Abstract
The influence of alcohol on albumin synthesis was studied in the isolated perfused rabbit liver. Carbonate-14C was used to label the intracellular arginine pool which serves as the precursor of both the carbon of urea and the guanido carbon of arginine in albumin. The control group synthesized albumin at a rate of 33 mg/100 g of wet liver weight during 2.5 hr of perfusion. When alcohol, 220 mg/100 ml, was added to the perfusate, albumin synthesis decreased to between 7 and 11 mg, less than one-third the control rate. The addition of 10 mM tryptophan to perfusates containing alcohol prevented most of the inhibitory effects and albumin synthesis increased to average 24 mg. Further, the addition of alcohol to the perfusate decreased the hepatic protein/DNA ratio from 70 to 54 and the RNA/DNA ratio from 2.3 to 1.8, changes equivalent to those seen after a 24 hr fast. The addition of tryptophan to the perfusate prevented these findings in both instances.
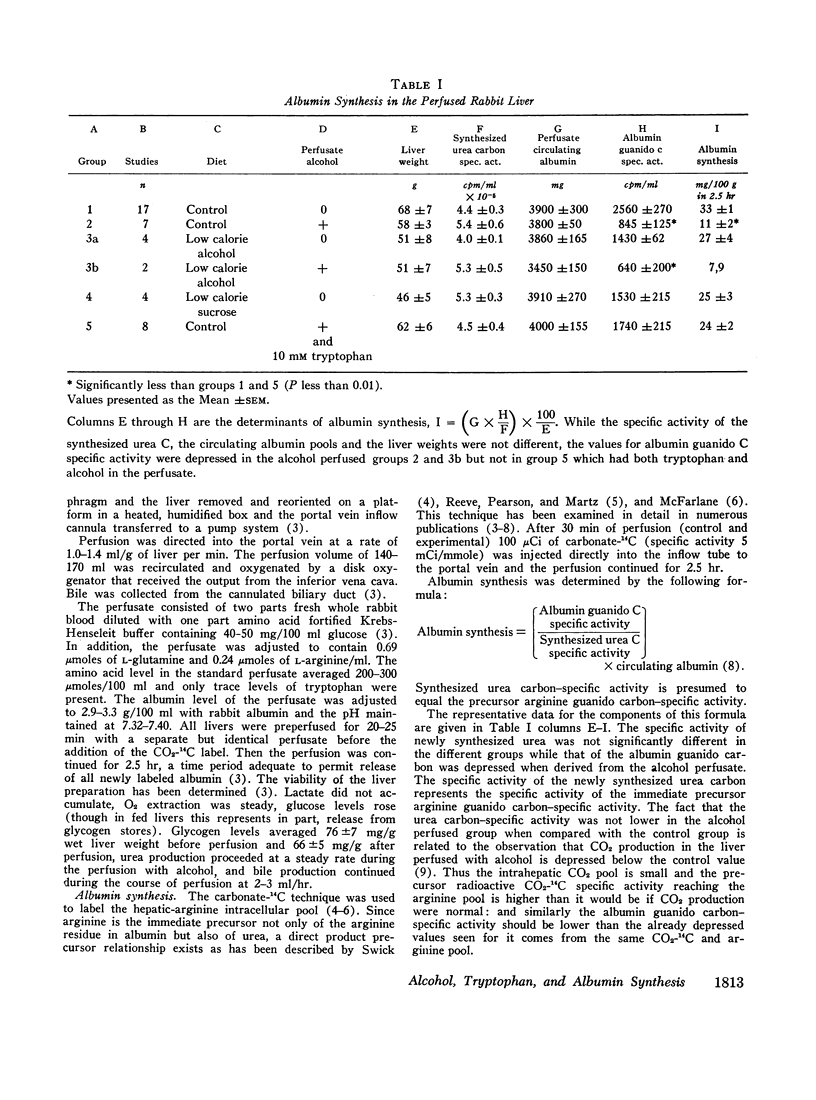
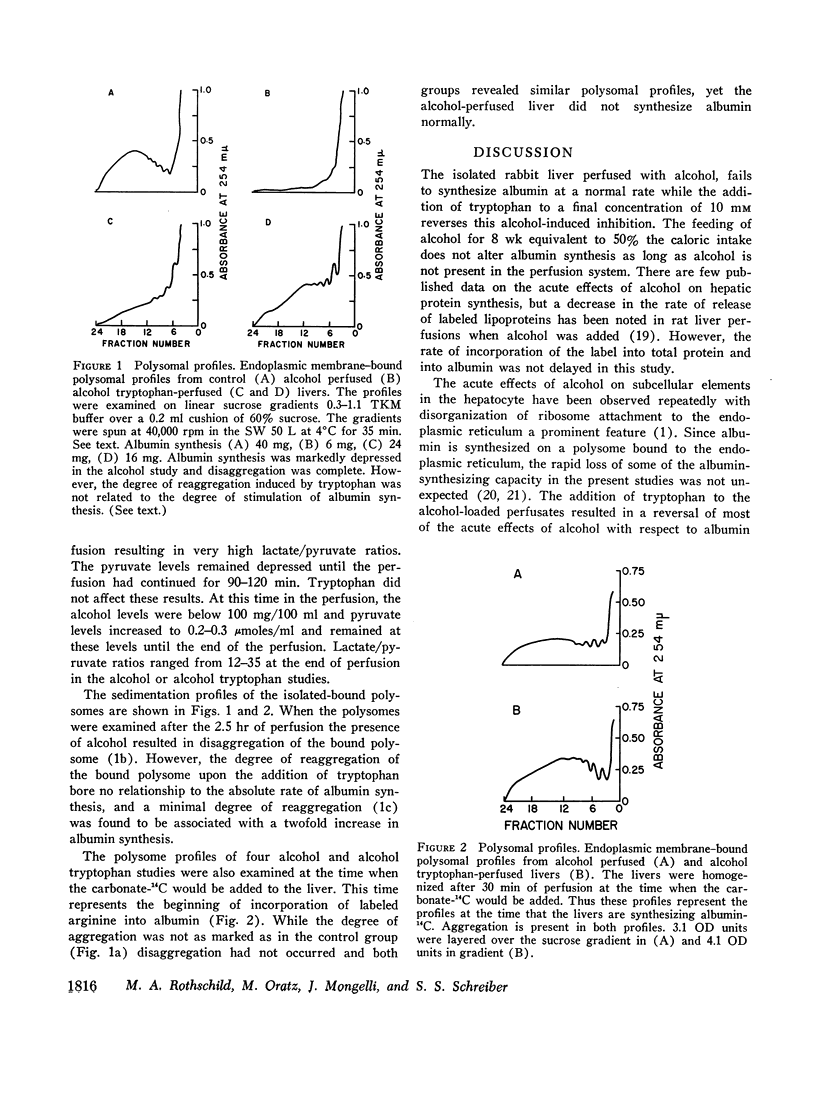
Endoplasmic membrane-bound polysomes were examined for aggregation. Alcohol decreased the quantity of heavier aggregates. Reaggregation occurred when tryptophan was added but quantitative changes in albumin synthesis could not be related to the degree of reaggregation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Ribosomes in rat liver: an estimate of the percentage of free and membrane-bound ribosomes interacting with messenger RNA in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1967 Sep 28;28(3):539–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. N., Serck-Hanssen G., Lowe E. Studies on the protein-synthesizing activity of the ribosomes of rat liver. The activity of free polysomes. Biochem J. 1965 Nov;97(2):422–431. doi: 10.1042/bj0970422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway E. J., Byrne A. An absorption apparatus for the micro-determination of certain volatile substances: The micro-determination of ammonia. Biochem J. 1933;27(2):419–429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELD J. B., WILLIAMS H. E., MORTIMORE G. E. Studies on the mechanism of ethanol-induced hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1963 Apr;42:497–506. doi: 10.1172/JCI104738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleck A., Begg D. The estimation of ribonucleic acid using ultraviolet absorption measurements. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 8;108(3):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks S. J., Drysdale J. W., Munro H. N. Preferential synthesis of ferritin and albumin by different populations of liver polysomes. Science. 1969 May 2;164(3879):584–585. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3879.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISSELBACHER K. J., GREENBERGER N. J. METABOLIC EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON THE LIVER. N Engl J Med. 1964 Feb 13;270:351–CONTD. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196402132700707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KECK K. An ultramicro technique for the determination of deoxypentose nucleic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Aug;63(2):446–451. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBER C. S., SCHMID R. The effect of ethanol on fatty acid metabolism; stimulation of hepatic fatty acid synthesis in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1961 Feb;40:394–399. doi: 10.1172/JCI104266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCFARLANE A. S. MEASUREMENT OF SYNTHESIS RATES OF LIVER-PRODUCED PLASMA PROTEINS. