Abstract
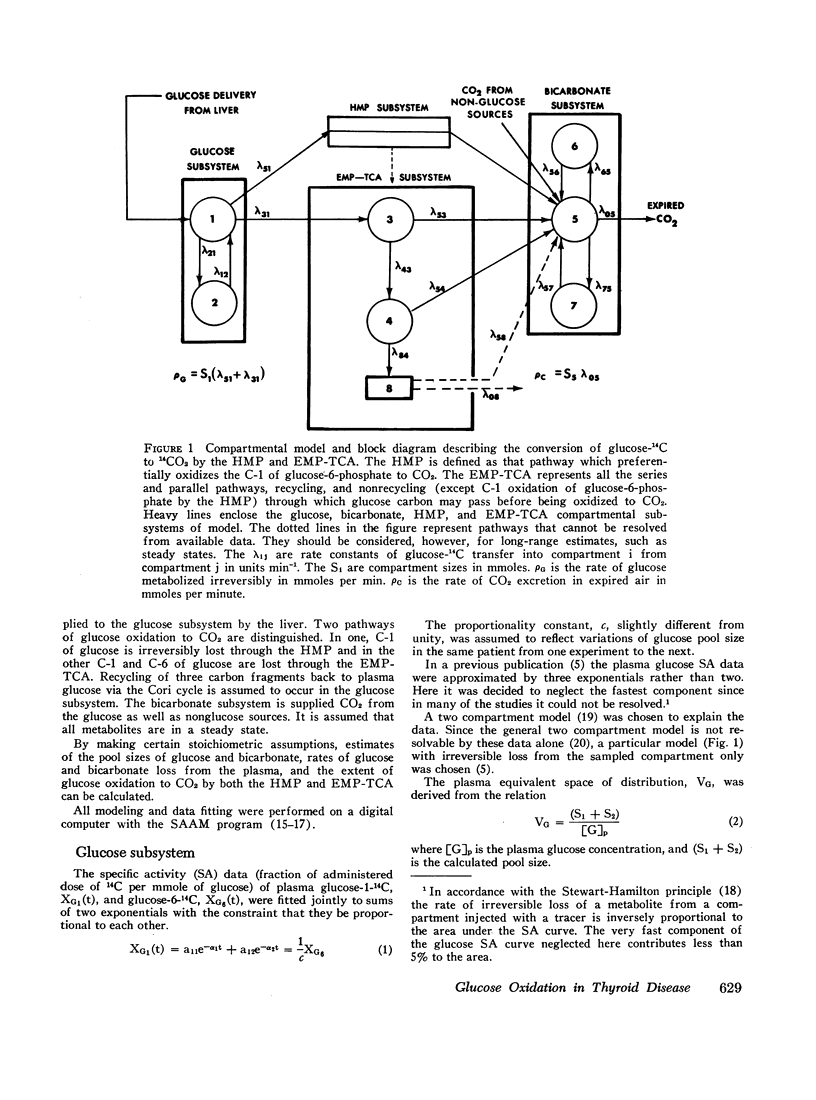
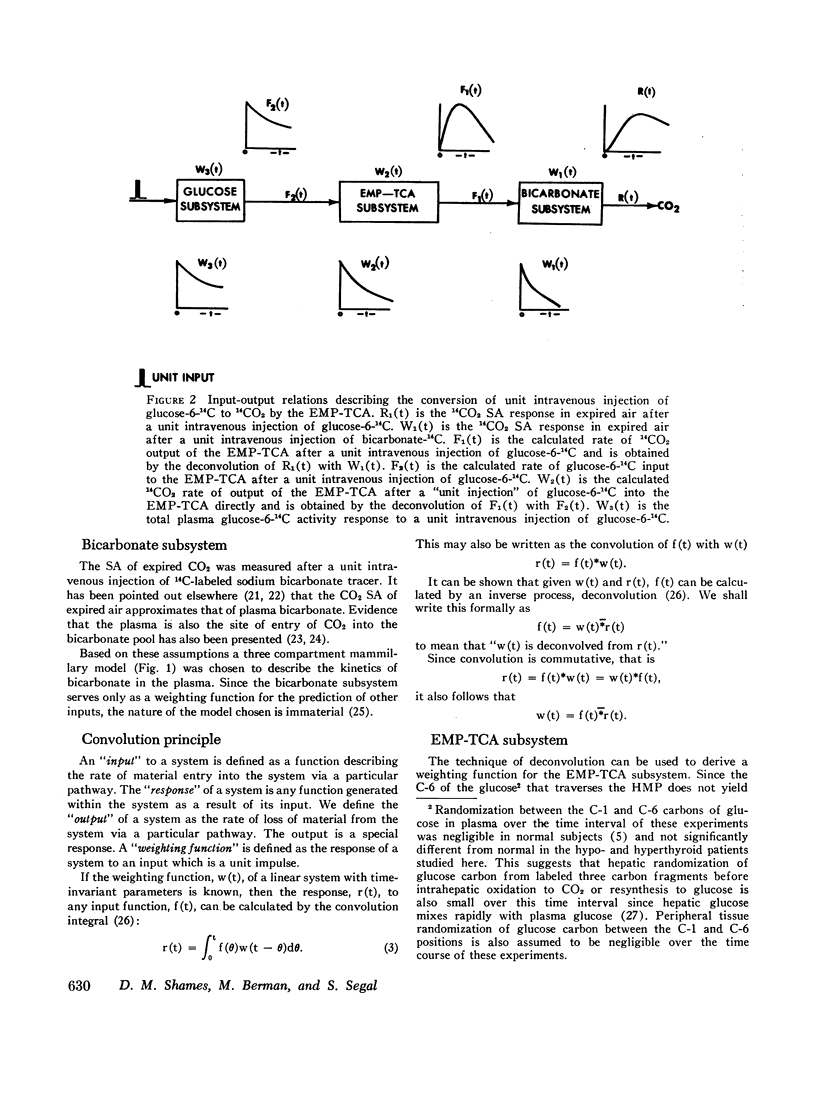
Glucose oxidation to CO2 in man at the fasted, steady state has been investigated in normal, hypothyroid, patients by monitoring the specific activity of plasma glucose and expired CO2 after intravenous injection of glucose-1-14C, glucose-6-14C, and sodium bicarbonate-24C in tracer amounts. Making certain stoichiometric assumptions about the oxidation of the C-1 and C-6 carbons of glucose to CO2, the data are incorporated into a multicompartmental model describing the kinetics of plasma glucose, plasma bicarbonate, and the conversion of glucose to CO2 by the hexose monophosphate pathway and all other series and parallel pathways which oxidize glucose carbon to CO2 (EMP-TCA). This formulation separates the distribution kinetics of glucose and bicarbonate from the kinetics of glucose oxidation to CO2. It allows the calculation of a minimal fraction (ϕt) of glucose irreversibly oxidized to CO2 which is based entirely on the duration of the experimental data. This calculation is independent of the extrapolative implications of the model beyond the experimental interval and of the particular model chosen to fit the data. All modeling and data fitting were performed on a digital computer with the SAAM program.
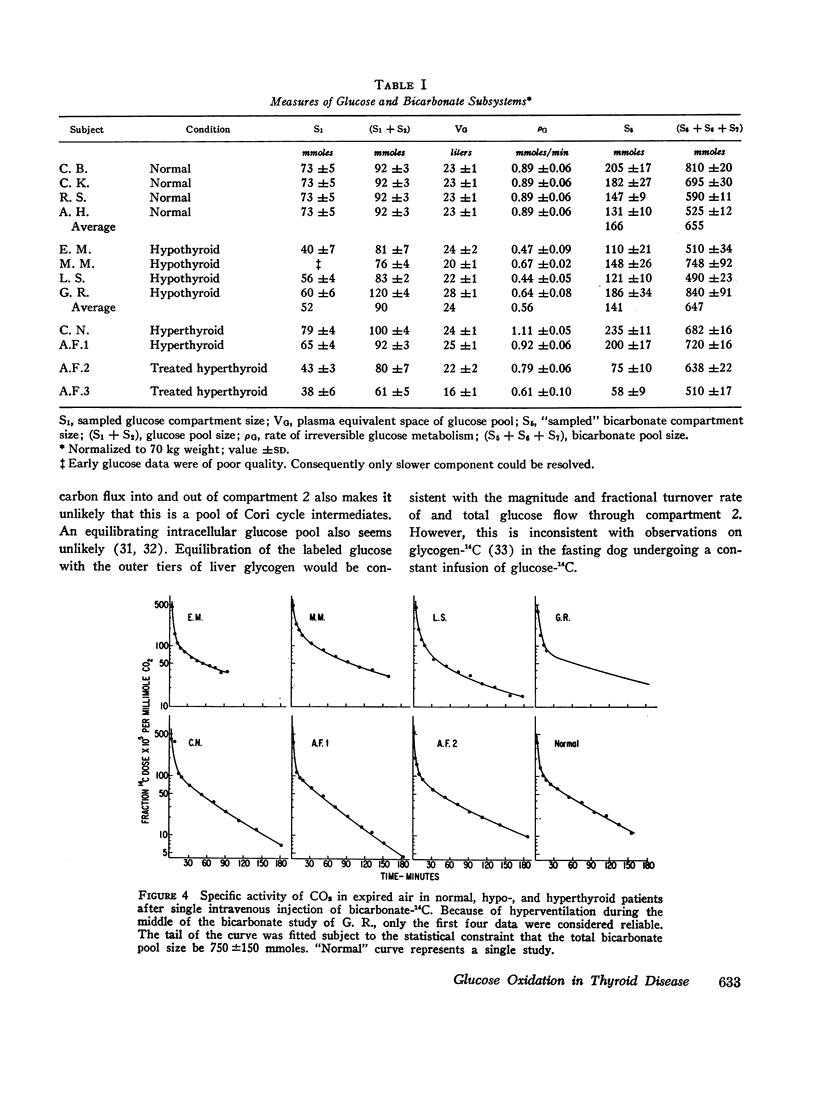
Based on a 300 min experiment the analysis suggests that in hypothyroidism there is a decrease in the rate of glucose metabolized irreversibly (ρG). There is also a decrease in the minimal fraction (ϕ300) which is completely oxidized to CO2 by way of the EMP-TCA. ρG and ϕ300 are 0.56 and 0.42 mmole/min respectively as compared to 0.89 and 0.50 mmole/min respectively in normals. However, the fraction of the C-1 of glucose metabolized irreversibly which undergoes oxidation to CO2 by the hexose monophosphate pathway (Ψ) is not different from normal (0.07 and 0.07 respectively). The hyperthyroid studies suggest that ρG and ϕ300 are within the normal range (1.01 and 0.46 mmoles/min respectively as compared to 0.89 and 0.50 mmole/min respectively in normals). However, Ψ is decreased to less than half the normal value (0.03 as compared to 0.07 in normals).
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMATUZIO D. S., STUTZMAN F. L., VANDERBILT M. J., NESBITT S. Interpretation of the rapid intravenous glucose tolerance test in normal individuals and in mild diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1953 May;32(5):428–435. doi: 10.1172/JCI102755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER N., HUEBOTTER R. GLUCOSE METABOLISM IN MICE. Am J Physiol. 1964 Nov;207:1155–1160. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.5.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER N., SHIPLEY R. A., CLARK R. E., INCEFY G. E., SKINNER S. S. C14 studies in carbohydrate metabolism. V. Glucose metabolism in alloxan-diabetic rats. Am J Physiol. 1961 Apr;200:863–870. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.4.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER N., SHREEVE W. W., SHIPLEY R. A., INCEFY G. E., MILLER M. C14 studies in carbohydrate metabolism. I. The oxidation of glucose in normal human subjects. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):575–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERKOWTZ J. M., SHERMAN J. L., Jr, HART H. E. The rate of decarboxylation of mevalonic acid-1-C-14 in man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 May 10;108:250–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERMAN M., SHAHN E., WEISS M. F. The routine fitting of kinetic data to models: a mathematical formalism for digital computers. Biophys J. 1962 May;2:275–287. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86855-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERMAN M., WEISS M. F., SHAHN E. Some formal approaches to the analysis of kinetic data in terms of linear compartmental systems. Biophys J. 1962 May;2:289–316. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86856-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP J. S., STEELE R., ALTSZULER N., DUNN A., BJERKNES C., DEBODO R. C. EFFECTS OF INSULIN ON LIVER GLYCOGEN SYNTHESIS AND BREAKDOWN IN THE DOG. Am J Physiol. 1965 Feb;208:307–316. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAIR A., SEGAL S. The isolation of blood glucose as potassium gluconate. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Jun;55:959–964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAIR A., SEGAL S. Use of filter paper mounting for determination of the specific activity of gluconate-C14 by liquid scintillation assay. Anal Biochem. 1962 Mar;3:221–229. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin N. I., Berman M., Berk P. D., Phang J. M., Waldmann T. A. The application of multicompartmental analysis to problems of clinical medicine. Combined clinical staff conference at the National Institutes of Health. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Feb;68(2):423–448. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-2-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M. A postulate to aid in model building. J Theor Biol. 1963 May;4(3):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(63)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell G. L., Berman M., Robertson J. S. Nomenclature for tracer kinetics. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1968 Mar;19(3):249–262. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(68)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAHILL G. F., Jr, ASHMORE J., EARLE A. S., ZOTTU S. Glucose penetration into liver. Am J Physiol. 1958 Mar;192(3):491–496. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.192.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOW D. S., ALLEN C. E. Steady-state oxidation of glucose in hyperthyroid and hypothyroid rats. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1961 Jun;39:981–990. doi: 10.1139/o61-098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn A., Chenoweth M., Schaeffer L. D. Estimation of glucose turnover and the Cori cycle using glucose-6-t-14C. Biochemistry. 1967 Jan;6(1):6–11. doi: 10.1021/bi00853a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDRICKSON D. S., ONO K. An improved technique for assay of C14O2 in expired air using the liquid scintillation counter. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Jan;51(1):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON E. S., GOLDBERG M. CARBON-14 STUDIES OF ENERGY METABOLISM IN VARIOUS THYROID STATES. Metabolism. 1964 Jul;13:591–608. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(64)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ J., WOOD H. G. The use of C14O2 yields from glucose-1- and -6-C14 for the evaluation of the pathways of glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:517–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ J., WOOD H. G. The use of glucose-C14 for the evaluation of the pathways of glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2165–2177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIPNIS D. M., HELMREICH E., CORI C. F. Studies of tissue permeability. IV. The distribution of glucose between plasma and muscle. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jan;234(1):165–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Dunn A. Glucose-2-t as a tracer for glucose metabolism. Biochemistry. 1967 Jan;6(1):1–5. doi: 10.1021/bi00853a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMURREY J. D., BOLING E. A., DAVIS J. M., PARKER H. V., MAGNUS I. C., BALL M. R., MOORE F. D. Body composition: simultaneous determination of several aspects by the dilution principle. Metabolism. 1958 Sep;7(5):651–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NECHELES T., SPRATT J., FORD E., BEUTLER E. Effect of thyroid hormone on the pathways of glucose oxidation in the intact rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Jan;109:114–115. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICHARD G. A., Jr, JACOBS A. G., KIMBEL P., HOCHELLA N. J., WEINHOUSE S. Blood glucose replacement rates in normal and diabetic humans. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Sep;16:789–795. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.5.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACKS W. Cerebral metabolism of isotopic glucose in normal human subjects. J Appl Physiol. 1957 Jan;10(1):37–44. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.10.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEGAL S., BERMAN M., BLAIR A. The metabolism of variously C14-labeled glucose in man and an estimation of the extent of glucose metabolism by the hexose monophosphate pathway. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jul;40:1263–1279. doi: 10.1172/JCI104356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIPLEY R. A., BAKER N., INCEFY G. E., CLARK R. E. C14 studies in carbohydrate metabolism. IV. Characteristics of bicarbonate pool system in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1959 Jul;197(1):41–46. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.197.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHREEVE W. W., HENNES A. R., SCHWARTZ R. Production of C14O2 from 1- and 2-C14-acetate by human subjects in various metabolic states. Metabolism. 1959 Sep;8:741–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN M., BURGEN A. S. Application of analogue computer to measurement of intestinal absorption rates with tracers. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Sep;16:911–913. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.5.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIRO M. J., BALL E. G. A comparison on the pathways of glucose catabolism in the normal and hyperthyroid rat. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):31–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segre G. Compartmental models in the analysis of intestinal absorption. Protoplasma. 1967;63(1):328–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterhouse C., Kemperman J. H. Changes in oxidative metabolism with glucose ingestion. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Aug;68(2):250–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. R., Pelligra R., Shapira J., Adachi R. R., Skrettingland K. Glucose oxidation and replacement during prolonged exercise in man. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Nov;23(5):734–741. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.23.5.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


