Abstract
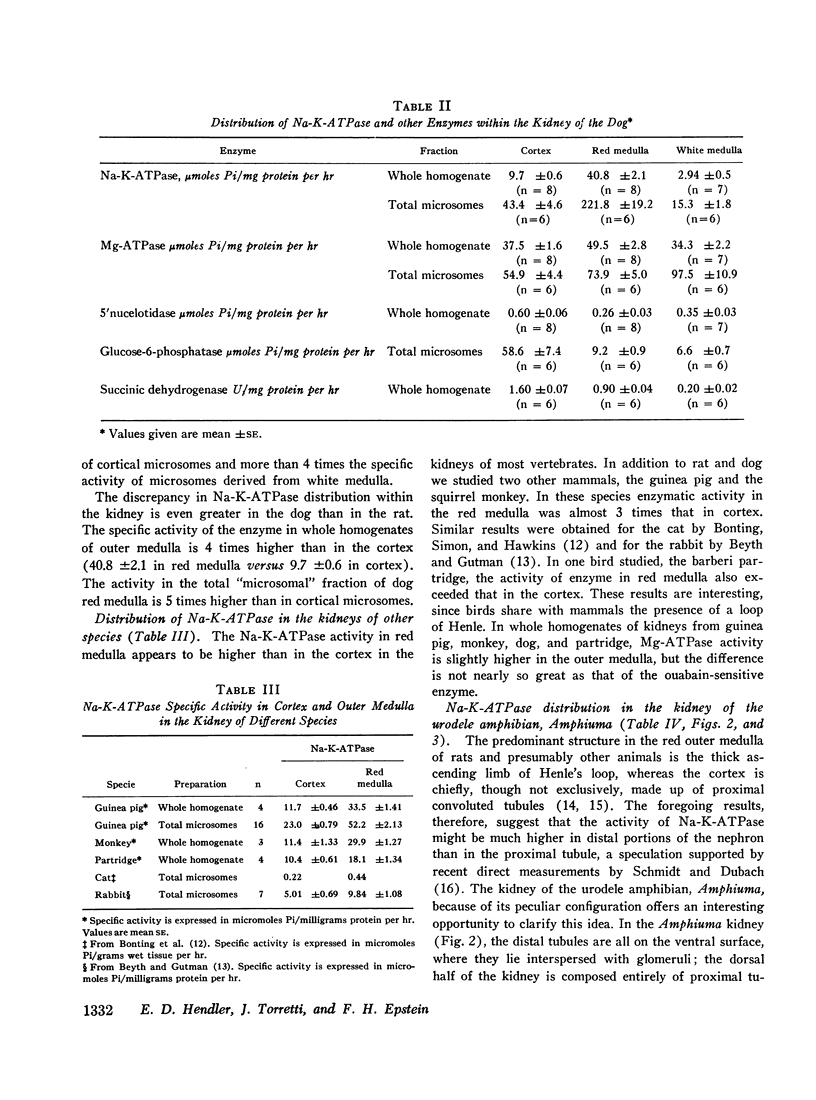
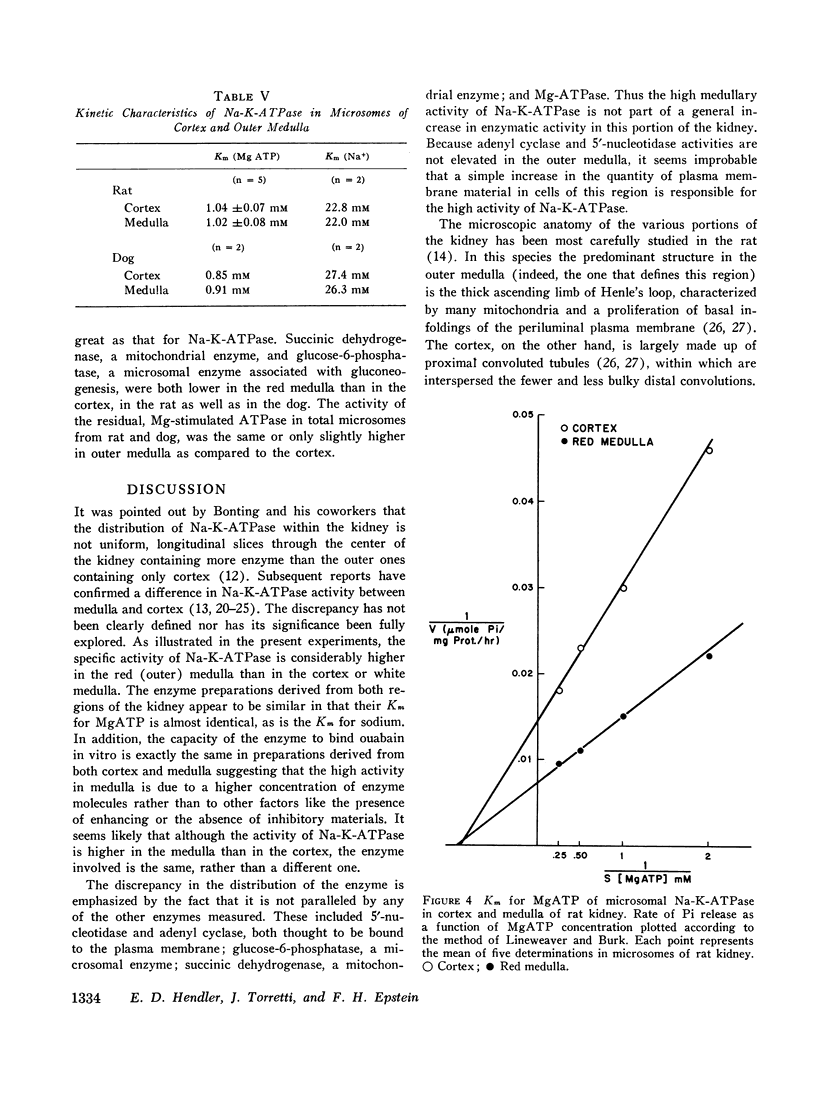
The activity of sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase (Na-K-ATPase) is considerably higher in homogenates of outer medulla than in the cortex or papilla of the kidney. The enzyme has similar kinetic characteristics in both cortex and medulla, and binds ouabain in the same proportion. The discrepancy in enzymatic activity is not paralleled by similar change in the activity of adenyl cyclase, 5′nucleotidase, glucose-6-phosphatase, or succinic dehydrogenase. Na-K-ATPase is also higher in distal convoluted tubules (ventral slices) than in the proximal tubules (dorsal slices) of the kidney of Amphiuma. The high concentration of Na-K-ATPase in the red medulla of the kidney is probably related to the presence here of the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, and this has important implications with regard to the mechanism of sodium reabsorption by different portions of the nephron.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BONTING S. L., CARAVAGGIO L. L., HAWKINS N. M. Studies on sodium-potassium-activated adenosinetriphosphatase. IV. Correlation with cation transport sensitive to cardiac glycosides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;98:413–419. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90206-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONTING S. L., SIMON K. A., HAWKINS N. M. Studies on sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. I. Quantitative distribution in several tissues of the cat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Dec;95:416–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckalew V. M., Jr, Ramirez M. A., Goldberg M. Free water reabsorption during solute diuresis in normal and potassium-depleted rats. Am J Physiol. 1967 Feb;212(2):381–386. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.2.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIGNELL C. F., RODDY P. M., TITUS E. O. EFFECT OF ADRENAL SEOIDS ON A NA+ K+ DEPENDENT ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE. Life Sci. 1965 Mar;4:559–566. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90265-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. Renal adenyl cyclase: anatomically separate sites for parathyroid hormone and vasopressin. Science. 1968 Feb 2;159(3814):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3814.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortney M. A., Mylle M., Lassiter W. E., Gottschalk C. W. Renal tubular transport of water, solute, and PAH in rats loaded with isotonic saline. Am J Physiol. 1965 Dec;209(6):1199–1205. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.6.