae lacks polyunsaturated fatty acids (17, 18). Thus, the underlying molecular mechanism for the vitamin E protective effect in the case of edelfosine-treated cells is unknown and could involve a non-antioxidant aspect of this compound.
FIGURE 2.
Chemical structures of α-tocopherol, derivatives, and analogues. A, chemical structure of α-tocopherol highlighting its functional Domain I, signaling Domain II, and structural Domain III. B, chemical structures of all compounds used in this study.
To examine the impact edelfosine has on membrane structure and to gain insight into relevant steps associated with its mode of action, we aimed to study the nature of the vitamin E protective effect as well as cellular response to a putative oxidative stress imposed by edelfosine. Tools were developed to distinguish between two hypotheses: (i) α-tocopherol acts as an antioxidant and prevents edelfosine-induced lipid peroxidation, or (ii) the α-tocopherol protective effect is due to a non-antioxidant activity, like membrane curvature stress correction due to its complementary cone shape in the presence of edelfosine (inverted cone shape). Our results indicate the antioxidant activity of α-tocopherol as well as its lipophilic nature are both necessary to exert its protective effect. Furthermore, edelfosine triggers an oxidative stress response that is prevented in the presence of α-tocopherol. This response differs from the one elicited by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), even though it also involves transcription factors Yap1 and Skn7 as well as the peroxiredoxin protein Tsa1.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Media, Plasmids, and Yeast Strain Construction
Standard molecular biology methods, yeast genetic techniques, and transformation methods were used (19, 20). In all experiments cells were grown to mid-log phase in yeast complex medium (YPD: 1% yeast extract, 2% bactopeptone, and 2% glucose) or synthetic minimal medium (SD: 0.67% yeast nitrogen base without amino acids and 2% glucose) supplemented as required for plasmid maintenance (20). All strains used in this study are listed in Table 1.
TABLE 1.
Strains used in this study
| Strain | Genotype | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| BY4741 | MATa his3 leu2 met15 ura3 | Euroscarf |
| yap1Δ | Mat a his3 leu2 met15 ura3 yap1Δ::kanMX4 | Euroscarf |
| skn7Δ | Mat a his3 leu2 met15 ura3 skn71Δ::kanMX4 | Euroscarf |
| tsa1Δ | Mat a his3 leu2 met15 ura3 tsa1Δ::kanMX4 | Euroscarf |
| gsh1Δ | Mat a his3 leu2 met15 ura3 gsh1Δ::kanMX4 | Euroscarf |
| gsh2Δ | Mat a his3 leu2 met15 ura3 gsh2Δ::kanMX4 | Euroscarf |
| glr1Δ | Mat α his3 leu2 met15 ura3 glr1Δ::kanMX4 | Euroscarf |
| trx2Δ | Mat α his3 leu2 met15 ura3 trx21Δ::kanMX4 | Euroscarf |
| ctt1Δ | Mat α his3 leu2 met15 ura3 ctt1Δ::kanMX4 | Euroscarf |
| cta1Δ | Mat α his3 leu2 met15 ura3 cta1Δ::kanMX4 | Euroscarf |
| gpx3Δ | Mat α his3 leu2 met15 ura3 gpx3Δ::kanMX4 | This study |
| SIK1-RFP | Mat α his3 leu2 lys2 ura3 SIK1::RFP::kanMX4 | Arvidson P. |
| PMA1-dsRFP | MATa ura3–52 leu2–3,112 his3–100 trp1–901 lys2–801 suc2–9 PMA1::tdimer2 (12)::kanMX4 | Malinska et al. (51) |
The YAP1 gene ±500 bp was amplified with specific primers (YAP1-XhoI-forward, 5′-CTCGAGCACTTACTCTCGCTTCTC-3′, and YAP1-EcoRI-reverse, 5′-GAATTCGAGTGCCGTGGAAAGGT-3′) using BY4741 genomic DNA as template. The PCR product was cloned into PCR2.1-TOPO cloning vector (Invitrogen) and then subcloned into XhoI-EcoRI sites of pRS416 (CEN, URA3). To generate the GFP-YAP1 plasmid, full-length YAP1 was amplified with specific primers (YAP1-EcoRI-forward, 5′-GACTGAATTCATGAGTGTGTCTACCGCC-3′ and YAP1-XhoI-reverse, 5′-ATTGCTCGAGCCCGCTTTAGTTCATATGC-3′) using BY4741 genomic DNA as template. The resulting digested fragments were cloned into EcoRI-XhoI sites of pUG36 (CEN6, URA3) (21) to create an in-frame fusion to the enhanced green fluorescent protein (yEGFP3). The protein expressed from this plasmid contains EGFP fused to the amino end of Yap1.
The SKN7 gene ±500 bp was amplified with specific primers (SKN7-XhoI-forward 5′-CTCGAGGGGCTAACACAAGTATAAGC-3′ and SKN7-EcoRI-reverse 5′-GAATTCCGCAGTGGATGAAAGATAAG-3′) using BY4741 genomic DNA as template. The PCR product was cloned into PCR2.1-TOPO cloning vector and then subcloned into XhoI-EcoRI sites of pRS416 (CEN, URA3).
The TSA1 gene ±500 bp was amplified with specific primers (TSA1-BamHI-forward 5′-CATGGGATCCCCTATGTGAAGGAGAAGC-3′ and TSA1-XhoI-reverse 5′-CATGCTCGAGGCGTTTGAAGTTTCCACG-3′) using BY4741 genomic DNA as template. The PCR product was subcloned into BamHI-XhoI sites of pRS415 (CEN, LEU2). All plasmids were sequenced to confirm the integrity of the inserts.
We noticed that the gpx3Δ strain from the Euroscarf deletion collection was a very slow growing strain and this phenotype could not be reverted by reintroducing the GPX3 gene in a plasmid. So a standard yeast one-step gene disruption cassette was constructed that replaced the entire open reading frame of GPX3 and was transformed into yeast to generate strain gpx3Δ::kanMX4. The gene disruption event was confirmed through genomic PCR and sequencing.
Drugs
Edelfosine (Medmark Pharma GmbH) was a kind gift of Dr. C. R. McMaster of Dalhousie University. Chromanol (2,2,5,7,8-Pentamethyl-6-chromanol), α-tocopherol, γ-tocopherol, α-tocopherol succinate, and TroloxTM ((±)-6-hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethylchromane-2-carboxylic acid) were purchased from Sigma. Methylated chromanol (Me-chromanol) and methylated α-tocopherol (Me-α-tocopherol) were synthesized in the laboratory of B. Heyne at the University of Calgary. Natamycin (Pimaricin) and Filipin were purchased from Sigma and dissolved in 85:15 Me2SO/H2O (v/v) and absolute ethanol, respectively.
Plate Growth Assays
Yeast were grown to mid-log phase and serial diluted 1/10 starting with an A600 of 1. The growth of the cells was monitored by spotting 5 μl of each dilution onto solid medium in the absence or presence of the indicated concentrations of edelfosine or H2O2. Stock solutions of edelfosine in ethanol were made fresh before every experiment and added to the various medium after autoclaving and cooling to at least 60 °C. The final ethanol concentration in control and edelfosine containing plates never exceeded 0.2%. Growth on control + ethanol plates was indistinguishable from that of control plates lacking ethanol. Plates were incubated at 25 °C for the indicated times. Plates were imaged using a GelDoc system (Bio-Rad) and Adobe Photoshop 7.0 software for image alignment and labeling.
