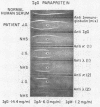
Abstract
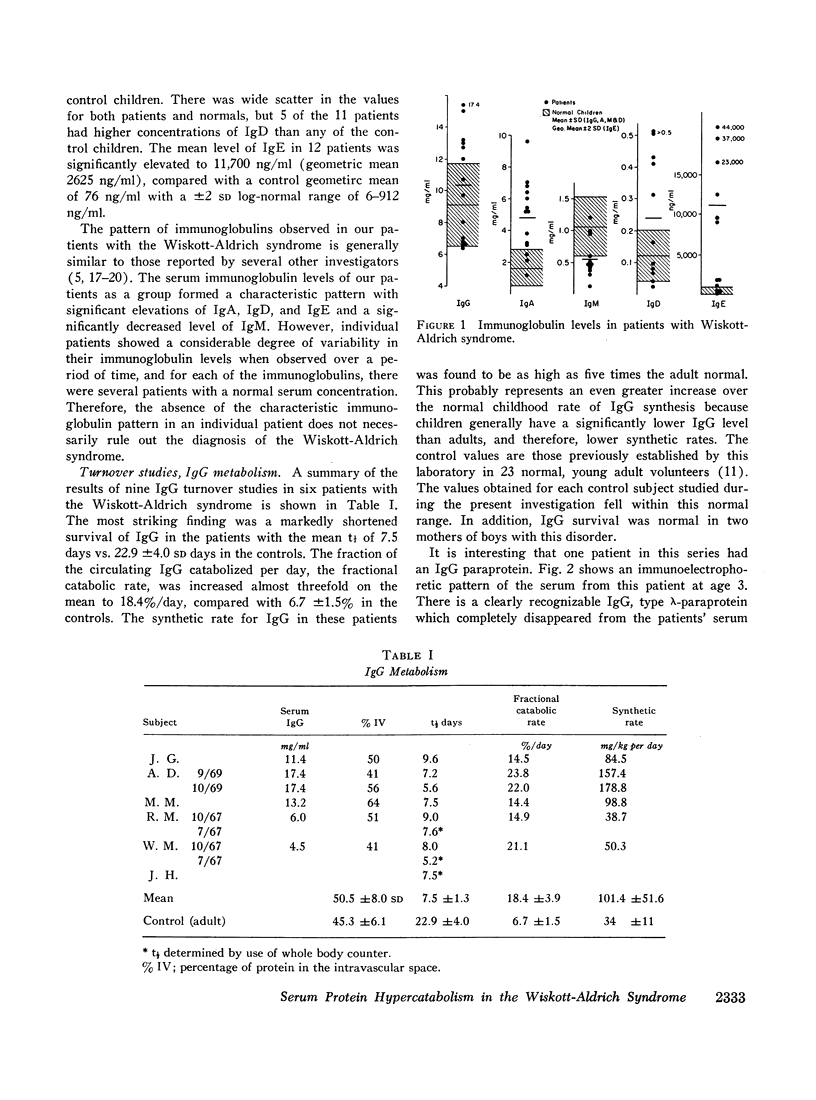
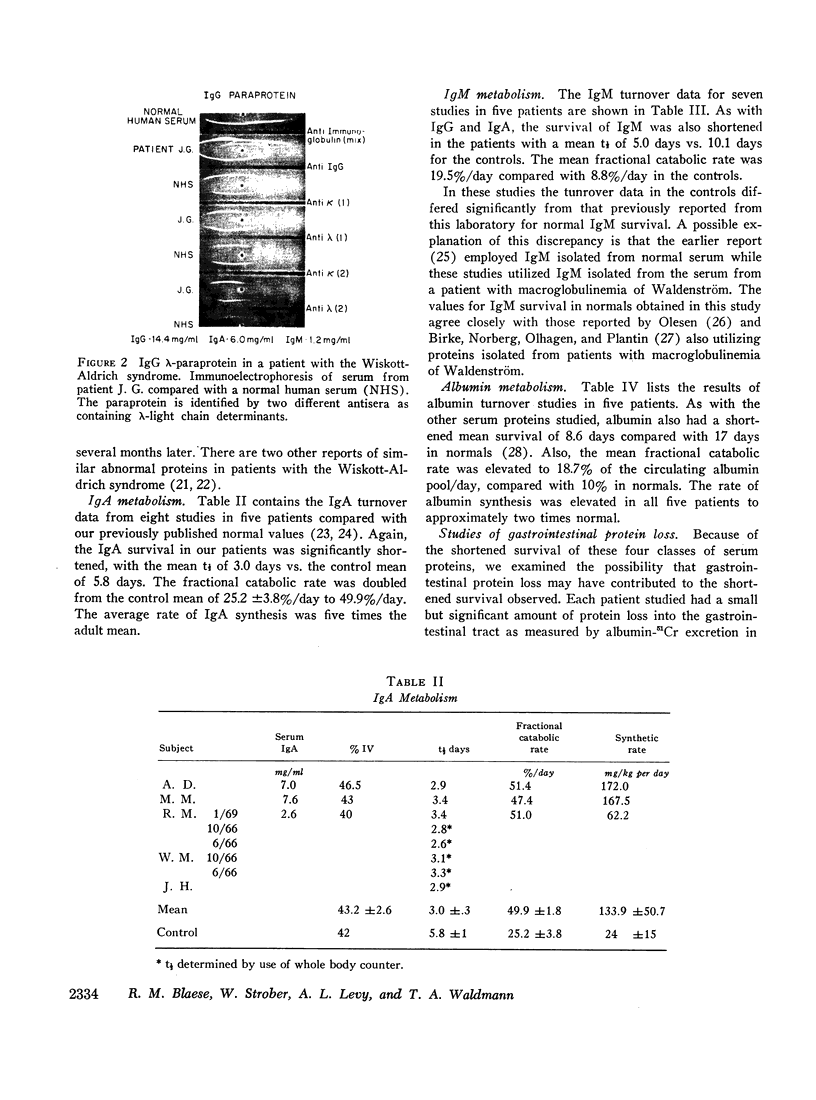
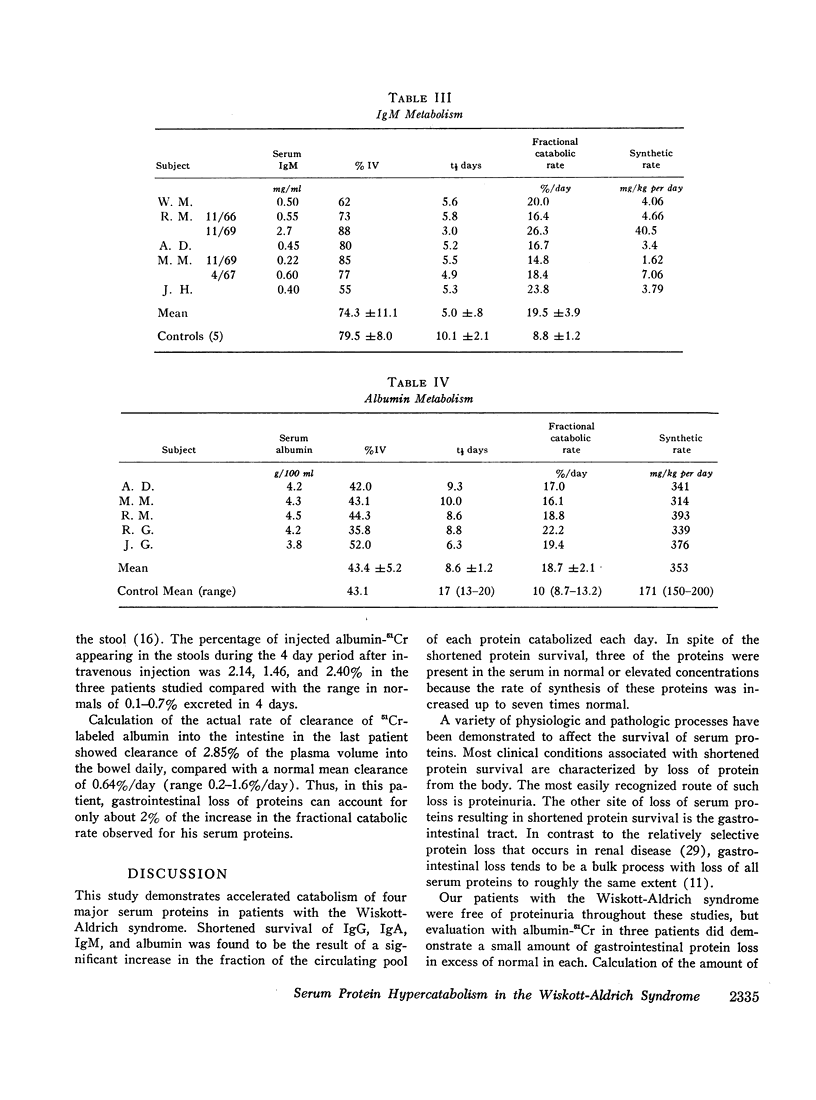
The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is an immune deficiency disorder with an impairment of both humoral and cellular immune responses. Metabolic turnover studies of IgG, IgA, IgM, and albumin were conducted in seven patients with the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome using purified radioiodinated proteins. The survival of each of the proteins studied was significantly shortened with a half-time of 7.5 days for IgG (normal 22.9 ±4 SD), 3.0 days for IgA (normal 5.8 ±1), 5.0 days for IgM (normal 10.1 ±2.1), and 8.6 days for albumin (normal 17, range 13-20); the fractional catabolic rates were correspondingly elevated and the distribution of protein among the body compartments was normal. For three of the four proteins. IgG, IgA, and albumin, the steady-state synthetic rates were generally elevated leading to normal or even elevated serum proteins levels. Thus, in the case of IgA, the synthetic rate averaged five times normal while the fractional degradative rate was twice normal. The resulting serum concentration was, therefore, significantly elevated, IgM represented an exception to this pattern in that the increased rate of degradation was not counterbalanced by an increased synthetic rate and, therefore, the serum levels were low.
Albumin clearance studies using albumin-51Cr showed gastrointestinal protein loss in these patients to be slightly greater than normal, but this could account for only a small fraction of the hypercatabolism observed. There was no proteinuria or abnormalities of thyroid, adrenal, renal, or liver function. Thus, none of the previously recognized causes of increased serum protein catabolism were present. Patients with the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, therefore, have a unique disorder of serum protein metabolism characterized by endogenous hypercatabolism of at least four major serum proteins. This phenomenon may be related to reticuloendothelial hyperfunction since the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is associated with reticuloendothelial hyperplasia and accelerated clearance of colloidal materials from the plasma.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRICH R. A., STEINBERG A. G., CAMPBELL D. C. Pedigree demonstrating a sex-linked recessive condition characterized by draining ears, eczematoid dermatitis and bloody diarrhea. Pediatrics. 