Abstract
The ability to assign function to proteins has become a major bottleneck for comprehensively understanding cellular mechanisms at the molecular level. Here we discuss the extent to which structural domain classifications can help in deciphering the complex relationship between the functions of proteins and their sequences and structures. Structural classifications are particularly helpful in understanding the mosaic manner in which new proteins and functions emerge through evolution. This is partly because they provide reliable and concrete domain definitions and enable the detection of very remote structural similarities and homologies. It is also because structural data can illuminate more clearly the mechanisms by which the functions of homologues can be modified during evolution and a broader functional repertoire emerge.
Background
The fact that genes and proteins can be assigned to families and superfamilies is a feature that many computational approaches exploit to interpret the flood of data from genomics projects [1]. Even though, as discussed in this review, families sometimes display unexpected diversity in terms of structure, function and sequence, the recognition of family membership for uncharacterised genes and proteins is often a first step towards understanding their biological role.
With the growth of data in the PDB it became apparent that protein structure was more highly conserved than sequence throughout evolution, and a number of structural classifications emerged to capture evolutionary relationships. The most comprehensive of these classifications are CATH [2] and SCOP [3], in which domains are identified within protein three-dimensional structures and are classified in the same superfamily if there is evidence of evolutionary relationships between them. Superfamilies are further grouped together if their members share a similar structural fold.
Since it is known that domains frequently combine to give proteins with new functions [4], and because we ultimately hope to exploit domain families to predict functions and understand how they are modified by domain context, we consider to what extent current structural knowledge supports the notion of a domain based grammar for describing protein functions. Such a grammar rests on the idea of domain families as individual functional units, with their association in proteins giving rise to novel functions according to complex combinatorial rules.
Challenges in Classifying Domain Structures into Superfamilies
Before examining the value of structure classifications for predicting protein functions, we should first consider the challenges faced in building these classifications. Although SCOP and CATH capture information on fold similarities between domain structures, both resources focus primarily on the characterisation of superfamilies, which, as explained below, is much more useful than the fold level for function inference [5]. However, the grouping of domain superfamilies into fold groups can be helpful as this structural similarity may suggest a very remote homology and the determination of further structures or sequences may provide additional clues to merge these superfamilies [11]. Although both classifications have adopted hierarchical schema with levels above the superfamily such as architecture and fold, these are largely aimed at organising the data and are not as rigorously defined as the superfamily level. For example, the subjective nature of fold identification results in much greater differences between CATH and SCOP at the fold level than at the superfamily level [6].
To address this issue, several authors have advocated fold classification schemes based on strict quantitative measures [7,8], on complex evolutionary models [9], or on the identification of folds that are defined similarly in several different classifications (i.e. meta-folds) [10]. However, fold subjectivity is barely an issue in terms of the usefulness of structural domain classifications for function prediction. Indeed, as mentioned already, existing structural domain classifications tend to consider the fold merely as a practical way to organise the superfamily data and group together putative homologies. Furthermore, the majority of folds (83%) comprise only one superfamily and folds with several superfamilies are often dominated by a very large one, with many very small superfamilies that could be homologues of the dominant superfamily [Cuff et al. submitted].
Thus, for function analysis and prediction, the superfamily is the primary unit of classification. Because structure is generally more conserved than sequence during evolution, structural data is often more appropriate to identify remote homologies [11]. However, in some superfamilies, there is increasing evidence that domains can undergo significant structural changes during evolution [6,9,12–14]. Such situations can occur via a number of different evolutionary mechanisms that include circular permutations [9], segment-swapping [14], addition of major structural embellishments to a conserved structural core [12], or more dramatic fold changes [13]. Furthermore, recent studies by Murzin and colleagues have also shown that a given protein can display very different structures in different situations [14,15], and that domains that seem unrelated as a whole may contain evolutionarily-conserved subparts [16,17] such as their active sites [18]. Many of these extremely structurally diverse relatives have only been identified because of the increase in sensitivity of profile-profile and HMM-HMM based strategies [19] that can detect the rare sequence signals which remain despite the large structural changes.
