Abstract
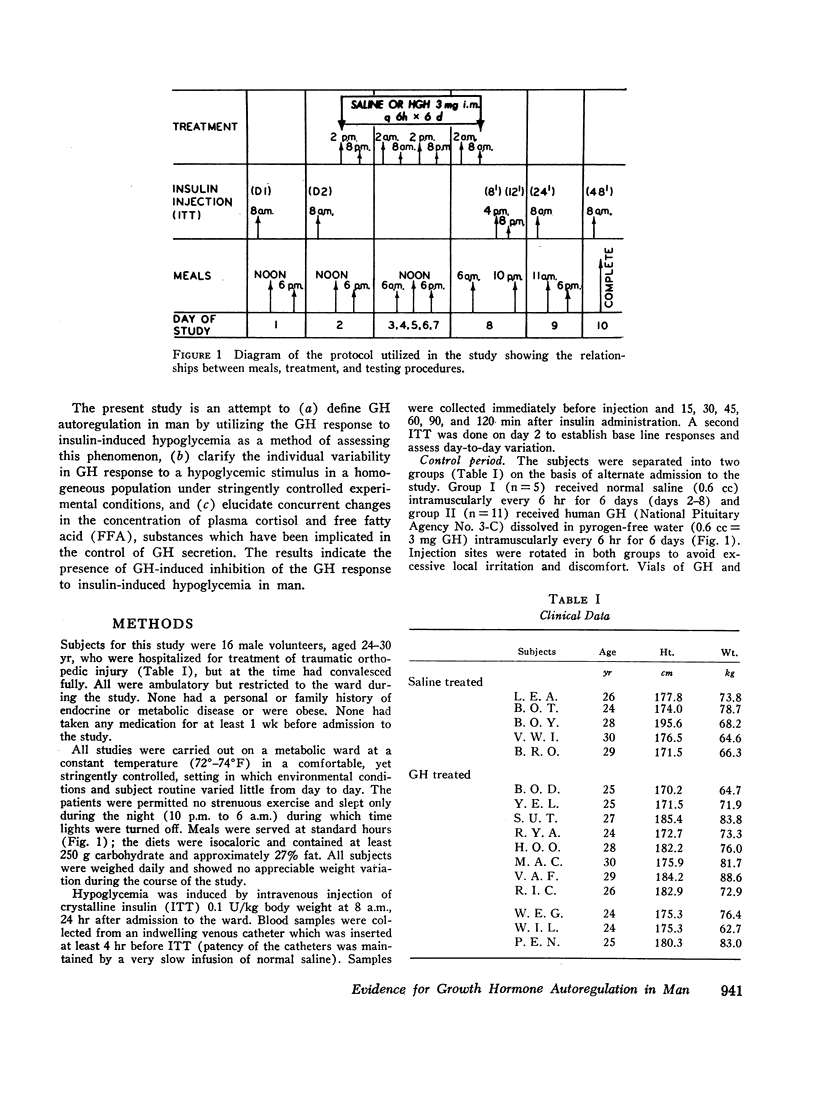
The effect of administration of human growth hormone (HGH) (3 mg every 6 hr for 6 days) on the endogenous GH response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia at 8, 12, 24, and 48 hr posttreatment was studied in 11 healthy male adults. Free fatty acid, cortisol, and glucose responses pre- and posttreatment with HGH were evaluated concurrently. Control subjects received saline injections to evaluate relationship of GH responses to the periodicity of insulin tolerance tests. The data were compared for each subject pre- and posttreatment with HGH as well as by comparison of the results of the saline-treated group with those of the HGH-treated group.
