Abstract
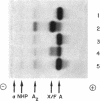
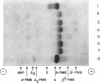
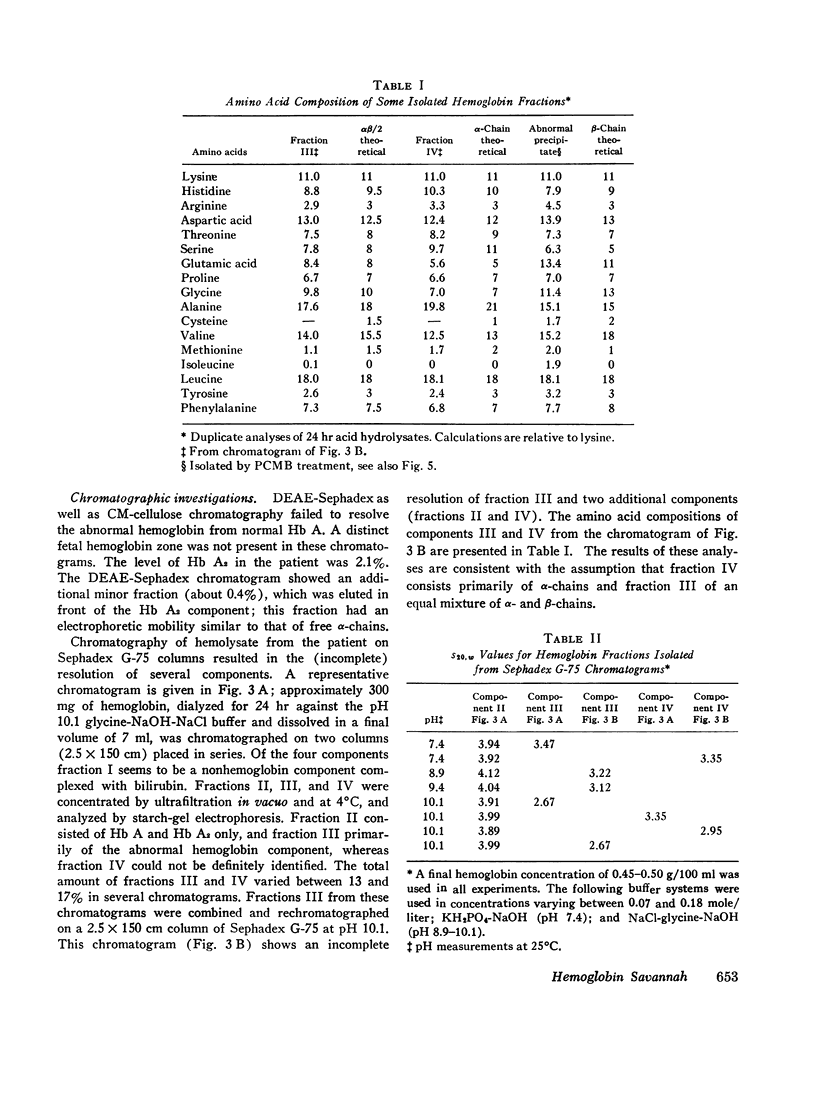
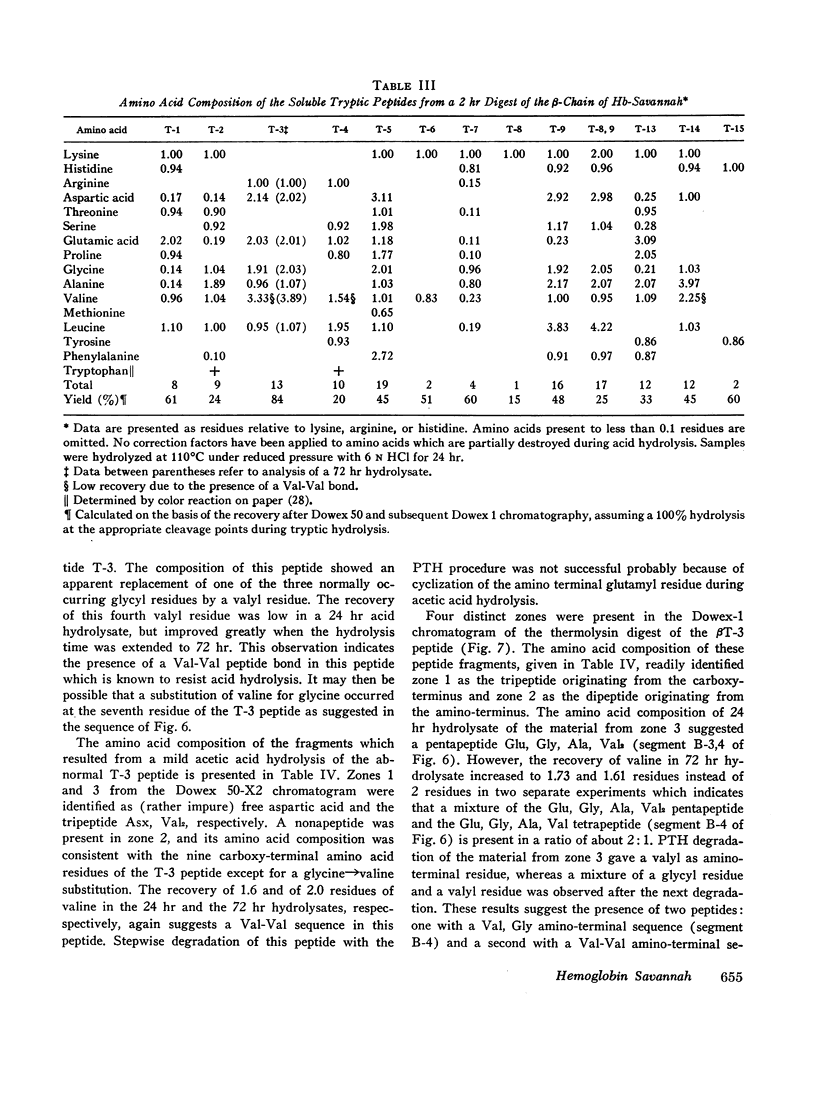
An abnormal hemoglobin, termed Hb Savannah, was found in red cell hemolysate of a young Caucasian girl with severe hemolytic anemia. The presence of this unstable variant became evident when inclusion bodies appeared rapidly upon exposure of red cells to redox dyes and a large percentage of hemoglobin in hemolysate precipitated on warming to 65°C. Treatment of the hemoglobin with p-hydroxymercuribenzoate (PMB) caused a rapid dissociation into monomers; starch-gel electrophoresis of PMB-treated hemoglobin showed the presence of abnormal β-chains. Data from structural studies of isolated β-chains indicated substitution of a valyl residue for the normally occurring glycyl residue at position 24, which corresponds to helical residue B6. A similar substitution but with an arginine replacing the glycyl residue has been observed in Hb Riverdale-Bronx. The glycine to valine substitution will change the relationship of the B and the E helices which results in extensive conformational changes in the β-chain. This change presumably causes an increased dissociation of the hemoglobin molecule into dimers and probably monomers, and a decreased stability of the αβ-dimers. The hemoglobin abnormality may be the result of a fresh mutation because the abnormality is not present in the parents nor in any of the seven siblings.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Meadway R. J. The use of thermolysin in amino acid sequence determination. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;108(5):893–895. doi: 10.1042/bj1080893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALDRIDGE R. C., LEWIS H. B. Diet and the ergothioneine content of blood. J Biol Chem. 1953 May;202(1):169–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BETKE K., MARTI H. R., SCHLICHT I. Estimation of small percentages of foetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1959 Dec 12;184(Suppl 24):1877–1878. doi: 10.1038/1841877a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babin D. R., Schroeder W. A., Shelton J. R., Shelton J. B., Robberson B. The amino acid sequence of the gamma chain of bovine fetal hemoglobin. Biochemistry. 1966 Apr;5(4):1297–1310. doi: 10.1021/bi00868a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson A. M., Yasunobu K. T. The action of the Bacillus subtilis neutral protease on S-beta-aminoethylcysteinyl ferredoxin from Clostridium pasteurianum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Aug;126(2):653–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90452-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A., Babin D. R., Nomoto M., Srinivasin N. G., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Neurath H. The amino acid sequence of bovine carboxypeptidase A. II. Tryptic and chymotryptic peptides of the cyanogen bromide fragment F-III. Biochemistry. 