Growth and Viability
Wild type (BY4741) cells were grown to mid-log phase in YPD at 30 °C. From this culture, 0.1 A600 were untreated (control) or incubated with the indicated concentrations of edelfosine, α-tocopherol, or related compounds. At the indicated time points samples were removed from the cultures and cell density was determined spectrophotometrically at 600 nm, as a measurement of growth. In addition, at each time point, an aliquot of the culture was serial diluted to plate 200 cells onto YPD plates to assess cell viability. Plates were incubated at 30 °C for 3 days, colonies were counted, and results expressed relative to control plates. Plates were imaged using a GelDoc system (Bio-Rad) and Adobe Photoshop 7.0 software for image alignment and labeling.
Microscopy
Cells were analyzed using a Zeiss Axiovert 200M microscope fitted with a plan-neofluor 100 oil immersion objective lens. Images were captured using a Zeiss Axio Cam HR and using Zeiss Axiovision 4.8 software. GFP, rhodamine, and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole filters were used to visualize GFP, RFP, and filipin, respectively. Colors were assigned using color settings from the Axiovision software. Adobe Photoshop 7.0 was used for image alignment and labeling.
Because the effect of edelfosine depends on cell inoculums (2, 22) the concentration of edelfosine and vitamin E were doubled with respect to growth and viability assays, to use high cell density preparations for live cell imaging. Because rich medium (YPD) is fluorescent, defined medium was used in all microscopy studies to keep the background signal low. One A600 of exponentially growing wild type cells untreated (control) or cells treated with 0.5 mm H2O2 or 20 μg/ml of edelfosine ± 50 μm vitamin E in defined medium for 10 min at 30 °C were centrifuged and resuspended in 100 μl of the same medium. The time indicated in the figure legends corresponds to the combined time resulting from incubation, processing, mounting, and visualization procedures. In all cases cells were placed in slabs of solid medium were made as described (23).
Cells were processed for indirect immunofluorescence microscopy for localization of Pma1p as described (2, 24). Anti-Pma1p specific antibody was a kind gift of Ramón Serrano, Universidad Politécnica de Valencia, and the secondary antibody was goat anti-rabbit conjugated to Alexa 488 (Invitrogen).
Filipin was freshly prepared as a 1 mg/ml stock in ethanol. Filipin was added to live cells at a final concentration of 10 μg/ml. Cells were then concentrated by brief centrifugation and imaged live within 5 min of filipin addition (2). As previously described (2), fluorescence of filipin in cells treated with edelfosine increases dramatically resulting in saturated images when the exposure time is kept constant with that of control samples. For this reason, images from cells treated with edelfosine, edelfosine plus Me-α-TOC, and edelfosine plus Me-chromanol were imaged using 50% of the lamp intensity, whereas full intensity was used for the rest of the conditions. At least 100 cells per condition were analyzed for quantification of microscopy images.
Data Analysis
GraphPad Prism 3.03 software was used for statistical analysis of data and preparation of figures.
RESULTS
Vitamin E Prevents Early Changes Induced by Edelfosine on Plasma Membrane Architecture
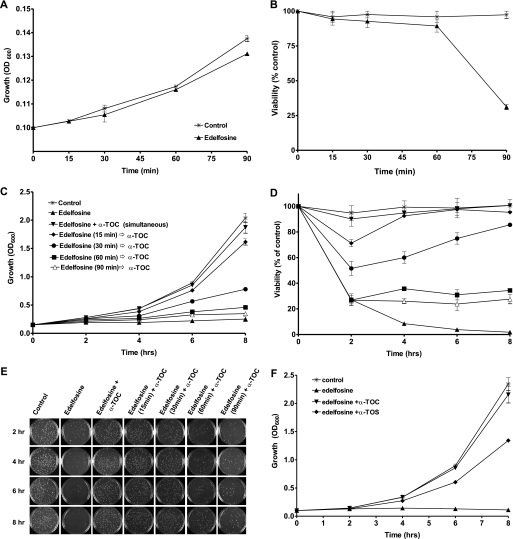
Treatment of wild type yeast (BY4741) with edelfosine (10 μg/ml) was cytotoxic, as shown by a significant decrease in cell viability after 90 min of treatment (Fig. 3, A and B). Edelfosine-induced cell death was completely abolished when cells were incubated in the presence of α-tocopherol (Fig. 3, C and D). The effect of α-tocopherol was concentration dependent (not shown) and strongly reliant on whether it was added before, simultaneously, or after edelfosine (Fig. 3, C–E). Addition of α-tocopherol together with edelfosine was the most effective condition, whereas partial effects were observed when added within the first 30 min of treatment with edelfosine (Fig. 3C). On the contrary, pre-treatment of cells with α-tocopherol for up to 1 h before its removal followed by addition of edelfosine failed to protect cells (not shown). It was also ineffective to add α-tocopherol after 1 h of treatment with edelfosine. It is worth noting cell viability is not compromised during the first hour (Fig. 3B), whereas edelfosine uptake is close to its maximum (2). When α-tocopherol was added within the first 30 min, the cells that remained viable after 2 h were able to keep proliferating, eventually reaching control conditions (Fig. 3, C–E). Interestingly, the ∼30% of cells that remained viable when the vitamin was added after 1 h of treatment with edelfosine were not able to proliferate, unveiling a cytostatic effect of edelfosine. We also analyzed the effect of two other vitamin E analogues: α-TOS and γ-tocopherol, which differ in domains I and II of α-tocopherol, respectively (Fig. 2B). It has been shown α-TOS prevented edelfosine cytotoxic effect when administered in micromolar concentrations to tumoral cells or wild type yeast (8, 9). Compared with α-tocopherol, α-TOS showed a delay in reaching full growth recovery (Fig. 3F), whereas no differences between α- and γ-tocopherol were observed (not shown).
FIGURE 3.
α-Tocopherol protects cells from edelfosine cytotoxic effect and this depends on its time of addition. A and B, edelfosine cytotoxic effect is detected after 90 min of treatment. Wild type cells were grown to mid-log phase (BY4741) and then treated with 10 μg/ml of edelfosine in rich medium. Growth was monitored by measuring optical density of the cultures at 600 nm (A). To determine cell viability, equal amounts of cells were plated at the indicated time points onto rich medium plates in the absence of edelfosine. Plates were incubated for 3 days at 30 °C, colonies were counted, and results expressed as percentage of control plates (B). C and D, wild type (BY4741) cells grown to mid-log phase were either untreated or incubated with edelfosine (10 μg/ml) for the indicated times before the addition of 25 μm α-TOC. C, growth, and D, viability. Representative plates used to count colonies (from duplicates) are shown (right panel). E, wild type (BY4741) cells grown to mid-log phase were either untreated or incubated with edelfosine (10 μg/ml) alone or in combination with 25 μm α-TOC or α-TOS. Growth was monitored for up to 8 h. Results are presented as the mean ± S.D. of a representative experiment performed at least three times.
In summary, these results suggest that to prevent edelfosine cytotoxicity, α-tocopherol needs to be added simultaneously with edelfosine, or at early times, when edelfosine exerts its effects mainly at the plasma membrane. Furthermore, the similar behavior between α- and γ-tocopherol suggests the methylation degree of domain II is not critical to exert the protective effect. On the other side, the differences with α-TOS point to domain I as key in this effect.