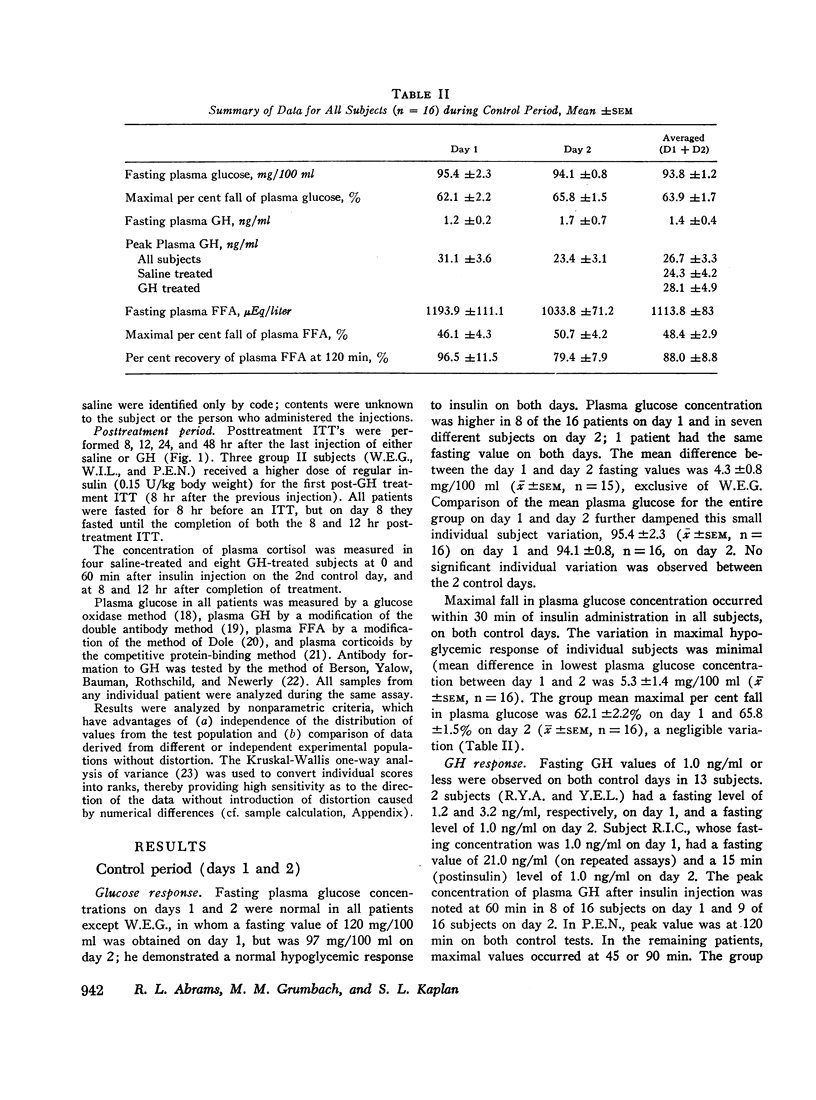
The mean maximal GH concentration in response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia for all the subjects (n = 16) was 31.1 ±3.6 ng/ml (±SEM) on day 1 of the control period and 23.4 ±3.1 (SEM) on day 2, not statistically significant.
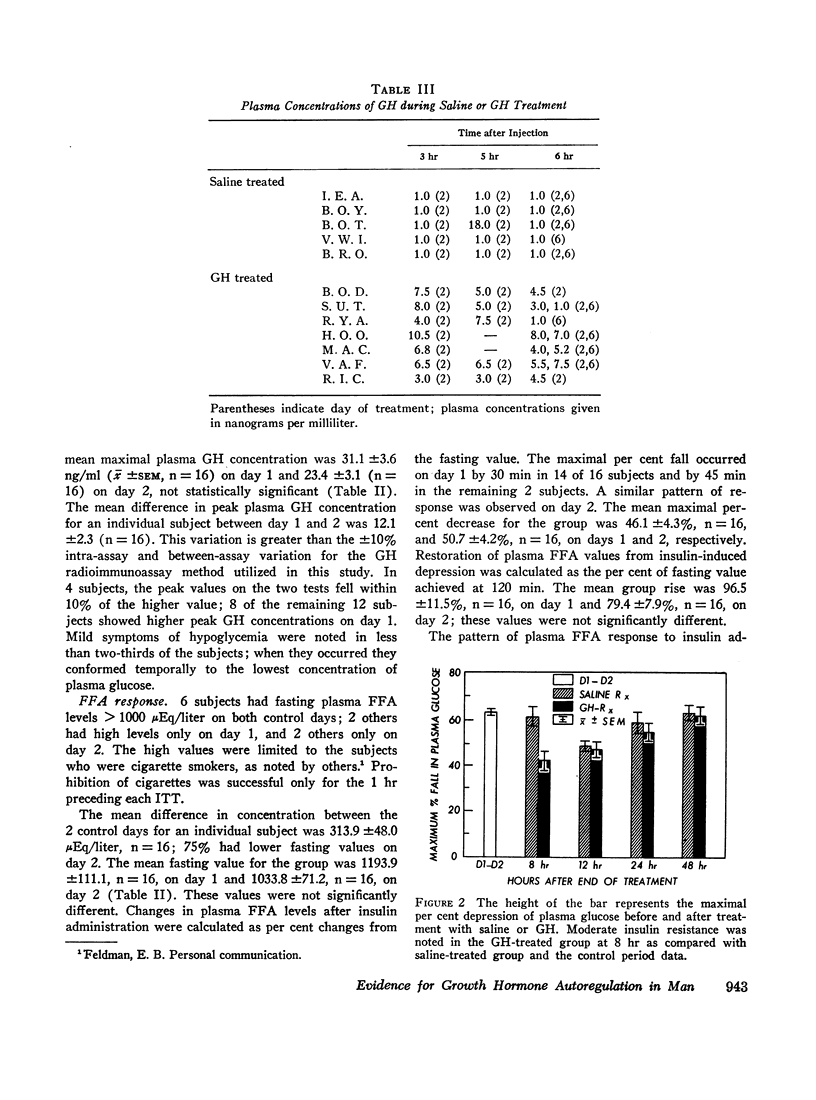
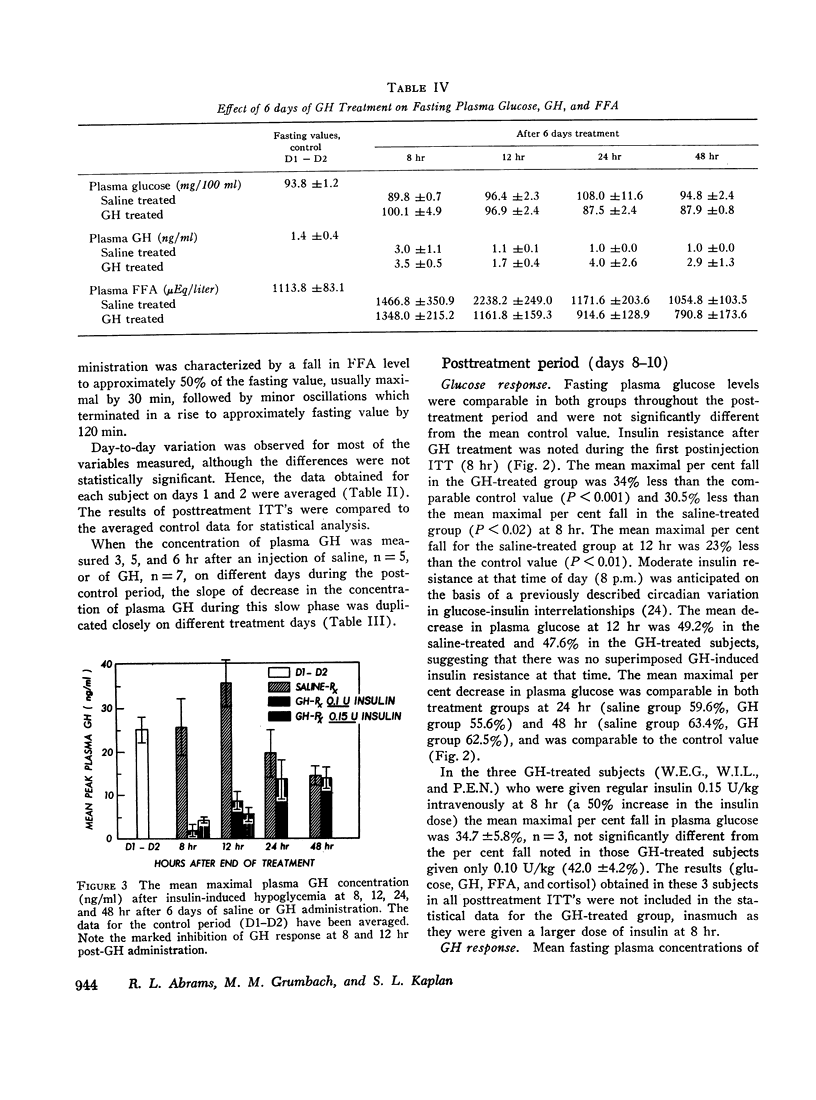
A significant decrease in the maximal peak GH response (n = 8) after insulin-induced hypoglycemia was observed at 8 and 12 hr after HGH administration was terminated with mean peak values for GH of 4.6 ±1.3 ng/ml and 10.4 ±1.9 ng/ml, respectively (P < 0.01). A progressive return to control values was noted between 12 and 24 hr. The GH responsiveness of the saline-treated group (n = 5) was unchanged from that observed during the control period.