1969 Sep;8(9):3859–3871. doi: 10.1021/bi00837a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Lehmann H. The unstable haemoglobin haemolytic anaemias. Semin Hematol. 1969 Apr;6(2):116–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Naughton M. A., Weatherball D. J. Abnormal human haemoglobins. Separation and characterization of the alpha and beta chains by chromatography, and the determination of two new variants, hb Chesapeak and hb J (Bangkok). J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(1):91–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dozy A. M., Kleihauer E. F., Huisman T. H. Studies on the heterogeneity of hemoglobin. 13. Chromatography of various human and animal hemoglobin types on DEAE-Sephadex. J Chromatogr. 1968 Feb 20;32(4):723–727. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80551-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efremov G. D., Huisman T. H., Smith L. L., Wilson J. B., Kitchens J. L., Wrightstone R. N., Adams H. R. Hemoglobin Richmond, a human hemoglobin which forms asymmetric hybrids with other hemoglobins. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6105–6116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIMES A. J., MEISLER A., DACIE J. V. CONGENITAL HEINZ-BODY ANAEMIA. FURTHER EVIDENCE ON THE CAUSE OF HEINZ-BODY PRODUCTION IN RED CELLS. Br J Haematol. 1964 Jul;10:281–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1964.tb00704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUISMAN T. H. NORMAL AND ABNORMAL HUMAN HEMOGLOBINS. Adv Clin Chem. 1963;6:231–261. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(08)60240-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huehns E. R., Bellingham A. J. Diseases of function and stability of haemoglobin. Br J Haematol. 1969 Jul;17(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb05659.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman T. H., Dozy A. M. Studies on the heterogeneity of hemoglobin. IX. The use of Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethanehcl buffers in the anion-exchange chromatography of hemoglobins. J Chromatogr. 1965 Jul;19(1):160–169. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)99434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES R. T. LONG-PATH FLOW CELLS FOR AUTOMATIC AMINO ACIDS ANALYSIS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Nov;9:377–382. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann H., Carrell R. W. Variations in the structure of human haemoglobin. With particular reference to the unstable haemoglobins. Br Med Bull. 1969 Jan;25(1):14–23. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Sasaki R., Singer A., Jukes T. H. Specific nature of hydrolysis of insulin and tobacco mosaic virus protein by thermolysin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Aug;115(2):324–331. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90282-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F., Lehmann H. Molecular pathology of human haemoglobin. Nature. 1968 Aug 31;219(5157):902–909. doi: 10.1038/219902a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F., Muirhead H., Cox J. M., Goaman L. C. Three-dimensional Fourier synthesis of horse oxyhaemoglobin at 2.8 A resolution: the atomic model. Nature. 1968 Jul 13;219(5150):131–139. doi: 10.1038/219131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Cole R. D. On the aminoethylation of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3457–3461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranney H. M., Jacobs A. S., Udem L., Zalusky R. Hemoglobin Riverdale-Bronx an unstable hemoglobin resulting from the substitution of arginine for glycine at helical residue B6 of the B beta polypeptide chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 30;33(6):1004–1005. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90413-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder R. F., Oski F. A., Clegg J. B. Hemoglobin Philly (beta 35 tyrosine phenylalanine): studies in the molecular pathology of hemoglobin. J Clin Invest. 1969 Sep;48(9):1627–1642. doi: 10.1172/JCI106128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemeyer M. A., Huehns E. R. On the mechanism of the dissociation of haemoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):253–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHROEDER W. A., SHELTON J. R., SHELTON J. B., CORMICK J., JONES R. T. THE AMINO ACID SEQUENCE OF THE GAMMA CHAIN OF HUMAN FETAL HEMOGLOBIN. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:992–1008. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. G., Ueda S., Alperin J. B., Brimhall B., Jones R. T. Hemoglobin sabine beta 91 (f 7) leu to pro. An unstable variant causing severe anemia with inclusion bodies. N Engl J Med. 1969 Apr 3;280(14):739–745. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196904032801402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder W. A., Robberson B. An improved gradient for ion exchange chromatography of peptides on Dowex-1. Anal Chem. 1965 Nov;37(12):1583–1585. doi: 10.1021/ac60231a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]