Abstract
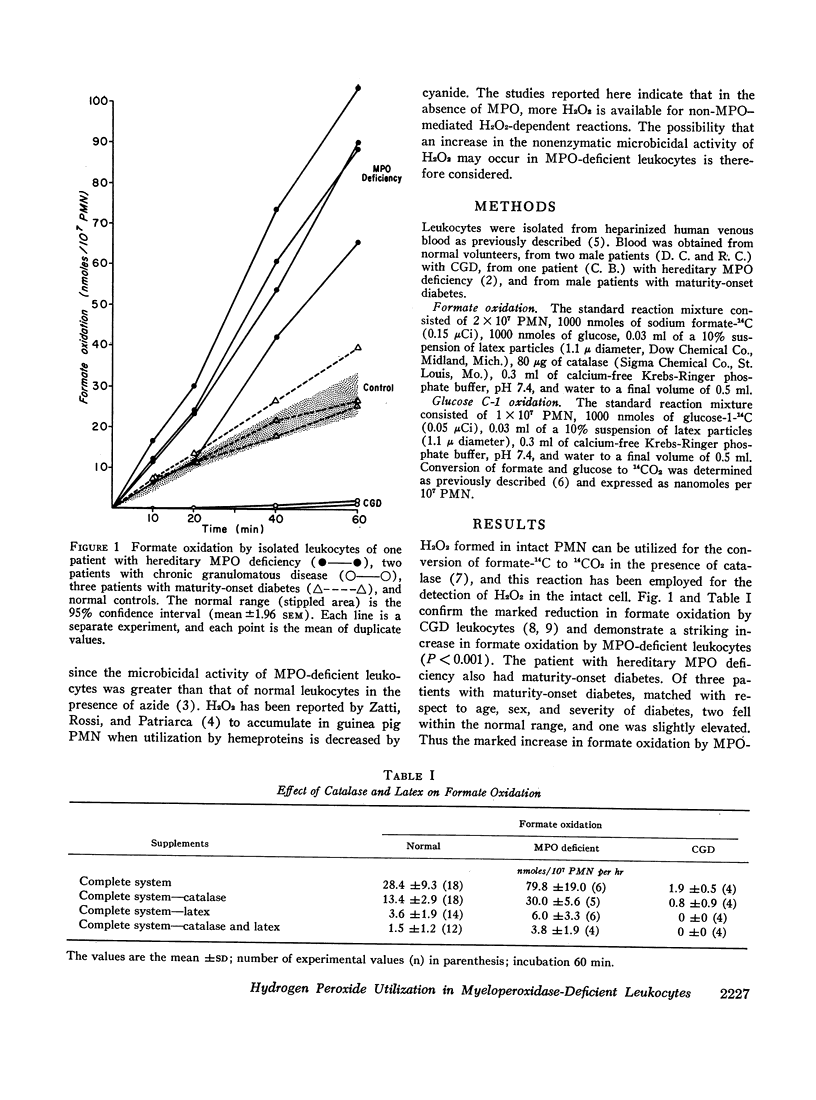
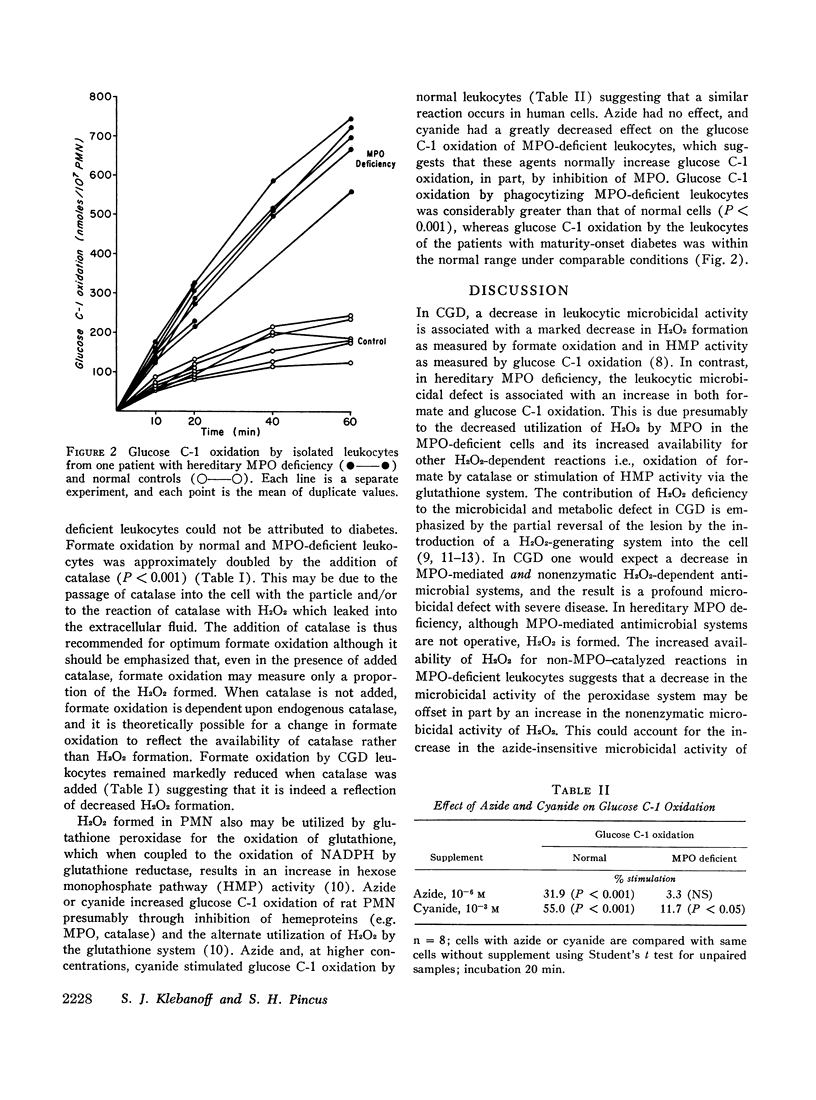
Phagocytosis-induced formate and glucose C-1 oxidation by the polymorphonuclear leukocytes of a patient with hereditary myeloperoxidase deficiency was considerably greater than normal. The addition of catalase to the leukocyte suspension was required for optimum formate oxidation. Azide and cyanide increased glucose C-1 oxidation by normal leukocytes but had little or no effect on myeloperoxidase-deficient leukocytes suggesting that these agents normally stimulate glucose C-1 oxidation, in part, by inhibition of myeloperoxidase. It is suggested that the inhibition or absence of myeloperoxidase results in an increased utilization of H2O2 in nonmyeloperoxidase-mediated H2O2-dependent reactions such as formate oxidation and hexose monophosphate pathway activation. The possibility of a microbicidal control mechanism in which a decrease in the microbicidal activity of myeloperoxidase is offset, in part, by an increase in the nonenzymatic microbicidal activity of H2O2 is considered.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehner R. L., Nathan D. G., Karnovsky M. L. Correction of metabolic deficiencies in the leukocytes of patients with chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):865–870. doi: 10.1172/JCI106305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Page A. R., Good R. A. Studies of the metabolic activity of leukocytes from patients with a genetic abnormality of phagocytic function. J Clin Invest. 1967 Sep;46(9):1422–1432. doi: 10.1172/JCI105634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Baehner R. L. Improvement of leukocyte bactericidal activity in chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1970 Mar;35(3):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Intraleukocytic microbicidal defects. Annu Rev Med. 1971;22:39–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.22.020171.000351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase: contribution to the microbicidal activity of intact leukocytes. Science. 1970 Sep 11;169(3950):1095–1097. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3950.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Smith D. C. The source of H2O2 for the uterine fluid-mediated sperm-inhibitory system. Biol Reprod. 1970 Oct;3(2):236–242. doi: 10.1093/biolreprod/3.2.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., White L. R. Iodination defect in the leukocytes of a patient with chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. N Engl J Med. 1969 Feb 27;280(9):460–466. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196902272800902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Leukocyte myeloperoxidase deficiency and disseminated candidiasis: the role of myeloperoxidase in resistance to Candida infection. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1478–1488. doi: 10.1172/JCI106114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L., Hook E. W. Leukocyte bactericidal activity in chronic granulomatous disease: correlation of bacterial hydrogen peroxide production and susceptibility to intracellular killing. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):531–532. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.531-532.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Klebanoff S. J. Quantitative leukocyte iodination. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 8;284(14):744–750. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104082841402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W. Glutathione and the hexose monophosphate shunt in phagocytizing and hydrogen peroxide-treated rat leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2459–2464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatti M., Rossi F., Patriarca P. The H2O2-production by polymorphonuclear leukocytes during phagocytosis. Experientia. 1968 Jul 15;24(7):669–670. doi: 10.1007/BF02138302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