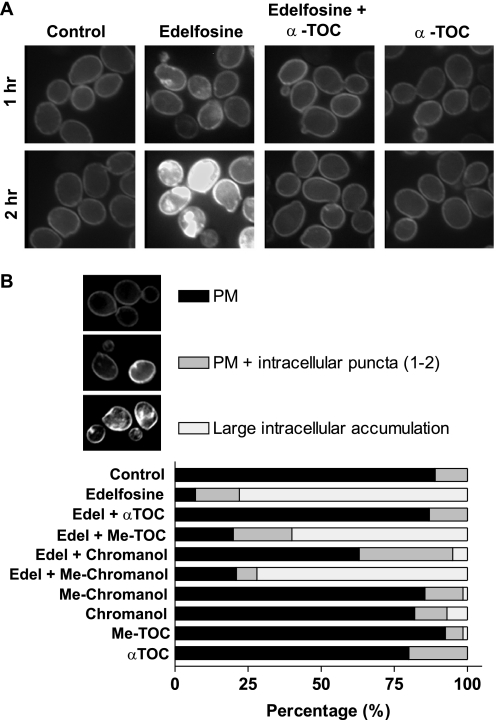
We have previously shown that treatment of wild type yeast with edelfosine results in movement of sterols out of the plasma membrane and displacement of the essential proton pump, Pma1p, from plasma membrane microdomains (2). Sterol redistribution is detectable as early as 15 min after edelfosine addition and is abolished in resistant cells with enfeebled endocytosis and vacuolar protease activities (2). We asked next whether early events like sterol redistribution and Pma1p partitioning out of lipid rafts, both occurring at the plasma membrane, were also prevented by co-treatment of cells with edelfosine and α-tocopherol. As shown by staining with filipin, α-tocopherol prevented sterol movement from the plasma membrane in the presence of edelfosine (Fig. 4A). Accordingly, α-tocopherol also impeded edelfosine induced Pma1p internalization (Fig. 5A). Taken together, these data show that α-tocopherol protection occurs early during the treatment with edelfosine, suggesting it may counter critical changes induced by edelfosine mostly at the plasma membrane.
FIGURE 4.
α-Tocopherol prevents sterol internalization induced by edelfosine and this depends on its antioxidant activity. A, wild type (BY4741) cells grown to mid-log phase were either untreated or incubated with edelfosine (20 μg/ml) alone or in combination with 50 μm α-TOC for the indicated time points. Sterol distribution was monitored by filipin staining in live cells as indicated under “Experimental Procedures.” B, images acquired as in A were analyzed and quantification was performed for each of the categories established in at least 100 cells per experimental condition. See “Experimental Procedures” for details on image acquisition. PM, plasma membrane.
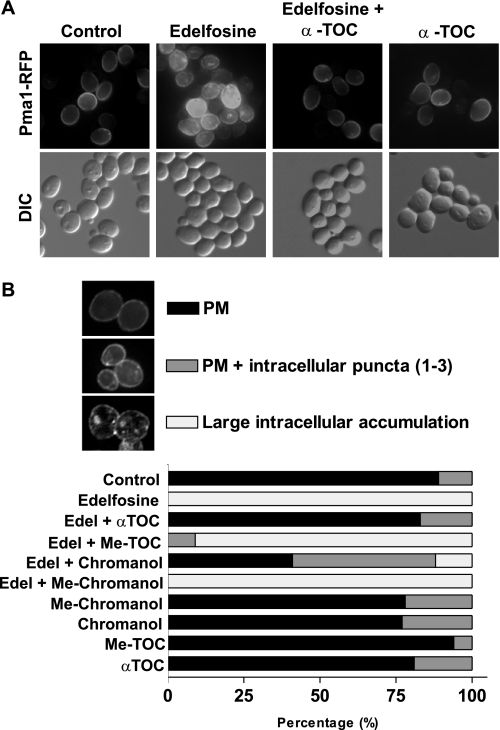
FIGURE 5.
α-Tocopherol prevents changes in Pma1 localization induced by edelfosine and this depends on its antioxidant activity. A, localization of Pma1p-RFP in live cells (SEY6210-Pma1p-dsRFP) either untreated or incubated with edelfosine (20 μg/ml) alone or in combination with 50 μm α-TOC for 1 h. B, wild type cells (BY4741) either untreated or incubated with edelfosine (20 μg/ml) alone or in combination with 50 μm α-tocopherol or related compounds were fixed and processed for detection of Pma1p by immunofluorescence. Images acquired were analyzed and quantification was performed for each of the categories established in at least 100 cells per experimental condition. PM, plasma membrane; DIC, differential interference contrast.
Antioxidant Activity of Vitamin E Is Necessary to Protect Cells from Edelfosine Cytotoxicity
We were intrigued by the fact that α-tocopherol is a well known antioxidant that interacts with polyunsaturated acyl chains of phospholipids, inhibiting lipid peroxidation, but S. cerevisiae does not synthesize this kind of fatty acids (18). Besides its well known antioxidant activity α-tocopherol also has the ability to alter the structure and dynamics of the membranes where it inserts. Interestingly, it is well documented that α-tocopherol associates with lysolipids like lysophosphatidylcholine, probably due to their complementary lipid shape (10). Such association would have opposite effects on membrane curvature, resulting in the bilayer maintaining its lamellar form. Taking into account that edelfosine is a lysophosphatidylcholine analogue, α-tocopherol could be reverting the curvature stress imposed by the insertion of edelfosine in cellular membranes. Considering this as an alternative explanation we next asked whether the antioxidant activity of α-tocopherol was necessary to exert its protective effect. In fact, the effect reported with the redox-silent analogue α-TOS could support this idea, although caution is required when interpreting those results because this compound could be hydrolyzed in vivo yielding active α-tocopherol (25, 26). Actually, the delay observed in the protective effect of α-TOS when compared with that of α-tocopherol (Fig. 3E) could be explained if processing α-TOS to the active vitamin form is a prerequisite.
