Abstract
The process by which various anions, including bilirubin and several dyes, drugs, hormones and their metabolites, are transferred from plasma into the liver cell is poorly understood. Two hepatic cytoplasmic proteins, Y and Z, that bind various organic anions in vivo and in vitro have been postulated to be involved in this process.
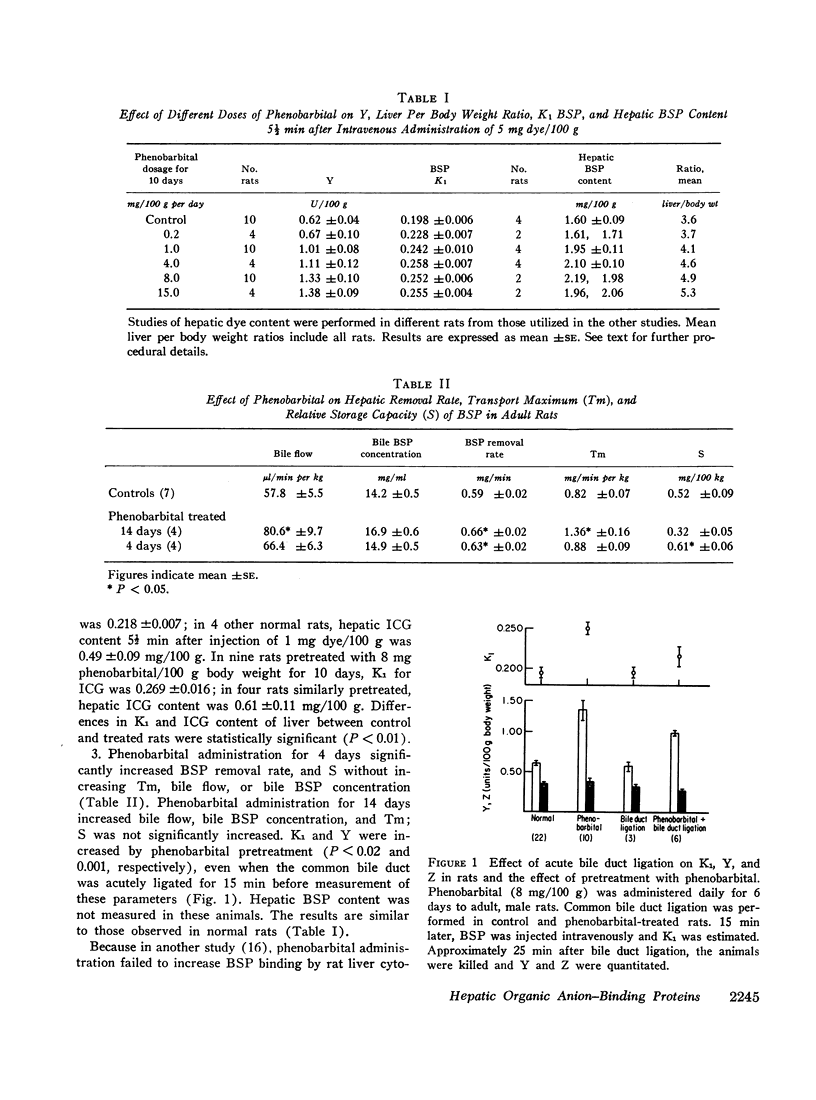
The concentration of Y, the major organic anion-binding protein, increases in rat liver after administration of phenobarbital in association with enhanced organic anion transfer from plasma into liver as determined by initial plasma disappearance rate (K1) and hepatic dye content for sulfobromophthalein (BSP) and indocyanine green (ICG), as well as increased relative hepatic storage of BSP. Acute bile duct ligation failed to alter plasma disappearance or hepatic content of BSP in normal or phenobarbital-treated rats.
