Abstract
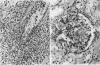
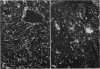
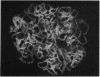
Equine immunoglobulin was detected along the glomerular basement membrane of three human homograft recipients who had been treated with equine anti-lymphocyte globulin. Anti-lymphocyte globulins, given these patients, were obtained by immunization of horses with lymphocytes from human spleens and/or lymph nodes and contained glomerular basement membrane-reactive antibodies. Quantitative paired-label isotope experiments (in rats) demonstrated that 30-170 μg/ml of kidney-fixing antibodies were present in these preparations. The anti-lymphocyte globulins formed a line of identity with a sheep anti-human glomerular basement serum when reacted against collagenase-solubilized human glomerular basement membrane in double diffusion in agar. The renal fixation of these antibodies was blocked by absorption with human glomerular basement membrane, but not by buffy-coat leukocytes, indicating that they were directed specifically toward antigens in the basement membrane and were not cross-reacting anti-lymphocyte antibodies.
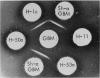
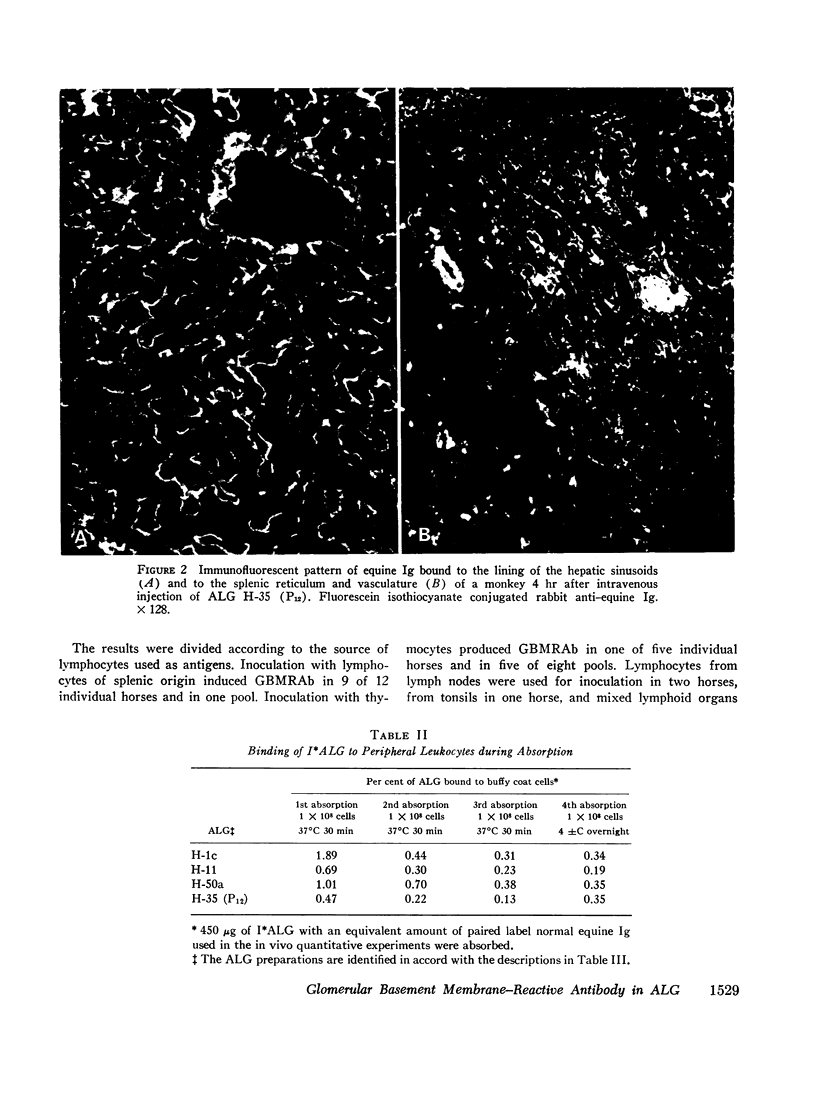
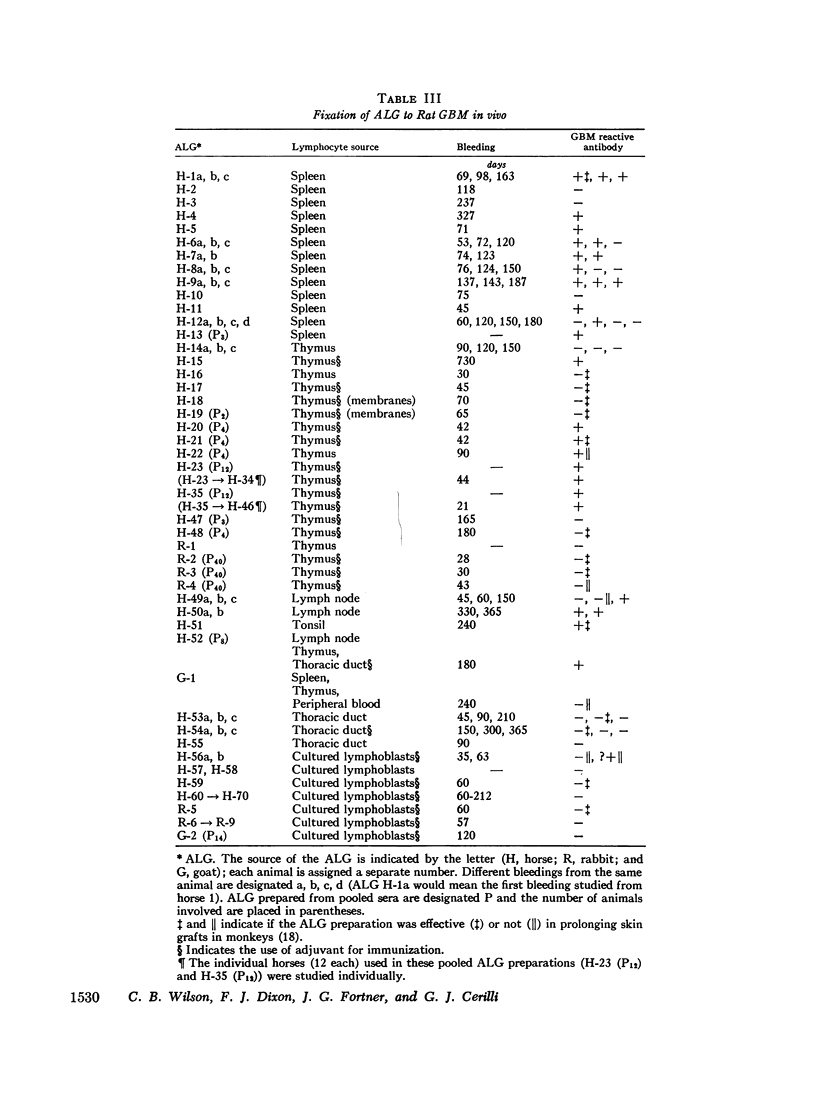
Anti-lymphocyte globulin preparations for human use were studied for glomerular basement membrane-reactive antibodies by a direct immunofluorescent assay in rats. Anti-lymphocyte globulin from 13 of 20 horses, and 7 of 10 serum pools from horses immunized with lymphocytes derived from solid lymphoid organs (spleen, thymus, lymph node, tonsil), contained glomerular basement membrane-reactive antibodies. Sera from 18 horses injected with thoracic duct cells or cultured lymphoblasts had no glomerular basement membrane-reactive antibodies.
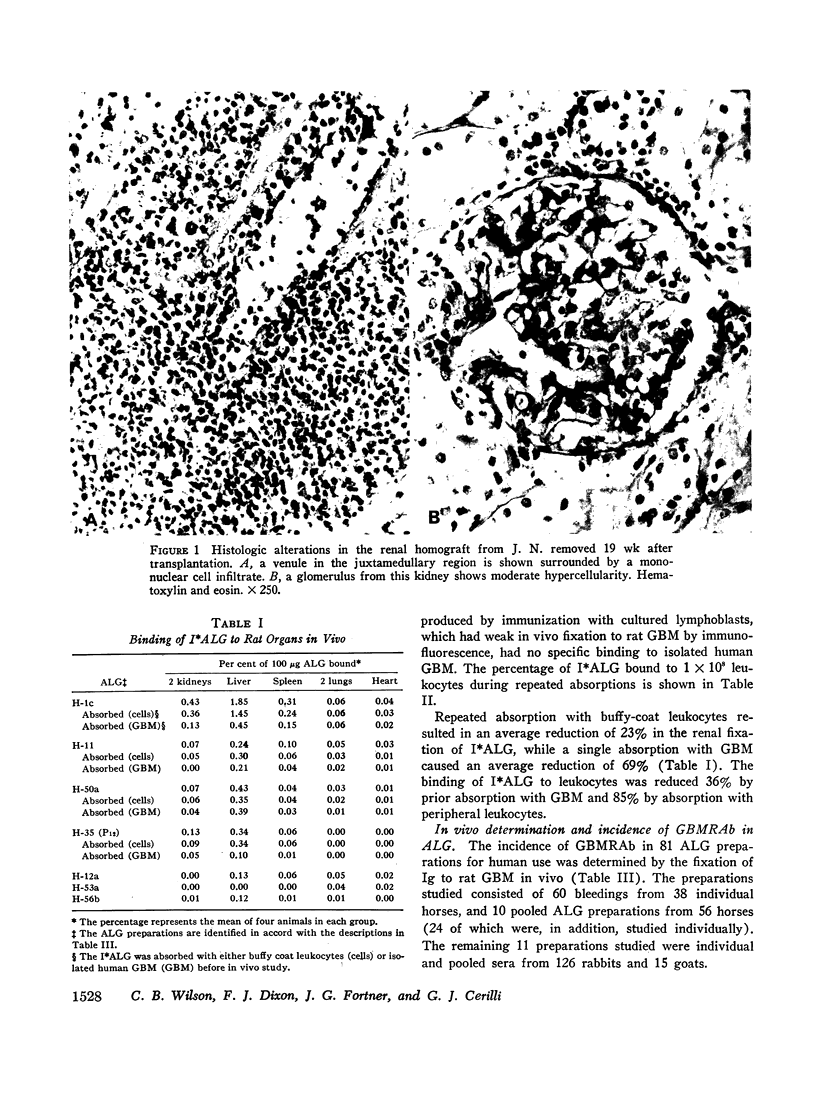
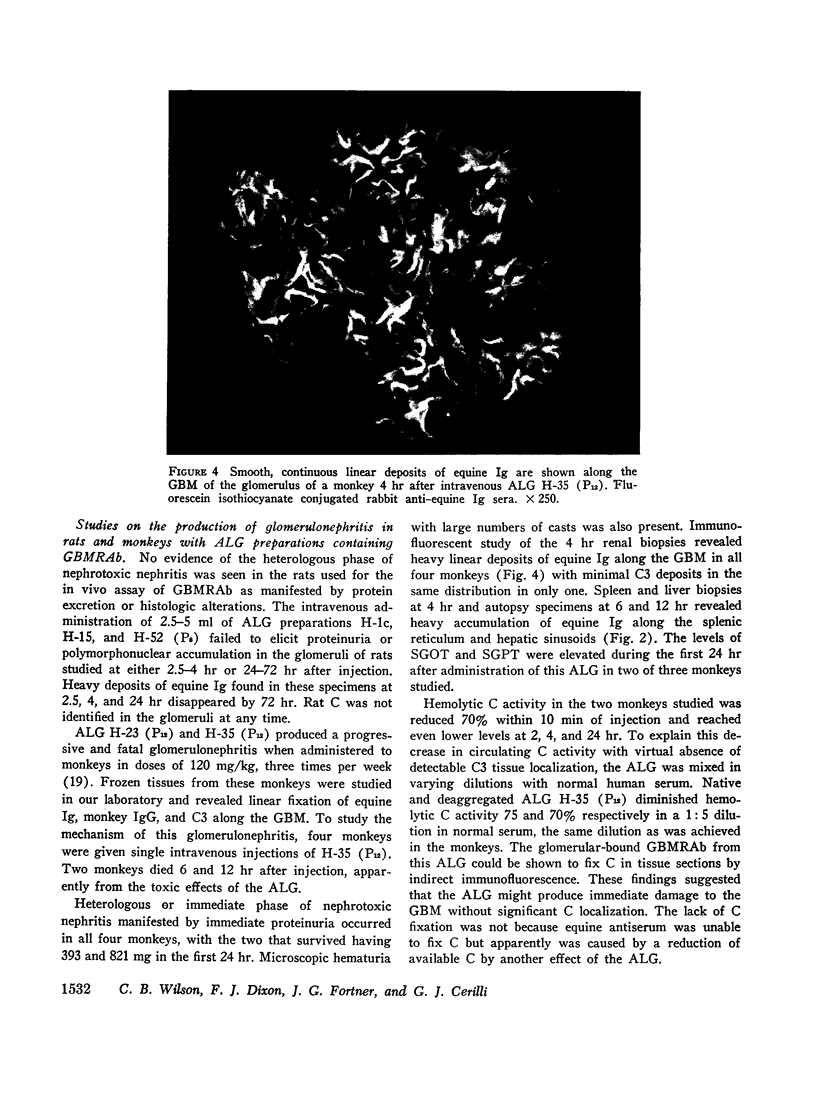