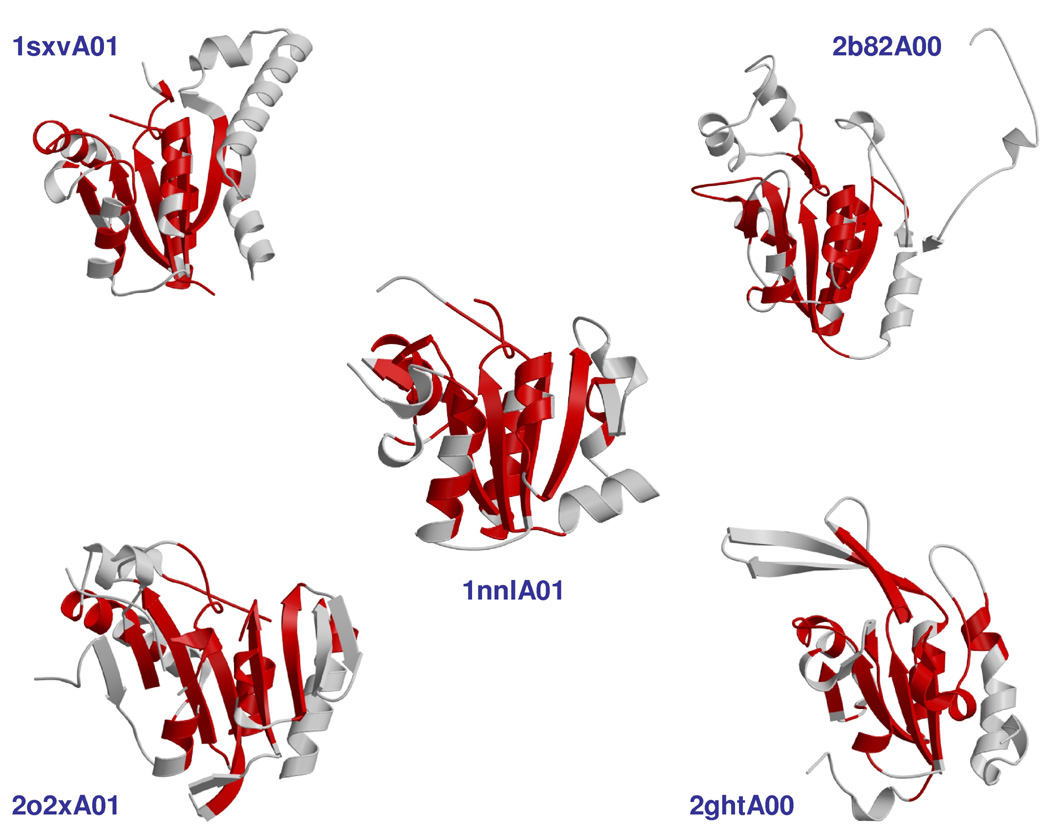
Recent research in our group shows that whilst there can be extensive structural diversity between homologues in CATH [12,20], with relatives varying up to 3-fold in size in some superfamilies [12], closer observation reveals that this structural diversity, including the global fold change that sometimes occurs, is generally due to extensive structural embellishments to a conserved ‘topological core’ rather than to dramatic changes in the core itself (see Figure 1) [Cuff et al. submitted]. Less than 100 superfamilies (<4% of CATH) exhibit substantial structural variation, though these superfamilies account for ~60% of non-redundant structures and 40% of predicted structures in the genomes.
Figure 1.
Structural embellishments to the core among members of the mechanistically diverse haloacid dehalogenase superfamily. Elements of secondary structure coloured in red represent the common structural core of the superfamily, whereas those coloured in grey represent embellishments. These enzymes catalyse different reactions although these reactions all share a common mechanistic attribute. Domain 1sxvA01 is part of M tuberculosis Pyrophosphate phospho-hydrolase, 2b82A00 is from E coli Class B acid phosphatase, 1nnlA01 is from Human Phosphoserine phosphatase, 2o2xA01 is from a Mesorhizobium loti putative phosphatase and 2ghtA00 is from Human Ctd phosphatase.
For both the SCOP and CATH classifications, homology takes precedence over fold similarities, so neither classification is strictly hierarchical anymore, since in some families a small percentage of homologues may have different folds and even occasionally architectures. However, it is important to remember that 1753 (84%) CATH domain families can be accommodated in a hierarchical classification whereby all homologues share a similar fold in the sense that they can be superposed with a normalized RMSD < 5Å [Cuff et al. submitted].
Fold and Function
Even though functional inference is generally made on the basis of evolutionary relationships, fold recognition can sometimes assist function prediction [21]. Some folds shared by proteins with different functions still maintain common functional characteristics. For example, the TIM-like (β/α)8 barrels or Rossmann folds, are characterised by super-sites, i.e. functional sites that often locate in similar regions of the three-dimensional structure [22]. These super-sites may hint at remote homologies but whatever the cause of the similarity, fold recognition can help in identifying residues that are likely to be functionally important.
Superfamily and Function
Duplication of a gene can give rise to homologous copies that may diverge in function [23,24]. By classifying remote evolutionary relationships, a major benefit of structural domain classifications is their capacity to reveal the structural variations that emerge during evolution and modify protein functions [25–27]. Analyses of superfamilies provide structural characterisation of conserved and variable features (see Figures 1 and 2) and comparative superfamily analyses can help rationalise the tendency for some to diverge further in structure and function than others. For example, superfamilies adopting layered domain architectures such as αβα, αβ and β-sandwiches appear more able to accommodate structural embellishments to the domain core. Such embellishments can modify active sites and domain or protein partnerships [12]. Yet, other factors such as functional properties that not directly related to structure may also affect the evolutionary expansion of superfamilies [28].
