Abstract
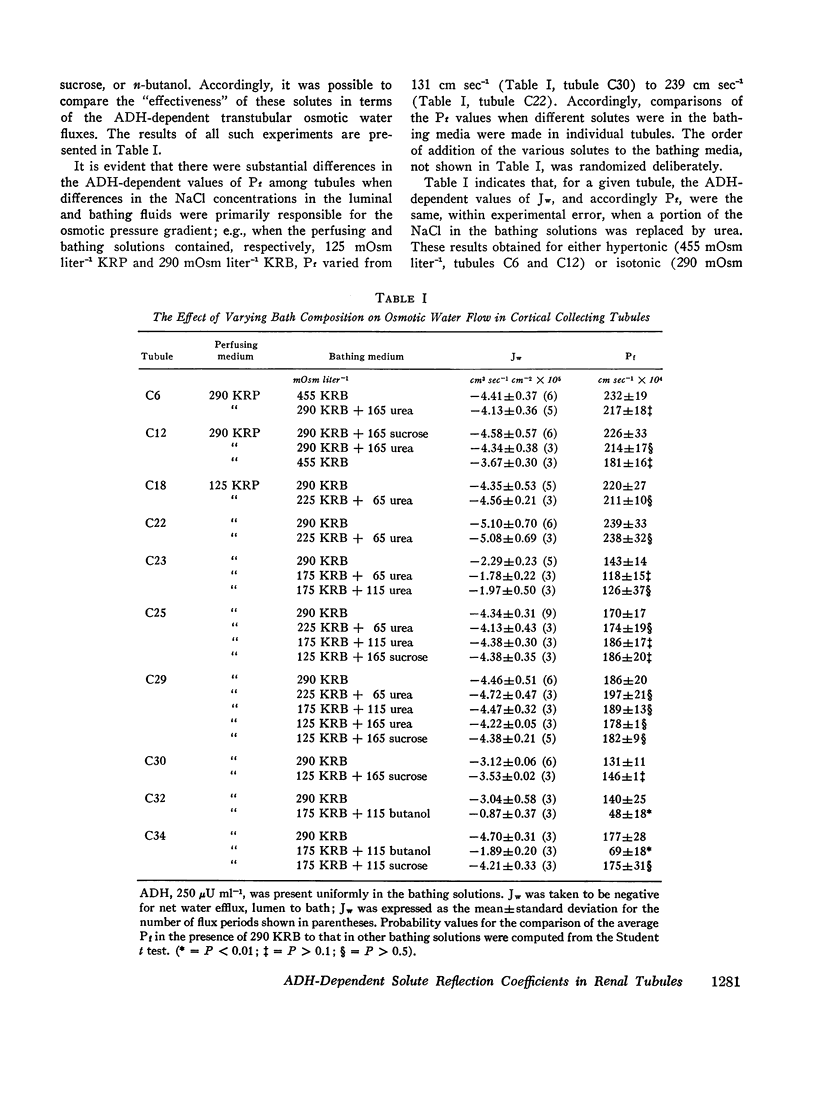
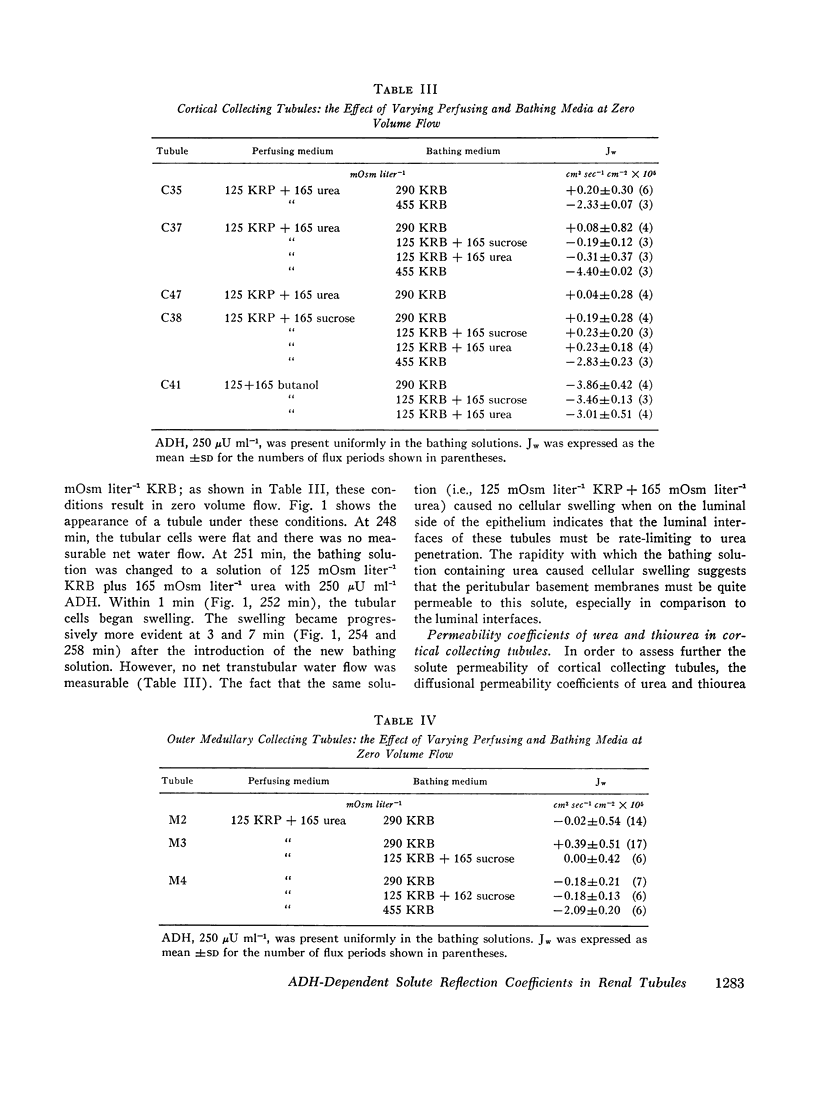
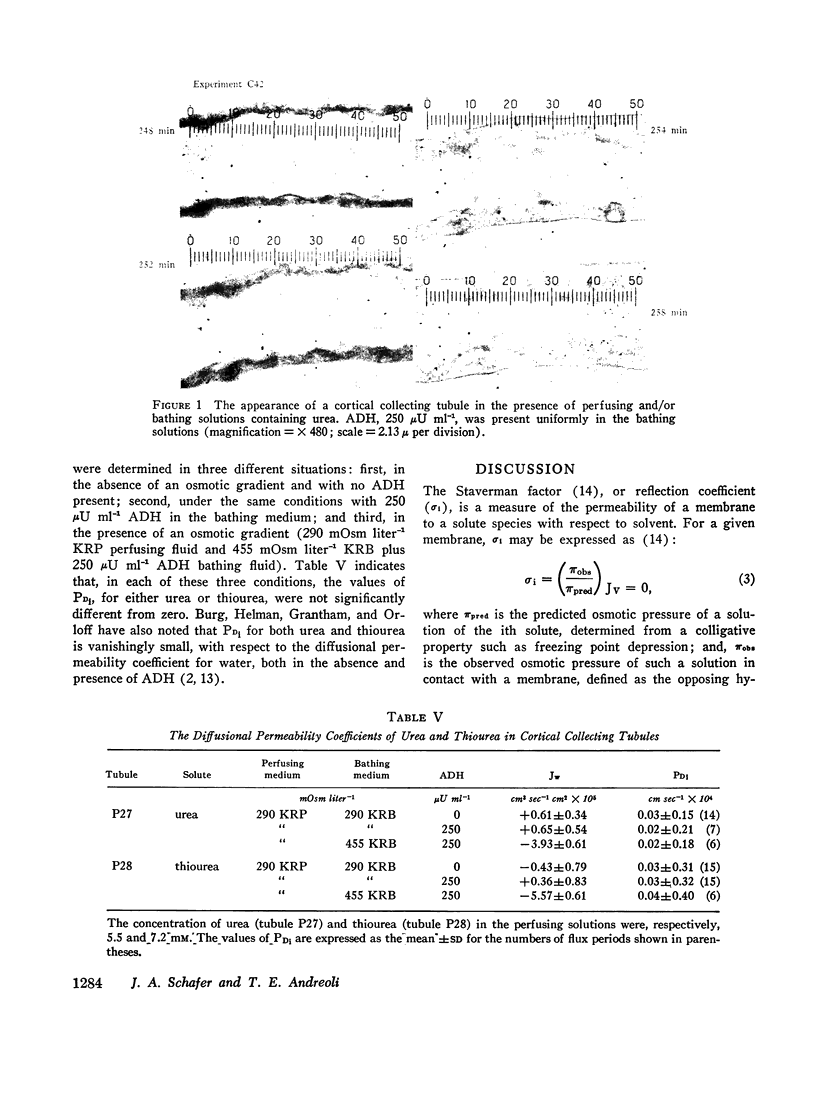
These experiments were intended to evaluate the antidiuretic hormone (ADH)-dependent reflection coefficients of urea, sucrose, and NaCl in cortical and outer medullary collecting tubules isolated from mammalian kidney. In one group of experiments, the ADH-dependent osmotic water flows, when the perfusing solutions contained hypotonic NaCl solutions, were indistinguishable from control observations when either urea or sucrose replaced, in part, NaCl in isotonic bathing solutions (cortical collecting tubules). Similarly, both in cortical and outer medullary collecting tubules exposed to ADH, there was zero net osmotic volume flow when a portion of the NaCl in the bathing and/or perfusing solutions was replaced by either sucrose or urea, so long as the perfusing and bathing solutions were isosmolal. Taken together, these observations suggest that the ADH-dependent reflection coefficients of NaCl, urea, and sucrose, in these tubules, were identical. Since the effective hydrodynamic radii of urea and sucrose are, respectively, 1.8 and 5.2 A, it is likely that σi, for urea, sucrose, and NaCl, was unity. In support of this, the diffusion permeability coefficient (PDi cm sec-1) of urea was indistinguishable from zero. Since the limiting sites for urea penetration were the luminal interfaces of the tubules, these data are consistent with the view that ADH increases diffusional water flow across such interfaces.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreoli T. E., Dennis V. W., Weigl A. M. The effect of amphotericin B on the water and nonelectrolyte permeability of thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Feb;53(2):133–156. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreoli T. E., Troutman S. L. An analysis of unstirred layers in series with "tight" and "porous" lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Apr;57(4):464–478. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.4.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Grantham J., Abramow M., Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cass A., Finkelstein A. Water permeability of thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6):1765–1784. