Abstract
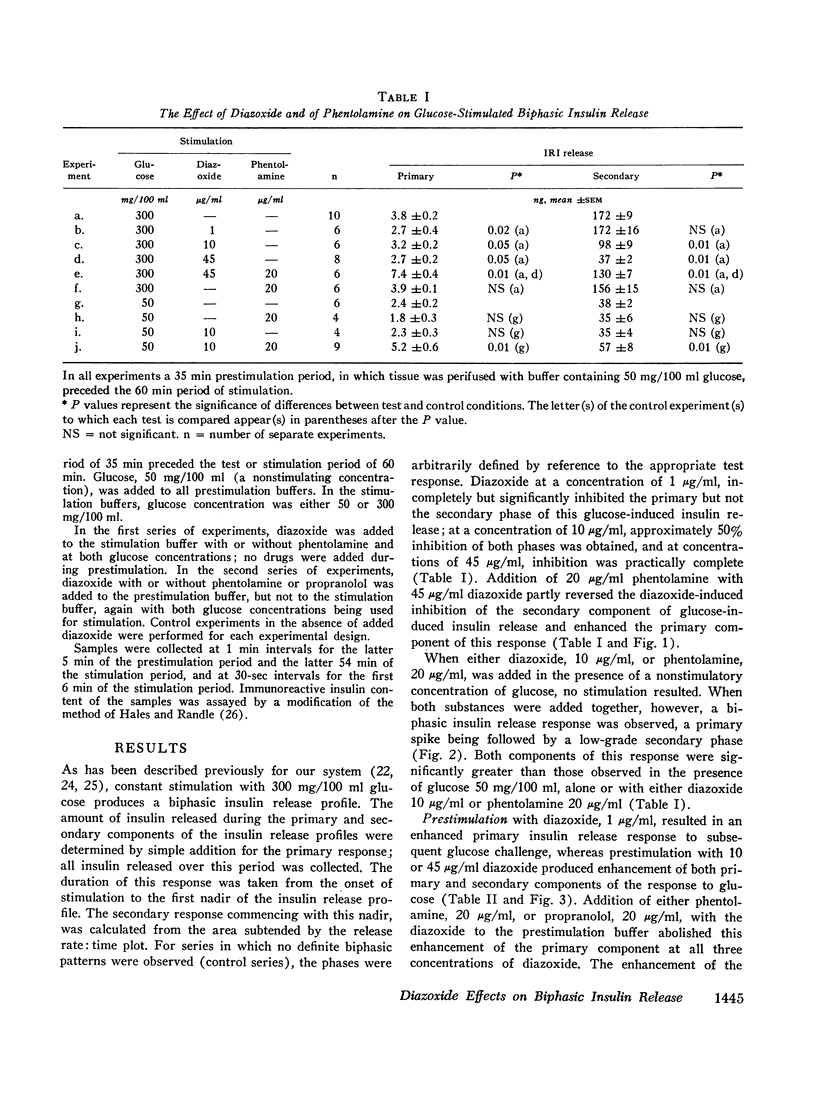
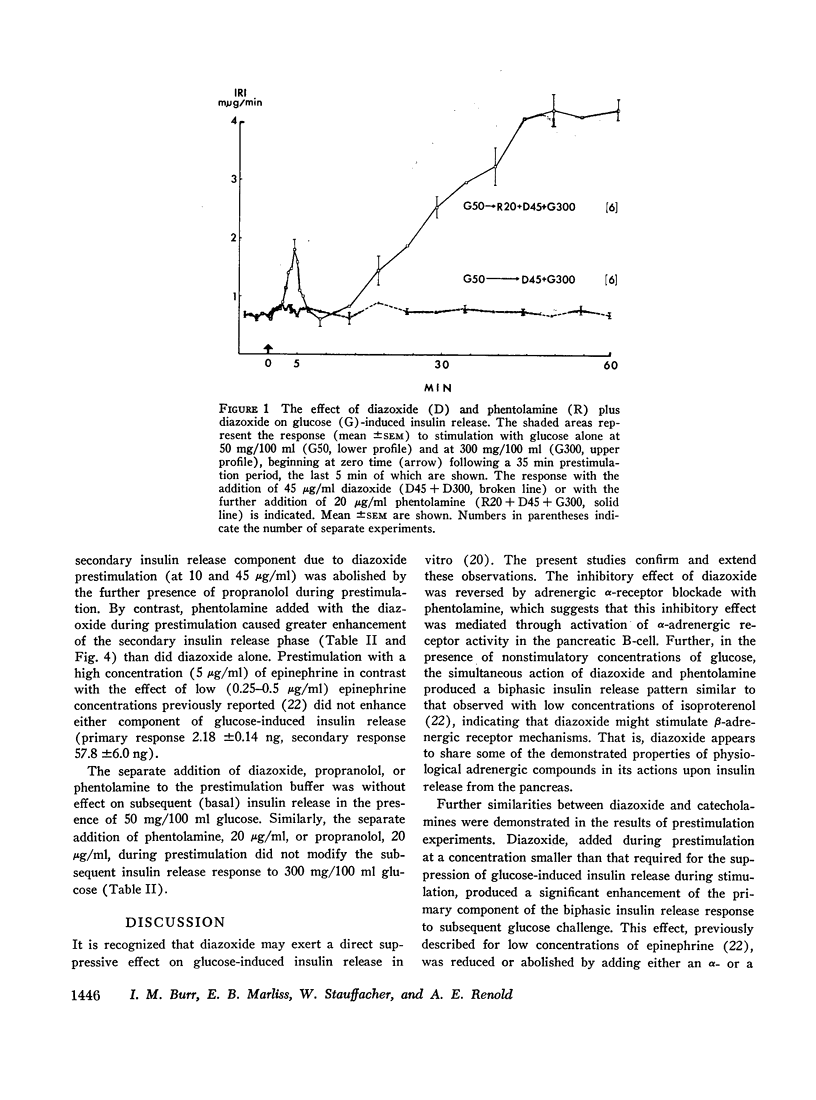
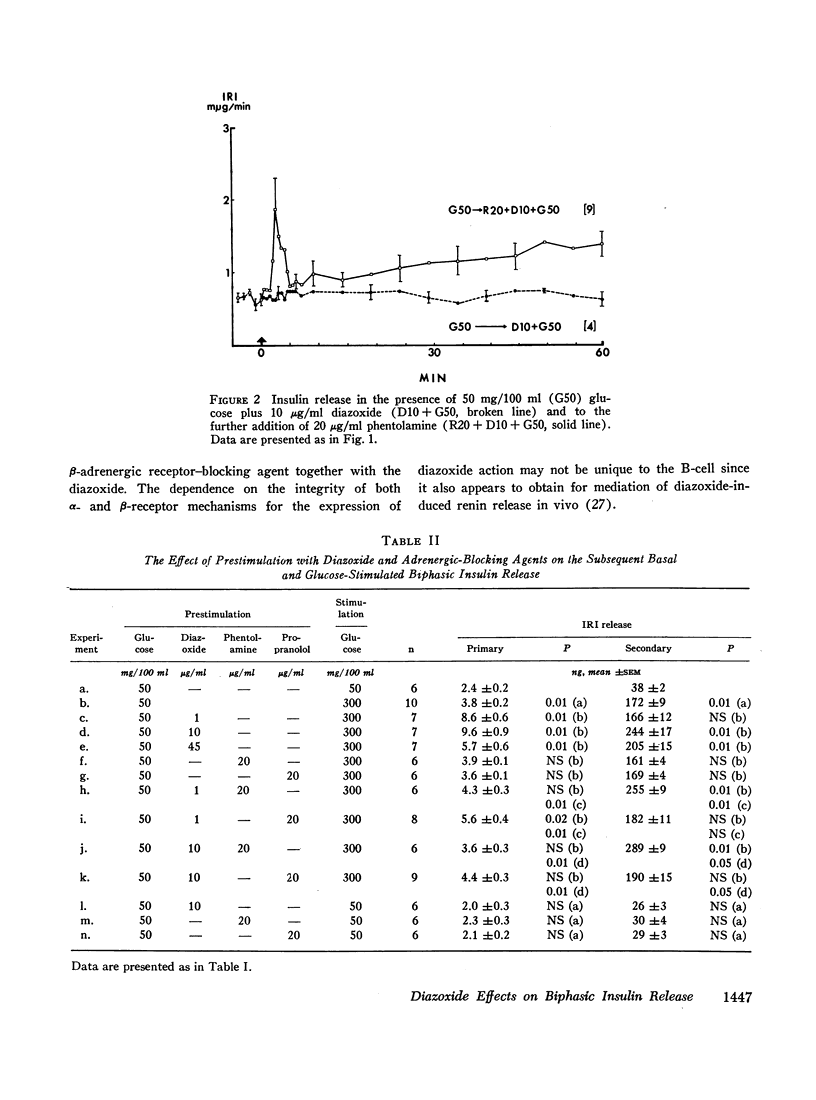
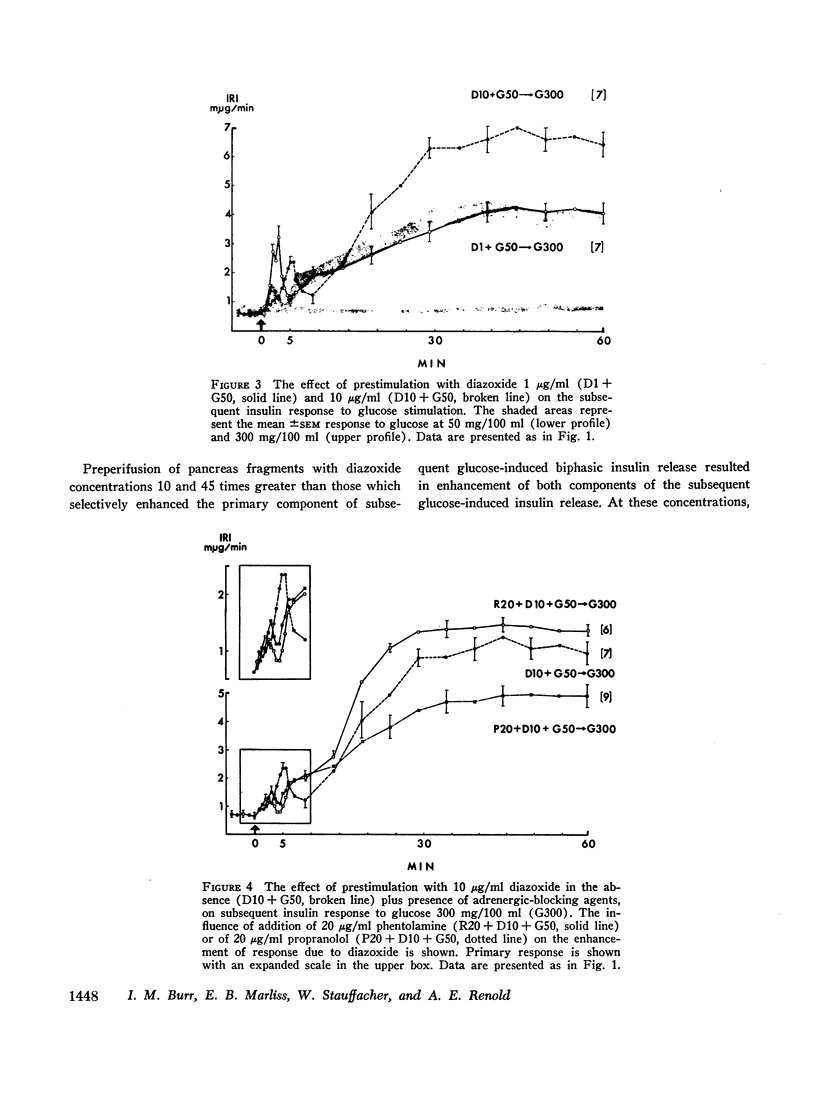
An in vitro system for perifusion of rat pancreas has been used to investigate the effects of diazoxide on glucose-induced insulin release. Administration of diazoxide with a stimulating concentration of glucose produced a dose-dependent suppression of insulin release. This effect was partly reversed by phentolamine. In the presence of nonstimulatory concentrations of glucose, diazoxide plus phentolamine, but neither alone, stimulated a biphasic release of insulin similar to that observed with 1-isopropyl norepinephrine. A prior period of perifusion with a low concentration of diazoxide enhanced the primary component of subsequent glucose-stimulated insulin release, an effect inhibited by addition of either phentolamine or propranolol to the diazoxide during this “prestimulation” period. These effects are similar to those observed with epinephrine. By contrast with epinephrine however, increasing the concentration of diazoxide during the period before glucose stimulation enhanced both the primary and secondary components of subsequent glucose-induced insulin release. These data suggest that at least some of the direct effects of diazoxide on the pancreas are mediated through α- and β-adrenergic receptor mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey R. E., Castro A., Kramer R. M., Macfarlane D. Enhancement of insulin release to acute glycaemic stimulation with depression of basal insulin production rates in insulinoma following diazoxide administration. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1970 Mar;63(3):392–404. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0630392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basabe J., Lopez N., Viktora J., Wolff F. Studies of insulin secretion in the perfused rat pancreas. Effect of diazoxide and A025. Diabetes. 1970 Apr;19(4):271–281. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.4.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. Diazoxide and the treatment of hypoglycemia: an historical review. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Apr 11;150(2):194–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb19045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Balant L., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. Adrenergic modification of glucose-induced biphasic insulin release from perifused rat pancreas. Eur J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;1(4):216–224. doi: 10.1111/eci.1971.1.4.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Balant L., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E., Grodsky G. Dynamic aspects of proinsulin release from perifused rat pancreas. Lancet. 1969 Oct 25;2(7626):882–883. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Balant L., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. Perifusion of rat pancreatic tissue in vitro: substrate modification of theophylline-induced biphasic insulin release. J Clin Invest. 1970 Nov;49(11):2097–2105. doi: 10.1172/JCI106427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Renold A. E., Stauffacher W., Grodsky G. M., Balant L. [Regulation of insulin release in perifused pancreatic tissue]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1969 Sep;6 (Suppl 1):580–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLLERY C. T., PENTECOST B. L., SAMAAN N. A. Drug-induced diabetes. Lancet. 1962 Oct 13;2(7259):735–737. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)90567-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajans S. S., Floyd J. C., Jr, Knopf R. F., Rull J., Guntsche E. M., Conn J. W. Benzothiadiazine suppression of insulin release from normal and abnormal islet tissue in man. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):481–492. doi: 10.1172/JCI105362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajans S. S., Floyd J. C., Jr, Thiffault C. A., Knopf R. F., Harrison T. S., Conn J. W. Further studies on diazoxide suppression of insulin release from abnormal and normal islet tissue in man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Apr 11;150(2):261–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb19051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant A. M., Basabe J. C., Lopez N. L., Krees S. V., Wolff F. W. Mode of action of a diazoxide analog (A025). Its effects on insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1970 Sep;19(9):630–638. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.9.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES C. N., RANDLE P. J. Immunoassay of insulin with insulin-antibody precipitate. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0880137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Taylor K. W. Effects of diazoxide on insulin secretion in vitro. Lancet. 1966 Jan 15;1(7429):128–129. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91263-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KVAM D. C., STANTON H. C. STUDIES ON DIAZOXIDE HYPERGLYCEMIA. Diabetes. 1964 Nov-Dec;13:639–644. doi: 10.2337/diab.13.6.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loubatières A., Mariani M. M., Alric R. The action of diazoxide on insulin secretion, medullo-adrenal secretion, and the liberation of catecholamines. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Apr 11;150(2):226–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb19048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. D., Hales C. N. The interaction of various inhibitors and stimuli of insulin release studied with rabbit pancreas in vitro. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(3):473–479. doi: 10.1042/bj1130473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Graber A. L., Kuzuya T., Williams R. H. The effect of epinephrine on immunoreactive insulin levels in man. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):228–236. doi: 10.1172/JCI105335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin A. A., Taylor R. M., Roth F. E. A brief review of the development of diazoxide as an antihypertensive agent. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Apr 11;150(2):457–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb19070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAQUET M., YABO R., VIKTORA J., WOLFF F. AN ADRENERGIC MECHANISM FOR HYPERGLYCEMIA INDUCED BY DIAZOXIDE. Metabolism. 