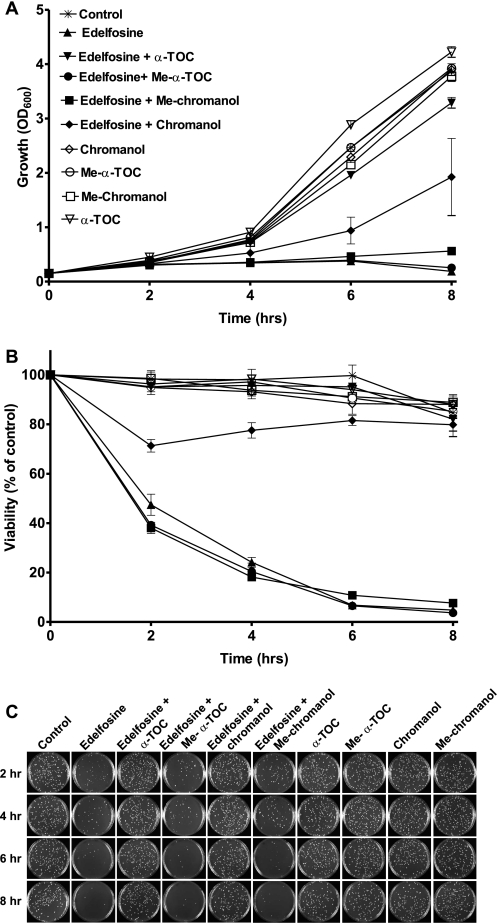
To distinguish between the two possibilities (antioxidant or curvature correction) we decided to create a compound that shares as much structure as possible with α-tocopherol, lacks antioxidant activity, and cannot be hydrolyzed by cellular esterases. We carried out the chemical synthesis and biophysical characterization of a 6-methoxy analogue of α-tocopherol (Me-α-TOC; Fig. 2). This molecule retains its ability to insert into membranes but lacks the H-atom-donating phenol required for its antioxidant mechanism.3 Also included in our analysis was the effect of the chromanol ring and its methylated analogue, which are both able to partition into membranes, although the lack of the phytil tail would abolish the ability to correct the curvature effect imposed by edelfosine. In addition, we tested the effect of the water-soluble derivative of α-tocopherol, Trolox. This compound maintains its antioxidant activity but cannot insert into membranes. When each of these compounds were added simultaneously with edelfosine only, α-tocopherol and, partially, its chromanol ring were able to protect cells from edelfosine cytotoxic effect (Fig. 6 and Table 2). Accordingly, the chromanol ring partially prevented sterol movement and Pma1p internalization induced by edelfosine (Figs. 4B and 5B). The protective effect was lost when these compounds lacked the hydroxyl group responsible for antioxidant activity. Similarly, the water-soluble analogue failed to protect cells even when added at millimolar concentrations to counteract the fact that its uptake by the cells may differ significantly from that of the lipophilic compounds tested (Table 2). None of the methoxy compounds (Me-α-TOC and Me-chromanol) were able to prevent sterol movement and Pma1p internalization (Figs. 4B and 5B), unveiling a critical role for the H donating hydroxyl group (domain I) in preventing lipid raft modifications induced by edelfosine. In summary, these results indicate both the antioxidant activity of α-tocopherol as well as its lipophilic nature are required to preclude changes in membrane microdomains and cell death induced by edelfosine.
FIGURE 6.
The antioxidant activity and lipophilic nature of α-tocopherol are required to protect cells from edelfosine. Wild type (BY4741) cells grown to mid-log phase were either untreated or incubated with edelfosine (10 μg/ml) alone or in combination with 25 μm of each of the following compounds: α-TOC, Me-α-TOC, chromanol, or methylated chromanol (Me-Chromanol). A, growth, and B, viability were determined as described in the legend to Fig. 3. Results are presented as the mean ± S.D. of a representative experiment performed at least three times.
TABLE 2.
Summary of properties of the different compounds used in this study
| Compound | Inserts in membranes | Antioxidant activity | Protects cells from edelfosinea |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-Tocopherol | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| γ-Tocopherol | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Chromanol | Yes | Yes | Partially |
| α-Tocopheryl succinate | Yes | After hydrolysis | Yes (delay) |
| Me-α-tocopherol | Yes | No | No |
| Me-chromanol | Yes | No | No |
| Trolox | No | Yes | No (even at mm) |
a All compounds were tested at 25 μm in the presence of 10 μg/ml (19 μm) of edelfosine.
Oxidative Stress Response Triggered by Edelfosine
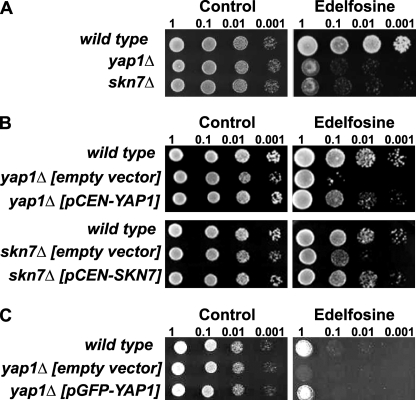
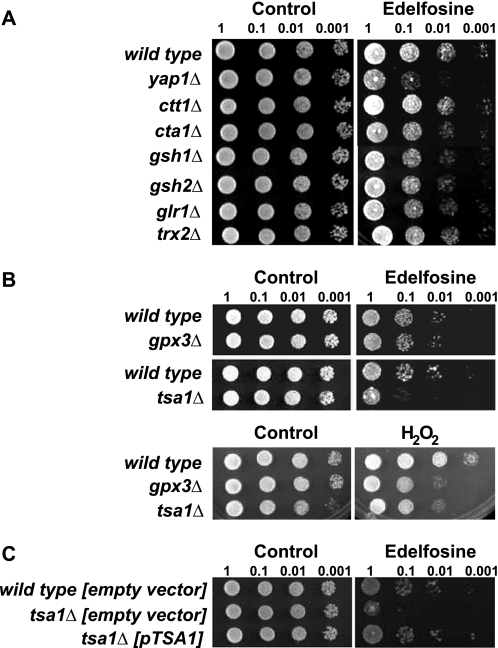
We reasoned that if the antioxidant activity of α-tocopherol is required to protect cells from edelfosine, then edelfosine interaction with cellular membranes must impose an oxidative stress to the cells. The source of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is most probably generated at the membrane because that is where both edelfosine and α-tocopherol reside. Given the lack of polyunsaturated fatty acids in yeast other lipids may be the target of oxidation triggered by edelfosine (see “Discussion”). Yeast cells respond differently depending on the nature of the ROS being generated (27). Therefore, characterization of the oxidative stress response to edelfosine may provide some insight into its mechanism of action, source of ROS, as well as a greater understanding of the potential cellular mechanisms leading to adaptation to the drug. The best studied cellular mechanism for ROS detection in yeast is the one involved in direct sensing of H2O2. S. cerevisiae senses and responds to H2O2 through the redox state of key proteins such as transcription factors Yap1 and Skn7. It has been shown that Yap1 not only mediates the response to H2O2 but also to other forms of oxidative stress. Interestingly, the response differs depending on the nature of the ROS and this seems to be related to the ROS sensing mechanism leading to a differential activation of Yap1 (27). Concurring with edelfosine triggering, a form of oxidative stress, both YAP1 and SKN7 deletion mutants were more sensitive to edelfosine than their isogenic wild type (Fig. 7A). Reintroduction of each of these genes back in the deletion mutants reverted the sensitive phenotype confirming their involvement in the cellular response to edelfosine (Fig. 7B). The mutant lacking YAP1 was slightly more sensitive than that lacking SKN7. Yap1 is known to play a more important role during oxidative stress and to be more specific to ROS than Skn7 (28, 29).
FIGURE 7.
The transcription factors Yap1 and Skn7 mediate the oxidative stress response triggered by edelfosine. A, deletion mutants yap1Δ and skn7Δ were compared with their isogenic wild type strain (BY4741). Cells were grown to mid-log phase and serial diluted onto rich medium + 0.2% ethanol (control) or rich medium containing edelfosine (10 μg/ml). Plates were incubated at 25 °C for 4 days. B, same strains as in A carrying the low copy vector pRS316 (empty vector) or the vector containing the indicated genes, were grown to mid-log phase and serial diluted onto selective medium + 0.1% ethanol (control) or 5 μg/ml of edelfosine. Plates were incubated for 5 days at 25 °C. C, yap1Δ cells carrying the pUG36 vector (empty vector) or pUG36 containing GFP-YAP1 were compared with its isogenic wild type carrying the empty vector. Cells were grown to mid-log phase and serial diluted onto selective medium + 0.1% ethanol (control) or 5 μg/ml of edelfosine. Plates were incubated for 3 days at 25 °C.
