Abstract
Using a new in vitro method of measuring the chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from peripheral blood, a chemotactic index has been calculated. The mean chemotactic index of 320 in 24 patients with definite rheumatoid arthritis, was significantly less (P < 0.0005) than the mean of 555 in 24 normal controls matched for age and sex.
The mean chemotactic index of 435 in eight patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis was also significantly less (P < 0.01) than that of 553 in similarly matched controls.
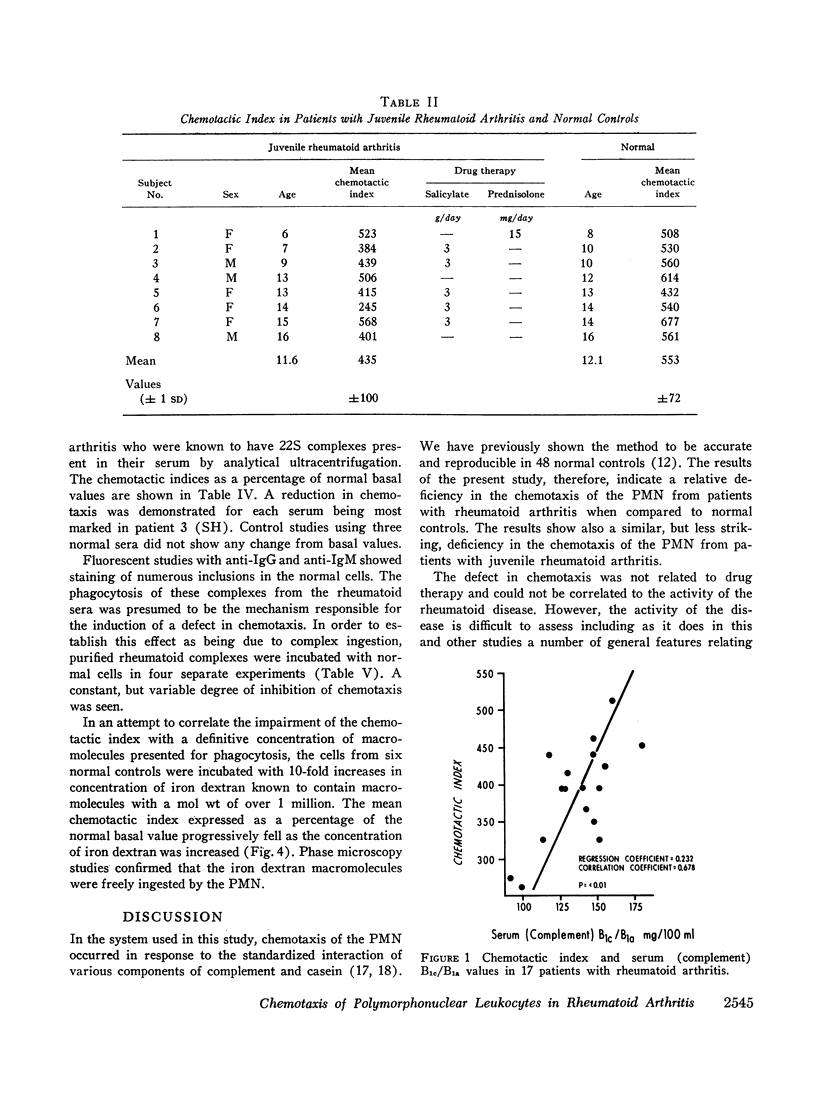
The chemotactic index could not be correlated with age, sex, disease activity, drugs used in treatment, latex titer, immunoglobulin levels, or protein coating on the cells. However, there was a correlation between the chemotactic index and the serum complement B1e/B1a value (P < 0.01) in 17 patients with adult onset rheumatoid arthritis. Although the serum complement B1e/B1a values were within the normal range, the lowest chemotactic indices were associated with the lowest complement values.
The chemotactic indices in three patients with severe connective tissue disease (seropositive rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and polymyositis) returned to normal after 5 days' treatment with 60 mg of prednisolone per day. Incubation of the cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis with hydrocortisone in vitro failed to alter the chemotactic indices.
Prior incubation of normal cells with purified rheumatoid factor complexes, rheumatoid serum, or macromolecules of iron dextran impaired their chemotaxis. It is suggested that phagocytosis of complexes in vivo is a possible mechanism by which the chemotaxis of the polymorphonuclear leukocytes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis is impaired.