An equine anti-human thymus serum containing glomerular basement membrane-reactive antibodies, which produced fatal glomerulonephritis in monkeys, was shown to cause both immediate and delayed glomerular injury in monkeys after intravenous injection. The reaction of this antibody with glomerular basement membrane in vivo was associated with little complement deposition in spite of the fact that the antibody could fix complement. This lack of glomerular complement fixation resulted from almost complete in vivo decomplementation of the monkeys receiving this anti-lymphocyte globulin.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balner H., Eysvoogel V. P., Cleton F. J. Testing of anti-human lymphocyte sera in chimpanzees and lower primates. Lancet. 1968 Jan 6;1(7532):19–22. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., KAPLAN M. H. Localization of antigen in tissue cells; improvements in a method for the detection of antigen by means of fluorescent antibody. J Exp Med. 1950 Jan 1;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. J., de Vries M. J., van Noord M. J., Lubbe F. H. Strain-specific renal toxicity of heterologous antilymphocyte gamma-globulin in mice. Transplantation. 1970 Jul;10(1):1–19. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197007000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diethelm A. G., Busch G. J., Dubernard J. M., Orr W. M., Glassock R. J., Birtch A. G., Murray J. E. Prolongation of canine renal allografts by horse anti-dog lymphocyte serum and globulin. Ann Surg. 1969 Apr;169(4):569–577. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196904000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortner J. G., Shiu M. H., Balner H., Wilson C. B., Sichuk G., Kawano N., Holmes J. T., Beattie E. J., Jr Observations on prolonged immune suppression for human liver homografts. Transplant Proc. 1971 Mar;3(1):383–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttmann R. D., Carpenter C. B., Lindquist R. R., Merrill J. P. Renal transplantation in the inbred rat. 3. A study of heterologous anti-thymocyte sera. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):1099–1126. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttmann R. D., Carpenter C. B., Lindquist R. R., Merrill J. P. Treatment with heterologous anithymus sera: nephritis associated with modification of renal allograft rejection and the immune status of the host to the foreign protein. Transplantation. 1967 Jul;5(4 Suppl):1115–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki Y., Porter K. A., Amend J. R., Marchioro T. L., Zühlke V., Starzl T. E. The preparation and testing of horse antidog and antihuman antilymphoid plasma or serum and its protein fractions. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1967 Jan;124(1):1–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAKOWER C. A., GREENSPON S. A. Localization of the nephrotoxic antigen within the isolated renal glomerulus. AMA Arch Pathol. 1951 Jun;51(6):629–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwagi N., Brantigan C. O., Brettschneider L., Groth C. G., Starzl T. E. Clinical reactions and serologic changes after the administration of heterologous antilymphocyte globulin to human recipients of renal homografts. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Feb;68(2):275–286. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-2-275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Unanue E. R., Dixon F. J. Nephritogenic properties of cross-reacting kidney-fixing antibodies to heart, spleen and muscle. J Immunol. 1967 Feb;98(2):260–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. The role of anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody in the pathogenesis of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):989–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist R. R., Guttmann R. D., Carpenter C. B., Merrill J. P. Nephritis induced by antilymphocyte serum. An electron microscopic and immunohistochemical study. Transplantation. 1969 Nov;8(5):545–557. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196911000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Wood M. L., Russell P. S. Some effects of purified heterologous antihuman lymphocyte serum in man. Transplantation. 