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMMELOT P., BOS C. J., BENEDETTI E. L., RUEMKE P. STUDIES ON PLASMA MEMBRANES. I. CHEMICAL COMPOSITION AND ENZYME CONTENT OF PLASMA MEMBRANES ISOLATED FROM RAT LIVER. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 15;90:126–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyth Y., Gutman Y. Ontogenesis of microsomal ATPase in the rabbit kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Sep 30;191(1):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90338-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebisch G., Malnic G., Klose R. M., Windhager E. E. Effect of ionic substitutions on distal potential differences in rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):560–568. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Regulation of the (Na+ equals K+)-activated ATP hydrolyzing enzyme system in rat kidney. II. The effect of aldosterone on the activity in kidneys of adrenalectomized rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 18;192(2):326–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. I., Epstein F. H. Physiologic role of sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase in the transport of cations across biologic membranes. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 1;278(5):253–261. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802012780506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. I., Epstein F. H. The role of sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase in the reabsorption of sodium by the kidney. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1999–2011. doi: 10.1172/JCI105689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Weiss B., Brodie B. B. A simple, sensitive method for the assay of adenyl cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Oct;163(2):379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriz W. Der architektonische und funktionelle Aufbau der Rattenniere. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;82(4):495–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landwehr D. M., Klose R. M., Giebisch G. Renal tubular sodium and water reabsorption in the isotonic sodium chloride-loaded rat. Am J Physiol. 1967 Jun;212(6):1327–1333. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.6.1327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., Klose R. M., Giebisch G. Micropuncture study of distal tubular potassium and sodium transport in rat nephron. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):529–547. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Maldonado M., Allen J. C., Eknoyan G., Suki W., Schwartz A. Renal concentrating mechanism: possible role for sodium-potassium activated adenosine triphosphatase. Science. 1969 Aug 22;165(3895):807–808. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3895.