Abstract
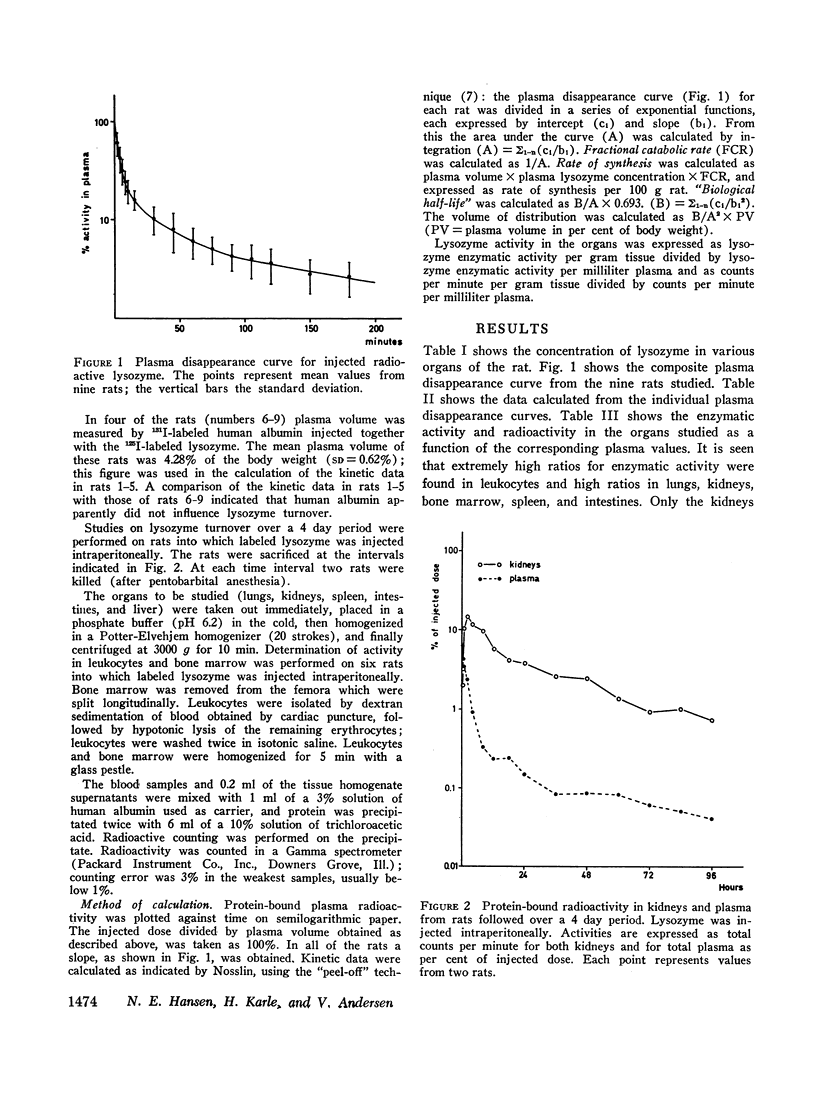
Lysozyme turnover in the rat was studied with 125I-labeled rat lysozyme. It was found that plasma lysozyme has a rapid disappearance rate with a half-life of 75 min. The rate of synthesis was calculated at 3.4 μg/min per 100 g rat. This rate of synthesis was compared with figures from the literature for the turnover rate of neutrophilic granulocytes, and the data were consistent with the concept that disintegrating neutrophils are the main source of plasma lysozyme.