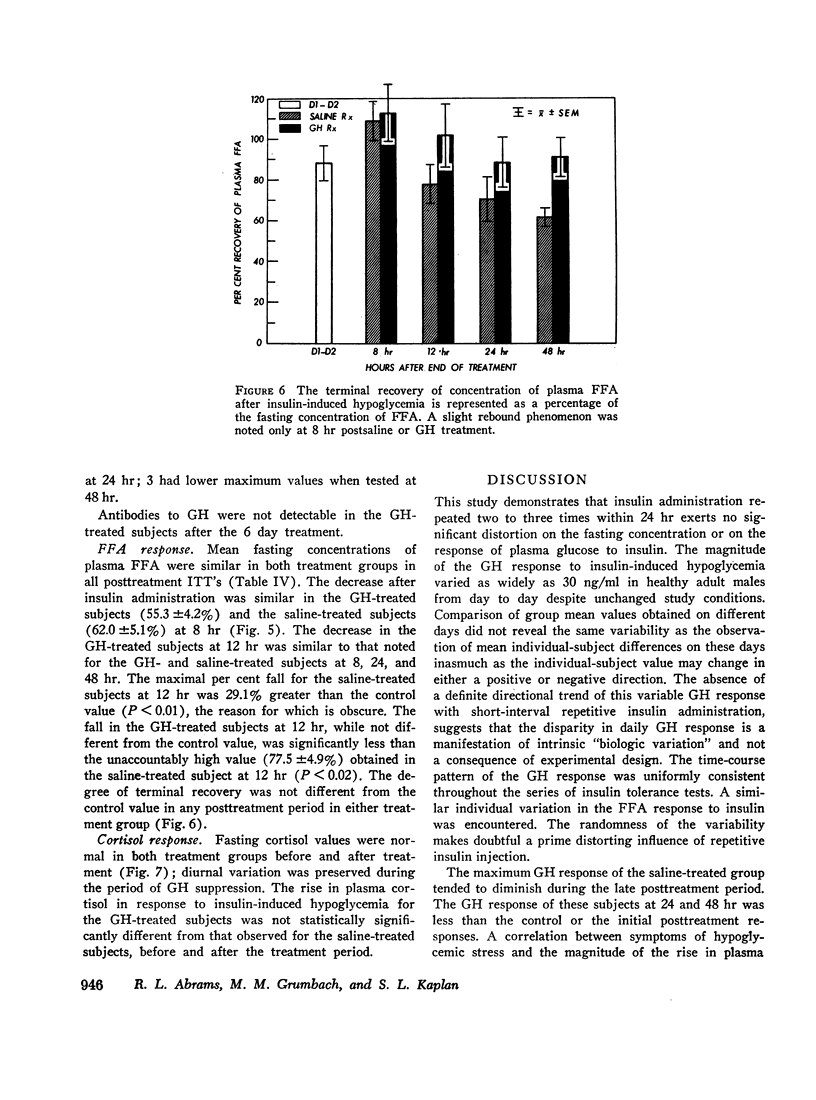
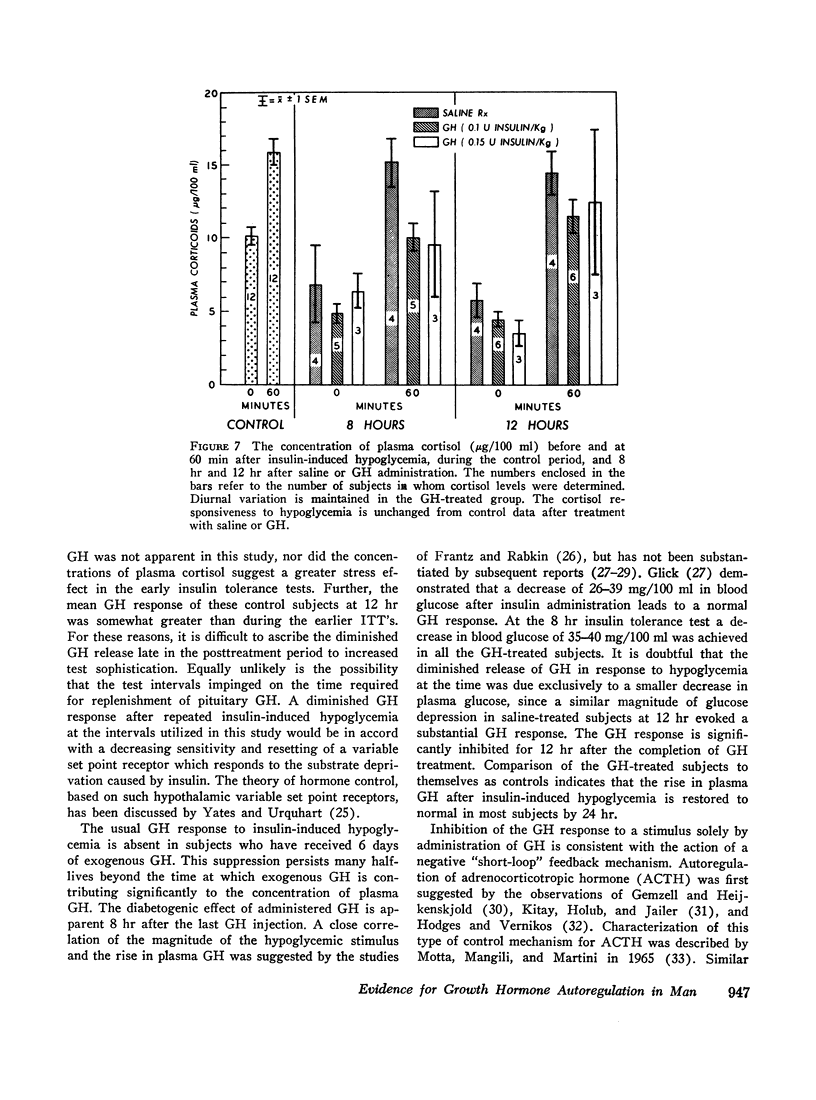
The fasting glucose values were unchanged in the GH-treated group from those of the control period or of the saline-treated controls. Insulin resistance was apparent at 8 hr posttreatment with HGH. No differences in FFA response after insulin-induced hypoglycemia were observed in GH-treated or saline-treated subjects. The rise in plasma cortisol after insulin-induced hypoglycemia was comparable in the GH-treated and saline-treated group. Diurnal variation in plasma cortisol was maintained during the period of GH suppression.