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui H., Schwartz A. Mechanism of cardiac glycoside inhibition of the (Na+-K+)-dependent ATPase from cardiac tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 25;151(3):655–663. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Hawthorne J. N. The site of diphosphoinositide synthesis in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osvaldo L., Latta H. The thin limbs of the loop of Henle. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Apr;15(1):144–168. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W., Gonick H. C. Response of rat kidney Na+ -K+ -activated adenosine triphosphatase to sodium deprivation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):1175–1177. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P. Disassociation of JG granularity and blood pressure in adrenal regeneration. Am J Physiol. 1967 Oct;213(4):947–953. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.4.947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOU J. C. ENZYMATIC BASIS FOR ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF NA+ AND K+ ACROSS CELL MEMBRANE. Physiol Rev. 1965 Jul;45:596–617. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.3.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt U., Dubach U. C. Activity of (Na+K+)-stimulated adenosintriphosphatase in the rat nephron. Pflugers Arch. 1969;306(3):219–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00592433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan W. J. Electrical potential differences across distal renal tubules of Amphiuma. Am J Physiol. 1968 May;214(5):1096–1103. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.5.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULLRICH K. J., KRAMER K., BOYLAN J. W. Present knowledge of the counter-current system in the mammalian kidney. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1961 Mar;3:395–431. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(61)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTEMBURY G., SUGINO N., SOLOMON A. K. Ionic permeability and electrical potential differences in Necturus kidney cells. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Mar;44:689–712. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.4.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDHAGER E. E., GIEBISCH G. ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY OF THE NEPHRON. Physiol Rev. 1965 Apr;45:214–244. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.2.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittembury G., Proverbio F. Two modes of Na extrusion in cells from guinea pig kidney cortex slices. Pflugers Arch. 1970;316(1):1–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00587893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