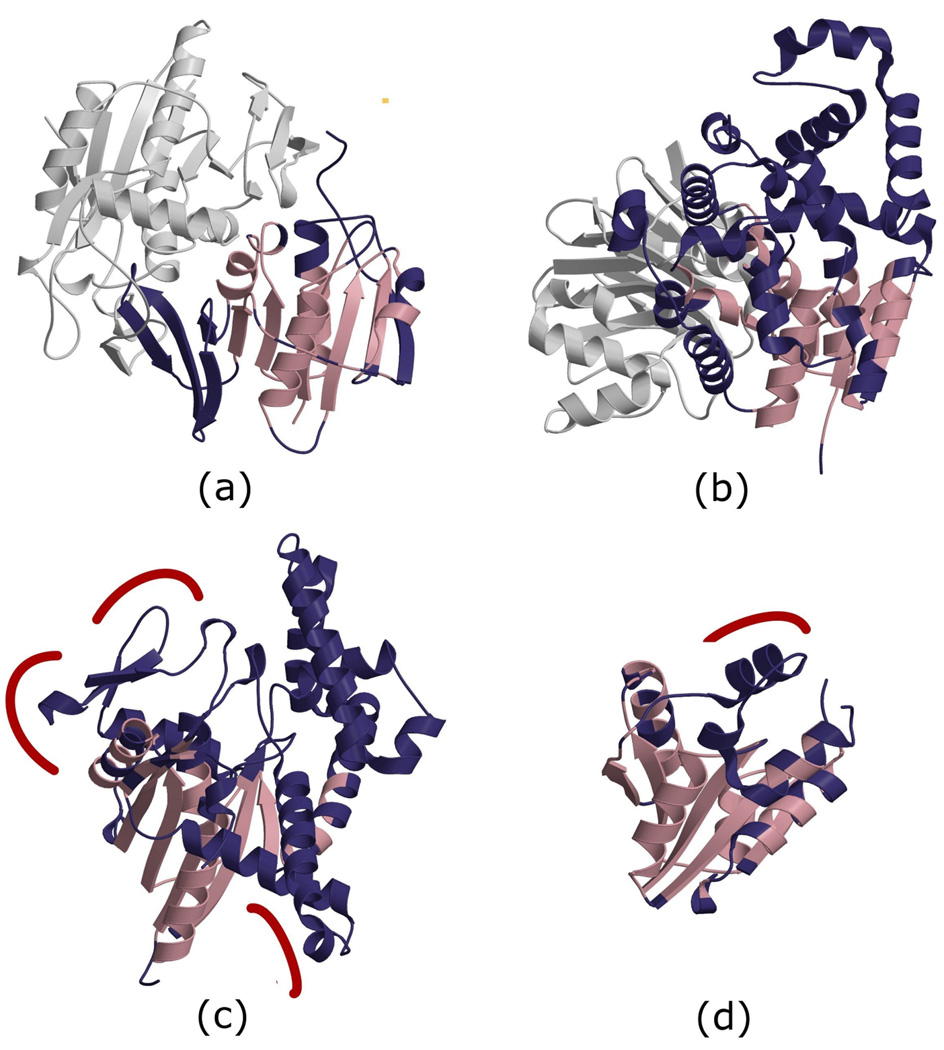
Figure 2.
Structural changes between homologous domains from the HUP superfamily mediate changes in molecular function, which in turn can affect the biological processes in which the proteins are involved. HUP domains are shown in colours; structural elements that are common to all HUP domains on the figure are coloured pink, and structural embellishments are coloured dark blue. (a) Electron Transfer Flavoprotein β (CATH domain 1o97D01); (b) Asparagine Synthetase B (1ct9B02); (c) Arginyl-tRNA synthetase (1f7uA01); (d) Phosphopantetheine Adenylyltransferase (1od6A00). The grey structure in sub-figure (a) represents the Electron transfer flavoprotein subunit α with which Electron Transfer Flavoprotein β interacts. The grey domain in (b) represents an extra domain of Asparagine Synthetase B. Red curves in (c) represent the binding sites for a tRNA ligand, whereas the red curve in (d) represent an interaction site with other subunits of the homo-hexamer.
Most structural domain superfamilies (>70% of superfamilies in CATH) are rather homogeneous functionally [27], and recognizing membership of a new domain to such superfamilies generally allows inheritance of the function of the other superfamily members [29,30]. For very remote homologues in these superfamilies, function can often be assigned using reliable structure comparison methods (e.g. CE [31], DALI [32], CATHEDRAL [33], FatCat [34]; see also [1,25] for reviews).
However, a relatively small number of domain superfamilies (less than 100 in CATH, i.e. <4%) are very diverse in terms of sequence, structure and function, and these superfamilies appear to account for disproportionate fractions of domain sequences. Indeed, 40% of domain sequences predicted to belong to CATH superfamilies are members of these large and diverse superfamilies [11,26,35], and characterisation of their functional diversity is a very active field of research [36–40]. Apart from directly modifying functional sites, structural changes can promote diverse domain and protein partnerships (see Figure 2) which enable homologues to participate in different biological pathways and functional networks [41].