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:277–290. doi: 10.1042/bj0890277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N. Role of amino acid supply in regulating ribosome function. Fed Proc. 1968 Sep-Oct;27(5):1231–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVE E. B., PEARSON J. R., MARTZ D. C. Plasma protein synthesis in the liver: method for measurement of albumin formation in vivo. Science. 1963 Mar 8;139(3558):914–916. doi: 10.1126/science.139.3558.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REITMAN S., FRANKEL S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957 Jul;28(1):56–63. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/28.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHSCHILD M. A., SCHREIBER S. S., ORATZ M., McGEE H. L. The effects of adrenocortical hormones on albumin metabolism studied with albumin-I 131. J Clin Invest. 1958 Sep;37(9):1229–1235. doi: 10.1172/JCI103711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild M. A., Oratz M., Mongelli J., Fishman L., Schreiber S. S. Amino acid regulation of albumin synthesis. J Nutr. 1969 Aug;98(4):395–403. doi: 10.1093/jn/98.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild M. A., Oratz M., Mongelli J., Schreiber S. S. Effects of a short-term fast on albumin synthesis studied in vivo, in the perfused liver, and on amino acid incorporation by hepatic microsomes. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2591–2599. doi: 10.1172/JCI105941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild M. A., Oratz M., Zimmon D., Schreiber S. S., Weiner I., Van Caneghem A. Albumin synthesis in cirrhotic subjects with ascites studied with carbonate-14C. J Clin Invest. 1969 Feb;48(2):344–350. doi: 10.1172/JCI105990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E., Lieber C. S. Alcohol-induced hepatic injury in nonalcoholic volunteers. N Engl J Med. 1968 Apr 18;278(16):869–876. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196804182781602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWICK R. W. Measurement of protein turnover in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1958 Apr;231(2):751–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salaspuro M. P., Mäenpä P. H. Influence of ethanol on the metabolism of perfused normal, fatty and cirrhotic rat livers. Biochem J. 1966 Sep;100(3):768–778. doi: 10.1042/bj1000768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidransky H., Sarma D. S., Bongiorno M., Verney E. Effect of dietary tryptophan on hepatic polyribosomes and protein synthesis in fasted mice. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1123–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavill A. S., Craigie A., Rosenoer W. M. The measurement of the synthetic rate of albumin in man. Clin Sci. 1968 Feb;34(1):1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Lund P., Krebs H. A. The redox state of free nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of rat liver. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):514–527. doi: 10.1042/bj1030514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuwiler A., Wetterberg L., Geller E. Alterations in induction of tyrosine aminotransferase and tryptophan oxygenase by glucose pretreatment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun;208(3):428–433. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90215-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


