Abstract
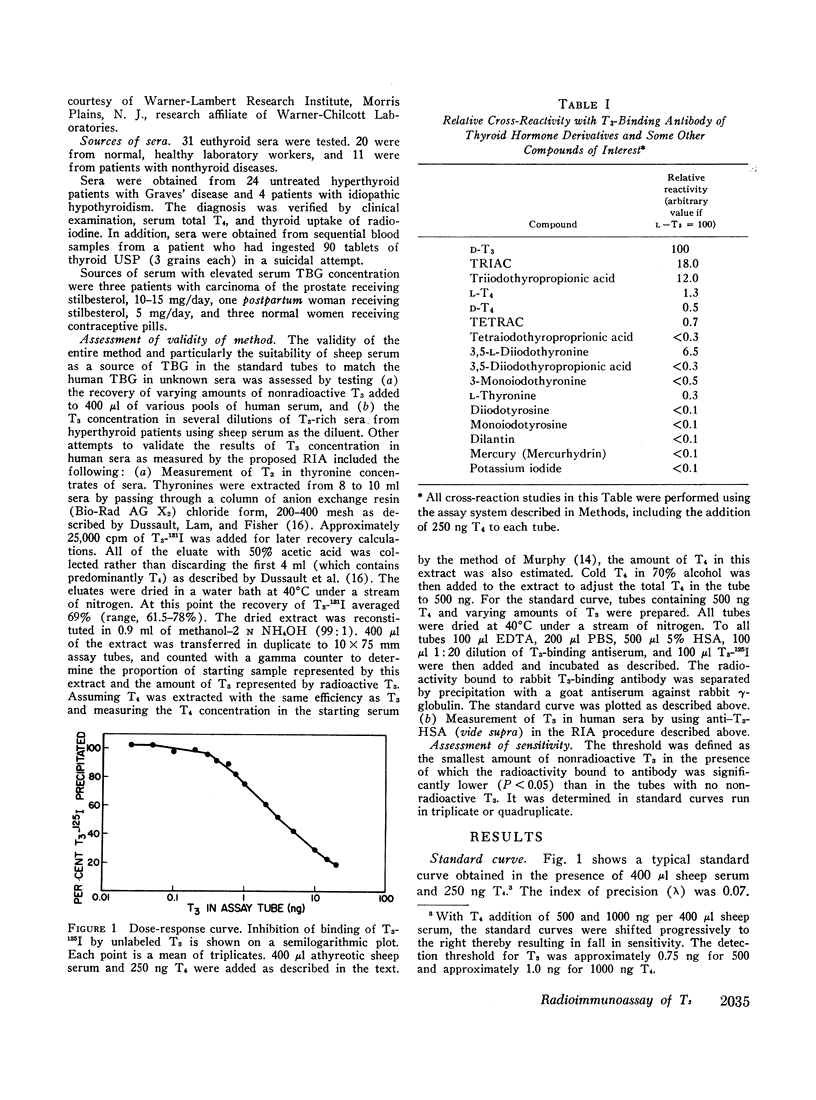
A convenient, specific, precise, and reproducible radioimmunoassay system for measurement of triiodothyronine (T3) in human serum has been developed. The procedure compares the ability of standards and unknowns to compete with radioactive T3 for binding sites on a T3-binding antiserum produced in rabbits by immunization with human thyroglobulin. The assay is set up in the presence of 250 ng thyroxine (T4) in all tubes, to mobilize T3 from its binding with the thyronine-binding globulin (TBG), and athyreotic sheep serum in standards to correct for the TBG in the unknowns. The method regularly detected 0.4 ng T3, which would correspond to a T3 concentration of 100 ng/100 ml when 400 μl of serum is analyzed. The mean recovery of unlabeled T3 added to normal serum pools was 106%. Serial dilution of hyperthyroid sera containing high concentrations of T3 with athyreotic sheep serum yielded expected values.