This impairment in chemotaxis may explain the increased incidence of bacterial infection, both during life and as a cause of death in these patients.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATWATER E. C., JACOX R. F. The latex-fixation test in patients with liver disease. Ann Intern Med. 1963 Mar;58:419–425. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-58-3-419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:453–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum J., Mowat A. G., Kirk J. A. A simplified method for the measurement of chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from human blood. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Mar;77(3):501–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt L., Hedberg H. Impaired phagocytosis by peripheral blood granulocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Haematol. 1969;6(5):348–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1969.tb02420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COBB S., ANDERSON F., BAUER W. Length of life and cause of death in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1953 Oct 1;249(14):553–556. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195310012491402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE J. J., BROWN P. E., TRUELOVE L. H., BARAGAR F. D., LAWRIE A. J. COURSE AND PROGNOSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. A FURTHER REPORT. Ann Rheum Dis. 1964 May;23:193–204. doi: 10.1136/ard.23.3.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. G. The role of infection in the causation of rheumatoid arthritis. Proc R Soc Med. 1968 Oct;61(10):971–972. doi: 10.1177/003591576806101007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KETCHEL M. M., FAVOUR C. B., STURGIS S. H. The in vitro action of hydrocortisone on leucocyte migration. J Exp Med. 1958 Feb 1;107(2):211–218. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. L. The metabolism of leukocytes. Semin Hematol. 1968 Apr;5(2):156–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEISELAS L. E., ZINGALE S. B., LEE S. L., RICHMAN S., SIEGEL M. Antibody production in rheumatic diseases. The effect of brucella antigen. J Clin Invest. 1961 Oct;40:1872–1881. doi: 10.1172/JCI104411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongan E. S., Cass R. M., Jacox R. F., Vaughen J. H. A study of the relation of seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis to each other and to necrotizing vasculitis. Am J Med. 1969 Jul;47(1):23–35. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. G., Hothersall T. E., Aitchison W. R. Nature of anaemia in rheumatoid arthritis. XI. Changes in iron metabolism induced by the administration of corticotrophin. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 May;28(3):303–309. doi: 10.1136/ard.28.3.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A., Baum J. Chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1971 Mar 25;284(12):621–627. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197103252841201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penny R., Galton D. A. Studies on neutrophil function. II. Pathological aspects. Br J Haematol. 1966 Sep;12(5):633–645. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1966.tb00146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., KARNOVSKY M. L. The biochemical basis of phagocytosis. I. Metabolic changes during the ingestion of particles by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1355–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEARN M. A., EPSTEIN W. V., ENGLEMAN E. P. ANTIBODY RESPONSE TO BRUCELLA ANTIGEN IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Aug-Sep;113:1001–1003. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonozaki H., Torisu M. Complement system in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Mar;29(2):164–172. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. M., Alexander W. R., Duthie J. J. Isolation of diphtheroid bacilli from synovial membrane and fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 Sep;28(5):477–487. doi: 10.1136/ard.28.5.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrigiani G., Roitt I. M., Lloyd K. N., Corbett M. Elevated IgG antiglobulins in patients with seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1970 Jan 3;1(7636):14–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90524-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uddin J., Kraus A. S., Kelly H. G. Survivorship and death in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Mar-Apr;13(2):125–130. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHAN J. H., BUTLER V. P., Jr Current status of the rheumatoid factor. Ann Intern Med. 1962 Jan;56:1–11. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-56-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. H., Barrnett E. V., Sobel M. V., Jacox R. F. Intracytoplasmic inclusions of immunoglobulins in rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Apr;11(2):125–134. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. H., Jacox R. J., Noell P. Relation of intracytoplasmic inclusions in joint fluid leukocytes to anti-gamma-G globulins. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Apr;11(2):135–144. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. C., Wright V. Pulmonary lesions and rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1968 Nov;47(6):501–520. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196811000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller M., Ellman H. M., Toone E. C. Brucella immunization in patients with seropositive and seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1966;12(4):250–260. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1966.12.issue-1-4.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. W. Hypersensitivity and infection in the pathogenesis of the rheumatic diseases. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1968;6:285–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A. Chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Mar;(Suppl):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90297-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Newman L. J. A neutrophil chemotactic factor from human C'5. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A. The chemosuppression of chemotaxis. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):209–226. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasastjerna C., Ekelund P. The serum immunoglobulin and beta-1-C-beta-1-A globulin levels in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Med Scand. 1969 Nov;186(5):469–473. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1969.tb01505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