Helpful illustrations of functional diversification mediated by structural changes between homologous domains can be found in the HUP domain superfamily [42], which we are currently studying in our group. HUP domains belong to an ancient superfamily, and are found in proteins involved in a wide variety of different functions. They share a common Rossmann-like core, with a central parallel β-sheet surrounded on both sides by α-helices. In addition to small-scale structural changes in their active sites, which allow different HUP domains to bind very different types of ligands, larger changes encompassing several elements of secondary structure, i.e. structural embellishments, are likely to have provided HUP domains with raw material for functional changes (see Figure 2). For example, the 3 extra anti-parallel β-strands found at the periphery of the central β-sheet in Electron Transfer Flavoproteins (Figure 2a) allow these domains to bind another protein to form a complex that is essential for their function. The large, mainly α-helical extension of the central β-sheet in Asparagine Synthetase B (Figure 2b) largely participates in contacts with an extra protein domain that is responsible for binding one of the substrates of that enzyme. Loops that are part of a major embellishment in Arginyl-tRNA synthetase (Figure 2c) participate in the binding of the tRNA ligand. And finally, Pantetheine-phosphate Adenylyltransferase is a homo-hexamer where each subunit consists of a single HUP domain, in which structural embellishments map to the inter-subunit interfaces (Figure 2d). These examples show that in a single superfamily, different structural embellishments of the common core, participate in binding specific ligands, other domains in the same protein, other identical subunits in a homo-multimer, or other proteins in a complex. In turn, these different molecular partners are generally crucial for mediating various changes in function.
Despite the functional diversity observed in such large and diverse superfamilies, particular functional features are often conserved. Thus, mechanistically diverse enzyme superfamilies comprise relatives that share a common mechanistic attribute in the different reactions they catalyse [43]. For instance, haloacid deholagenases catalyse a wide variety of reactions that all involve the formation of a covalent enzyme-substrate intermediate through a conserved aspartate, that in turn facilitates cleavage of C-Cl, P-C or P-O bonds [43] (see also Figure 1). Mechanistically diverse superfamilies are catalogued by Babbitt and colleagues in the Structure-Function Linkage Database [44] and have been the subject of increased attention in recent years [43,45–47], notably via a specific structural genomics initiative [48]. Several scenarios have been suggested to explain the evolution of such superfamilies; for instance, large scale studies of enzyme superfamilies have shown that homologues are frequently recruited to different pathways where perhaps they bring a chemical activity characteristic of their superfamily [27,49]. Other large, diverse, superfamilies display conservation of parts of their ligands [37], possibly as the result of metabolic pathway retrograde evolution where the duplicated copy of an enzyme is recruited to catalyse the previous reaction in the same metabolic pathway [27,50]. A well-known possible example of such an evolutionary process may be found in enzymes of the tryptophan biosynthesis pathway [49].
If we aim to achieve a domain grammar for protein function, the large diverse superfamilies are clearly more problematic for function assignment. However, there have been encouraging developments in sequence [51–54] and/or structure based methods [55–57] for characterising functional sub-groups within these superfamilies. The SCI-PHY method from the Sjölander group appears particularly promising for recognising distinct sequence patterns between functional subfamilies. When sufficient structural data is available the FLORA method, adopted for CATH, is able to capture structural characteristics that are highly distinctive for a set of functionally related homologues [Redfern et al. submitted] (see Figure 3). Pair-wise and template based structure-function methods can also be applied across a superfamily to locate conserved features (for reviews see [25,58]) and the Profunc [59], ProKnow [60] and JAFA [61] servers combine multiple approaches to predict functional annotations.
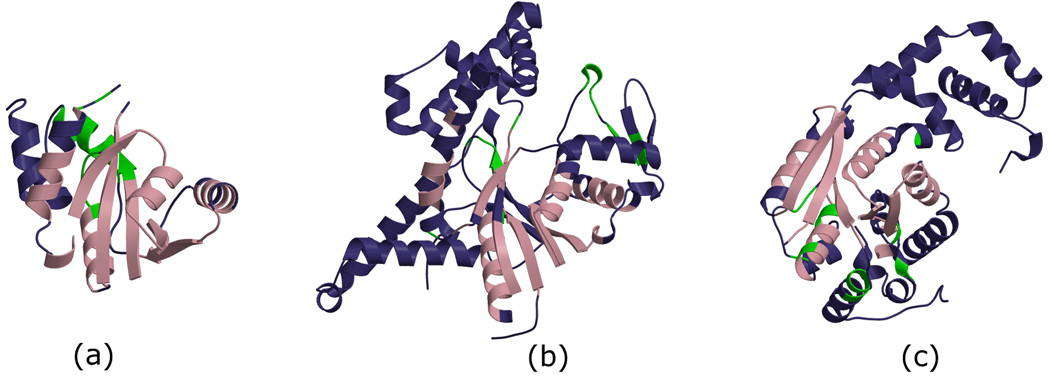
Figure 3.