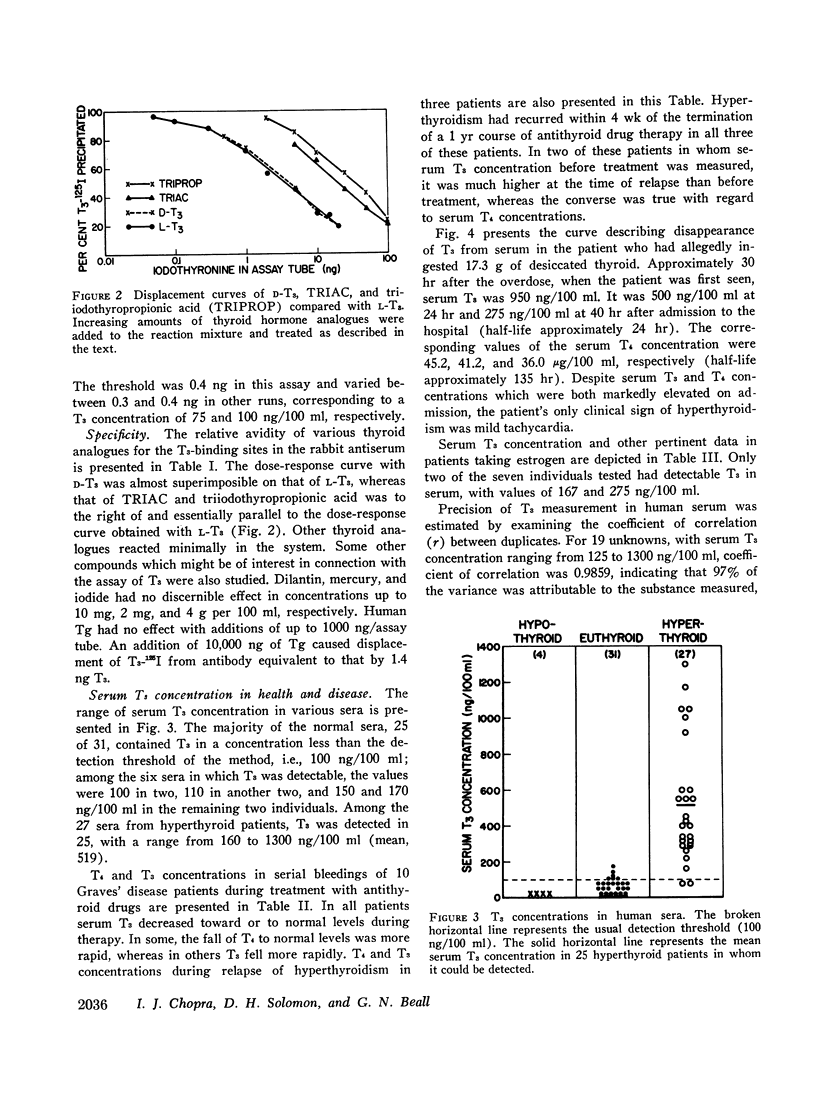
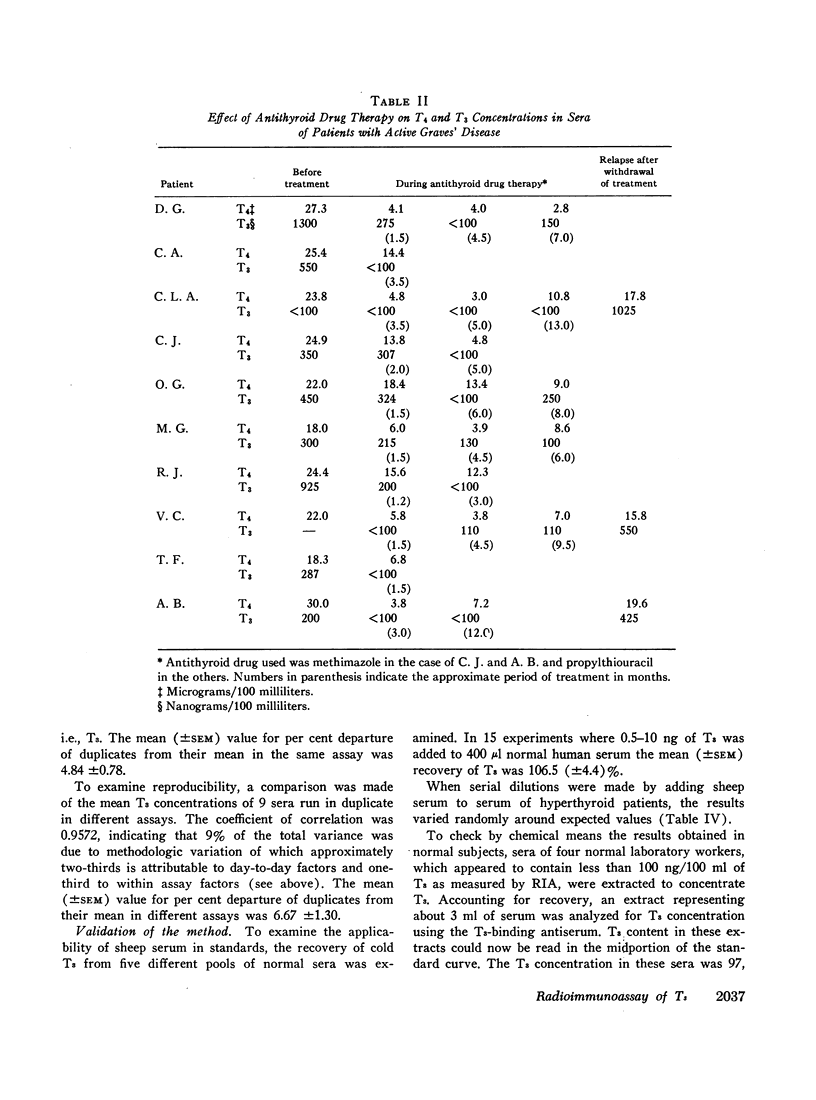
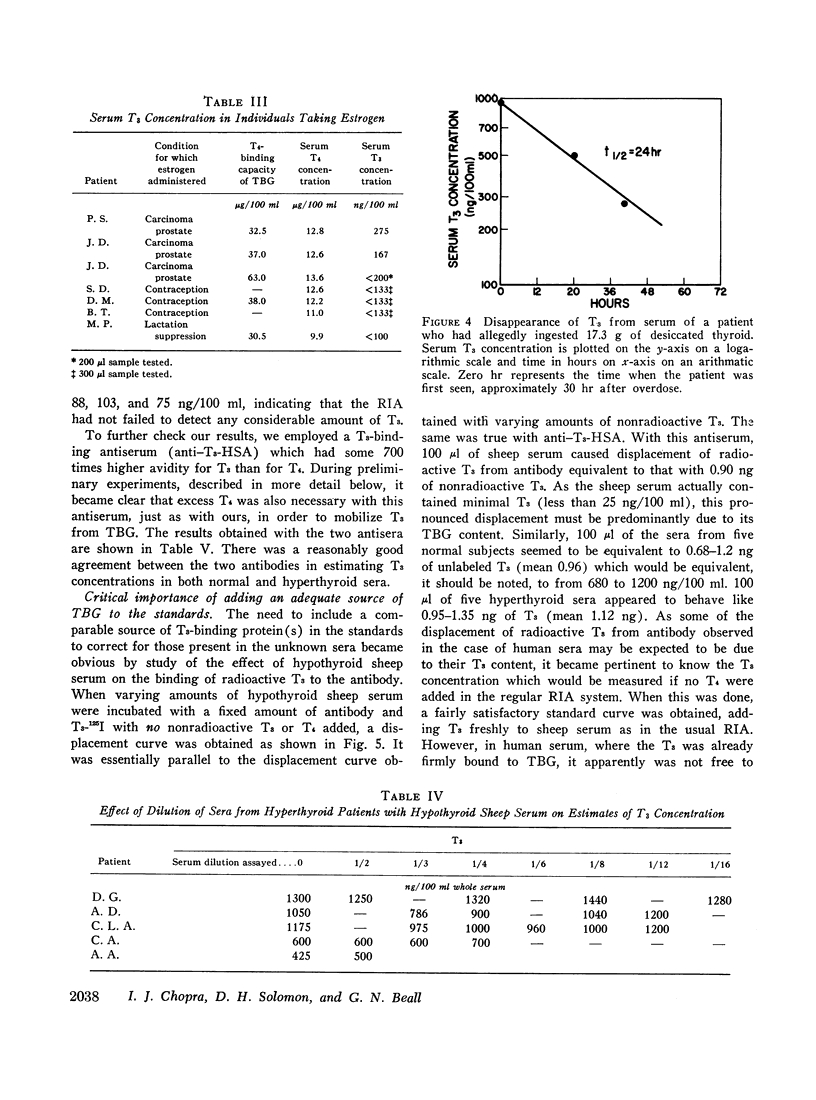
The serum T3 concentration in 80% of 31 euthyroid normal subjects was less than 100 ng/100 ml (range < 100-170 ng/100 ml); it was greater than 170 ng/100 ml in 89% of 27 sera of hyperthyroid patients with untreated Graves' disease (range < 100-1300, mean 519 in 25 sera with detectable T3). The concentration of serum T3 fell, frequently to undetectable levels, during treatment of hyperthyroid patients with antithyroid drugs. The serum T3 concentration in four hypothyroid patients was less than 100 ng/100 ml.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braverman L. E., Ingbar S. H., Sterling K. Conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3) in athyreotic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):855–864. doi: 10.1172/JCI106304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Nelson J. C., Solomon D. H., Beall G. N. Production of antibodies specifically binding triiodothyronine and thyroxine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Mar;32(3):299–308. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-3-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dussault J. H., Lam R., Fisher D. A. The measurement of serum triiodothyronine by double column chromatography. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jun;77(6):1039–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A., Dussault J. H. Contribution of methodological artifacts to the measurement of T3 concentration in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 May;32(5):675–679. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-5-675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., PITT-RIVERS R., TROTTER W. R. Effect of 3:5:3'-L-triiodothyronine in myxoedema. Lancet. 