These observations support the concept that GH can modulate its secretion by means of an auto-feedback mechanism.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams R. L., Parker M. L., Blanco S., Reichlin S., Daughaday W. H. Hypothalamic regulation of growth hormone secretion. Endocrinology. 1966 Mar;78(3):605–613. doi: 10.1210/endo-78-3-605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antony G. J., Van Wyk J. J., French F. S., Weaver R. P., Dugger G. S., Timmons R. L., Newsome J. F. Influence of pituitary stalk section on growth hormone, insulin and TSH secretion in women with metastatc breast cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Sep;29(9):1238–1250. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-9-1238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATES R. W., MILKOVIC S., GARRISON M. M. Concentration of prolactin, growth hormone and ACTH in blood and tumor. of rats with transplantable mammotropic pituitary tumor. Endocrinology. 1962 Dec;71:943–948. doi: 10.1210/endo-71-6-943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S., BAUMAN A., ROTHSCHILD M. A., NEWERLY K. Insulin-I131 metabolism in human subjects: demonstration of insulin binding globulin in the circulation of insulin treated subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):170–190. doi: 10.1172/JCI103262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Heidingsfelder S. A. Effect of adrenergic receptor blackade on nicotinic acid-induced plasma FFA rebound. Metabolism. 1969 Mar;18(3):226–233. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin A. Pituitary and plasma LH of ovariectomized rats with median eminence implants of LH. Endocrinology. 1966 Apr;78(4):893–896. doi: 10.1210/endo-78-4-893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin A., Story J. C. "Internal" feedback mechanism: response of pituitary FSH and of stalk-median eminence follicle stimulating hormone-releasing factor to median eminence implants of FSH. Endocrinology. 1967 Jun;80(6):1006–1012. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-6-1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P. A relation between non-esterified fatty acids in plasma and the metabolism of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):150–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI103259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M. A., Fraschini F., Martini L. Control of LH secretion: role of a "short" feedback mechanism. Endocrinology. 1966 Jan;78(1):55–60. doi: 10.1210/endo-78-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANTZ A. G., RABKIN M. T. HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE. CLINICAL MEASUREMENT, RESPONSE TO HYPOGLYCEMIA AND SUPPRESSION BY CORTICOSTEROIDS. N Engl J Med. 1964 Dec 31;271:1375–1381. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196412312712701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraschini F., Motta M., Martini L. A 'short1 feedback mechanism controlling FSH secretion. Experientia. 1968 Mar 15;24(3):270–271. doi: 10.1007/BF02152814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEMZELL C. A., HEIJKENSKJOLD F. Effect of corticotrophin on the content of corticotrophin in the pituitary glands of adrenalectomized rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1957 Mar;24(3):249–254. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0240249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick S. M. Hypoglycemic threshold for human growth hormone release. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 May;30(5):619–623. doi: 10.1210/jcem-30-5-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumbach M. M., Kaplan S. L., Sciarra J. J., Burr I. M. Chorionic growth hormone-prolactin (CGP): secretion, disposition, biologic activity in man, and postulated function as the "growth hormone" of the 2d half of pregnancy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Feb 5;148(2):501–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb20372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGES J. R., VERNIKOS J. Influence of circulating adrenocorticortophin on the pituitary pituitary adrenocorticotrophic response to stress in the adrenalectomized rat. Nature. 1958 Sep 13;182(4637):725–725. doi: 10.1038/182725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITAY J. I., HOLUB D. A., JAILER J. W. Inhibition of pituitary ACTH release; an extra-adrenal action of exogenous ACTH. Endocrinology. 1959 Apr;64(4):475–482. doi: 10.1210/endo-64-4-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. L., Abrams C. A., Bell J. J., Conte F. A., Grumbach M. M. Growth and growth hormone. I. Changes in serum level of growth hormone following hypoglycemia in 134 children with growth retardation. Pediatr Res. 1968 Jan;2(1):43–63. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196801000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. L., Abrams C. A., Bell J. J., Conte F. A., Grumbach M. M. Growth and growth hormone. I. Changes in serum level of growth hormone following hypoglycemia in 134 children with growth retardation. Pediatr Res. 1968 Jan;2(1):43–63. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196801000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz H. P., Grumbach M. M., Kaplan S. L. Diminished growth hormone response to arginine in the puerperium. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Nov;29(11):1414–1419. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-11-1414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh C. S., Kohn J., Catt K. J., Burger H. G. Lack of relation between plasma-growth-hormone levels and small decrements in blood-sugar. Lancet. 1968 Jan 6;1(7532):13–14. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger D. T., Glick S., Silverberg A., Krieger H. P. A comparative study of endocrine tests in hypothalamic disease. Circadian periodicity of plasma 11-OHCS levels, plama 11-OHCS and growth hormone response to insulin hypoglycemia and metyrapone responsiveness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Nov;28(11):1589–1598. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-11-1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulich L., McCann S. M. Influence of growth hormone (GH) on content of GH in the pituitaries of normal rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Apr;121(4):1114–1117. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDON J., WYNN V., JAMES V. H. THE ADRENOCORTICAL RESPONSE TO INSULIN-INDUCED HYPOGLYCAEMIA. J Endocrinol. 1963 Nov;27:183–192. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0270183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landon J., Greenwood F. C., Stamp T. C., Wynn V. The plasma sugar, free fatty acid, cortisol, and growth hormone response to insulin, and the comparison of this procedure with other tests of pituitary and adrenal function. II. In patients with hypothalamic or pituitary dysfunction or anorexia nervosa. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):437–449. doi: 10.1172/JCI105358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Grumbach M. M., Kaplan S. L., Josimovich J. B., Friesen H., Catt K. J. Human chorionic somato-mammotropin (HCS), proposed terminology for designation of a placental hormone. Experientia. 1968 Dec 15;24(12):1288–1288. doi: 10.1007/BF02146676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod R. M., DeWitt G. W., Smith M. C. Suppression of pituitary gland hormone content by pituitary tumor hormones. Endocrinology. 1968 May;82(5):889–894. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-5-889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod R. M., Smith M. C., DeWitt G. W. Hormonal properties of transplanted pituitary tumors and their relation to the pituitary gland. Endocrinology. 1966 Dec;79(6):1149–1156. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-6-1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann S. M., Porter J. C. Hypothalamic pituitary stimulating and inhibiting hormones. Physiol Rev. 1969 Apr;49(2):240–284. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1969.49.2.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz D. H., Stock R., Finster J. L., Taylor A. L. The effect of normal and diabetic pregnancies on growth hormone responses to hypoglycemia. Metabolism. 1968 Jan;17(1):54–61. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(68)80007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motta M., Mangili G., Martini L. A "short" feedback loop in the control of ACTH secretion. Endocrinology. 1965 Aug;77(2):392–395. doi: 10.1210/endo-77-2-392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller E. E., Sawano S., Arimura A., Schally A. V. Mechanism of action of growth hormone in altering its own secretion rate: comparison with the action of dexamethasone. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 Nov;56(3):499–509. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0560499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. E. Some studies of the protein-binding of steroids and their application to the routine micro and ultramicro measurement of various steroids in body fluids by competitive protein-binding radioassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Jul;27(7):973–990. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-7-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller E., Pecile A. Influence of exogenous growth hormone on endogenous growth hormone release. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Aug-Sep;122(4):1289–1291. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peake G. T., Mariz I. K., Daughaday W. H. Radioimmunoassay of growth hormone in rats bearing somatotropin producing tumors. Endocrinology. 1968 Oct;83(4):714–720. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-4-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH J., GLICK S. M., YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Secretion of human growth hormone: physiologic and experimental modification. Metabolism. 1963 Jul;12:577–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAIFER A., GERSTENFELD S. The photometric microdetermination of blood glucose with glucose oxidase. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Mar;51(3):448–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma M., Knobil E. Inhibition of endogenous growth hormone secretion by exogenous growth hormone infusion in the rhesus monkey. Endocrinology. 1970 Apr;86(4):890–894. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-4-890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawano S., Arimura A., Bowers C. Y., Schally A. V. Effect of CNS-depressants, dexamethasone and growth hormone on the response to growth hormone-releasing factor. Endocrinology. 1967 Dec;81(6):1410–1412. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-6-1410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson J. E., Rabinowitz D., Merimee T. J., Friesen H. Response of plasma insulin and human growth hormone to arginine in pregnant and postpartum females. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1969 Feb 1;103(3):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(69)90488-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YATES F. E., URQUHART J. Control of plasma concentrations of adrenocortical hormones. Physiol Rev. 1962 Jul;42:359–433. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1962.42.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. S., Samaan N., Pearson O. H. Growth hormone levels in pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Sep;27(9):1341–1347. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-9-1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youlton R., Kaplan S. L., Grumbach M. M. Growth and growth hormone. IV. Limitations of the growth hormone response to insulin and arginine and of the immunoreactive insulin response to arginine in the assessment of growth hormone deficiency in children. Pediatrics. 1969 Jun;43(6):989–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