Residue positions identified by our in-house method FLORA in domains from different functional sub-groups within the HUP superfamily. FLORA analyses structural alignments of domains within superfamilies to identify residues that are specific to a set of protein domains having the same function [Redfern et al. submitted]. HUP superfamily domains vary a lot in terms of function and structure. We have identified several functional sub-groups that correspond to different broad categories of molecular functions in this superfamily. Representatives from three of them are displayed here: (a) phosphopantetheine adenyltransferase (CATH domain ID 1od6A00 EC 2.7.7.3) belongs to the sub-group of nucleotidyltransferases, (b) arginyl-tRNA synthetase (CATH domain ID 1f7uA01, EC 6.1.1.19) belongs to the sub-group of class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, and (c) asparagine synthetase B (CATH domain ID 1ct9B02, EC 6.3.5.4) belongs to the sub-group of N-type ATP pyrophosphatases. The three structures are shown in a similar orientation. Residues that belong to the common core of the whole superfamily are coloured pink, residues that are part of embellishments of each particular domain are coloured dark blue, and residues identified by FLORA as being specific to all domains in a functional sub-group are coloured green. All three domains have FLORA positions detected in the typical Rossmann fold active site located at the C-terminal half of the central β-sheet; these are most likely detected by FLORA due to slight but significant variations in the local structure of this main active site. In 1od6A00, another FLORA motif is identified in a region involved in inter-subunit contacts, whereas an extra FLORA motif in 1f7uA01 maps to sub-group specific tRNA-binding loops.
Domain Combinations and Function
Domains frequently combine to give multi-domain proteins with diverse functions (see Figure 4) [4,62] and structural classifications can enable the description of more accurate multi-domain architectures by providing domain boundaries that are often more reliable than those based purely on sequence information (as in Pfam [63] and ProDom [64], for example). The potential leverage of domain definitions from structural domain resources has increased greatly due to the development of protocols and associated resources (Gene3D [29], SUPERFAMILY [30]) that predict structural domain annotations in genome sequences [29].
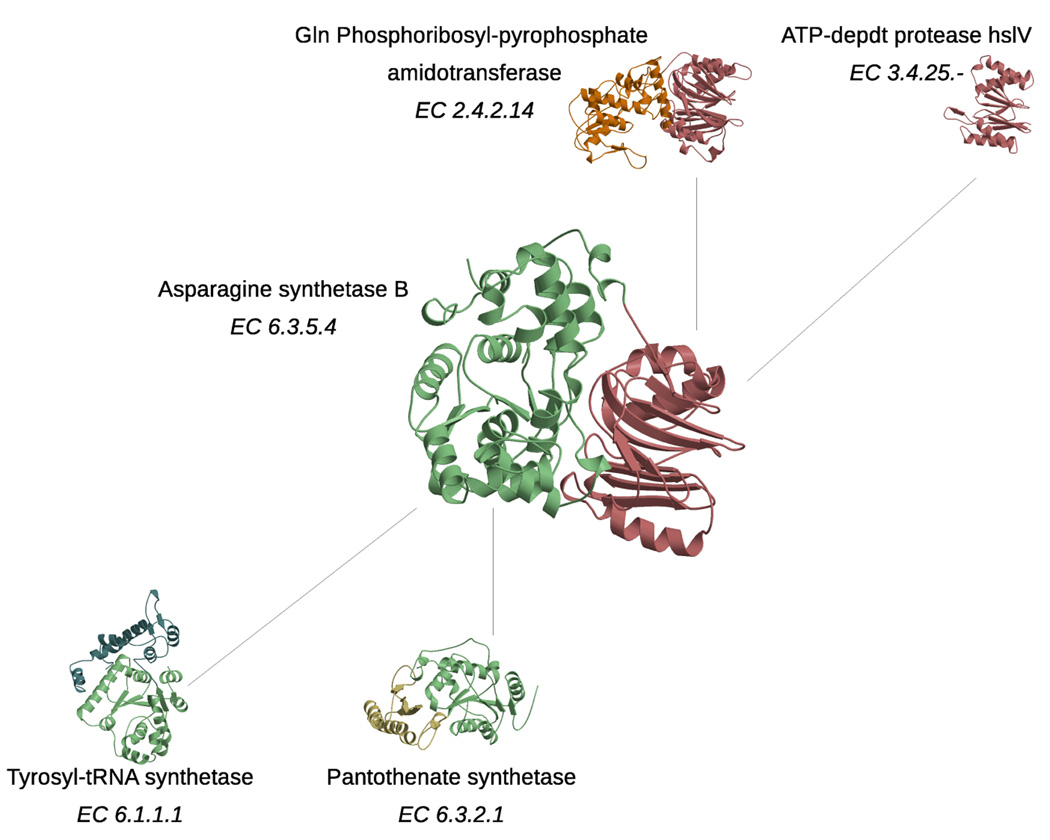
Figure 4.
Function diversity in domain superfamilies, and generation of new functions via domain combinations. The central protein contains two domains from CATH superfamily 3.40.50.620 (coloured green) and 3.60.20.10 (coloured pink), and functions as an asparagine synthetase. Each of these domain superfamilies contain other domains that are part of proteins with very different functions, as illustrated by their EC numbers (top and bottom of figure for 3.60.20.10 and 3.40.50.620 domains, respectively).
