Abstract
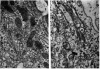
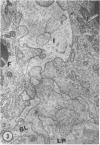
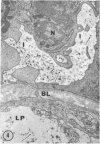
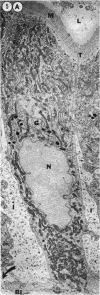
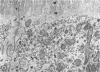
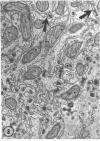
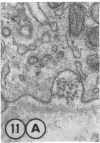
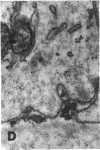
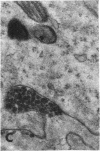
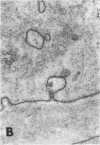
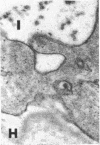
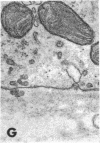
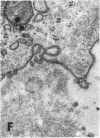
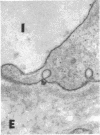
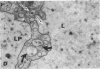
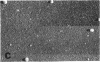
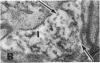
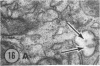
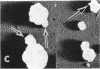
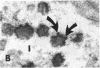
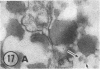
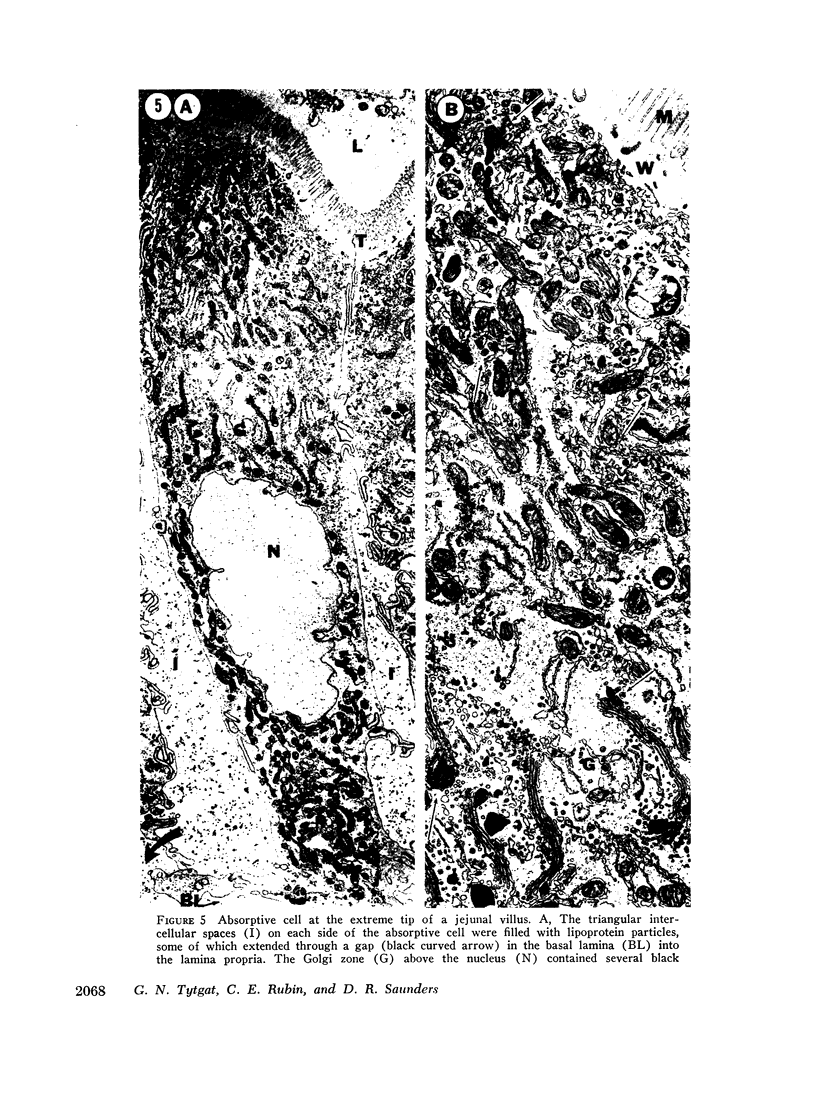
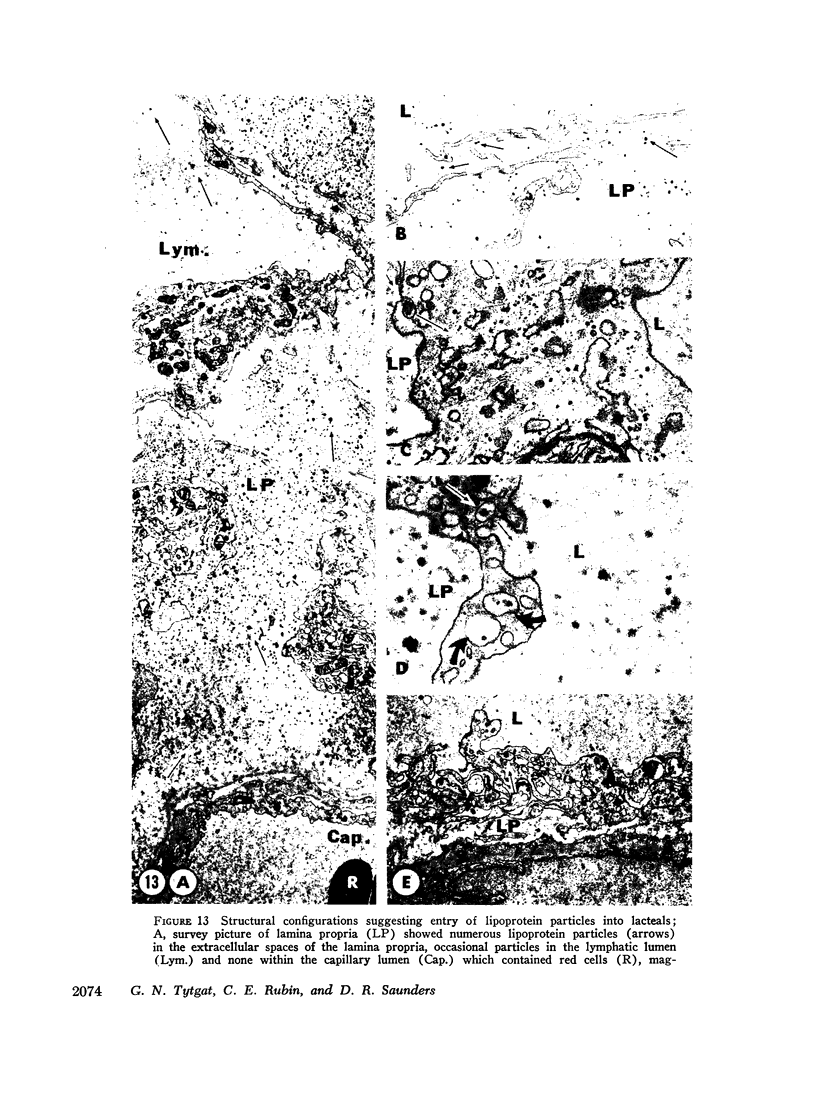
The site of synthesis and some new details of lipoprotein particle transport have been demonstrated within the jejunal mucosa of man. In normal fasting volunteers, lipoprotein particles (88%, 150-650 A diameter) were visualized within the smooth endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi cisternae of absorptive cells covering the tips of jejunal villi. Electron microscopic observations suggested that these particles exited through the sides and bases of absorptive cells by reverse pinocytosis and then passed through the extracellular matrix of the lamina propria to enter lacteal lumina.
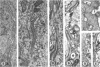
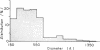
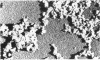
When these lipid particles were isolated from fasting intestinal biopsies by preparative ultracentrifugation, their size distribution was similar to that of very low density (Sf 20-400) lipoprotein (VLDL) particles in plasma.
