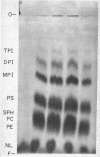
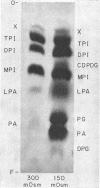
Abstract
Platelets are a rich source for the study of inositol lipids in man. The substitution of an EDTA-KCl solution for the water component of the Bligh and Dyer procedure permitted quantitative extraction of polyphosphoinositides. The latter, with monophosphoinositide, were found to comprise, on a molar basis, 6.7% of total platelet phospholipids. Study of the incorporation of orthophosphate-32P into platelet phospholipids was further simplified by separating eight 32P-labeled lipids, including the inositides, with a single chromatographic development on formaldehyde-treated paper. Particular attention was paid to the influence of ionic environment on the pattern and degree of labeling.
In 300 mOsm media major phospholipids other than the inositides were not labeled. Small amounts of label appeared in certain trace phospholipids, notably phosphatidic acid. In 150 mOsm media, labeling of inositides was moderately increased, that of trace phospholipids enormously so. The increased labeling was not solely due to thrombocytolysis since (a) platelet disruption by sonication or freeze-thawing abolished 32P incorporation into phospholipids and (b) in timed studies, restoration of osmolarity to 300 mOsm by addition of hypertonic sorbitol blunted the enhancement effect of previous 150 mOsm exposure. Lowering K and compensatorily increasing Na concentration of 300 mOsm media also stimulated 32P labeling of inositides and, to a lesser extent, the trace phospholipids. However, the pattern and degree of stimulation were not as strikingly altered as in the osmolarity studies.
These data show that drastic alterations of ionic environment can sharply influence the platelet's ability to incorporate orthophosphate-32P into its phospholipids.
Full text
PDF

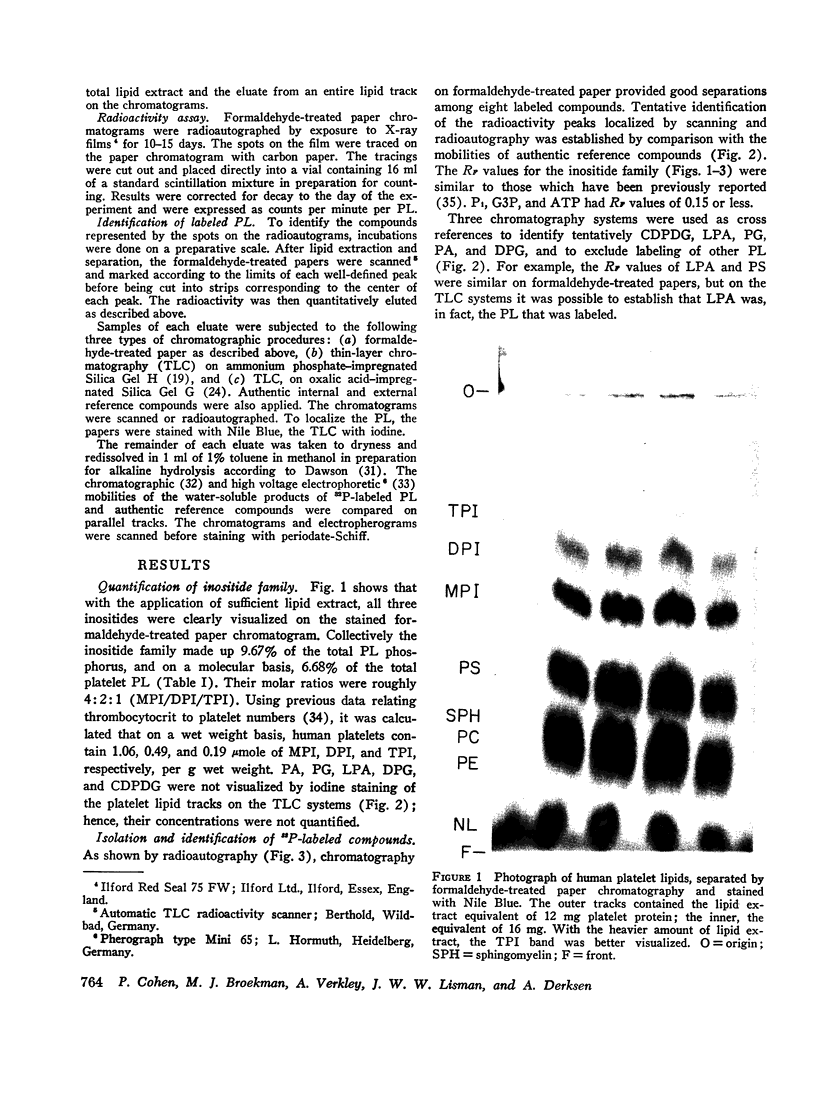
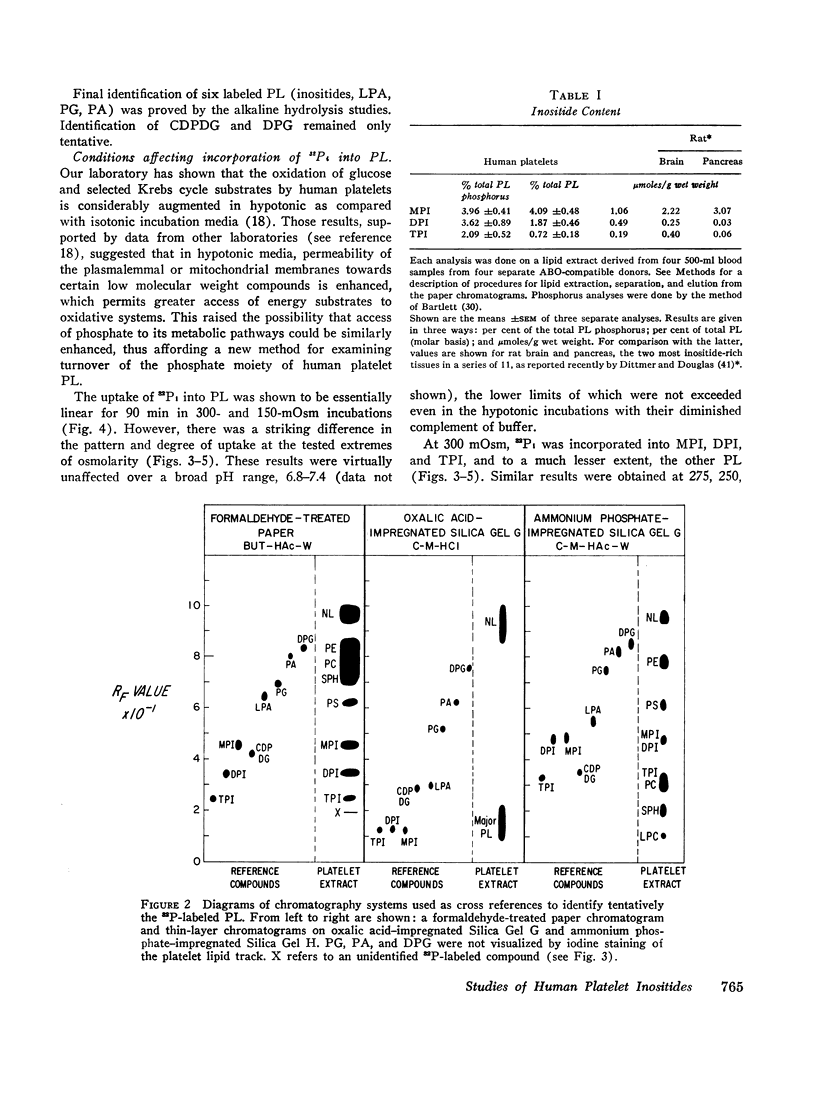
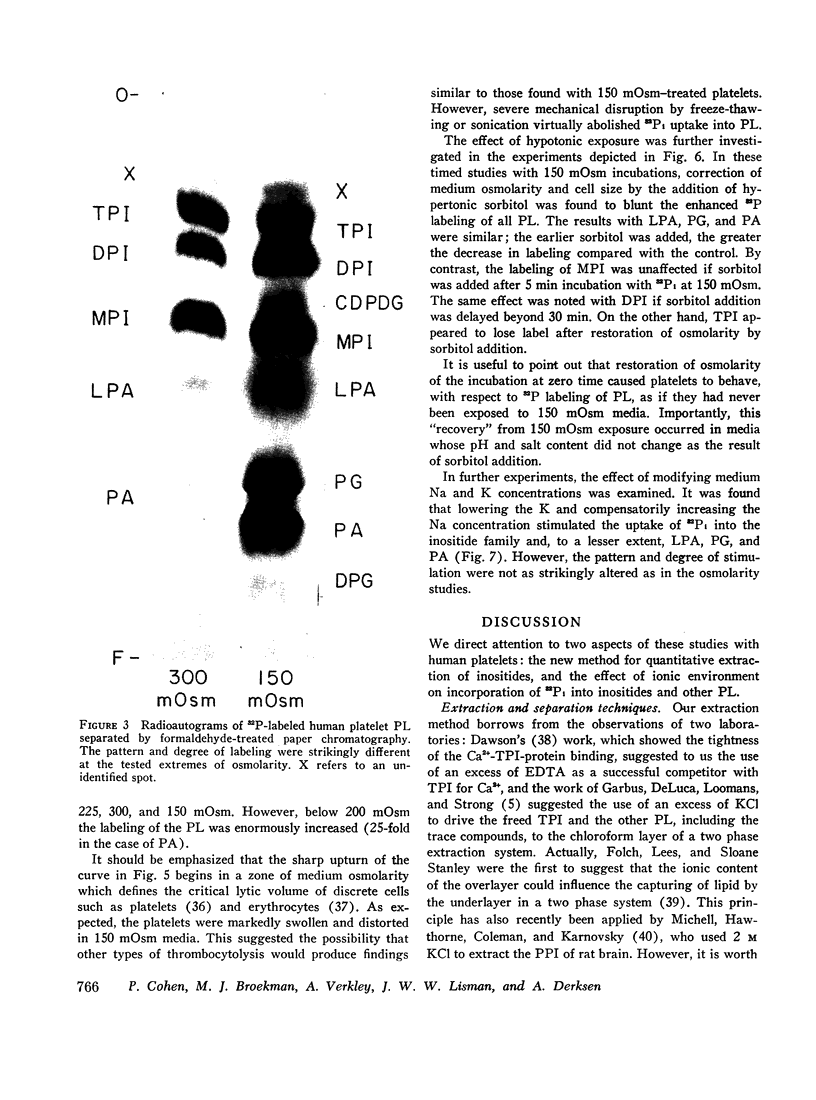
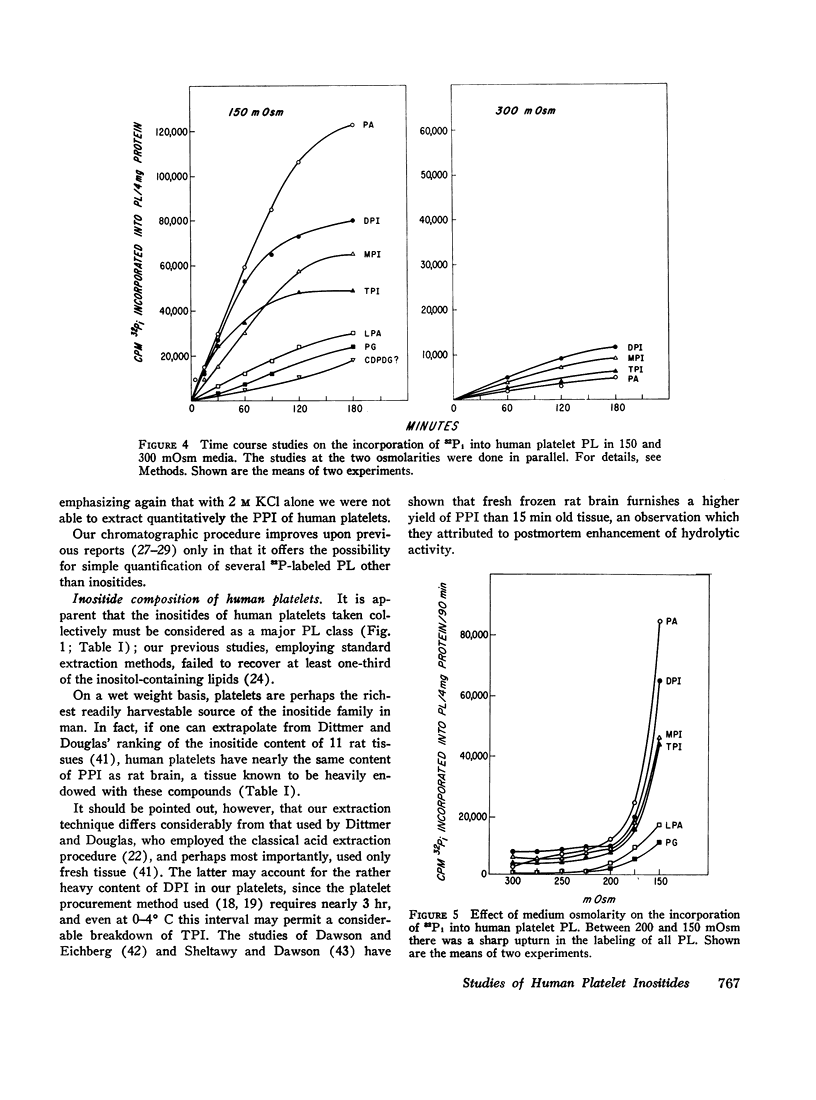
