Abstract
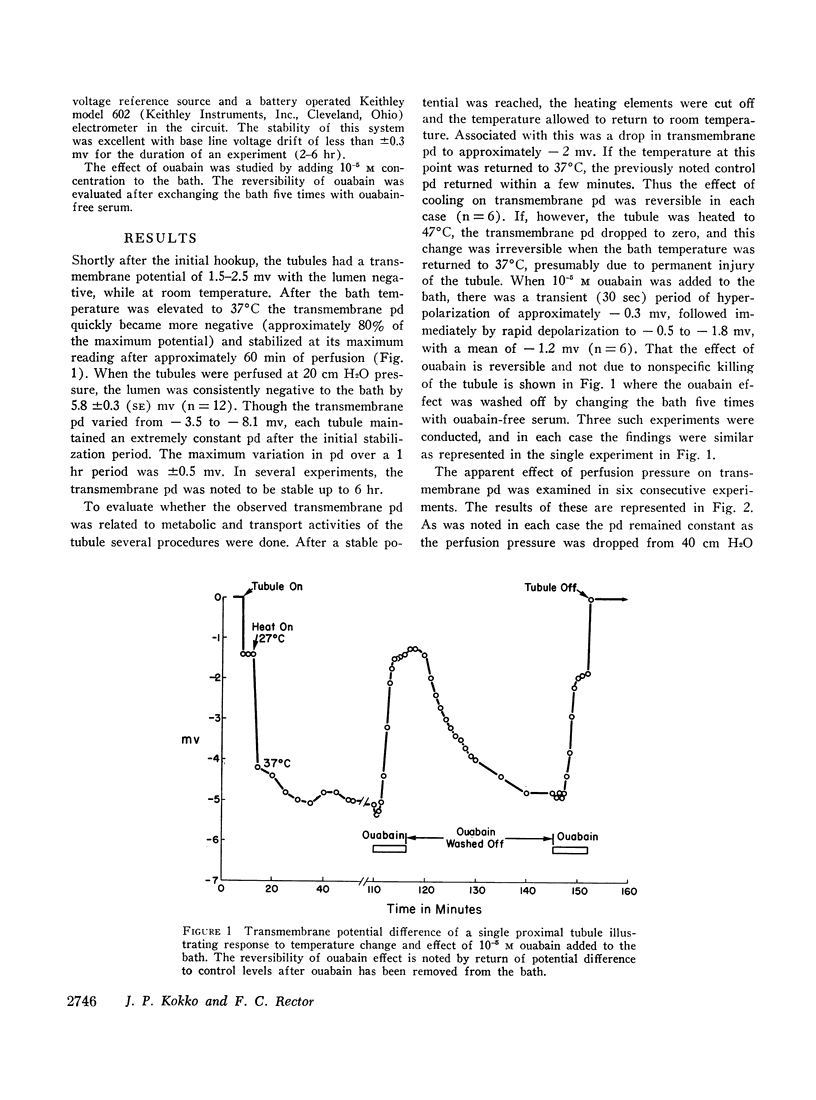
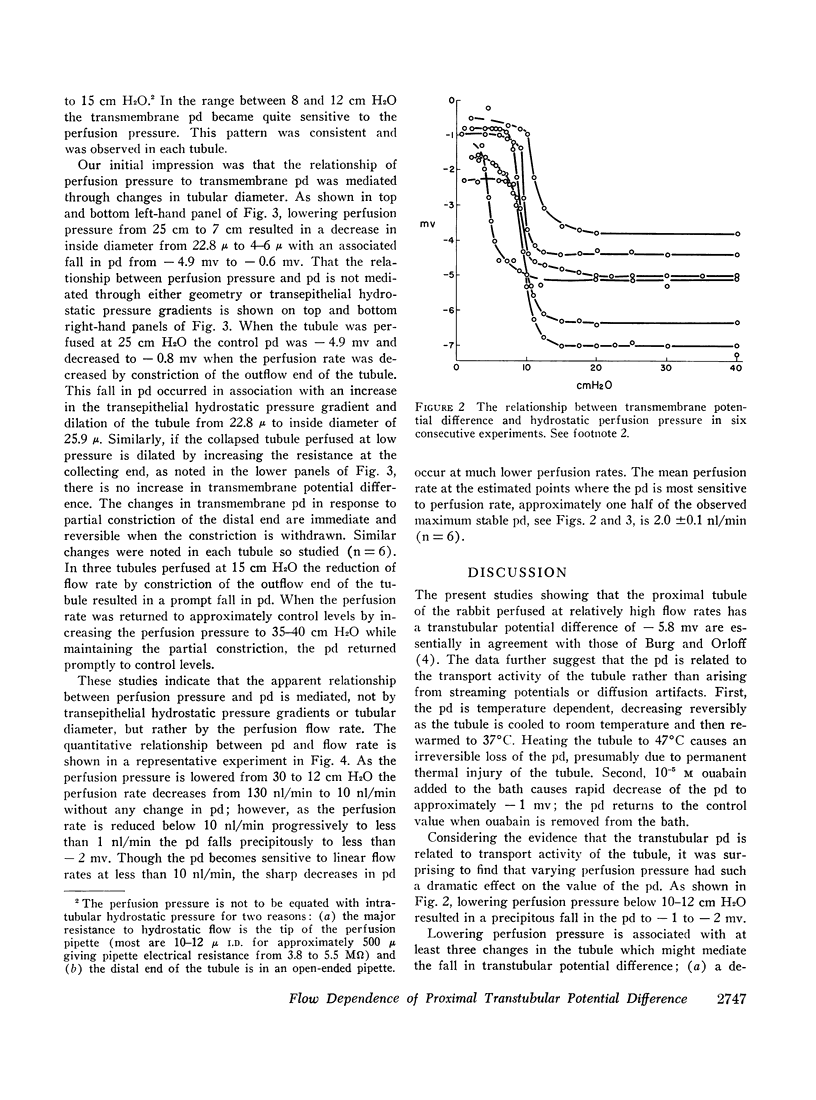
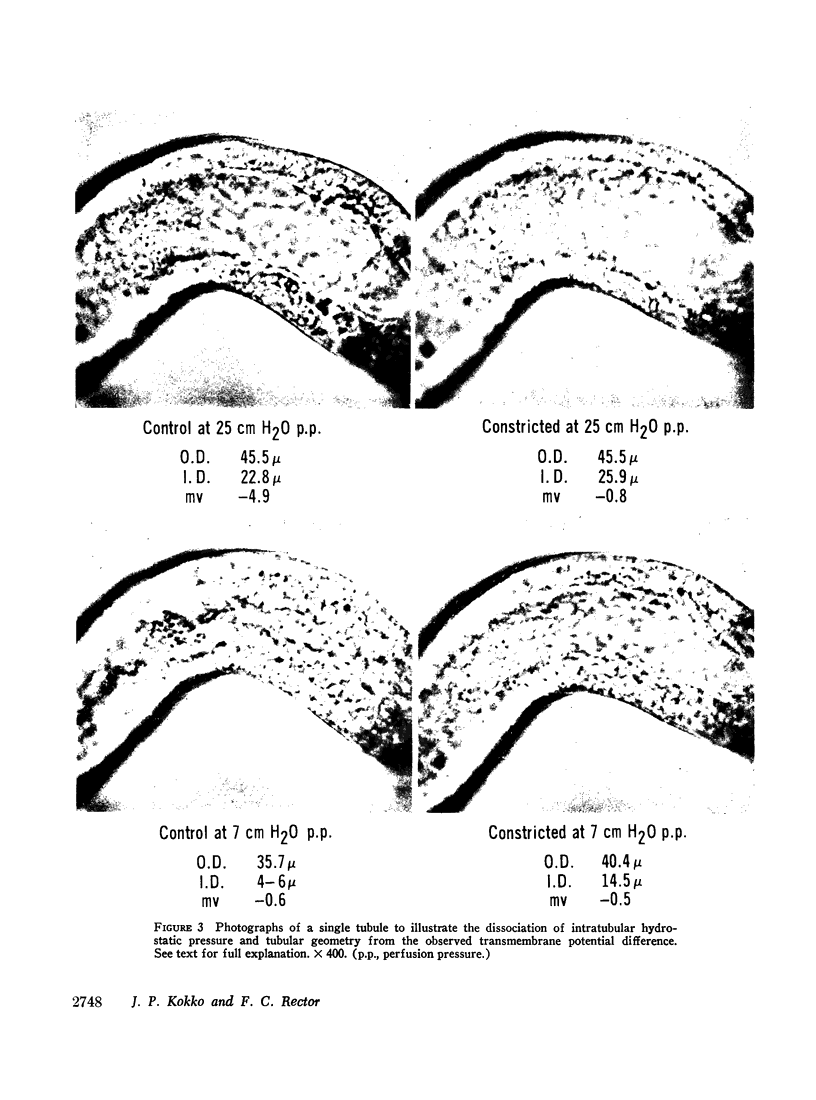
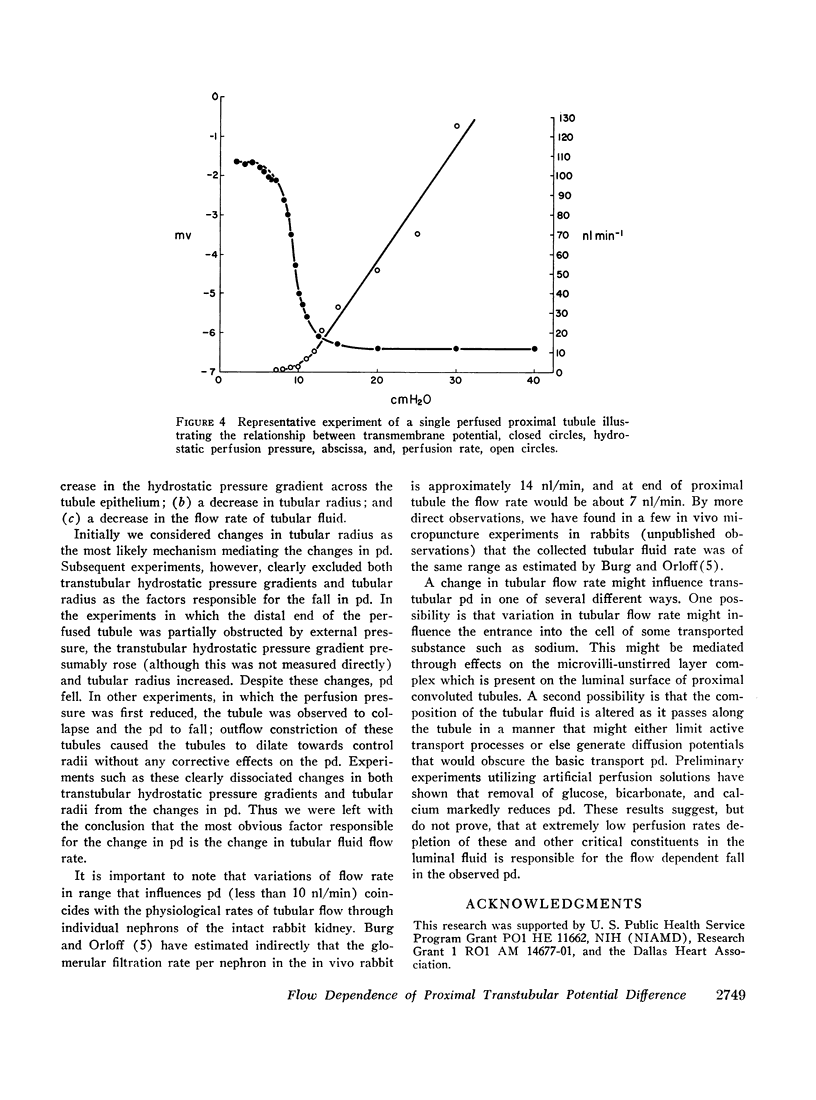
Transmembrane potential difference (pd) was studied in isolated perfused segments of rabbit proximal convoluted tubules. At perfusion flow rates above 10 nl/min the pd was -5.80 ±0.3 mv (lumen negative) when perfusing with isosmolal ultrafiltrate of same rabbit serum as the bath. That this pd is generated by transport activity of the tubule is supported by three separate observations: (a) pd reversibly decreased with cooling from 37°C to 25°C; (b) pd decreased when 10-5 M ouabain was added to the bath and reversed to control levels when ouabain was removed; and (c) heating to 47°C irreversibly decreased pd to zero. The magnitude of the pd was related to perfusion flow rate at slower rates than 10 nl/min. A decrease in flow rate was associated with a decrease in pd. The tubular geometry and transmembrane hydrostatic pressure were ruled out as the mediating factors governing the magnitude of observed pd.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burg M. B., Issaacson L., Grantham J., Orloff J. Electrical properties of isolated perfused rabbit renal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1968 Oct;215(4):788–794. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.4.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B., Orloff J. Control of fluid absorption in the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2016–2024. doi: 10.1172/JCI105888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B., Orloff J. Electrical potential difference across proximal convoluted tubules. Am J Physiol. 1970 Dec;219(6):1714–1716. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.6.1714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Hegel U. Transtubuläre Potentialdifferenzen an proximalen und distalen Tubuli der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;291(1):107–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON S. Transtubular potential differences of rat kidney. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Apr;49(2):351–365. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030490215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]