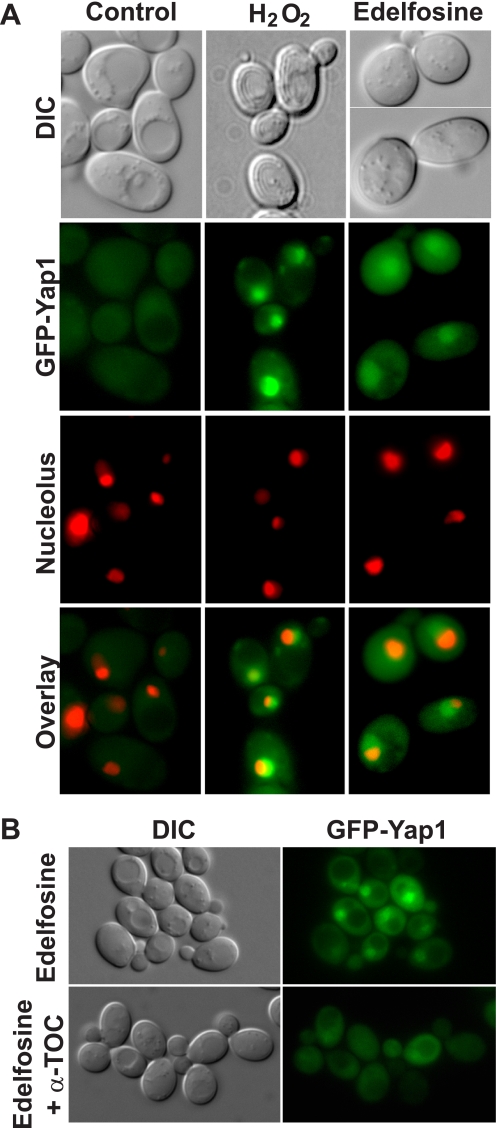
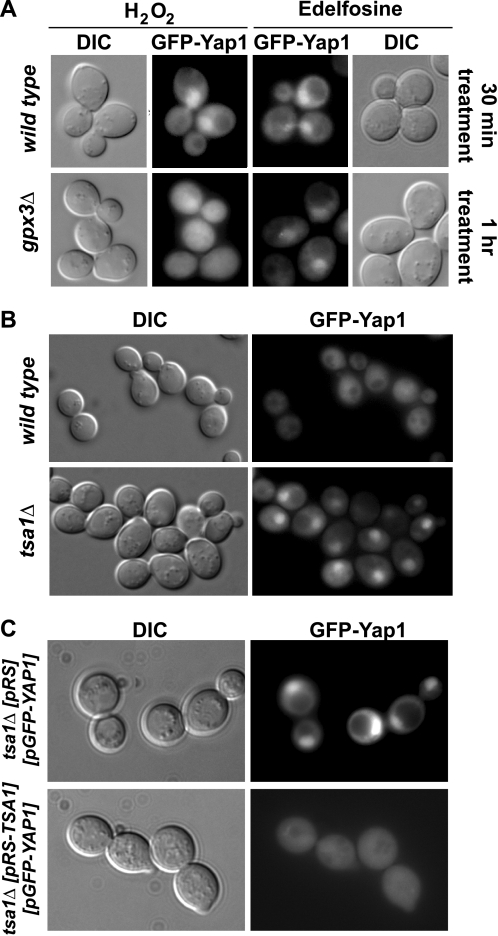
It is well known that under non-stressed conditions Yap1 is predominantly localized to the cytoplasm, but upon exposure of cells to H2O2, Yap1 accumulates in the nucleus (27). Thus, Yap1 translocation to the nucleus in response to a cellular insult is the first level of control of its activity. We then fused the GFP to the amino end of Yap1 to assess its localization in the presence of edelfosine. This GFP-Yap1 fusion protein was functional because it was able to revert the edelfosine-sensitive phenotype of cells lacking the endogenous YAP1 gene (Fig. 7C). Consistent with previous studies we found Yap1 to be predominantly localized to the cytoplasm in wild type cells under non-stress conditions, but mainly nuclear in the presence of H2O2 (Fig. 8). Similar to H2O2, treatment of yeast with edelfosine for a short period of time (10–20 min) induced nuclear translocation of Yap1, as indicated by co-localization of GFP-Yap1 with the nucleolus marker Sik1-RFP (Fig. 8A). Interestingly, simultaneous addition of α-tocopherol with edelfosine prevented Yap1 translocation to the nucleus (Fig. 8B) but had no effect on growth impairment or Yap1 nuclear localization in response to H2O2 (not shown). Furthermore, it is well known that H2O2-induced activation and translocation of Yap1 to the nucleus alters the expression of several genes involved in glutathione synthesis (GSH1), thioredoxins (TRX2), catalases (CTT1), and superoxide dismutases (SOD) (27). In fact, deletion mutants for TRX2, SOD2, GSH1, and glutathione reductase GLR1 have been shown to be hypersensitive to H2O2 (30–32), whereas yeast lacking catalases CTT1 and CTA1 are defective in the adaptive response to oxidative stress triggered by polyunsaturated fatty acids and H2O2 (33, 34). None of these deletion mutants displayed increased sensitivity toward edelfosine (Fig. 9A), suggesting the ROS sensing pathway triggered by edelfosine differs from that described for H2O2, despite the fact Yap1 mediates both responses.
FIGURE 8.
Nuclear translocation of Yap1 in response to edelfosine is prevented by α-tocopherol. GFP fluorescence was visualized in living wild type cells carrying pUG36-GFP-YAP1 either untreated or incubated for a short period of time (20 min) with edelfosine (see “Experimental Procedures”). A, wild type cells expressing the nucleolus marker Sik1 fused to RFP (endogenously tagged) were used. B, wild type (BY4741) cells carrying the pUG36-GFP-YAP1 were incubated for a short period of time (20 min) with edelfosine in the absence or presence of α-TOC (see “Experimental Procedures”). DIC, differential interference contrast.
FIGURE 9.
The oxidative stress response triggered by edelfosine differs from that induced by H2O2. A, deletion mutants for the indicated genes were compared with their isogenic wild type strain (BY4741). Cells were grown to mid-log phase and serial diluted onto rich medium + 0.2% ethanol (control) or rich medium containing edelfosine (10 μg/ml). B, strains lacking peroxiredoxins Gpx3 and Tsa1 were compared with their isogenic wild type strain (BY4741). Cells were grown to mid-log phase and serial diluted onto rich medium + 0.2% ethanol (control) or rich medium containing edelfosine (10 μg/ml) or H2O2 (4 mm). C, tsa1Δ cells carrying the pRS316 vector (empty vector) or containing TSA1 under its own promoter were compared with its isogenic wild type carrying the empty vector. Cells were grown to mid-log phase and serial diluted onto selective medium ± 5 μg/ml edelfosine. In all cases plates were incubated for 4 days at 25 °C.