1965 Sep;14:1000–1009. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(65)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer H. S., Allen E. W. Hyperglycemia and inhibition of insulin secretion during administration of diazoxide and trichlormethiazide in man. Diabetes. 1969 Jan;18(1):19–28. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokal J. E. Failure of diazoxide to affect carbohydrate metabolism of the isolated liver. Diabetes. 1968 May;17(5):256–260. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.5.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABACHNICK I. I., GULBENKIAN A., SEIDMAN F. THE EFFECT OF A BENZOTHIADIAZINE, DIAZOXIDE, ON CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM. Diabetes. 1964 Jul-Aug;13:408–418. doi: 10.2337/diab.13.4.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabachnick I. I., Gulbenkian A. Mechanism of diazoxide hyperglycemia in animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Apr 11;150(2):204–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb19046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walfish P. G., Natale R., Chang C. Beta adrenergic receptor mechanisms in the metabolic effects of diazoxide in fasted rats. Diabetes. 1970 Apr;19(4):228–233. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.4.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer N., Chokshi D. S., Yoon M. S., Freedman A. D. Adrenergic receptor mediation of renin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Sep;29(9):1168–1175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-9-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff F., Grant A., Wales J., Viktora J. Experimental diabetes due to insulin inhibition. Lancet. 1968 Apr 13;1(7546):818–818. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92260-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarday Z., Viktora J., Wolff F. The effect of diazoxide on catecholamines. Metabolism. 1966 Mar;15(3):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(66)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]