Abstract
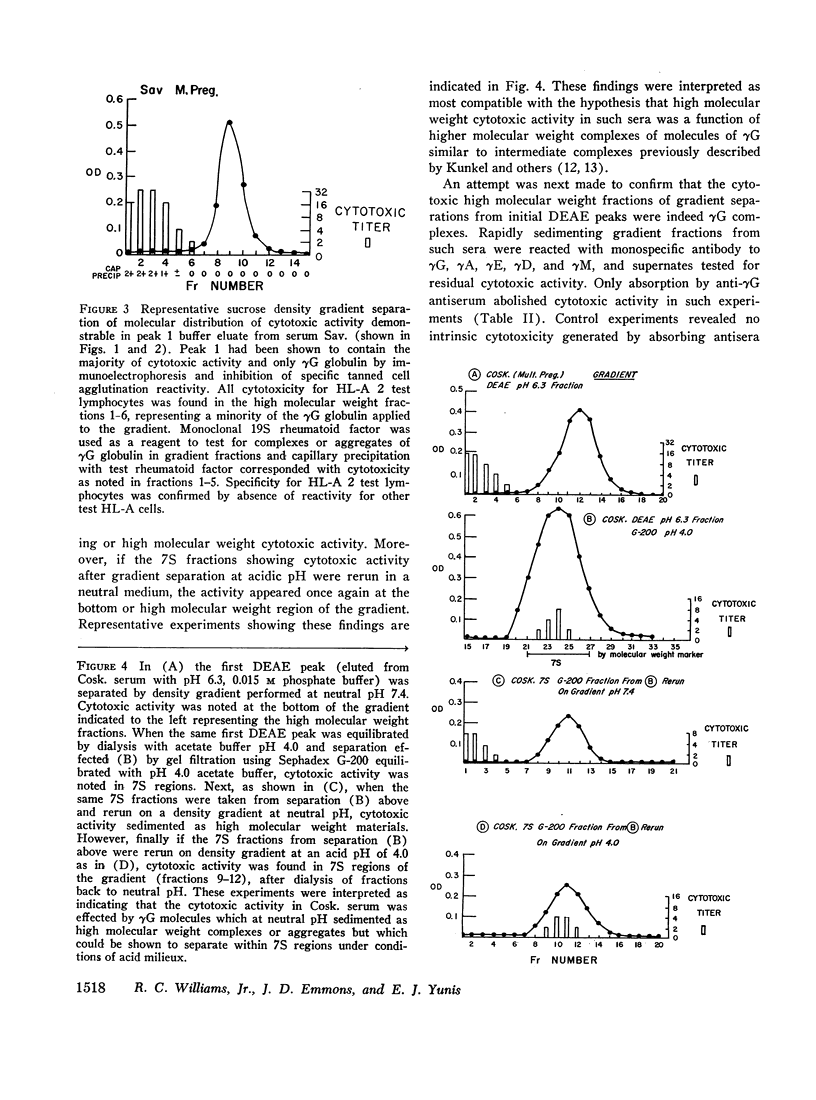
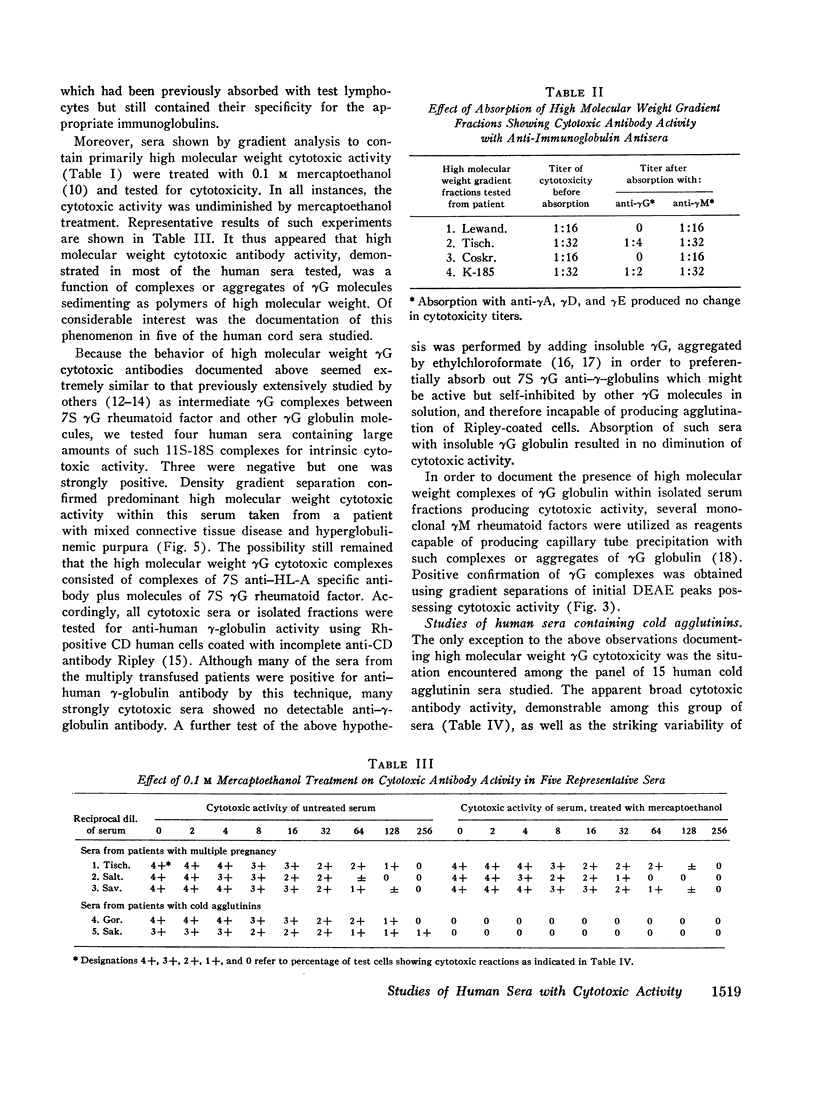
42 human sera showing in vitro cytotoxic activity of restricted or broad HL-A specificities with test human lymphocytes were studied for the molecular and immunoglobulin class of cytotoxic antibody using sucrose gradient separations, DEAE-cellulose chromatography, and Sephadex G-200 gel filtration. Sera originated from patients with previous multiple pregnancies (19), multiply transfused patients (8), subacute bacterial endocarditis (4), systemic lupus (2), and human umbilical cord sera (9). In 32 of 42 instances, predominant cytotoxic activity was found in high molecular weight gradient fractions; however, DEAE chromatographic separations revealed cytotoxic activity in initial buffer fractions containing primarily γG globulin. Gradient separations of cytotoxic activity within initial γG DEAE fractions showed localization of cytotoxicity only in high molecular weight materials. Confirmation of high molecular weight γG cytotoxic activity was obtained by resistance to mercaptoethanol treatment, abolition of activity after absorption only with specific anti-γG antisera, and by the finding that high molecular weight cytotoxic activity in gradients or gel filtration run at neutral pH 7.4 became 7S when separations were rerun at an acidic pH of 4.0. Such 7S activity again became rapidly sedimenting when the same fractions were again rerun in gradients at neutral pH.
