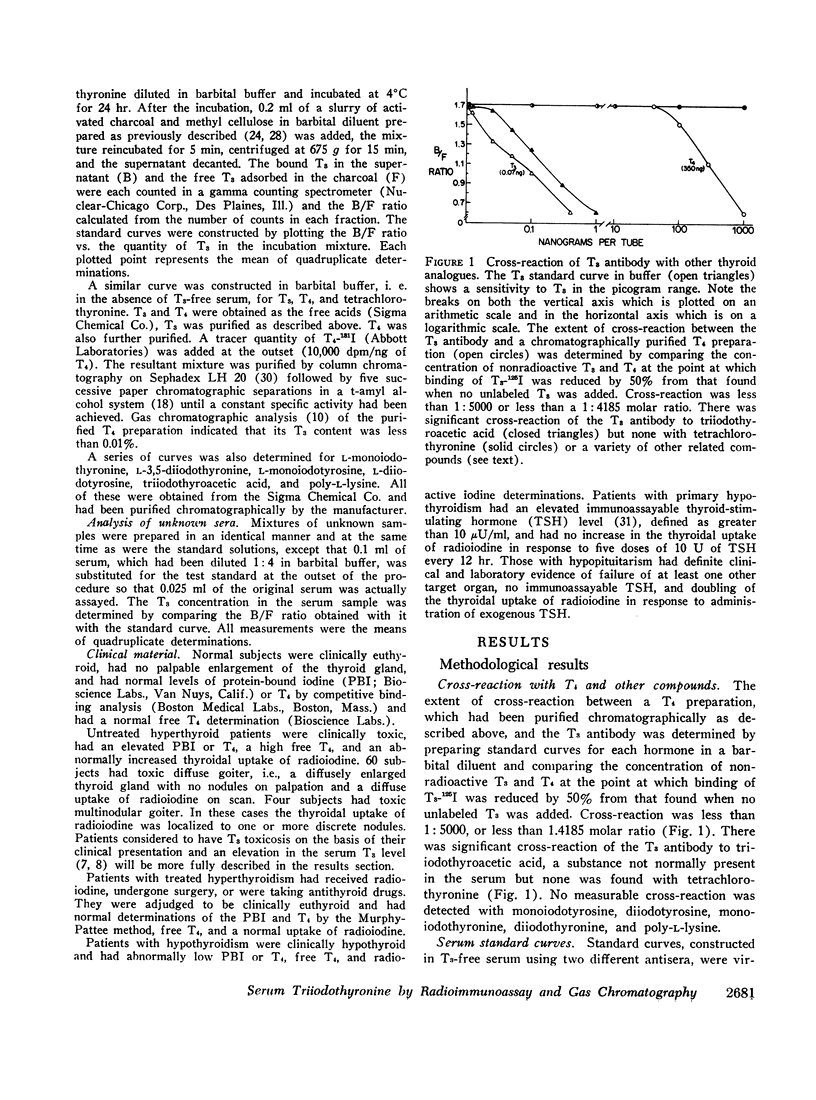
Abstract
Serum triiodothyronine (T3) has been measured by radioimmunoassay and corroborated by analysis of the identical samples with a previously described gas-liquid chromatographic technique. Special features of the radioimmunoassay procedure which permit determinations in unextracted serum include the use of a T3-free serum preparation for the construction of the standard curve and of tetrachlorothyronine to inhibit binding of T3 to thyroxine-binding globulin.