Peroxiredoxin Tsa1 Mediates the Oxidative Stress Response Triggered by Edelfosine
Yap1 is kept out of the nucleus due to a nuclear export signal in its carboxy end that is exposed during resting conditions. Hydrogen peroxide induces the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond between two cysteine residues in Yap1 masking the nuclear export signal and thus allowing its retention in the nucleus (35, 36). Two different peroxiredoxin-dependent ROS sensing pathways leading to activation and nuclear translocation of Yap1 have been well characterized. Peroxiredoxins Gpx3 and Tsa1 sense ROS upstream of Yap1 (35, 37). Gpx3 can act as a sensor and activator of Yap1p in response to H2O2, by inducing the formation of disulfide bond formation in Yap1. Analogous to the mechanism proposed for Gpx3, Tsa1 has also been shown to induce the formation of disulfide bonds in Yap1, resulting in its activation in response to H2O2 (37). To identify which pathway is activated upon treatment of yeast with edelfosine we then analyzed the sensitivity of GPX3 and TSA1 deletion mutants toward the lipid drug.
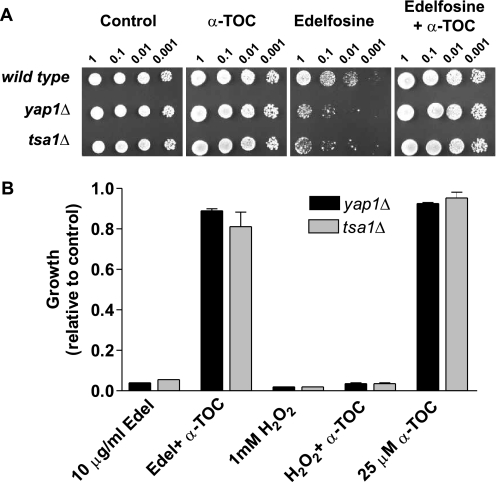
Cells lacking Tsa1 were very sensitive to edelfosine and this phenotype was reverted by introducing the gene back under its own promoter in a single copy plasmid (Fig. 9, B and C). On the other side, whereas lack of Gpx3 conferred hypersensitivity to H2O2 it did not have a marked effect on sensitivity of the cells toward edelfosine (Fig. 9B). To assess Yap1 responsiveness to edelfosine in the absence of Gpx3 or Tsa1, its capacity to translocate to the nucleus was evaluated in peroxiredoxin-deficient cells treated with edelfosine in comparison to H2O2. It has been shown that GPX3 deletion mutants (in the BY4742 background) fail to translocate/activate Yap1p in response to low concentrations of H2O2 (35). Similar results were obtained with the gpx3Δ deletion mutant we generated (in the BY4741 background) (Fig. 10A). Although these cells showed a delay in Yap1 translocation in response to edelfosine no changes in their response to low concentrations of H2O2 were observed up to 1 h of treatment. Surprisingly, TSA1 deletion mutants showed Yap1 to be constitutively localized to the nucleus, even in resting (control) conditions (Fig. 10B). This constitutive nuclear localization was reverted when TSA1 was reintroduced in the deletion mutant in a one copy (CEN) plasmid under its own promoter (Fig. 10C). No changes in Yap1 nuclear localization were observed when tsa1Δ deletion mutants were exposed to either edelfosine or H2O2 (data not shown). Hence, constitutive nuclear localization of Yap1 in cells lacking Tsa1 does not confer any advantage in the response to the lipid drug. In summary, edelfosine triggers an oxidative stress response that differs from that elicited by H2O2, because it is sensed mainly by Tsa1 and not Gpx3. Moreover, α-TOC prevented cytotoxicity of edelfosine in cells lacking Yap1 and Tsa1, suggesting α-TOC acts upstream of these proteins. On the contrary, as observed for wild type cells, sensitivity of yap1Δ and tsa1Δ mutants to H2O2 did not change in the presence of α-TOC (Fig. 11). In addition, pre-treatment of wild type yeast with sublethal concentrations of H2O2 does not confer an adaptive response to edelfosine, further supporting our findings (data not shown).
FIGURE 10.
Constitutive nuclear localization of Yap1 in tsa1Δ cells. A, GFP fluorescence was monitored in gpx3Δ cells and their isogenic wild type (BY4741) expressing GFP-fused Yap1 as described above, after treatment with 0.5 mm H2O2 or 20 μg/ml of edelfosine (see “Experimental Procedures”). Nuclear translocation of Yap1 was evident within 30 min of treatment of wild type cells with either H2O2 or edelfosine, whereas 60 min were required to detect its nuclear localization in gpx3Δ cells treated with edelfosine. No Yap1 nuclear localization was detected in gpx3Δ cells treated with 0.5 mm H2O2 up to 1 h. B, GFP fluorescence was monitored in untreated tsa1Δ cells and their isogenic wild type (BY4741) expressing GFP-fused Yap1, or C, untreated tsa1Δ cells expressing GFP-fused Yap1 carrying an empty pRS316 vector or containing the TSA1 gene.
FIGURE 11.
α-Tocopherol acts upstream of Tsa1 and Yap1 and has no protective effect toward H2O2. A, deletion mutants for Yap1 and Tsa1 were compared with their isogenic wild type strain (BY4741). Cells were grown to mid-log phase and serial diluted onto rich medium + 0.2% ethanol (control) or rich medium containing edelfosine (20 μg/ml), α-tocopherol (50 μm), or both combined. Plates were incubated for 3 days at 25 °C. B, strains lacking Tsa1 and Yap1 were grown to mid-log phase and then treated with the indicated concentrations of edelfosine and H2O2 in rich medium. 25 and 100 μm α-tocopherol is shown in combination with edelfosine (10 μg/ml) and H2O2 (1 mm), respectively. Similar curves were obtained for the isogenic wild type BY4741 (not shown) in all conditions. Results are presented as the mean ± S.D. of a representative experiment performed at least three times.