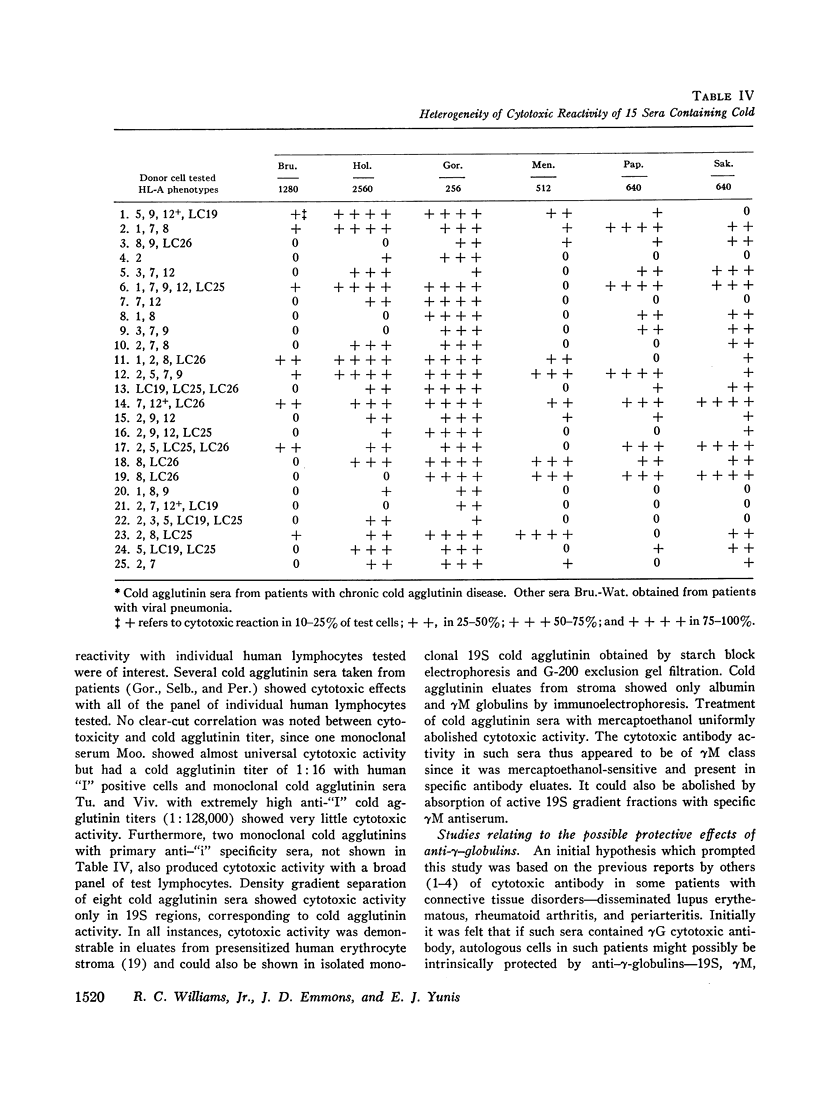
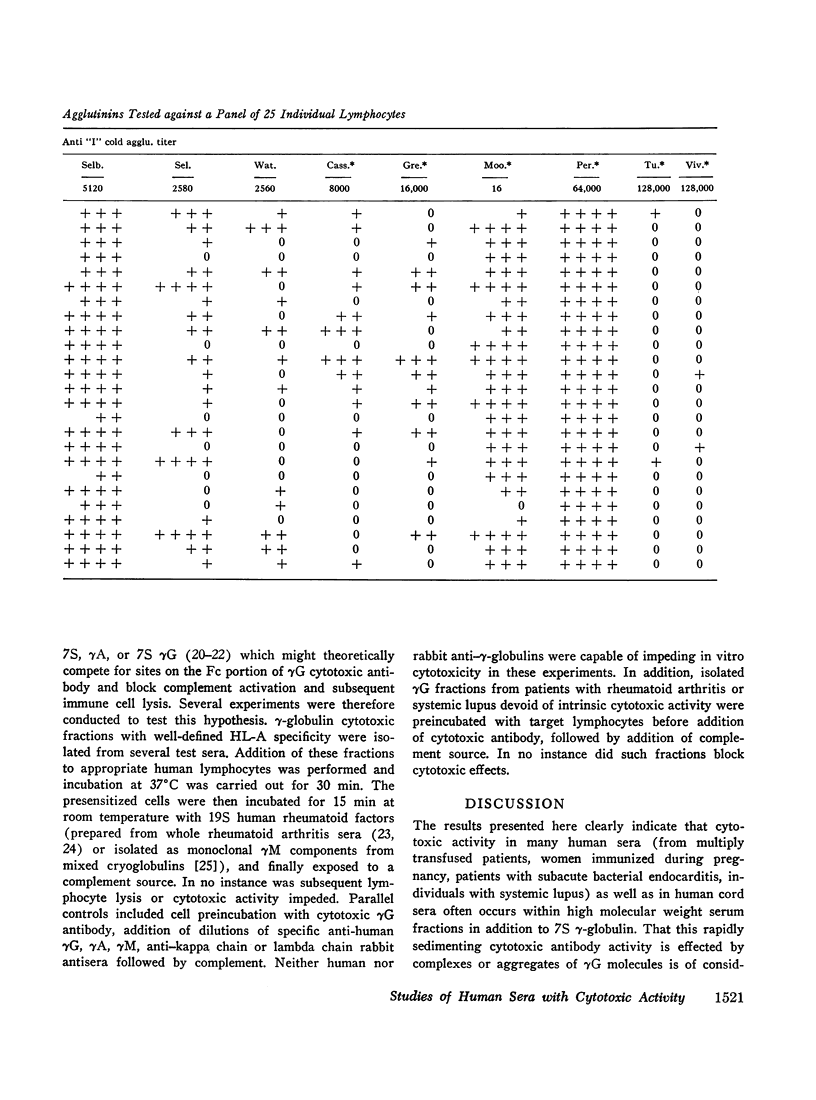
19S γM cytotoxic activity was documented in a panel of 15 human sera containing anti-“I” cold agglutinins. In this instance the cytotoxic activity appeared to be related to the cold agglutinin antibody since it was mercaptoethanol sensitive and could be demonstrated in monoclonal antibody eluates containing primarily γM.
No in vitro protection again cytotoxic effect was demonstrated when isolated human 19S anti-γ-globulins were aded to the lymphocytotoxic assay system.
With the exception of cold agglutinins, human cytotoxic antibodies appear to be primarily γG producing in vitro lymphocyte killing either as 7S γG globulin or as rapidly sedimenting aggregates or complexes of γG molecules.
Full text
PDF
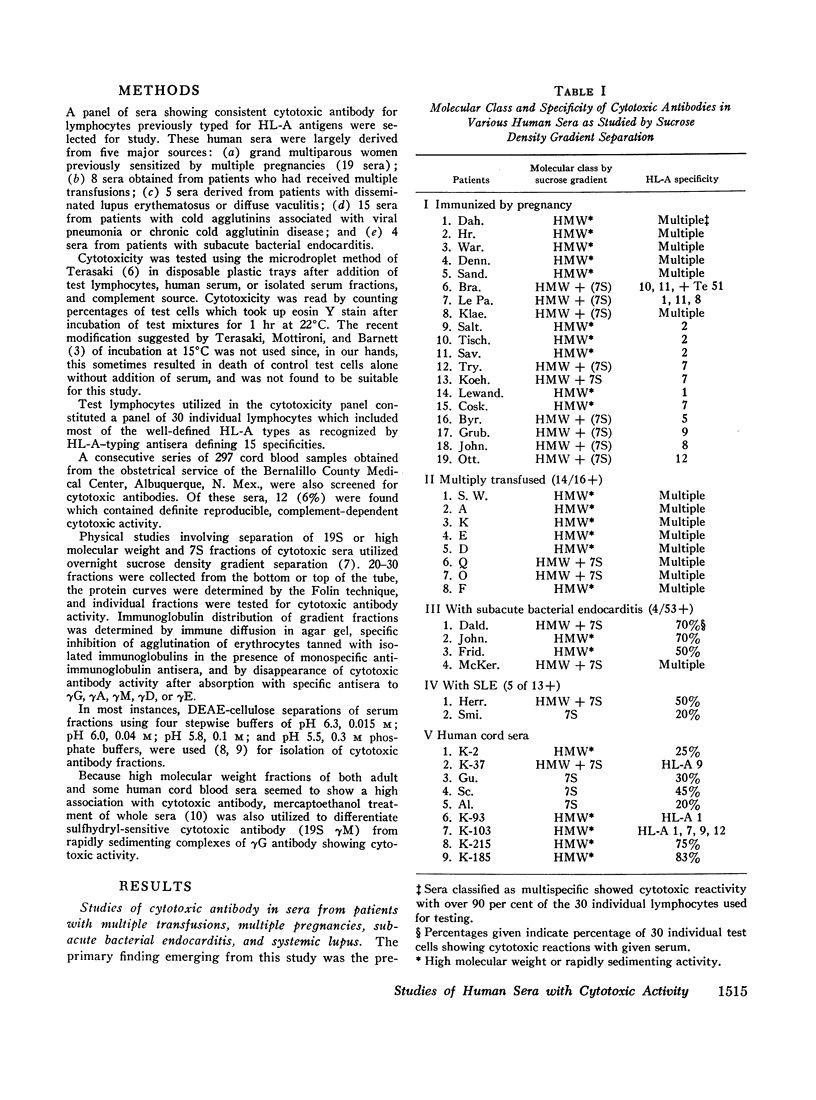
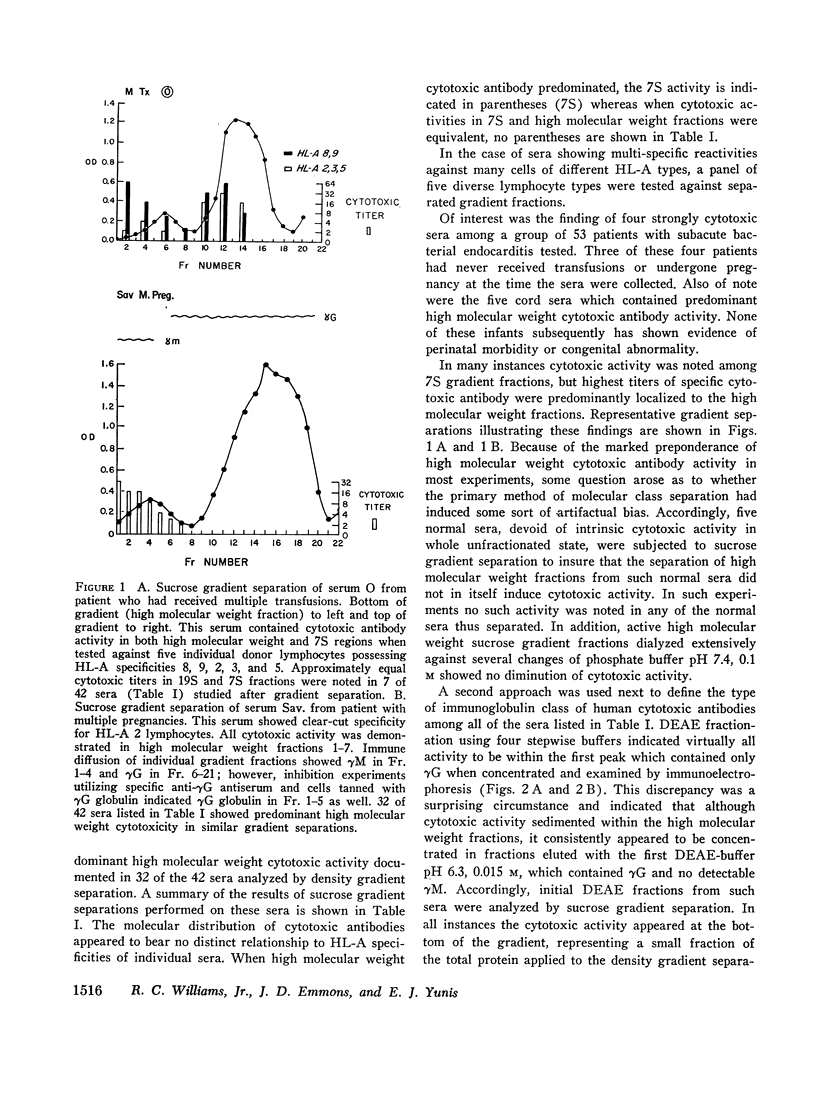
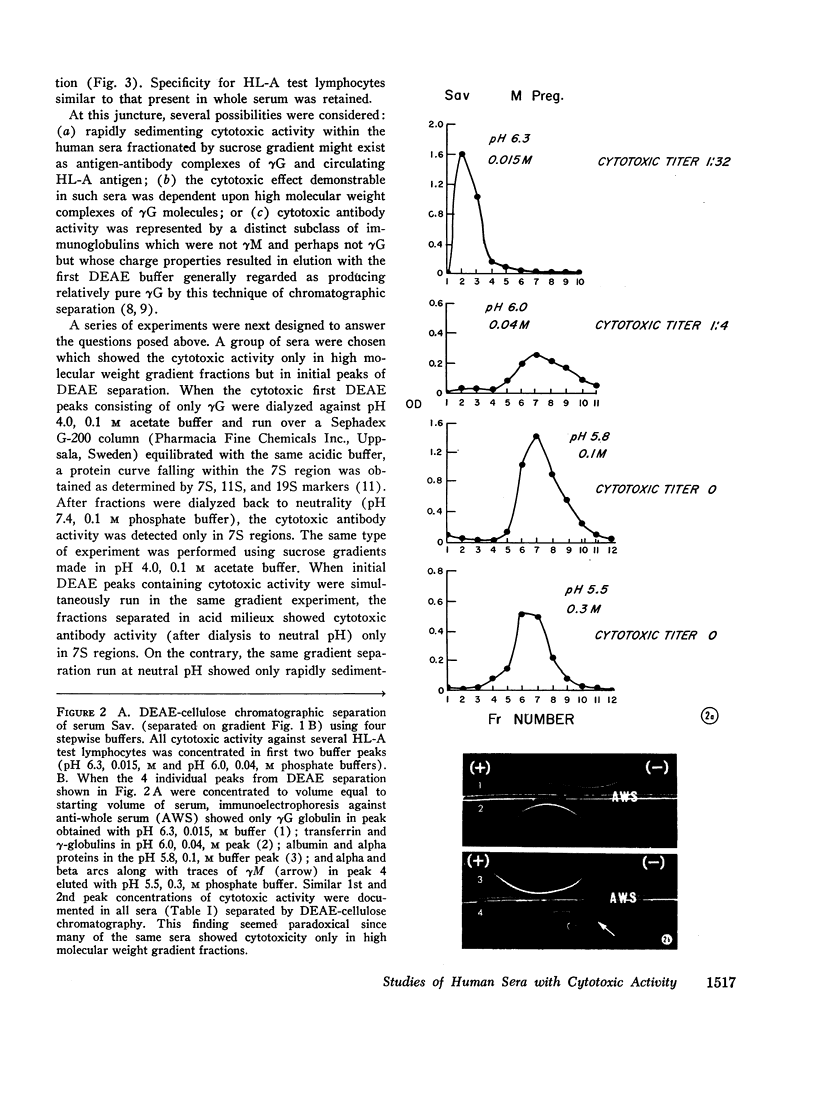



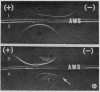
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. K., Jenness R., Brumfield H. P., Gough P. Brucella-Agglutinating Antibodies: Relation of Mercaptoethanol Stability to Complement Fixation. Science. 1964 Mar 20;143(3612):1334–1335. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3612.1334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. Biologically active water-insoluble protein polymers. I. Their use for isolation of antigens and antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1651–1659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHODIRKER W. B., TOMASI T. B., Jr Low-molecular-weight rheumatoid factor. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jun;42:876–884. doi: 10.1172/JCI104780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caperton E. M., Jr, Williams R. C., Jr In vivo study of IgM rheumatoid factors from mixed cryoglobulins. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Aug;74(2):239–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer R., Levin F. M. On the distribution of rheumatoid factors among the immunoglobulins. Immunochemistry. 1966 Jan;3(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90276-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Wicher K., Arbesman C. E. Insoluble immunoadsorbents containing anti-IgE: removal of reaginic activity and subsequent elution. J Immunol. 1969 Sep;103(3):622–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIM Y. B., BRADLEY S. G., WATSON D. W. CHARACTERIZATION OF EARLY 19 S AND LATE 7 S IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN THE MOUSE. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:798–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., FUDENBERG H. H., TOMASI T. B. Gamma globulin complexes in rheumatoid arthritis and certain other conditions. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jan;40:117–129. doi: 10.1172/JCI104224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F., Farr R. S. Elevation of cord over maternal IgG immunoglobulin: evidence for an active placental IgG transport. Nature. 1966 Jun 4;210(5040):1070–1071. doi: 10.1038/2101070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Caperton E. M., Jr, King R. A., Williams R., Jr Interactions among rheumatoid factors, gammaG antibodies, lymphocytes, and phagocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Dec 10;168(1):93–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb43098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Laxdal T., Quie P. G., Williams R. C., Jr Rheumatoid factors in subacute bacterial endocarditis--bacterium, duration of disease or genetic predisposition? Ann Intern Med. 1968 Apr;68(4):746–756. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-4-746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Laxidal T., Quie P. G., Williams R. C., Jr Serum opsonin, bacteria, and polymorphonuclear leukocyte interactions in subacute bacterial endocarditis. Anti-gamma-globulin factors and their interaction with specific opsonins. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1109–1120. doi: 10.1172/JCI105800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. K., Rossen R. D., Sharp J. T., Lidsky M. D., Butler W. T. Lymphocyte cytotoxic antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nature. 1970 Mar 28;225(5239):1255–1256. doi: 10.1038/2251255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Sherwood J. B. Cold-reacting antibodies: differences in the reaction of anti-I antibodies with adult and cord red blood cells. Blood. 