1967 Jul;5(4 Suppl):1106–1114. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196707001-00046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moppert J., Thiel G., Mahlich J., Bühler F., Vischer T., Enderlin F., Weber H., Zollinger H. U. Glomerular damage after intravenous administration of antilymphocyte globulin (ALG) in man and rhesus monkeys. Transplant Proc. 1971 Mar;3(1):741–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W. M., Birtch A. G., Diethelm A. G., Dubernard J. M., Duquella J., Glassock R. J. A study of the potential nephrotoxicity of heterologous anti-lymphocyte serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Feb;6(2):305–311. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESSMAN D., DAY E. D., BLAU M. The use of paired labeling in the determination of tumor-localizing antibodies. Cancer Res. 1957 Oct;17(9):845–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Studies on the renal glomerular basement membrane. Preparation and chemical composition. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1915–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traeger J., Fries D., Revillard J. P., Brochier J., Brunat-Blanc N. Antilymphocyte globulins in kidney transplantation: effects on glomerular disease. Transplant Proc. 1969 Dec;1(4):1006–1012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Dixon F. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis: immunological events and pathogenetic mechanisms. Adv Immunol. 1967;6:1–90. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60521-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODRUFF M. F., ANDERSON N. A. EFFECT OF LYMPHOCYTE DEPLETION BY THORACIC DUCT FISTULA AND ADMINISTRATION OF ANTILYMPHOCYTIC SERUM ON THE SURVIVAL OF SKIN HOMOGRAFTS IN RATS. Nature. 1963 Nov 16;200:702–702. doi: 10.1038/200702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. Antigen quantitation in experimental immune complex glomerulonephritis. I. Acute serum sickness. J Immunol. 1970 Aug;105(2):279–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]