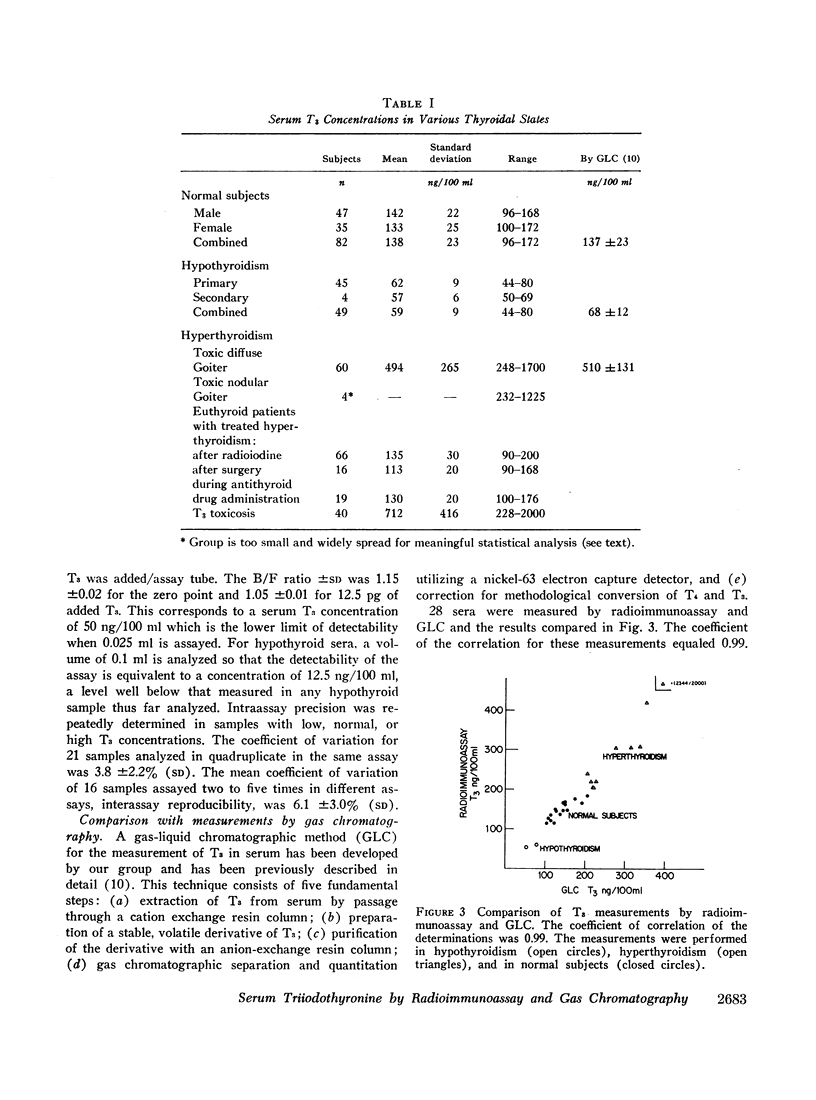
T3 values by radioimmunoassay were 138 ±23 ng/100 ml (mean ±SD) in 82 normal subjects, 62 ±9 ng/100 ml in 45 hypothyroid patients, and 494 ±265 ng/100 ml in 60 patients with toxic diffuse goiter. In the hypothyroid group, the range was similar in patients with both primary and secondary hypothyroidism. There was no overlap between the three thyroidal states. Elevated T3 levels were seen in 40 cases that appeared clinically hyperthyroid but had normal serum thyroxine (T3) determinations, a syndrome we have called T3 toxicosis. Values obtained with radioimmunoassay agreed closely with those we had previously found by gas-liquid chromatography which were 68 ±2 ng/100 ml in hypothyroidism, 137 ±23 ng/100 ml in normal subjects, and 510 ±131 ng/100 ml in untreated toxic diffuse goiter.
Since T3 is very potent and its level varies in different clinical states, accurate T3 measurements are required to assess a patient's thyroid status properly. The radioimmunoassay for T3 appears to be sufficiently sensitive, precise, and simple to permit its routine clinical application for this purpose.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowers C. Y., Schally A. V., Hawley W. D., Gual C., Parlow A. Effect of thyrotropin-releasing factor in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Jul;28(7):978–982. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-7-978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman L. E., Ingbar S. H., Sterling K. Conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3) in athyreotic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):855–864. doi: 10.1172/JCI106304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. L., Ekins R. P., Ellis S. M., Reith W. S. Specific antibodies to triiodothyronine hormone. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):359–359. doi: 10.1038/226359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Nelson J. C., Solomon D. H., Beall G. N. Production of antibodies specifically binding triiodothyronine and thyroxine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Mar;32(3):299–308. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-3-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dussault J. H., Lam R., Fisher D. A. The measurement of serum triiodothyronine by double column chromatography. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jun;77(6):1039–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A., Dussault J. H. Contribution of methodological artifacts to the measurement of T3 concentration in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 May;32(5):675–679. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-5-675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer N., Burgus R., Vale W., Dunn T., Guillemin R. Preliminary observations on the effect of synthetic thyrotropin releasing factor on plasma thyrotropin levels in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Jul;31(1):109–112. doi: 10.1210/jcem-31-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., PITT-RIVERS R. The identification of 3:5:3'-L-triiodothyronine in human plasma. Lancet. 1952 Mar 1;1(6705):439–441. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)91952-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharib H., Mayberry W. E., Ryan R. J. Radioimmunoassay for triiodothyronine: A preliminary report. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Dec;31(6):709–712. doi: 10.1210/jcem-31-6-709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer M. A., Grimm Y., Studer H. Qualitative changes in the secretion of thyroid hormones induced by iodine deficiency. Endocrinology. 1968 Dec;83(6):1193–1198. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-6-1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABER E., PAGE L. B., JACOBY G. A. SYNTHESIS OF ANTIGENIC BRANCH-CHAIN COPOLYMERS OF ANGIOTENSIN AND POLY-L-LYSINE. Biochemistry. 1965 Apr;4:693–698. doi: 10.1021/bi00880a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heninger R. W., Albright E. C. Effect of iodine deficiency on iodine-containing compounds of rat tissues. Endocrinology. 1966 Aug;79(2):309–315. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander C. S. On the nature of the circulating thyroid hormone: clinical studies of triiodothyronine and thyroxine in serum using gas chromatographic methods. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1968;81:76–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander C. S., Shenkman L., Mitsuma T., Blum M., Kastin A. J., Anderson D. G. Hypertriiodothyroninaemia as a premonitory manifestation of thyrotoxicosis. Lancet. 1971 Oct 2;2(7727):731–733. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Simultaneous estimation of rates of thyroxine degradation and thyroid hormone synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jun;34(6):808–819. doi: 10.1172/JCI103136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. R. Technical aspects of the estimation of triiodothyronine in human serum: evidence of conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine during assay. Metabolism. 1971 Jun;20(6):609–624. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musa B. U., Kumar R. S., Dowling J. T. Role of thyroxine-binding globulin in the early distribution of thyroxine and triiodothyronine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 May;29(5):667–674. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-5-667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAVA M., DE GROOT L. J. Resin uptake of I-131-labeled triiodothyronine as a test of thyroid function. N Engl J Med. 1962 Jun 21;266:1307–1310. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196206212662504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauman J. A., Nauman A., Werner S. C. Total and free triiodothyronine in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1967 Aug;46(8):1346–1355. doi: 10.1172/JCI105627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nihei N. N., Gershengorn M. C., Mitsuma T., Stringham L. R., Cordy A., Kuchmy B., Hollander C. S. Measurements of triiodothyronine and thyroxine in human serum by gas-liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1971 Oct;43(2):433–445. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell W. D., Wilber J. F., Utiger R. D. Studies of thyrotropin physiology by means of radioimmunoassay. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1967;23:47–85. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9826-2.50005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver G. C., Jr, Parker B. M., Brasfield D. L., Parker C. W. The measurement of digitoxin in human serum by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1035–1042. doi: 10.1172/JCI105793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITT-RIVERS R., STANBURY J. B., RAPP B. Conversion of thyroxine to 3-5-3'-triiodothyronine in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1955 May;15(5):616–620. doi: 10.1210/jcem-15-5-616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman C. S., Chambers J. B., Jr, Read V. H. The extrathyroidal conversion rate of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1187–1196. doi: 10.1172/JCI106596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada T., Saito S., Inagaki K., Tayama S., Torikai T. Quantitative determination of total and free triiodothyronine and thyroxine. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1969 Oct;99(2):179–188. doi: 10.1620/tjem.99.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber B. E., Ortner H. M., Spitzy H. Ein neues Isolierverfahren für die Schilddrüsenhormone und ihre Vorstufen aus dem Blutserum. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Oct;30(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90201-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Quantitation of extrathyroidal conversion of L-thyroxine to 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1124–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI106584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Bellabarba D., Newman E. S., Brenner M. A. Determination of triiodothyronine concentration in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jun;48(6):1150–1158. doi: 10.1172/JCI106072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Refetoff S., Selenkow H. A. T3 thyrotoxicosis. Thyrotoxicosis due to elevated serum triiodothyronine levels. JAMA. 1970 Jul 27;213(4):571–575. doi: 10.1001/jama.213.4.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUROG A. Spontaneous deiodination of I-131-labeled thyroxine and related iodophenols on filter paper. Endocrinology. 1963 Jul;73:45–56. doi: 10.1210/endo-73-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF J., STANDAERT M. E., RALL J. E. Thyroxine displacement from serum proteins and depression of serum protein-bound iodine by certain drugs. J Clin Invest. 1961 Aug;40:1373–1379. doi: 10.1172/JCI104368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. D., Freeman D. E., Florsheim W. H. Sephadex LH-20 column separation of thyroidal iodoamino acids. J Chromatogr. 1969 Dec 23;45(3):371–380. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)86233-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woeber K. A., Hecker E., Ingbar S. H. The effects of an acute load of thyroxine on the transport and peripheral metabolism of triiodothyronine in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):650–654. doi: 10.1172/JCI106276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woeber K. A., Sobel R. J., Ingbar S. H., Sterling K. The peripheral metabolism of triiodothyronine in normal subjects and in patients with hyperthyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):643–649. doi: 10.1172/JCI106275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaninovich A. A., Farach H., Ezrin C., Volpé R. Lack of significant binding of L-triiodothyronine by thyroxine-binding globulin in vivo as demonstrated by acute disappearance of 131-I-labeled triiodothyronine. J Clin Invest. 1966 Aug;45(8):1290–1301. doi: 10.1172/JCI105436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaninovich A. A., Volpe R., Ezrin C. Effects of variations of thyroxine-binding globulin capacity on the disappearance of triiodothyronine from the plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Dec;29(12):1601–1607. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-12-1601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


