Abstract
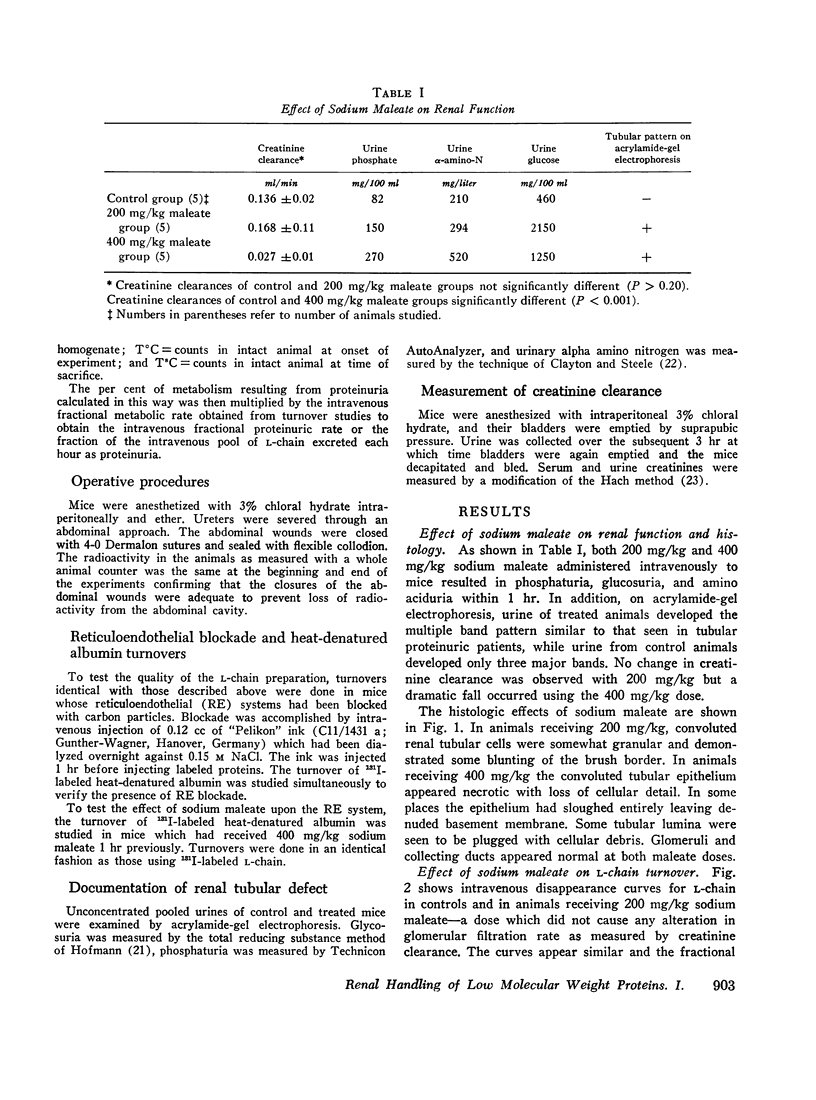
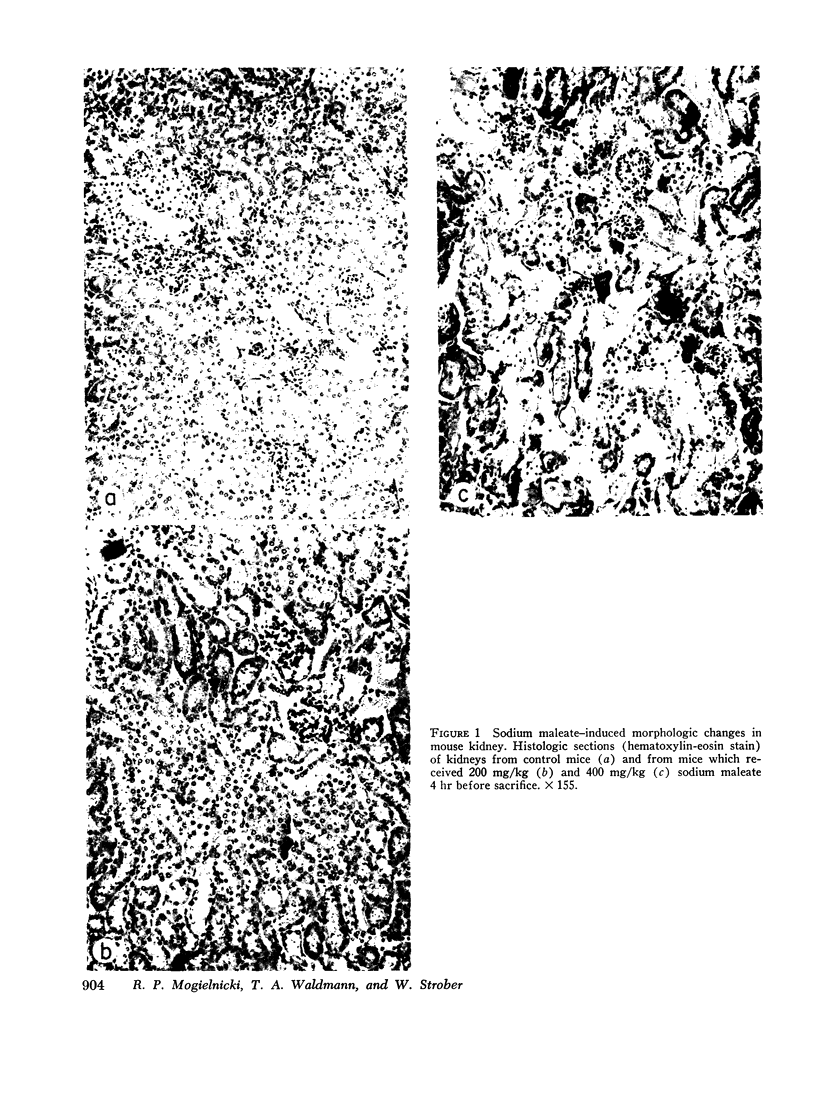
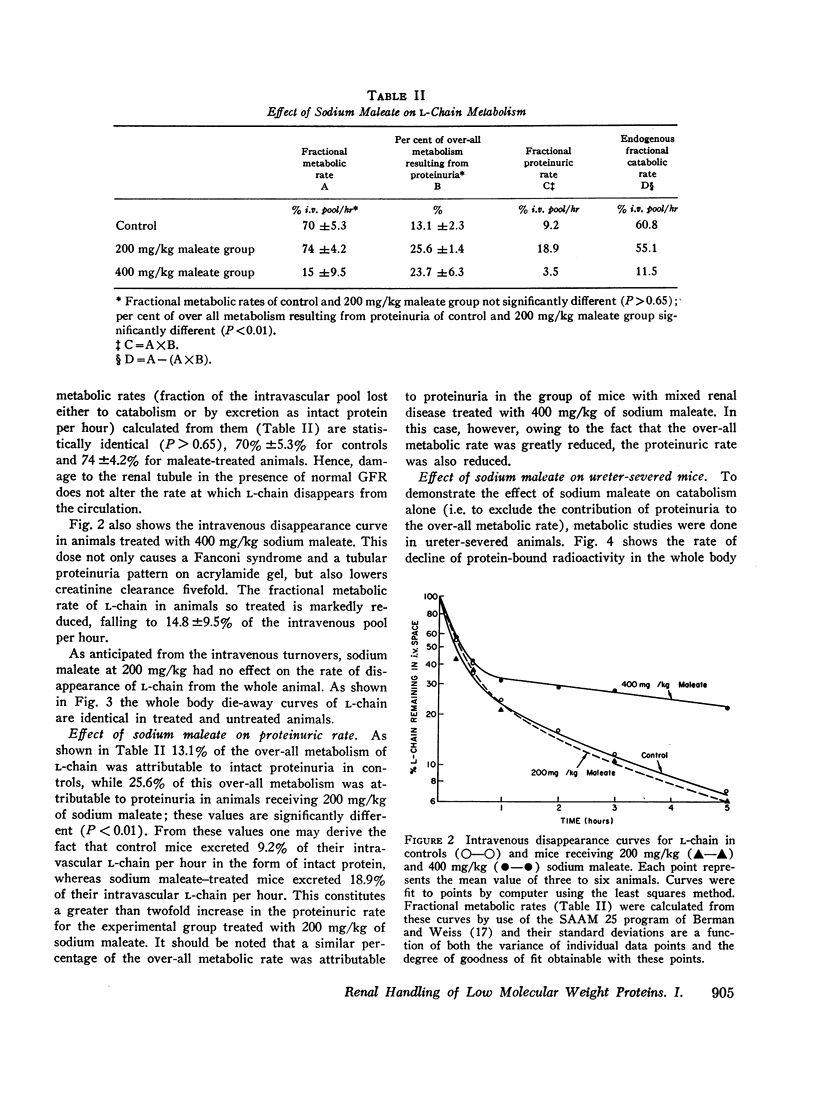
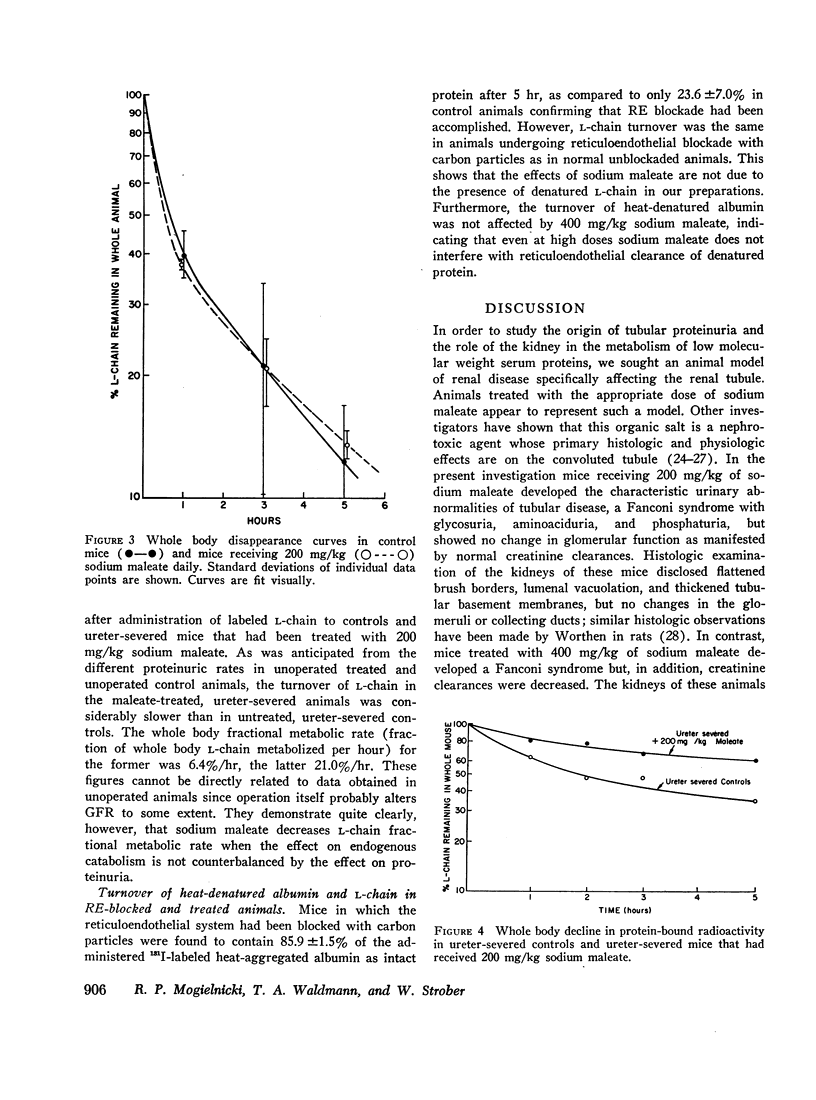
Immunoglobulin L-chain metabolism was studied in normal mice, mice with sodium maleate-induced renal tubular disease but normal glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and mice with both tubular disease and decreased GFR. The proteinuric rate of L-chain was increased twofold in mice with tubular disease alone though there was no alteration in the over-all rate at which L-chain disappeared from the circulation in these animals. This was in sharp contrast to findings in mice with tubular disease and a decreased glomerular filtration rate in which L-chain disappearance rates were markedly reduced. These findings demonstrate that in the normal state, L-chain and presumably other proteins of similar size pass through the glomerulus and are avidly taken up and catabolized by the convoluted tubular cells. In tubular proteinuric states this linked uptake-catabolic function fails, resulting in elevated urinary excretion but normal serum levels and turnover rates of these proteins. In uremic states with decreased glomerular filtration, less small protein is delivered into the tubular lumen and the processes of excretion and catabolism are reduced. This results in prolongation of the survival of small proteins and explains the elevated serum concentrations of these proteins observed in uremia.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERLINER R. W., KENNEDY T. J., HILTON J. G. Effect of maleic acid on renal function. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Dec;75(3):791–794. doi: 10.3181/00379727-75-18344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER E. A., FLYNN F. V., HARRIS H., ROBSON E. B. A study of urine proteins by two-dimensional electrophoresis with special reference to the proteinuria of renal tubular disorders. Clin Chim Acta. 1962 Jan;7:34–41. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(62)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER E. A., FLYNN F. V. The occurrence of post-gamma protein in urine: a new protein abnormality. J Clin Pathol. 1961 Mar;14:172–178. doi: 10.1136/jcp.14.2.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER E. A., FLYNN F. V. The proteinuria of renal tubular disorders. Lancet. 1958 Nov 8;2(7054):978–980. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)90473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREETH J. M., KEKWICK R. A., FLYNN F. V., HARRIS H., ROBSON E. B. An ultracentrifuge study of urine proteins with particular reference to the proteinuria of renal tubular disorders. Clin Chim Acta. 1963 May;8:406–414. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(63)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. C., Steele B. F. A modified copper method for the estimation of alpha-amino nitrogen in urine. Clin Chem. 1967 Jan;13(1):49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debray-Sachs M., Sachs C. Proteinuria in patients with homotransplanted kidneys. Nature. 1966 Oct 8;212(5058):209–210. doi: 10.1038/212209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn F. V., Platt H. S. The origin of the proteins excreted in tubular proteinuria. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Sep;21(3):377–399. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., JANEWAY C. A., FARR L. E. Studies on the metabolism of plasma proteins in the nephrotic syndrome. I. Albumin, gamma-globulin and iron-binding globulin. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jan;35(1):44–56. doi: 10.1172/JCI103251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON H. E., HARRISON H. C. Experimental production of renal glycosuria, phosphaturia, and aminoaciduria by injection of maleic acid. Science. 1954 Oct 15;120(3120):606–608. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3120.