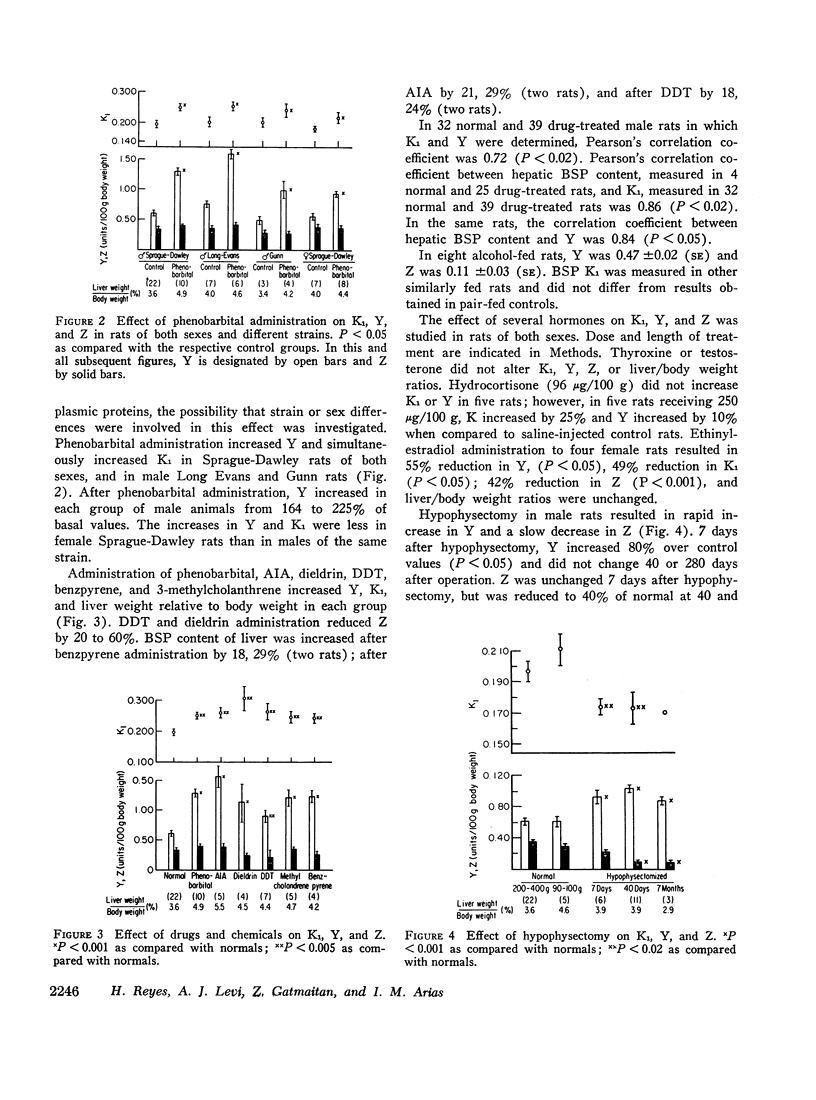
Other drugs and chemicals which cause proliferation of hepatic smooth endoplasmic reticulum and enhancement of drug metabolism, such as allylisopropylacetamide, dieldrin, DDT, 3-methylcholanthrene, and benzpyrene increased Y and BSP K1 and, where studied, hepatic BSP content. Alcohol feeding had no effect on Y, Z, or K1 for BSP.
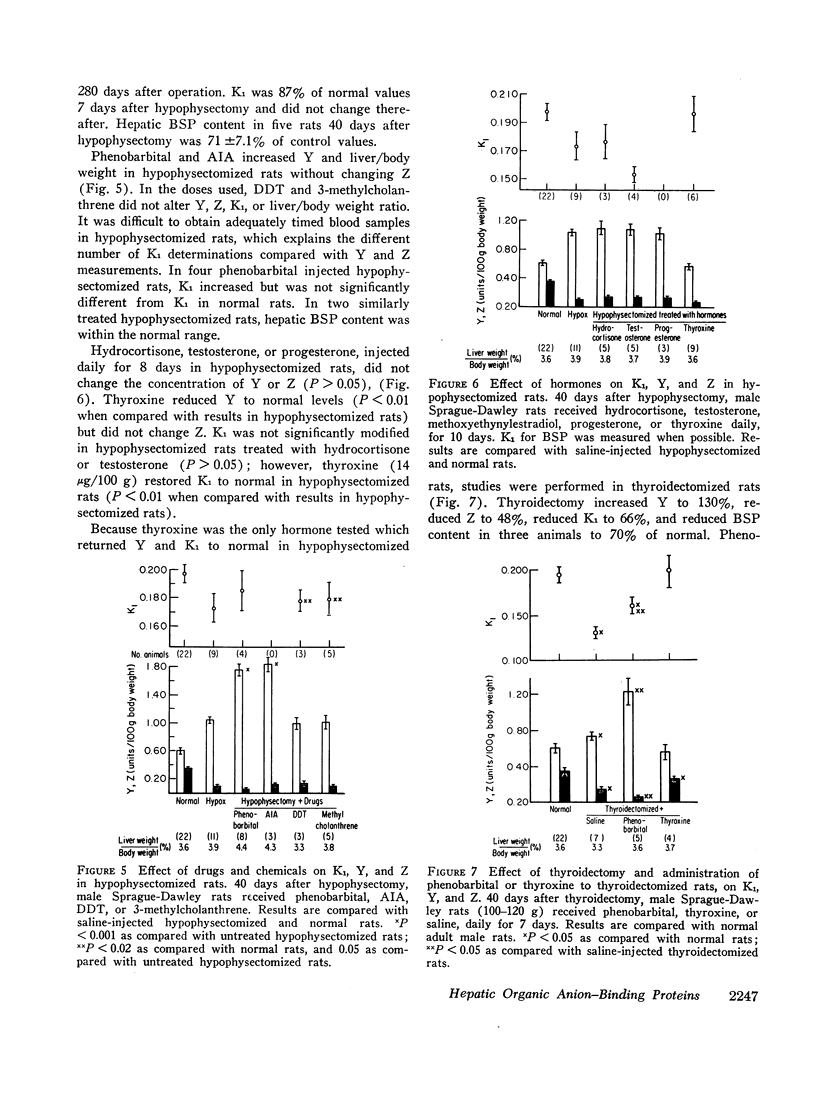
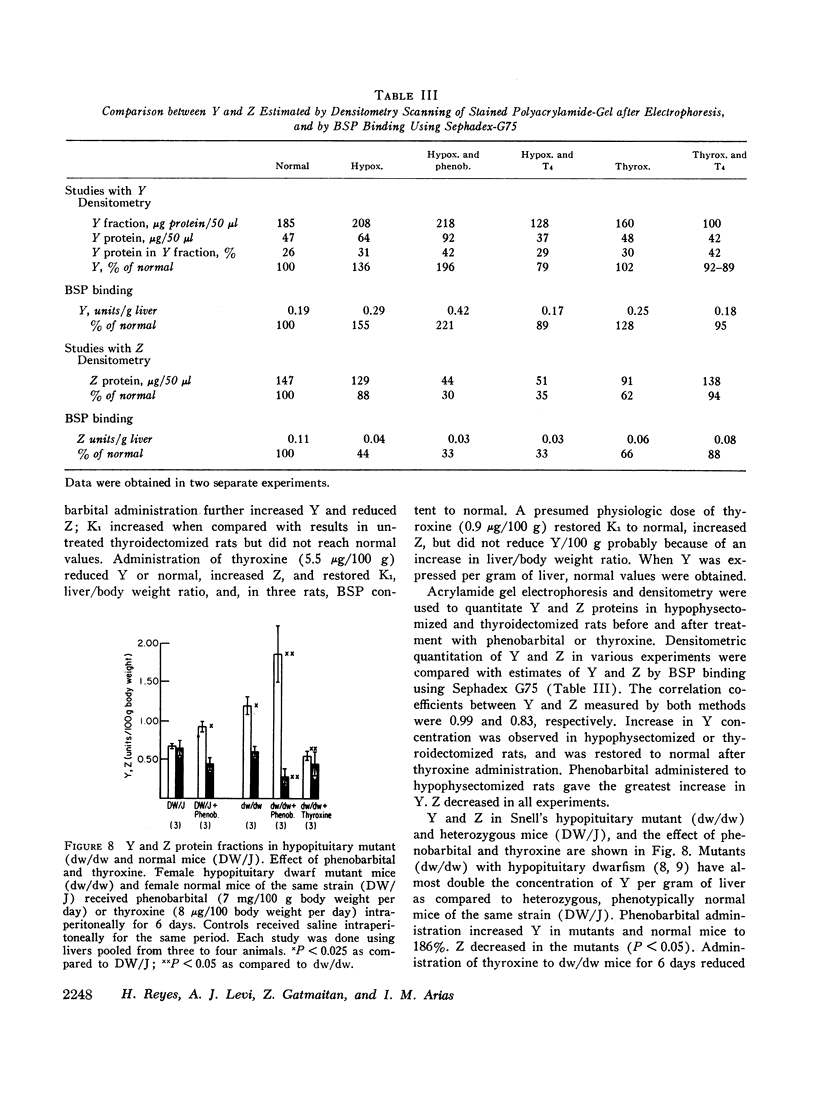
Hypophysectomy and thyroidectomy increased Y but decreased K1 and, where studied, hepatic content of BSP. Of several hormones studied, only thyroxine restored Y and K1 to normal in hypophysectomized or thyroidectomized rats. Mice with congenital pituitary insufficiency also manifested increased Y which returned to normal after thyroxine administration. In hormone-deficient rats and mice, phenobarbital administration produced a further increase in Y suggesting that different mechanisms may be responsible for the change in Y resulting from drug administration and hormonal deprivation. Thyroxine, testosterone, or hydrocortisone did not alter BSP K1 or Y in normal rats.