DISCUSSION
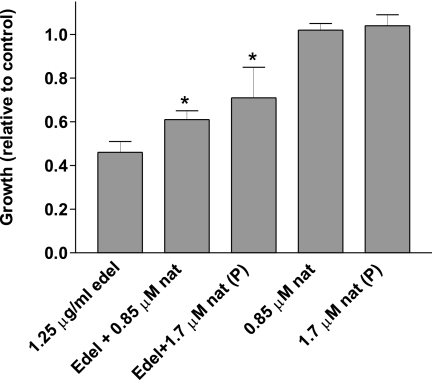
How changes in lipid composition at the plasma membrane impact the balance between apoptotic and survival signals remains largely unknown. We and others have shown previously that the alkylphospholipid edelfosine inserts into the plasma membrane of yeast and mammalian cells and induces changes in microdomains rich in sterols and sphingolipids, known as lipid rafts (2, 38, 39). In S. cerevisiae these changes include sterol internalization and displacement of the essential proton pump Pma1p from lipid rafts followed by endocytosis and degradation of the protein in the vacuole (2). In this work we show that α-tocopherol prevents these changes from happening, but only when added simultaneously or within 30 min of treatment of yeast with edelfosine. Considering sterol internalization could be detected as early as 15 min after edelfosine addition, and pre-treatment of cells with α-tocopherol does not prevent the edelfosine cytotoxic effect, we interpreted that α-tocopherol must be present at the same time in the same membrane where edelfosine is found, early enough, before cells are committed to die. In trying to understand the nature of this protective effect we contemplated two non-mutually exclusive explanations: (i) edelfosine may trigger lipid peroxidation and this would be reverted by the well known antioxidant activity of α-tocopherol, or (ii) similar to lysophosphatidylcholine, edelfosine has an inverted cone shape that could be complemented by α-tocopherol (cone shape) when packed in the same membrane. As a result of this interaction α-tocopherol could stabilize the curvature stress imposed by edelfosine, maintaining a lamellar (flat) structure. To distinguish between these possibilities we tested a series of compounds bearing modifications in all three domains of α-tocopherol (Fig. 2). Ordered from the most to the least effective, the following compounds were found to protect cells from edelfosine cytotoxic effect: α-tocopherol = γ-tocopherol > α-TOS > chromanol ring. On the other side the methylated versions of α-tocopherol and the chromanol ring as well as the water-soluble derivative Trolox failed to protect cells. These results strongly suggest that to exert its protective effect, the compound should (i) have a functional hydroxyl group in domain I and (ii) be lipophilic and able to insert in membranes. Furthermore, only redox active compounds were able to prevent lipid raft modifications induced by edelfosine. The phytil tail was not necessary but improved its efficacy. The fact that the chromanol ring was sufficient to protect cells challenges the hypothesis of curvature correction by α-tocopherol. Although α-TOS is considered a redox-silent compound it has been shown to act as a pro-vitamin, releasing α-tocopherol after the succinate group is hydrolyzed in vivo (26). The delay observed in the effect of this compound in preventing edelfosine cytotoxicity in yeast could indicate it needs to be hydrolyzed to be effective. Altogether these results could be interpreted as edelfosine triggers oxidation in a membrane environment that lacks polyunsaturated fatty acids and α-tocopherol prevents its propagation. Considering it is well documented that edelfosine interacts with sterols (40, 41), we are currently evaluating the possible role of ergosterol in mediating oxidative stress induced by edelfosine. It has been recently shown that the polyene antibiotic natamycin binds specifically to ergosterol without changing the permeability of the yeast plasma membrane under conditions that block cellular growth (42). Interestingly, incubation of yeast cells with natamycin alleviated the inhibitory growth effect of edelfosine (Fig. 12). This protective effect could be attributed to the formation of relatively stable stoichiometric complexes between ergosterol and natamycin (42), suggesting ergosterol availability modulates the effect of edelfosine.
FIGURE 12.
Ergosterol accessibility is associated with growth inhibition induced by edelfosine. Wild type cells (BY4741) were grown to mid-log phase and then treated with the indicated sublethal concentrations of edelfosine (1.25 μg/ml) and natamycin (0.85 μm) in rich medium. Additionally, cells were preincubated (P) with 1.7 μm natamycin for 10 min at 30 °C, washed twice, and resuspended in rich medium or medium containing edelfosine (1.25 μg/ml). Note that 1.7 μm natamycin has been shown to block growth of RH488 wild type cells (42) as well as BY4741 (not shown).3 Growth (A600) is expressed relative to the control after 16 h incubation at 30 °C in the indicated experimental conditions. Results are presented as the mean ± S.D. of a representative experiment that was performed at least three times. The asterisk denotes significantly (p < 0.05) different result than that of edelfosine treatment alone (one-way analysis of variance test, n = 4).
It is not clear at this point if the interaction of edelfosine with the plasma membrane could result in ergosterol oxidation or if sterol internalization and mislocalization could mediate oxidation of intracellular membranes. Oxidized ergosterol derivatives have been detected before, as a consequence of photodynamic treatment of yeast with the singlet oxygen sensitizer toluidine blue (43). A buildup of ergosterol polar derivatives as a consequence of edelfosine treatment could affect the plasma membrane sterol-retention capacity inducing its accumulation in internal compartments, as those seen in edelfosine-treated cells (Fig. 4A and see Ref. 2) and the sphingolipid synthesis mutant lcb1–100 (44). In support of this hypothesis, a recent unbiased gene dosage screen has identified an oxysterol binding protein as modulator of edelfosine sensitivity in yeast.4 Studies are underway to assess the role of such proteins as well as oxysterols in the edelfosine mode of action and how tocopherols could interfere with it. In this regard, a recent study indicates that cholesterol oxide 7-ketocholesterol localizes in lipid rafts and treatment with α-tocopherol induces its redistribution out of these domains, preventing its cytotoxic effect (45).
We show in this study that a brief treatment of yeast with edelfosine triggers a cellular stress response, involving Yap1, a member of the AP-1 family of transcription factors, and the two-component response regulator protein, Skn7. These two transcription factors function in collaboration, inducing expression of stress response genes (46). It is well known that Yap1 is regulated in a redox sensitive way by changing its subcellular localization in response to oxidative stress triggered by H2O2 (47). Translocation of Yap1 to the nucleus in the beginning of treatment with edelfosine points, once again, to a response to the effect the drug has early on, at the plasma membrane. Interestingly this response seems to differ from the one elicited by H2O2 in that it can be prevented by α-tocopherol and is principally mediated by Tsa1, the most abundant peroxiredoxin in budding yeast (37). It has been previously shown that activation of Yap1 in response to H2O2 involves post-translational modifications that differ from those implicated in response to metals and electrophiles like menadione (48), and this could be the case for edelfosine. Alternatively, Yap1 activation by edelfosine may resemble that of H2O2 but the difference could reside in the simultaneous activation of other transcription factors or signaling cascades that convergence is a distinct response.
We show that cells lacking TSA1 are hypersensitive to edelfosine, and that Yap1 is constitutively localized to the nucleus in resting conditions. To our knowledge this is the first time constitutive nuclear localization of Yap1 in tsa1Δ cells has been detected. This finding is in agreement with an increase in basal expression of genes up-regulated by Yap1 in tsa1Δ cells from a similar genetic background (BY4742) with a functional Gpx3 pathway (35). Likewise, an increase in basal expression of Yap1 responsive genes was shown to occur in tsa1Δ cells made in the YPH250 genetic background (49). Although expected, the authors failed to detect any constitutive nuclear localization of Yap1 in these cells (49). Additionally, researchers working with tsa1Δ cells in the W303 background have reported Yap1 is localized to the cytosol in these cells (50), but this has been shown to depend on a mutation in the YBP1 gene found in W303-derived cells (35). Taking into account the discrepancies between different genetic backgrounds we can conclude that in BY4741 the constitutive activation/translocation of Yap1 in tsa1Δ cells (Fig. 10B) (35) results in desensitization of the redox sensing pathway in response to edelfosine.
The results presented here may have important implications for improving the use and efficacy of edelfosine and tocols as chemotherapeutic agents. Evidence supporting anticarcinogenic activities of vitamin E lead to the idea it could be an appropriate candidate for the adjuvant treatment of cancer (11). Although alkylphospholipids like edelfosine, as well as vitamin E analogues, selectively induce apoptosis in several cancer cell types it is clear they counteract each others effect when added simultaneously. Our studies in yeast have identified structural components of vitamin E that play a key role in exerting this effect. Further studies will focus on investigating the role sterols may have in mediating the cytotoxic effect of edelfosine and how tocols could interfere with them. Additionally, we have determined yeast would serve as an excellent model to study the cellular response to membrane oxidative stress independent of polyunsaturated fatty acid peroxidation. Future efforts will try to address the molecular determinants leading to differential activation of Yap1 as well as studies assessing global gene expression triggered by edelfosine and vitamin E analogues. This would have important implications in understanding adaptation and development of drug resistance and the link between cellular redox status and sensitivity threshold of different eukaryotic cells toward the ATL class of drugs.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ramón Serrano and Widmar Tanner for their kind gifts of antibodies and strains, respectively. The thoughtful comments of G. Bertolesi and P. F. Murray are gratefully acknowledged.