Many of the largest most structurally diverse superfamilies mentioned previously are also highly promiscuous or versatile, combining with many other domains [41], and recent work has focussed on better characterising the functional properties of this domain promiscuity [65,66]. In addition, some domain families with particular molecular functions that can be ascribed to specific structural features, may make them more amenable to combine with other domains to form proteins with novel functions. For example, domain families with a Rossmann-like topology can usually accommodate nucleotides in a cleft formed by the C-termini of the strands in the central β-sheet. The inherent structural ability to bind nucleotides may drive domains with Rossmann folds to combine with different domain types performing functions that require nucleotide hydrolysis. In this line of thought, a recent survey of function evolution upon changes in domain context by Bashton and Chothia, showed that a number of domain types conserved a specific function that they were able to carry out in different domain contexts [4].
The conservation of function in the majority (>70%) of superfamilies and the ability to locate conserved features or distinguish functional subtypes in the diverse superfamilies has prompted efforts to provide domain-centric function annotation schemes [67,68], where the function of a full-length protein can be inferred from the combination of molecular functions contributed by the individual domains [4]. The fact that structural domain classifications provide much fewer domain types with more general functional characteristics could make them more appropriate and flexible in this complex combinatorial process.
Conclusion
Comprehensive structural domain classifications were set-up more than fifteen years ago, with the aim of exploiting structural data to recognise evolutionary superfamilies. Despite the challenges involved in this, particularly the fact that homologous domains can undergo major structural changes during evolution, analysis of domain structure superfamilies has enabled major advances in our understanding of the evolution of protein function. First, these resources allow the systematic identification of very remote evolutionary relationships, which can in turn shed light on sequence and structure changes that bring about functional variation across a superfamily. Secondly, increasing body of evidence suggests that domains are a useful level of protein organisation for analysing and predicting protein function. Taken together, and with the expected expansions in structural data from the structural genomics projects, combined with the increased ability to predict structural domains in genomic sequences, structural family resources should contribute significantly to our attempts to move towards a domain grammar of protein function.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Protein Structure Initiative (PSI) of the National Institute for General Medicine at the National Institutes of Health, and by the European Union Framework Program 7 Impact grant.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Lee D, Redfern O, Orengo C. Predicting protein function from sequence and structure. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:995–1005. doi: 10.1038/nrm2281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Greene LH, Lewis TE, Addou S, Cuff A, Dallman T, Dibley M, Redfern O, Pearl F, Nambudiry R, Reid A, Sillitoe I, Yeats C, Thornton JM, Orengo CA. The CATH domain structure database: new protocols and classification levels give a more comprehensive resource for exploring evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:D291–D297. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Andreeva A, Howorth D, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE, Hubbard TJ, Chothia C, Murzin AG. Data growth and its impact on the SCOP database: new developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:D419–D425. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Bashton M, Chothia C. The generation of new protein functions by the combination of domains. Structure. 2007;15:85–99. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2006.11.009. ** This paper provides a very complete and well-structured analysis of mechanisms by which acquisition of new domains and recombination of domains allow proteins to adopt novel functions.
- 5.Martin AC, Orengo CA, Hutchinson EG, Jones S, Karmirantzou M, Laskowski RA, Mitchell JB, Taroni C, Thornton JM. Protein folds and functions. Structure. 1998;6:875–884. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(98)00089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kolodny R, Petrey D, Honig B. Protein structure comparison: implications for the nature of 'fold space', and structure and function prediction. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006;16:393–398. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sippl MJ, Suhrer SJ, Gruber M, Wiederstein M. A discrete view on fold space. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:870–871. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sippl MJ. On distance and similarity in fold space. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:872–873. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Taylor WR. Evolutionary transitions in protein fold space. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2007;17:354–361. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2007.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Alva V, Koretke KK, Coles M, Lupas AN. Cradle-loop barrels and the concept of metafolds in protein classification by natural descent. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008;18:358–365. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Orengo CA, Jones DT, Thornton JM. Protein superfamilies and domain superfolds. Nature. 1994;372:631–634. doi: 10.1038/372631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Reeves GA, Dallman TJ, Redfern OC, Akpor A, Orengo CA. Structural diversity of domain superfamilies in the CATH database. J Mol Biol. 2006;360:725–741. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.05.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Grishin NV. Fold change in evolution of protein structures. Journal of Structural Biology. 2001;134:167–185. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.2001.4335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Andreeva A, Murzin AG. Evolution of protein fold in the presence of functional constraints. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006;16:399–408. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Murzin AG. Biochemistry. Metamorphic proteins. Science. 2008;320:1725–1726. doi: 10.1126/science.1158868. * Interesting and well-documented short article exploring the notion of metamorphic proteins, i.e. proteins whose structure changes during their lifetime.
- 16.Manikandan K, Pal D, Ramakumar S, Brener NE, Iyengar SS, Seetharaman G. Functionally important segments in proteins dissected using Gene Ontology and geometric clustering of peptide fragments. Genome Biol. 2008;9:R52. doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-3-r52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Soding J, Lupas AN. More than the sum of their parts: on the evolution of proteins from peptides. Bioessays. 2003;25:837–846. doi: 10.1002/bies.10321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Xie L, Bourne PE. Detecting evolutionary relationships across existing fold space, using sequence order-independent profile-profile alignments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:5441–5446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704422105. *This paper presents a novel method for predicting similarity in ligand binding sites. The authors compare their method to other published approaches and demonstrate its superiority for predicting the binding of adenine-containing compounds. Their results also suggest that these binding sites have arisen from divergent rather than convergent evolution, as similarities are found across different SCOP superfamilies.