1954 Feb;13(2):133–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayoub E. M., Dudding B. A., Cooper M. D. Dichotomy of antibody response to group A streptococcal antigens in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Dec;72(6):971–979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTH W. F., WOCHNER R. D., WALDMANN T. A., FAHEY J. L. METABOLISM OF HUMAN GAMMA MACROGLOBULINS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jun;43:1036–1048. doi: 10.1172/JCI104987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., SEBESTYEN M., COOPER N. S. The clearance of antigen antibody complexes from the blood by the reticuloendothelial system. J Immunol. 1959 Feb;82(2):131–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S., SCHREIBER S. S., POST J. Tracer experiments with I131 labeled human serum albumin: distribution and degradation studies. J Clin Invest. 1953 Aug;32(8):746–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI102789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaese R. M., Strober W., Brown R. S., Waldmann T. A. The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. A disorder with a possible defect in antigen processing or recognition. Lancet. 1968 May 18;1(7551):1056–1061. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., Chae H. P., Lowman J. T., Krivit W., Good R. A. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. An immunologic deficiency disease involving the afferent limb of immunity. Am J Med. 1968 Apr;44(4):499–513. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALLOZ J. C., CASTAING N., NEZELOF C., SELIGMANN M. PARAPROT'EIN'EMIE TRANSITOIRE DE TYPE GAMMA. OBSERVATION CHEZ UN NOURRISSON ATTEINT DU SYNDROME D'ALDRICH. Presse Med. 1965 May 26;73:1541–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARTHING C. P., GERWING J., SHEWELL J. The catabolism of 131I-labelled homologous gamma-globulin in normal, hyperthyroid and hypothyroid rats. J Endocrinol. 1960 Sep;21:83–89. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0210083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARTHING C. P., GERWING J., SHEWELL J. The influence of the thyroid gland on the catabolism of 131I-labelled homologous gamma-globulin in the guinea-pig. J Endocrinol. 1960 Sep;21:91–96. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0210091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN T., GORDON A. H., HUMPHREY J. H. Distinction between catabolism of native and denatured proteins by the isolated perfused liver after carbon loading. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Oct;39(5):459–471. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON A. H. The use of the isolated perfused liver to detect alterations to plasma proteins. Biochem J. 1957 Jun;66(2):255–264. doi: 10.1042/bj0660255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Averbeck A. K., Swedlund H. A. Measurement of IgE in normal and allergic serum by radioimmunoassay. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Apr;77(4):690–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOACHIM G. R., CAMERON J. S., SCHWARTZ M., BECKER E. L. SELECTIVITY OF PROTEIN EXCRETION IN PATIENTS WITH THE NEPHROTIC SYNDROME. J Clin Invest. 1964 Dec;43:2332–2346. doi: 10.1172/JCI105107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy A. L., Waldmann T. A. The effect of hydrocortisone on immunoglobulin metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1970 Sep;49(9):1679–1684. doi: 10.1172/JCI106385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLESEN H. TURNOVER STUDIES WITH IODINE-LABELED GAMMA-MACROGLOBULIN AND ALBUMIN. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1963;15:497–510. doi: 10.1080/00365516309079778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Blaese R. M., Waldmann T. A. Defective lymphocyte transformation and delayed hypersensitivity in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):835–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rádl J., Masopust J., Houstek J., Hrodek O. Paraproteinaemia and unusual dys-gamma-globulinaemia in a case of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. An immunochemical study. Arch Dis Child. 1967 Dec;42(226):608–614. doi: 10.1136/adc.42.226.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELL S. EVIDENCE FOR SPECIES' DIFFERENCES IN THE EFFECT OF SERUM GAMMA-GLOBULIN CONCENTRATION ON GAMMA-GLOBULIN CATABOLISM. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:967–986. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELL S., FAHEY J. L. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN GAMMA-GLOBULIN METABOLISM AND LOW SERUM GAMMA-GLOBULIN IN GERMFREE MICE. J Immunol. 1964 Jul;93:81–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON A., WALDMANN T. A., FAHEY J. L. Clinical and experimental metabolism of normal 6.6s gamma-globulin in normal subjects and in patients with macroglobulinemia and multiple myeloma. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Jul;62:1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheagren J. N., Block J. B., Wolff S. M. Reticuloendothelial system phagocytic function in patients with Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):855–862. doi: 10.1172/JCI105585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Fudenberg H. H. Serum levels of immune globulins in health and disease: a survey. Pediatrics. 