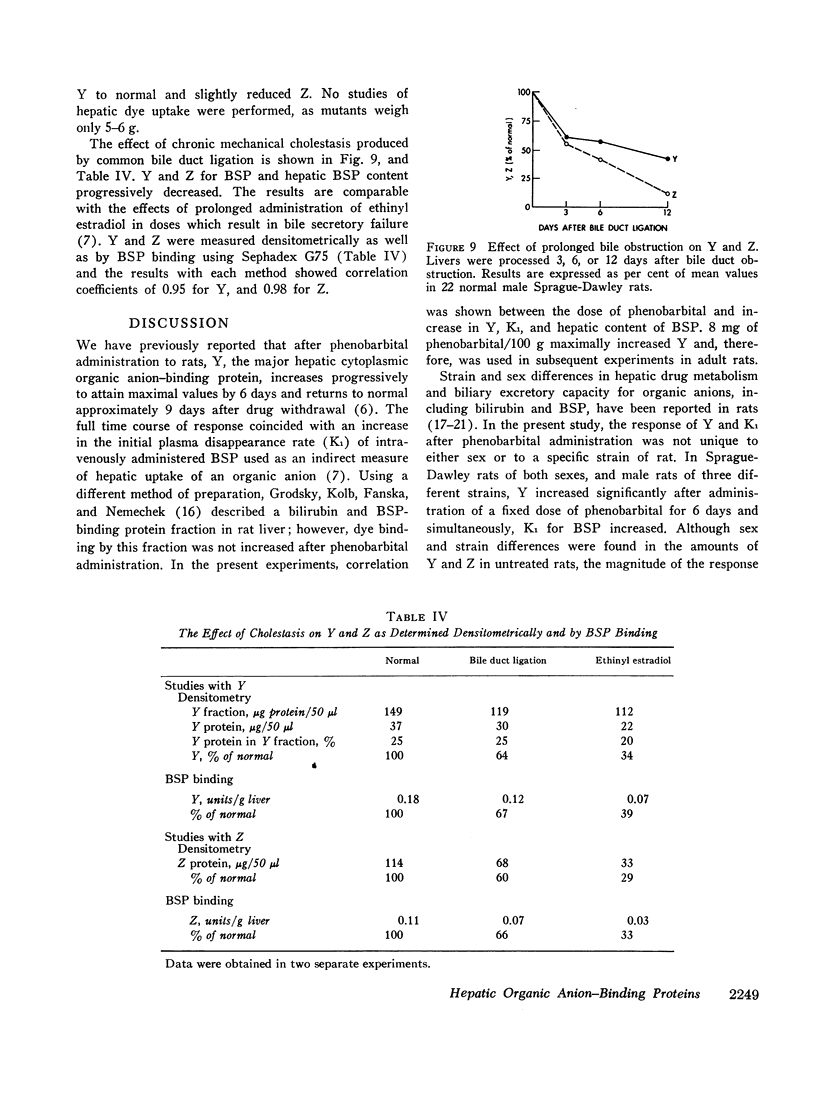
Cholestasis produced by ethinyl estradiol administration or biliary obstruction reduced Y, Z, BSP K1 and hepatic BSP content.