- 19.Reid AJ, Yeats C, Orengo CA. Methods of remote homology detection can be combined to increase coverage by 10% in the midnight zone. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:2353–2360. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Harrison A, Pearl F, Mott R, Thornton J, Orengo C. Quantifying the similarities within fold space. J Mol Biol. 2002;323:909–926. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00992-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Moult J, Melamud E. From fold to function. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2000;10:384–389. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(00)00101-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Russell RB, Sasieni PD, Sternberg MJ. Supersites within superfolds. Binding site similarity in the absence of homology. J Mol Biol. 1998;282:903–918. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhang J. Evolution by gene duplication: an update. Trends in Ecology and Evolution. 2003;18:292–298. [Google Scholar]
- 24. Conant GC, Wolfe KH. Turning a hobby into a job: how duplicated genes find new functions. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:938–950. doi: 10.1038/nrg2482. * An exhaustive review that provides an update on the mechanisms by which the function of proteins changes after duplication.
- 25.Redfern OC, Dessailly B, Orengo CA. Exploring the structure and function paradigm. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008;18:394–402. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dessailly BH, Orengo CA. Function diversity within folds and superfamilies. In: Rigden DJ, editor. From Protein Structure to Function with Bioinformatics. Springer; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Todd AE, Orengo CA, Thornton JM. Evolution of function in protein superfamilies, from a structural perspective. J Mol Biol. 2001;307:1113–1143. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shakhnovich BE, Koonin EV. Origins and impact of constraints in evolution of gene families. Genome Res. 2006;16:1529–1536. doi: 10.1101/gr.5346206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yeats C, Lees J, Reid A, Kellam P, Martin N, Liu X, Orengo C. Gene3D: comprehensive structural and functional annotation of genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:D414–D418. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wilson D, Madera M, Vogel C, Chothia C, Gough J. The SUPERFAMILY database in 2007: families and functions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:D308–D313. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE. Protein structure alignment by incremental combinatorial extension (CE) of the optimal path. Protein Eng. 1998;11:739–747. doi: 10.1093/protein/11.9.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Holm L, Sander C. Protein structure comparison by alignment of distance matrices. J Mol Biol. 1993;233:123–138. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Redfern OC, Harrison A, Dallman T, Pearl FM, Orengo CA. CATHEDRAL: a fast and effective algorithm to predict folds and domain boundaries from multidomain protein structures. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007;3:e232. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ye Y, Godzik A. Flexible structure alignment by chaining aligned fragment pairs allowing twists. Bioinformatics. 2003;19 Suppl 2:ii246–ii255. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Goldstein RA. The structure of protein evolution and the evolution of protein structure. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008;18:170–177. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.01.006. ** In this review, the author systematically explores the different hypotheses that attempt to explain why some superfamilies and folds have expanded and diverged much more than others during the course of evolution.
- 36.lali-Hassani A, Pan PW, Dombrovski L, Najmanovich R, Tempel W, Dong A, Loppnau P, Martin F, Thornton J, Edwards AM, Bochkarev A, Plotnikov AN, Vedadi M, Arrowsmith CH. Structural and chemical profiling of the human cytosolic sulfotransferases. PLoS Biol. 2007;5:e97. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Chiang RA, Sali A, Babbitt PC. Evolutionarily conserved substrate substructures for automated annotation of enzyme superfamilies. PLoS Comput Biol. 2008;4:e1000142. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000142. ** This paper presents an automated method for annotating members of different superfamilies with likely substrates. The authors' analysis looks at the sub-structures of the substrates that are conserved among different relatives. It highlights the fact that different superfamilies often need to be treated individually to predict aspects of their function using structural data.
- 38.Favia AD, Nobeli I, Glaser F, Thornton JM. Molecular docking for substrate identification: the short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases. J Mol Biol. 2008;375:855–874. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.10.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Shah PK, Tripathi LP, Jensen LJ, Gahnim M, Mason C, Furlong EE, Rodrigues V, White KP, Bork P, Sowdhamini R. Enhanced function annotations for Drosophila serine proteases: a case study for systematic annotation of multi-member gene families. Gene. 2008;407:199–215. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2007.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ojha S, Meng EC, Babbitt PC. Evolution of Function in the "Two Dinucleotide Binding Domains" Flavoproteins. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007;3:e121. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bornberg-Bauer E, Beaussart F, Kummerfeld SK, Teichmann SA, Weiner J., III The evolution of domain arrangements in proteins and interaction networks. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005;62:435–445. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4416-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Aravind L, Anantharaman V, Koonin EV. Monophyly of class I aminoacyl tRNA synthetase, USPA, ETFP, photolyase, and PP-ATPase nucleotide-binding domains: implications for protein evolution in the RNA. Proteins. 2002;48:1–14. doi: 10.1002/prot.10064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Glasner ME, Gerlt JA, Babbitt PC. Evolution of enzyme superfamilies. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2006;10:492–497. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pegg SC, Brown SD, Ojha S, Seffernick J, Meng EC, Morris JH, Chang PJ, Huang CC, Ferrin TE, Babbitt PC. Leveraging enzyme structure-function relationships for functional inference and experimental design: the structure-function linkage database. Biochemistry. 2006;45:2545–2555. doi: 10.1021/bi052101l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Hermann JC, Marti-Arbona R, Fedorov AA, Fedorov E, Almo SC, Shoichet BK, Raushel FM. Structure-based activity prediction for an enzyme of unknown function. Nature. 2007;448:775–779. doi: 10.1038/nature05981. * This paper describes the successful prediction of the activity of an enzyme that belongs to the very large and diverse amidohydrolase superfamily, by docking it against a list of high-energy intermediate forms of candidate metabolites. The list of these candidate metabolites is derived from a list of compounds appearing in reactions catalysed by other members of the superfamily.