1970 Jul;36(1):28–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid F. R., Roitt I. M., Rocha M. J. Complement fixation by a two-component antibody system: immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M anti-globulin (rheumatoid factor). Parodoxical effect related to immunoglobulin G concentration. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):673–693. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrohenloher R. E. Characterization of the gamma-globulin complexes present in certain sera having high titers of anti-gamma-globulin activity. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):501–512. doi: 10.1172/JCI105364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASAKI P. I., MCCLELLAND J. D. MICRODROPLET ASSAY OF HUMAN SERUM CYTOTOXINS. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:998–1000. doi: 10.1038/204998b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASI T. B., Jr, FUDENBERG H. H., FINBY N. Possible relationship of rheumatoid factors and pulmonary disease. Am J Med. 1962 Aug;33:243–248. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(62)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki P. I., Mottironi V. D., Barnett E. V. Cytotoxins in disease. Autocytotoxins in lupus. N Engl J Med. 1970 Oct 1;283(14):724–728. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197010012831403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrigiani G., Roitt I. M. Antiglobulin factors in sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and normal subjects. Quantitative estimation in different immunoglobulin classes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1967 Jul;26(4):334–340. doi: 10.1136/ard.26.4.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLER M., LAWLER S. D. A study of the properties of the Rhesus antibody (Ri) diagnostic for the rheumatoid factor and its application to Gm grouping. Vox Sang. 1962 Sep-Oct;7:591–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1962.tb04289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. C., Jr, KUNKEL H. G. Rheumatoid factor, complement, and conglutinin aberrations in patients with subacute bacterial endocarditis. J Clin Invest. 1962 Mar;41:666–675. doi: 10.1172/JCI104523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willims R. C., Jr, Kunkel H. G., Capra J. D. Antigenic specificities related to the cold agglutinin activity of gamma M globulins. Science. 1968 Jul 26;161(3839):379–381. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3839.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Agnello V., Kunkel H. G. Gamma globulin complexes in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Partial characterization and relationship to lowered complement levels. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):689–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yust I., Schwartz J., Dreyfuss F. A cytotoxic serum factor in polyarteritis nodosa and related conditions. Am J Med. 1970 Apr;48(4):472–476. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(70)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]