This work was supported by operating grants from the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) (to B. H. and V. Z.) and a University Faculty Award from NSERC (to V. Z.).
C. E. Sveen, V. Zaremberg, and B. Heyne, unpublished results.
V. Zaremberg and C. R. McMaster, unpublished results.
- ATL
- antitumor lipid
- α-TOC
- α-tocopherol
- α-TOS
- α-tocopheryl succinate
- Me-chromanol
- methylated chromanol
- Me-α-TOC
- methylated α-tocopherol
- GFP
- green fluorescent protein
- ET-18-OCH3
- O-octadecyl-2-O-methyl-rac-glycero-3-phosphocholine
- EGFP
- enhanced green fluorescent protein
- ROS
- reactive oxygen species
- RFP
- red fluorescent protein.
REFERENCES
- 1.Escribá P. V. (2006) Trends Mol. Med. 12, 34–43 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zaremberg V., Gajate C., Cacharro L. M., Mollinedo F., McMaster C. R. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280, 38047–38058 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Munder P. G., Westphal O. (1990) Chem. Immunol. 49, 206–235 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mollinedo F., Gajate C., Martín-Santamaría S., Gago F. (2004) Curr. Med. Chem. 11, 3163–3184 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wright M. M., Howe A. G., Zaremberg V. (2004) Biochem. Cell Biol. 82, 18–26 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.van Blitterswijk W. J., Verheij M. (2008) Curr. Pharm. Des. 14, 2061–2074 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hanson P. K., Malone L., Birchmore J. L., Nichols J. W. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 36041–36050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhang H., Gajate C., Yu L. P., Fang Y. X., Mollinedo F. (2007) Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 28, 888–894 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Vrablic A. S., Albright C. D., Craciunescu C. N., Salganik R. I., Zeisel S. H. (2001) FASEB J. 15, 1739–1744 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Atkinson J., Epand R. F., Epand R. M. (2008) Free Radic. Biol. Med. 44, 739–764 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Constantinou C., Papas A., Constantinou A. I. (2008) Int. J. Cancer 123, 739–752 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ricciarelli R., Tasinato A., Clément S., Ozer N. K., Boscoboinik D., Azzi A. (1998) Biochem. J. 334, 243–249 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Neuzil J. (2002) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 293, 1309–1313 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wagner B. A., Buettner G. R., Burns C. P. (1992) Cancer Res. 52, 6045–6051 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wagner B. A., Buettner G. R., Burns C. P. (1996) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 334, 261–267 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wagner B. A., Buettner G. R., Oberley L. W., Burns C. P. (1998) Cancer Res. 58, 2809–2816 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ejsing C. S., Sampaio J. L., Surendranath V., Duchoslav E., Ekroos K., Klemm R. W., Simons K., Shevchenko A. (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 2136–2141 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schneiter R., Brügger B., Sandhoff R., Zellnig G., Leber A., Lampl M., Athenstaedt K., Hrastnik C., Eder S., Daum G., Paltauf F., Wieland F. T., Kohlwein S. D. (1999) J. Cell Biol. 146, 741–754 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sambrook J., Russell D. W. (2001) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd Ed., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY [Google Scholar]
- 20.Guthrie C., Fink G. R. (1991) Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 194, Academic Press, San Diego, CA [Google Scholar]
- 21.Niedenthal R. K., Riles L., Johnston M., Hegemann J. H. (1996) Yeast 12, 773–786 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zaremberg V., McMaster C. R. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 39035–39044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tatchell K., Robinson L. C. (2002) Methods Enzymol. 351, 661–683 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Howe A. G., Zaremberg V., McMaster C. R. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 44100–44107 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fariss M. W., Nicholls-Grzemski F. A., Tirmenstein M. A., Zhang J. G. (2001) Free Radic. Biol. Med. 31, 530–541 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Neuzil J., Massa H. (2005) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 327, 1024–1027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Temple M. D., Perrone G. G., Dawes I. W. (2005) Trends Cell Biol. 15, 319–326 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee J., Godon C., Lagniel G., Spector D., Garin J., Labarre J., Toledano M. B. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 16040–16046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Thorpe G. W., Fong C. S., Alic N., Higgins V. J., Dawes I. W. (2004) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 6564–6569 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jamieson D. J. (1998) Yeast 14, 1511–1527 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Outten C. E., Falk R. L., Culotta V. C. (2005) Biochem. J. 388, 93–101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Izawa S., Inoue Y., Kimura A. (1995) FEBS Lett. 368, 73–76 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cipak A., Jaganjac M., Tehlivets O., Kohlwein S. D., Zarkovic N. (2008) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1781, 283–287 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Izawa S., Inoue Y., Kimura A. (1996) Biochem. J. 320, 61–67 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Okazaki S., Naganuma A., Kuge S. (2005) Antioxid. Redox Signal. 7, 327–334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yan C., Lee L. H., Davis L. I. (1998) EMBO J. 17, 7416–7429 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tachibana T., Okazaki S., Murayama A., Naganuma A., Nomoto A., Kuge S. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284, 4464–4472 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.van der Luit A. H., Budde M., Ruurs P., Verheij M., van Blitterswijk W. J. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 39541–39547 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gajate C., Del Canto-Jañez E., Acuña A. U., Amat-Guerri F., Geijo E., Santos-Beneit A. M., Veldman R. J., Mollinedo F. (2004) J. Exp. Med. 200, 353–365 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Busto J. V., Sot J., Goni F. M., Mollinedo F., Alonso A. (2007) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1768, 1855–1860 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Busto J. V., Del Canto-Jañez E., Goñi F. M., Mollinedo F., Alonso A. (2008) J. Chem. Biol. 1, 89–94 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.te Welscher Y. M., ten Napel H. H., Balagué M. M., Souza C. M., Riezman H., de Kruijff B., Breukink E. (2008) J. Biol. Chem. 283, 6393–6401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Böcking T., Barrow K. D., Netting A. G., Chilcott T. C., Coster H. G., Höfer M. (2000) Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 1607–1618 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Baumann N. A., Sullivan D. P., Ohvo-Rekilä H., Simonot C., Pottekat A., Klaassen Z., Beh C. T., Menon A. K. (2005) Biochemistry 44, 5816–5826 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Royer M. C., Lemaire-Ewing S., Desrumaux C., Monier S., Pais de Barros J. P., Athias A., Néel D., Lagrost L. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284, 15826–15834 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Toone W. M., Morgan B. A., Jones N. (2001) Oncogene 20, 2336–2346 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kuge S., Jones N., Nomoto A. (1997) EMBO J. 16, 1710–1720 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Azevedo D., Tacnet F., Delaunay A., Rodrigues-Pousada C., Toledano M. B. (2003) Free Radic. Biol. Med. 35, 889–900 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Inoue Y., Matsuda T., Sugiyama K., Izawa S., Kimura A. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 27002–27009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ross S. J., Findlay V. J., Malakasi P., Morgan B. A. (2000) Mol. Biol. Cell 11, 2631–2642 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Malínská K., Malínský J., Opekarová M., Tanner W. (2003) Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 4427–4436 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]