- 46.Song L, Kalyanaraman C, Fedorov AA, Fedorov EV, Glasner ME, Brown S, Imker HJ, Babbitt PC, Almo SC, Jacobson MP, Gerlt JA. Prediction and assignment of function for a divergent N-succinyl amino acid racemase. Nat Chem Biol. 2007;3:486–491. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2007.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Nguyen TT, Brown S, Fedorov AA, Fedorov EV, Babbitt PC, Almo SC, Raushel FM. At the periphery of the amidohydrolase superfamily: Bh0493 from Bacillus halodurans catalyzes the isomerization of D-galacturonate to D-tagaturonate. Biochemistry. 2008;47:1194–1206. doi: 10.1021/bi7017738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gerlt JA. A Protein Structure (or Function ?) Initiative. Structure. 2007;15:1353–1356. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2007.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gerlt JA, Babbitt PC. Divergent evolution of enzymatic function: mechanistically diverse superfamilies and functionally distinct suprafamilies. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:209–246. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.70.1.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rison SC, Thornton JM. Pathway evolution, structurally speaking. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2002;12:374–382. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(02)00331-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Brown DP, Krishnamurthy N, Sjolander K. Automated protein subfamily identification and classification. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007;3:e160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Reva B, Antipin Y, Sander C. Determinants of protein function revealed by combinatorial entropy optimization. Genome Biol. 2007;8:R232. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-11-r232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Capra JA, Singh M. Characterization and prediction of residues determining protein functional specificity. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:1473–1480. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ye K, Anton FK, Heringa J, Ijzerman AP, Marchiori E. Multi-RELIEF: a method to recognize specificity determining residues from multiple sequence alignments using a Machine-Learning approach for feature weighting. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:18–25. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Shakhnovich BE, Dokholyan NV, DeLisi C, Shakhnovich EI. Functional fingerprints of folds: evidence for correlated structure-function evolution. J Mol Biol. 2003;326:1–9. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bandyopadhyay D, Huan J, Liu J, Prins J, Snoeyink J, Wang W, Tropsha A. Structure-based function inference using protein family-specific fingerprints. Protein Sci. 2006;15:1537–1543. doi: 10.1110/ps.062189906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Polacco BJ, Babbitt PC. Automated discovery of 3D motifs for protein function annotation. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:723–730. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btk038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Friedberg I. Automated protein function prediction--the genomic challenge. Brief Bioinform. 2006;7:225–242. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbl004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Laskowski RA, Watson JD, Thornton JM. ProFunc: a server for predicting protein function from 3D structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:W89–W93. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Pal D, Eisenberg D. Inference of protein function from protein structure. Structure. 2005;13:121–130. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2004.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Friedberg I, Harder T, Godzik A. JAFA: a protein function annotation meta-server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:W379–W381. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Moore AD, Bjorklund AK, Ekman D, Bornberg-Bauer E, Elofsson A. Arrangements in the modular evolution of proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008;33:444–451. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2008.05.008. * An interesting review of evolutionary insights into the diverse modes and origins of arrangements and combinations of domains in proteins.
- 63.Finn RD, Tate J, Mistry J, Coggill PC, Sammut SJ, Hotz HR, Ceric G, Forslund K, Eddy SR, Sonnhammer EL, Bateman A. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:D281–D288. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Bru C, Courcelle E, Carrere S, Beausse Y, Dalmar S, Kahn D. The ProDom database of protein domain families: more emphasis on 3D. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:D212–D215. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Basu MK, Carmel L, Rogozin IB, Koonin EV. Evolution of protein domain promiscuity in eukaryotes. Genome Res. 2008;18:449–461. doi: 10.1101/gr.6943508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Weiner J, III, Moore AD, Bornberg-Bauer E. Just how versatile are domains? BMC Evol Biol. 2008;8:285. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-8-285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Vogel C, Bashton M, Kerrison ND, Chothia C, Teichmann SA. Structure, function and evolution of multidomain proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004;14:208–216. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2004.03.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Bashton M, Nobeli I, Thornton JM. Cognate ligand domain mapping for enzymes. J Mol Biol. 2006;364:836–852. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.09.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]