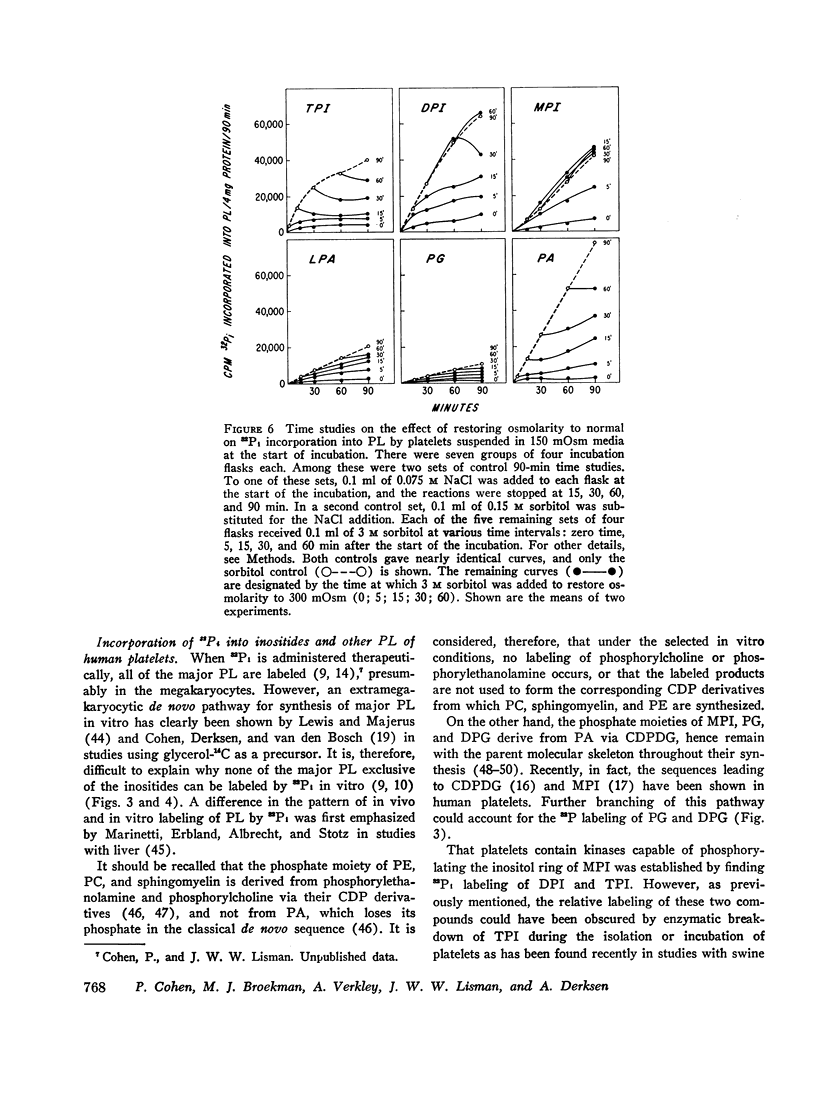
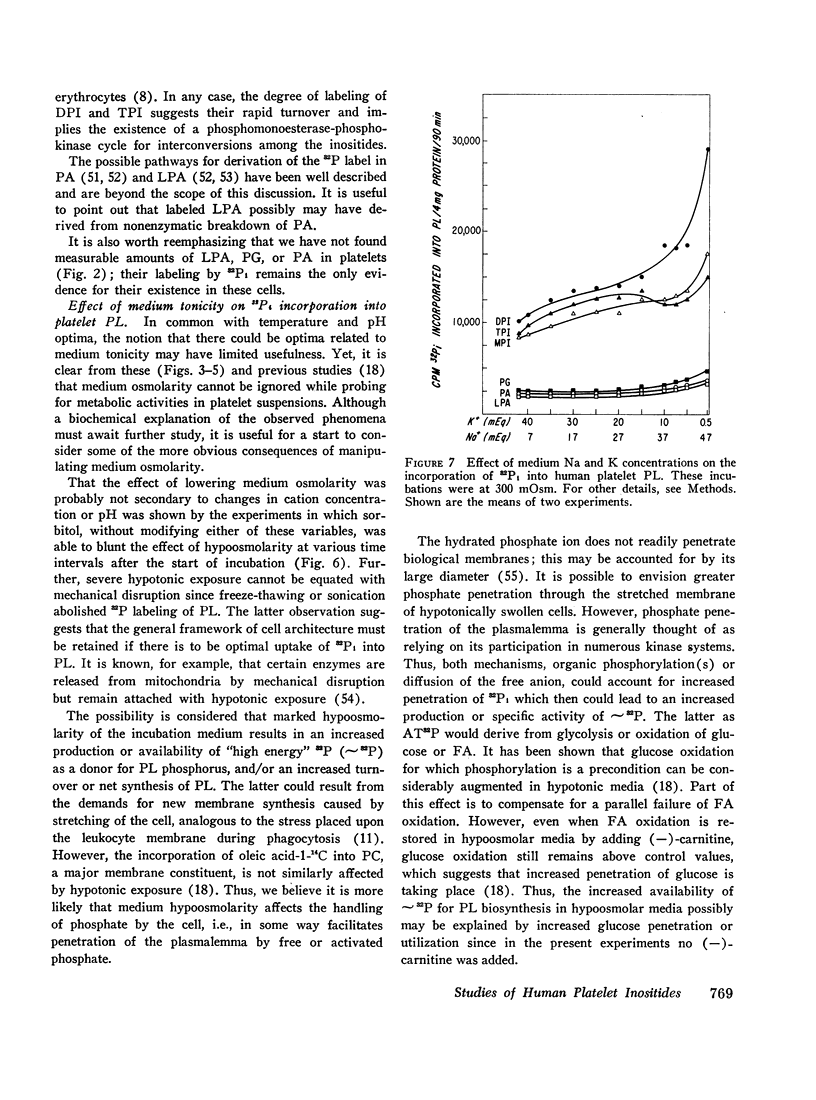



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRADE F., HUGGINS C. G. MYO-INOSITOL PHOSPHATES IN A PHOSPHOINOSITIDE COMPLEX FROM KIDNEY. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 2;84:681–693. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENDALL D. S., DE DUVE C. Tissue-fractionation studies. 14. The activation of latent dehydrogenases in mitochondria from rat liver. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:444–450. doi: 10.1042/bj0740444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECHER G., CRONKITE E. P. Morphology and enumeration of human blood platelets. J Appl Physiol. 1950 Dec;3(6):365–377. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1950.3.6.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call F. L., 2nd, Williams W. J. Biosynthesis of cytidine diphosphate diglyceride by human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1970 Feb;49(2):392–399. doi: 10.1172/JCI106248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Derksen A. Comparison of phospholipid and fatty acid composition of human erythrocytes and platelets. Br J Haematol. 1969 Oct;17(4):359–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb01382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Derksen A., Van den Bosch H. Pathways of fatty acid metabolism in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jan;49(1):128–139. doi: 10.1172/JCI106211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Wittels B. Energy substrate metabolism in fresh and stored human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jan;49(1):119–127. doi: 10.1172/JCI106210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooley M. H., Cohen P. Potassium transport in human blood platelets. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jul;70(1):69–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. A hydrolytic procedure for the identification and estimation of individual phospholipids in biological samples. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:45–53. doi: 10.1042/bj0750045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. Studies on the labelling of brain phospholipids with radioactive phosphorus. Biochem J. 1954 Jun;57(2):237–245. doi: 10.1042/bj0570237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. The measurement of 32P labelling of individual kephalins and lecithin in a small sample of tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Jul;14(3):374–379. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., DAWSON R. M. The isolation of a new lipid, triphosphoinositide, and monophosphoinositide from ox brain. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:535–540. doi: 10.1042/bj0810535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M. 'Phosphatido-peptide'-like complexes formed by the interaction of calcium triphosphoinositide with protein. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):134–138. doi: 10.1042/bj0970134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Eichberg J. Diphosphoinositide and triphosphoinositide in animal tissues. Extraction, estimation and changes post mortem. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):634–643. doi: 10.1042/bj0960634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittmer J. C., Douglas M. G. Quantitative determination of phosphoinositides. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Oct 17;165(2):515–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIRKIN B. G., WILLIAMS W. J. The incorporation of radioactive phosphorus into the phospholipids of human leukemic leukocytes and platelets. J Clin Invest. 1961 Feb;40:423–432. doi: 10.1172/JCI104270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARBUS J., DELUCA H. F., LOOMANS M. E., STRONG F. M. The rapid incorporation of phosphate into mitochondrial lipids. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:59–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSSMAN C. M., KOHN R. ENZYMATIC CHARACTERISTICS OF IN-VITRO INCORPORATION OF P32 ORTHOPHOSPHATE INTO HUMAN PLATELET PHOSPHATIDE. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Mar 15;13:126–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUREVITCH J., NELKEN D. Osmotic fragility of human blood platelets. Blood. 1956 Oct;11(10):924–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galliard T., Michell R. H., Hawthorne J. N. Incorporation of phosphate into diphosphoinositide by subcellular fractions from liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Dec 2;106(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman C. M., Bartos F. Succinate dependence of in vitro incorporation of 32P-orthophosphate into human platelet phosphatide. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Oct;128(1):231–235. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANES C. S., ISHERWOOD F. A. Separation of the phosphoric esters on the filter paper chromatogram. Nature. 1949 Dec 31;164(4183):1107-12, illust. doi: 10.1038/1641107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN L. E., HOKIN M. R. Diglyceride kinase and other path ways for phosphatidic acid synthesis in the erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 12;67:470–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91852-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN L. E., HOKIN M. R. Effects of acetylcholine on the turnover of phosphoryl units in individual phospholipids of pancreas slices and brain cortex slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Sep;18(1):102–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN L. E., HOKIN M. R. Studies on the carrier function of phosphatidic acid in sodium transport. I. The turnover of phosphatidic acid and phosphoinositide in the avian salt gland on stimulation of secretion. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Sep;44:61–85. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN L. E., HOKIN M. R. THE INCORPORATION OF 32P FROM TRIPHOSPHATE INTO POLYPHOSPHOINOSITIDES (GAMMA-32P)ADENOSINE AND PHOSPHATIDIC ACID IN ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 2;84:563–575. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORHAMMER L., WAGNER H., RICHTER G. Zur papierchromatographischen Auftrennung von Phosphatiden. I. Biochem Z. 1959;331(3):155–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajra A. K. Biosynthesis of phosphatidic acid from dihydroxyacetone phosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 30;33(6):929–935. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Functional activity in glands and synaptic tissue and the turnover of phosphatidylinositol. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Oct 17;165(2):695–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITO M., KOSTYUK P. G., OSHIMA T. Further study on anion permeability of inhibitory post-synaptic membrane of cat motoneurones. J Physiol. 1962 Oct;164:150–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. L., WALLACH D. F. The metabolic basis of phagocytosis. III. Incorporation of inorganic phosphate into various classes of phosphatides during phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jul;236:1895–1901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY E. P., WEISS S. B. The function of cytidine coenzymes in the biosynthesis of phospholipides. J Biol Chem. 1956 Sep;222(1):193–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIYASU J. Y., PIERINGER R. A., PAULUS H., KENNEDY E. P. The biosynthesis of phosphatidylglycerol. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jul;238:2293–2298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai M., Hawthorne J. N. Incorporation of injected [32P] phosphate into the phosphoinositides of subcellular fractions from young rat brain. Biochem J. 1966 Jan;98(1):62–67. doi: 10.1042/bj0980062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai M., Hawthorne J. N. Physiological significance of polyphosphoinositides in brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Oct 17;165(2):761–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennarz W. J., Bonsen P. P., van Deenen L. L. Substrate specificity of O-L-lysylphosphatidylglycerol synthetase. Enzymatic studies on the structure of O-L-lysylphosphatidylglycerol. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2307–2312. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letters R. The application of a two-dimensional paper-chromatographic technique to the analysis of phospholipids. Biochem J. 1964 Nov;93(2):313–316. doi: 10.1042/bj0930313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis N., Majerus P. W. Lipid metabolism in human platelets. II. De novo phospholipid synthesis and the effect of thrombin on the pattern of synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2114–2123. doi: 10.1172/JCI106178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C. T., Call F. L., 2nd, Williams W. J. The biosynthesis of phosphatidylinositol in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1949–1955. doi: 10.1172/JCI106414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARINETTI G. V., ERBLAND J., ALBRECHT M., STOTZ E. The application of chromatographic methods to study the incorporation of 32P-labeled orthophosphate into the phosphatides of rat liver homogenates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Sep;25(3):585–591. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90531-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Hawthorne J. N., Coleman R., Karnovsky M. L. Extraction of polyphosphoinositides with neutral and acidified solvents. A comparison of guinea-pig brain and liver, and measurements of rat liver inositol compounds which are resistant to extraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun 9;210(1):86–91. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90064-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULUS H., KENNEDY E. P. The enzymatic synthesis of inositol monophosphatide. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1303–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson S. C., Kirschner L. B. Di- and triphosphoinositide metabolism in intact swine erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 10;202(2):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SRIBNEY M., KENNEDY E. P. The enzymatic synthesis of sphingomyelin. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1315–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry P. S., Hokin L. E. Studies on the role of phospholipids in phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 25;241(14):3354–3361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheltawy A., Dawson R. M. The deposition and metabolism of polyphosphoinositides in rat and guinea-pig brain during development. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(2):147–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1110147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheltawy A., Dawson R. M. The metabolism of polyphosphoinositides in hen brain and sciatic nerve. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(2):157–165. doi: 10.1042/bj1110157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheltawy A., Dawson R. M. The polyphosphoinositides and other lipids of peripheral nerves. Biochem J. 1966 Jul;100(1):12–18. doi: 10.1042/bj1000012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanacev N. Z., Chang Y. Y., Kennedy E. P. Biosynthesis of cardiolipin in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):3018–3019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROUP S. B., REED C. F., MARINETTI G. V., SWISHER S. N. Thromboplastic factors in platelets and red blood cells: observations on their chemical nature and function in vitro coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1960 Feb;39:342–351. doi: 10.1172/JCI104045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESTERMAN M. P., JENSEN W. N. IN VITRO INCORPORATION OF RADIOPHOSPHORUS INTO THE PHOSPHATIDES OF NORMAL HUMAN BLOOD CELLS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Feb;118:315–319. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]