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUCK J. C., BERMAN L. B. Serum ribonuclease activity. J Appl Physiol. 1958 May;12(3):473–476. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1958.12.3.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. F., Blainey J. D. Low molecular weight proteinuria in chronic renal disease. Clin Sci. 1967 Oct;33(2):381–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. F., Lunt G. S., Scott P., Blainey J. D. Urinary lysozyme, ribonuclease, and low-molecular-weight protein in renal disease. Lancet. 1968 Feb 24;1(7539):371–375. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. F., Northam B. E. Low molecular weight urine protein investigated by gel filtration. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Nov;14(5):679–688. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90195-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ J., SELLERS A. L., BONORRIS G. PLASMA ALBUMIN METABOLISM DURING TRANSIENT RENIN PROTEINURIA. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Nov;64:709–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFF E. L., POTTER M., MCINTIRE K. R., ROBERTS N. E. THE IN VITRO SYNTHESIS OF SPECIFIC SECRETORY PROTEIN BY AN ASCITES PLASMA-CELL TUMOR. Biochemistry. 1964 Nov;3:1707–1712. doi: 10.1021/bi00899a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LATHEM W., DAVIS B. B., ZWEIG P. H., DEW R. The demonstration and localization of renal tubular reabosorption of hemoglobin by stop flow analysis. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jun;39:840–845. doi: 10.1172/JCI104104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER F., PALADE G. E. LYTIC ACTIVITIES IN RENAL PROTEIN ABSORPTION DROPLETS. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPICAL CYTOCHEMICAL STUDY. J Cell Biol. 1964 Dec;23:519–552. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maunsbach A. B. Absorption of I-125-labeled homologous albumin by rat kidney proximal tubule cells. A study of microperfused single proximal tubules by electron microscopic autoradiography and histochemistry. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Jun;15(3):197–241. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER J., MACDOWELL M., LEE Y. C. Cellular mechanisms of protein metabolism in the nephron. I. The structural aspects of proteinuria; tubular absorption, droplet formation, and the disposal of proteins. J Exp Med. 1954 Jun 1;99(6):589–604. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.6.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piscator M. Proteinuria in chronic cadmium poisoning. 3. Electrophoretic and immunoelectrophoretic studies on urinary proteins from cadmium workers, with special reference to the excretion of low molecular weight proteins. Arch Environ Health. 1966 Mar;12(3):335–344. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1966.10664380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. E., Segal S. Maleic acid-induced inhibition of amino acid transport in rat kidney. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):345–352. doi: 10.1042/bj0920345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON A., WALDMANN T. A., FAHEY J. L., MCFARLANE A. S. METABOLISM OF BENCE JONES PROTEINS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jan;43:103–117. doi: 10.1172/JCI104884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORTHEN H. G. RENAL TOXICITY OF MALEIC ACID IN THE RAT: ENZYMATIC AND MORPHOLOGIC OBSERVATIONS. Lab Invest. 1963 Aug;12:791–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Strober W. Metabolism of immunoglobulins. Prog Allergy. 1969;13:1–110. doi: 10.1159/000385919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wochner R. D., Strober W., Waldmann T. A. The role of the kidney in the catabolism of Bence Jones proteins and immunoglobulin fragments. J Exp Med. 1967 Aug 1;126(2):207–221. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]