1966 May;37(5):715–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober W., Wochner R. D., Barlow M. H., McFarlin D. E., Waldmann T. A. Immunoglobulin metabolism in ataxia telangiectasia. J Clin Invest. 1968 Aug;47(8):1905–1915. doi: 10.1172/JCI105881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober W., Wochner R. D., Carbone P. P., Waldmann T. A. Intestinal lymphangiectasia: a protein-losing enteropathy with hypogammaglobulinemia, lymphocytopenia and impaired homograft rejection. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1643–1656. doi: 10.1172/JCI105656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORBECKE G. J., SEBESTYEN M., BENACERRAF B., GREEN H. Influence of reticulo endothelial blockade on turnover rate of homologous plasma proteins in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Nov;99(2):439–441. doi: 10.3181/00379727-99-24376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Johnson J. S., Talal N. Hypogammaglobulinemia associated with accelerated catabolism of IgG secondary to its inteaction with an IgG-reactive monoclonal IgM. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):951–959. doi: 10.1172/JCI106567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Strober W. Metabolism of immunoglobulins. Prog Allergy. 1969;13:1–110. doi: 10.1159/000385919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Wochner R. D., Strober W. The role of the gastrointestinal tract in plasma protein metabolism. Studies with 51Cr-albumin. Am J Med. 1969 Feb;46(2):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wochner R. D., Drews G., Strober W., Waldmann T. A. Accelerated breakdown of immunoglobulin G (IgG) in myotonic dystrophy: a hereditary error of immunoglobulin catabolism. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):321–329. doi: 10.1172/JCI105346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J. A. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: clinical, immunologic, and pathologic observations. J Pediatr. 1967 Feb;70(2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80417-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Bensel R. W., Stadlan E. M., Krivit W. The development of malignancy in the course of the Aldrich syndrome. J Pediatr. 1966 May;68(5):761–767. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(66)80450-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]