These results support the hypothesis that Y and Z are involved in the transfer of BSP, ICG, and possibly other organic anions from plasma into the liver. The concentration of Y increased after administration of various drugs and chemicals as well as in thyroid deficiency. Thyroid hormone appears to be important in regulation of the intracellular concentration of Y. Because thyroid deficiency increased Y but decreased BSP K1 and hepatic BSP content, other factors beside Y and Z influence hepatic organic anion uptake.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDREWS W. H., RICHARDS T. G. The activity of bile salts and certain detergents on the hepatic storage and protein-binding of sulphobromophthalein. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1960 Jul;45:275–283. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1960.sp001472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias I. M., Doyle D., Schimke R. T. Studies on the synthesis and degradation of proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3303–3315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBIER F., DEWEERDT G. A. CHROMATOGRAPHY AND I.R. SPECTROGRAPHY OF INDOCYANINE GREEN. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Dec;10:549–554. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker K. J., Bradley S. E. Binding of sulfobromophthalein (BSP) sodium by plasma albumin. Its role in hepatic BSP extraction. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):281–287. doi: 10.1172/JCI105341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthelot P., Billing B. H. Effect of bunamiodyl on hepatic uptake of sulfobromophthalein in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1966 Aug;211(2):395–399. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.2.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biempica L., Kosower N. S., Nivikoff A. B. Cytochemical and ultrastructural changes in rat liver in experimental porphyria. I. Effects of a single injection of allylisopropylacetamide. Lab Invest. 1967 Aug;17(2):171–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conney A. H. Pharmacological implications of microsomal enzyme induction. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Sep;19(3):317–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelius C. E., Ben-Ezzer J., Arias I. M. Binding of sulfobromophthalein sodium (BSP) and other organic anions by isolated hepatic cell plasma membranes in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Feb;124(2):665–667. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furner R. L., Gram T. E., Stitzel R. E. The influence of age, sex and drug treatment on microsomal drug metabolism in four rat strains. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Jul;18(7):1635–1641. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Kolb H. J., Fanska R. E., Nemechek C. Effect of age of rat on development of hepatic carriers for bilirubin: a possible explanation for physiologic jaundice and hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn. Metabolism. 1970 Mar;19(3):246–252. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(70)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart L. G., Guarino A. M., Adamson R. H. Effects of phenobarbital on biliary excretion of organic acids in male and female rats. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jul;217(1):46–52. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato R., Gillette J. R. Sex differences in the effects of abnormal physiological states on the metabolism of drugs by rat liver microsomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Nov;150(2):285–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaassen C. D., Plaa G. L. Determination of sulfobromophthalein storage and exertory rate in small animals. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Jun;22(6):1151–1155. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.6.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaassen C. D., Plaa G. L. Studies on the mechanism of phenobarbital-enhanced sulfobromophthalein disappearance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Jun;161(2):361–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaassen C. E., Roberts R. J., Plaa G. L. Maximal biliary excretion of bilirubin and sulfobromophthalein during various rates of infusion in rats of different weights and strains. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1969 Jul;15(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(69)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A. J., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Deficiency of hepatic organic anion-binding protein as a possible cause of non-haemolytic unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia in the newborn. Lancet. 1969 Jul 19;2(7612):139–140. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92444-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A. J., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Deficiency of hepatic organic anion-binding protein, impaired organic amnion uptake by liver and "physiologic" jaundice in newborn monkeys. N Engl J Med. 1970 Nov 19;283(21):1136–1139. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197011192832104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A. J., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Two hepatic cytoplasmic protein fractions, Y and Z, and their possible role in the hepatic uptake of bilirubin, sulfobromophthalein, and other anions. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2156–2167. doi: 10.1172/JCI106182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. I., Reyes H., Levi A. J., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Phylogenetic study of organic anion transfer from plasma into the liver. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 30;231(26):277–279. doi: 10.1038/newbio231277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page J. G., Vesell E. S. Hepatic drug metabolism in ten strains of Norway rat before and after pretreatment with phenobarbital. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 May;131(1):256–261. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes H., Levi A. J., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Organic anion-binding protein in rat liver: drug induction and its physiologic consequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):168–170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J., Plaa G. L. Effect of phenobarbital on the excretion of an exogenous bilirubin load. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 May;16(5):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell G. D. DWARF, A NEW MENDELIAN RECESSIVE CHARACTER OF THE HOUSE MOUSE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1929 Sep 15;15(9):733–734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.15.9.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEELER H. O., CRANSTON W. I., MELTZER J. I. Hepatic uptake and biliary excretion of indocyanine green in the dog. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Oct;99(1):11–14. doi: 10.3181/00379727-99-24229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEELER H. O., MELTZER J. I., BRADLEY S. E. Biliary transport and hepatic storage of sulfobromophthalein sodium in the unanesthetized dog, in normal man, and in patients with hepatic disease. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1131–1144. doi: 10.1172/JCI104128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