1952 May 24;1(6717):1044–1045. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)90695-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharib H., Mayberry W. E., Ryan R. J. Radioimmunoassay for triiodothyronine: A preliminary report. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Dec;31(6):709–712. doi: 10.1210/jcem-31-6-709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander C. S. On the nature of the circulating thyroid hormone: clinical studies of triiodothyronine and thyroxine in serum using gas chromatographic methods. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1968;81:76–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H. Observations concerning the binding of thyroid hormones by human serum prealbumin. J Clin Invest. 1963 Feb;42:143–160. doi: 10.1172/JCI104701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inada M., Sterling K. Thyroxine transport in thyrotoxicosis and hypothyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1967 Sep;46(9):1442–1450. doi: 10.1172/JCI105636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERMAN J. The physiologic activity of l-triiodothyronine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1953 Nov;13(11):1341–1346. doi: 10.1210/jcem-13-11-1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. E., Pattee C. J., Gold A. Clinical evaluation of a new method for the determination of serum thyroxine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Mar;26(3):247–256. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-3-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauman J. A., Nauman A., Werner S. C. Total and free triiodothyronine in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1967 Aug;46(8):1346–1355. doi: 10.1172/JCI105627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oddie T. H., Meade J. H., Jr, Fisher D. A. An analysis of published data on thyroxine turnover in human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Apr;26(4):425–436. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-4-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., Robin N. I., Fang V. S. Parameters of thyroid function in serum of 16 selected vertebrate species: a study of PBI, serum T4, free T4, and the pattern of T4 and T3 binding to serum proteins. Endocrinology. 1970 Apr;86(4):793–805. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-4-793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Bellabarba D., Newman E. S., Brenner M. A. Determination of triiodothyronine concentration in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jun;48(6):1150–1158. doi: 10.1172/JCI106072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A., Newman E. S. Conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in normal human subjects. Science. 1970 Sep 11;169(3950):1099–1100. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3950.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Refetoff S., Selenkow H. A. T3 thyrotoxicosis. Thyrotoxicosis due to elevated serum triiodothyronine levels. JAMA. 1970 Jul 27;213(4):571–575. doi: 10.1001/jama.213.4.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woeber K. A., Sobel R. J., Ingbar S. H., Sterling K. The peripheral metabolism of triiodothyronine in normal subjects and in patients with hyperthyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):643–649. doi: 10.1172/JCI106275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