After a fatty meal, jejunal absorptive cells and extracts of their homogenates contained lipid particles of VLDL-size as well as chylomicrons of various sizes. The percentage of triglyceride in isolated intestinal lipid particles increased during fat absorption. Our interpretation of these data is that chylomicrons are probably derived from intestinal lipoprotein particles by addition of triglyceride.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRANDBORG L. L., RUBIN G. E., QUINTON W. E. A multipurpose instrument for suction biopsy of the esophagus, stomach, small bowel, and colon. Gastroenterology. 1959 Jul;37(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. Origin and characteristics of endogenous lipid in thoracic duct lymph in rat. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jan;7(1):158–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierman E. L., Hayes T. L., Hawkins J. N., Ewing A. M., Lindgren F. T. Particle-size distribution of very low density plasma lipoproteins during fat absorption in man. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jan;7(1):65–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASLEY-SMITH J. R. The identification of chylomicra and lipoproteins in tissue sections and their passage into jejunal lacteals. J Cell Biol. 1962 Nov;15:259–277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.15.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLICK A. L., QUINTON W. E., RUBIN C. E. A peroral hydraulic biopsy tube for multiple sampling at any level of the gastro-intestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1961 Jan;40:120–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson D. S., Levy R. I., Lees R. S. Fat transport in lipoproteins--an integrated approach to mechanisms and disorders. N Engl J Med. 1967 Jan 19;276(3):148–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196701192760305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Levy R. I., Rosenthal A. S., Birnbaumer M. E., Fredrickson D. S. The structure and properties of human beta-lipoprotein and beta-apoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jun 10;31(5):699–705. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90618-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYES T. L., HEWITT J. E. Visualization of individual lipoprotein macromolecules in the electron microscope. J Appl Physiol. 1957 Nov;11(3):425–428. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.11.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYES T. L., LINDGREN F. T., GOFMAN J. W. A QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF THE OSMIUM TETROXIDE-LIPOPROTEIN INTERACTION. J Cell Biol. 1963 Oct;19:251–255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.19.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch F. T., Aso Y., Hagopian L. M., Rubenstein J. J. Biosynthesis of lipoprotein by rat intestinal mucosa. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 25;241(8):1655–1665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazzard W. R., Lindgren F. T., Bierman E. L. Very low density lipoprotein subfractions in a subject with broad-beta disease (Type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia) and a subject with endogenous lipemia (Type IV). Chemical composition and electrophoretic mobility. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 5;202(3):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90122-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher G., West G. R., Brindley D. N. Studies on the fractionation of mucosal homogenates from the small intestine. Biochem J. 1965 Dec;97(3):629–642. doi: 10.1042/bj0970629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISSELBACHER K. J., BUDZ D. M. SYNTHESIS OF LIPOPROTEINS BY RAT INTESTINAL MUCOSA. Nature. 1963 Oct 26;200:364–365. doi: 10.1038/200364b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Price J. M. Some methods of electron microscopic visualization of lipoproteins in plasma and chyle. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 May;16(5):366–370. doi: 10.1177/16.5.366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., TRAUTMAN R. The alpha2 lipoproteins of human serum; correlation of ultracentrifugal and electrophoretic properties. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jun;35(6):641–648. doi: 10.1172/JCI103320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lossow W. J., Lindgren F. T., Murchio J. C., Stevens G. R., Jensen L. C. Particle size and protein content of six fractions of the Sf 20 plasma lipoproteins isolated by density gradient centrifugation. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):68–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra D. N., Das Gupta N. N. Distortion in dimensions produced by shadowing for electron microscopy. J R Microsc Soc. 1965 Sep;84(3):373–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols A. V. Functions and interrelationships of different classes of plasma lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1128–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Hughes F. B., Isselbacher K. J. Very low density lipoproteins in intestinal lymph: origin, composition, and role in lipid transport in the fasting state. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2079–2088. doi: 10.1172/JCI106174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Jones A. L. An electron microscopic and functional study of very low density lipoproteins in intestinal lymph. J Lipid Res. 1970 Jul;11(4):284–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter H. P., Saunders D. R., Tytgat G., Brunser O., Rubin C. E. Fat absorption in bile fistula man. A morphological and biochemical study. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jun;60(6):1008–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., JARETT L., FINKE E. H. Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1960 Nov;35:313–323. doi: 10.3109/10520296009114754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBLUTH J. Contrast between osmium-fixed and permanganate-fixed toad spinal ganglia. J Cell Biol. 1963 Jan;16:143–157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers J. B., Riley E. M., Drummey G. D., Isselbacher K. J. Lipid absorption in adrenalectomized rats: the role of altered enzyme activity in the intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1967 Oct;53(4):547–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roheim P. S., Gidez L. I., Eder H. A. Extrahepatic synthesis of lipoproteins of plasma and chyle: role of the intestine. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):297–300. doi: 10.1172/JCI105343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. E. Electron microscopic studies of triglyceride absorption in man. Gastroenterology. 1966 Jan;50(1):65–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders D. R., Ways P. O., Parmentier C. M., Rubin C. E. Studies on the lipid composition of human small bowel mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1966 Sep;45(9):1516–1525. doi: 10.1172/JCI105458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava B. K., Redgrave T. G., Simmonds W. J. The source of endogenous lipid in the thoracic duct lymph of fasting rats. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1967 Jul;52(3):305–312. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1967.sp001916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD R. L., LUFT J. H. THE INFLUENCE OF BUFFER SYSTEMS ON FIXATION WITH OSMIUM TETROXIDE. J Ultrastruct Res. 1965 Feb;12:22–45. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(65)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Levy R. I. Production of beta-lipoprotein by intestine in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 25;243(18):4878–4884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]