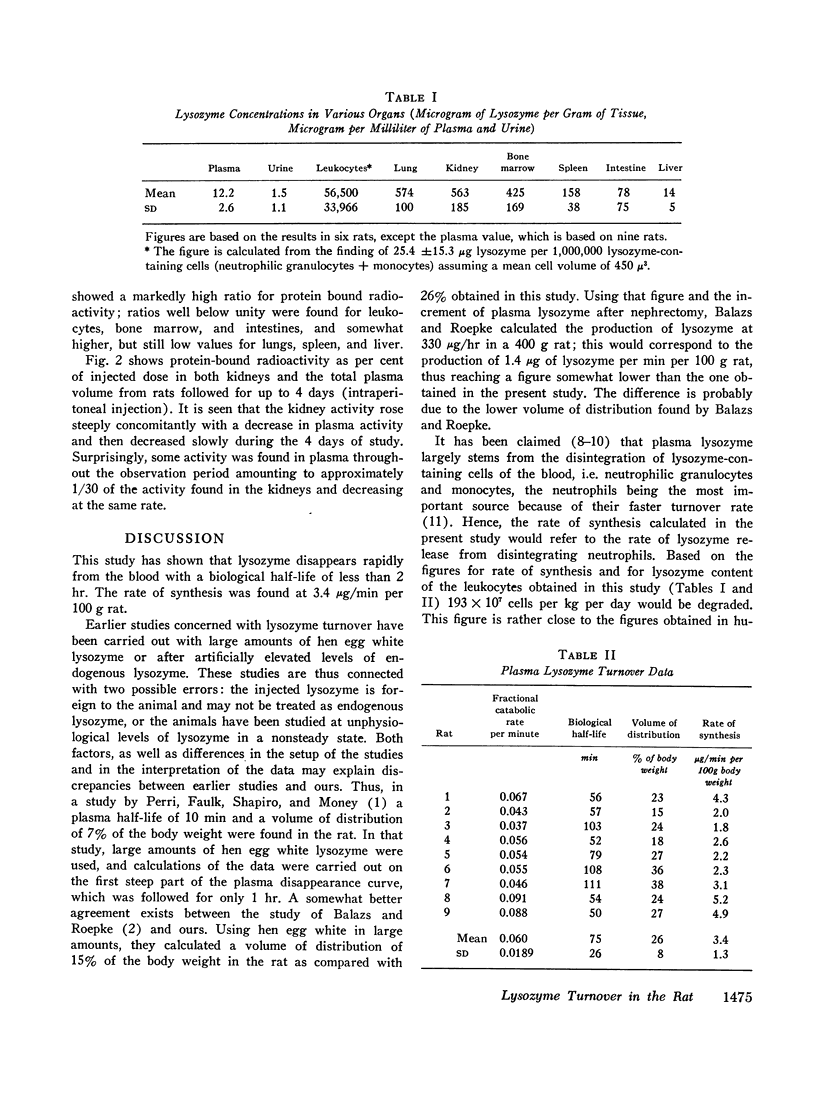
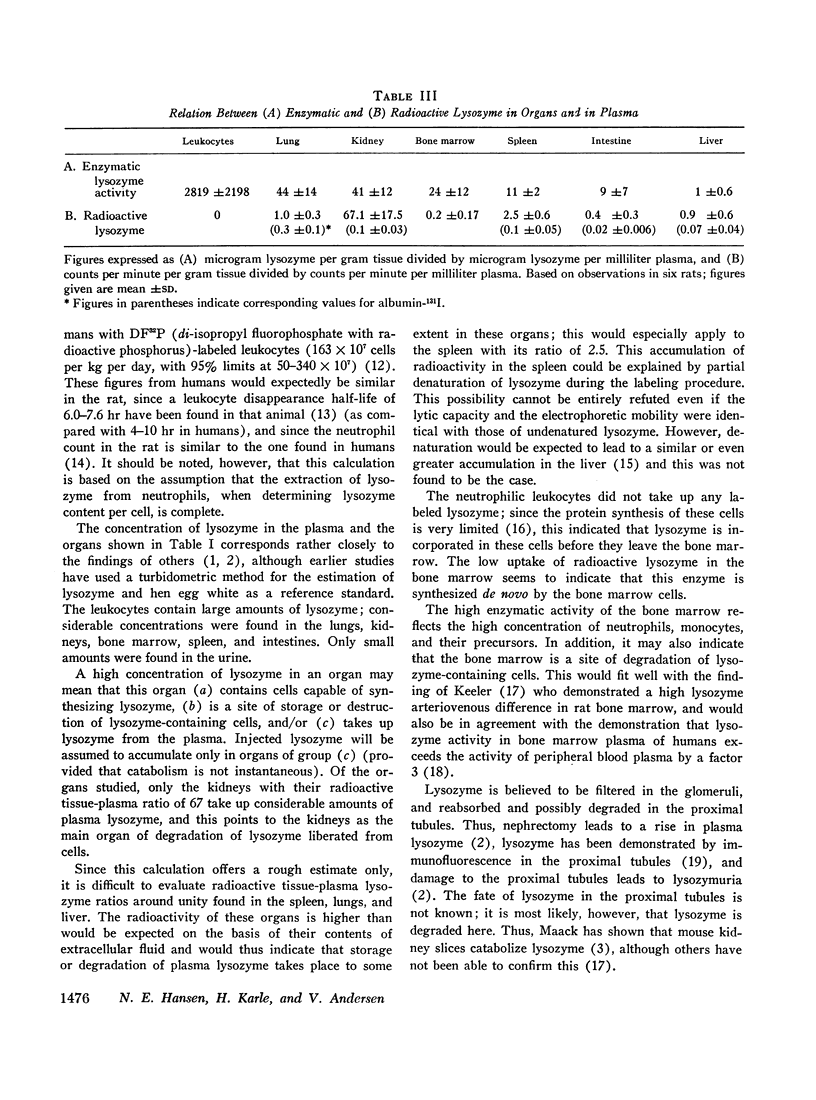
The distribution of enzymatic lysozyme activity and of radioactive lysozyme was studied in several organs. Very high enzymatic activity was found in leukocytes as were considerable activities in lungs, kidneys, bone marrow, spleen, and intestine; little enzymatic activity was found in the urine. High radioactive levels as compared with plasma radioactivity were demonstrated only in the kidneys. This indicates that of the organs studied, the kidney is the predominant site of storage and destruction of plasma lysozyme.
Lysozyme was found to disappear only slowly from the kidneys over a period of 4 days. The data obtained seem to indicate that lysozyme or a lysozyme degradation product precipitable by trichloroacetic acid was released in small amounts from the kidneys to plasma throughout this period.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balazs T., Roepke R. R. Lysozymuria induced in rats by nephrotoxic agents. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Nov;123(2):380–385. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTWRIGHT G. E., ATHENS J. W., WINTROBE M. M. THE KINETICS OF GRANULOPOIESIS IN NORMAL MAN. Blood. 1964 Dec;24:780–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWEY W. C., HUNTER J. D. Inhomogeneity of iodinated human serum albumin as detected with rat liver. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Sep;15:961–962. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.5.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink M. E., Finch S. C. Serum muramidase and granulocyte turnover. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Feb;127(2):365–367. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerecke D., Schultze B., Maurer W. Autoradiographische Bestimmung der mittleren Verweilzeit neutrophiler Granulozyten im Blut der Ratte mittels Dauerinfusion von 3H- Thymidin. Experientia. 1970 Mar 15;26(3):311–312. doi: 10.1007/BF01900116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen N. E., Karle H., Andersen V. Muramidase activity of bone marrow plasma. Studies in haematologically normal individuals and in granulocytopenic patients. Acta Med Scand. 1969 May;185(5):387–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeler R. The effect of bilateral nephrectomy on the production and distribution of muramidase (lysozyme) in the rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1970 Feb;48(2):131–138. doi: 10.1139/y70-021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maack T. Changes in the activity of acid hydrolases during renal reabsorption of lysozyme. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):268–273. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osserman E. F., Lawlor D. P. Serum and urinary lysozyme (muramidase) in monocytic and monomyelocytic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):921–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRI G. C., FAULK M., SHAPIRO E., MONEY W. L. ROLE OF THE KIDNEY IN ACCUMULATION OF EGG WHITE MURAMIDASE IN EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jan;115:189–192. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R. Origin and kinetics of monocytes and macrophages. Semin Hematol. 1970 Apr;7(2):125–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