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURBIN R. P., FRANK H., SOLOMON A. K. Water flow through frog gastric mucosa. J Gen Physiol. 1956 Mar 20;39(4):535–551. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dainty J. Osmotic flow. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1965;19:75–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis V. W., Stead N. W., Andreoli T. E. Molecular aspects of polyene- and sterol-dependent pore formation in thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Mar;55(3):375–400. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.3.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everitt C. T., Redwood W. R., Haydon D. A. Problem of boundary layers in the exchange diffusion of water across bimolecular lipid membranes. J Theor Biol. 1969 Jan;22(1):20–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(69)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganote C. E., Grantham J. J., Moses H. L., Burg M. B., Orloff J. Ultrastructural studies of vasopressin effect on isolated perfused renal collecting tubules of the rabbit. J Cell Biol. 1968 Feb;36(2):355–367. doi: 10.1083/jcb.36.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Burg M. B. Effect of vasopressin and cyclic AMP on permeability of isolated collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):255–259. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Ganote C. E., Burg M. B., Orloff J. Paths of transtubular water flow in isolated renal collecting tubules. J Cell Biol. 1969 May;41(2):562–576. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.2.562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays R. M., Franki N., Soberman R. Activation energy for water diffusion across the toad bladder: evidence against the pore enlargement hypothesis. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1016–1018. doi: 10.1172/JCI106572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R., Finkelstein A. The water and nonelectrolyte permeability induced in thin lipid membranes by the polyene antibiotics nystatin and amphotericin B. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jul;56(1):125–145. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C., Thompson T. E. Properties of lipid bilayer membranes separating two aqueous phases: water permeability. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):539–554. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEDEM O., KATCHALSKY A. A physical interpretation of the phenomenological coefficients of membrane permeability. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Sep;45:143–179. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEFOED-JOHNSEN V., USSING H. H. The contributions of diffusion and flow to the passage of D2O through living membranes; effect of neurohypophyseal hormone on isolated anuran skin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953 Mar 31;28(1):60–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb00959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A., HAYS R. M. Permeability of the isolated toad bladder to solutes and its modification by vasopressin. J Gen Physiol. 1962 May;45:921–932. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T., Sakai F., Berliner R. W. In vitro permeability of medullary collecting ducts to water and urea. Am J Physiol. 1968 Mar;214(3):574–581. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.3.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHEIMER J. R., RENKIN E. M., BORRERO L. M. Filtration, diffusion and molecular sieving through peripheral capillary membranes; a contribution to the pore theory of capillary permeability. Am J Physiol. 1951 Oct;167(1):13–46. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.167.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENKIN E. M. Filtration, diffusion, and molecular sieving through porous cellulose membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Nov 20;38(2):225–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS E., MAURO A. Experimental study of the independence of diffusion and hydrodynamic permeability coefficients in collodion membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jan;43:523–532. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., SOLOMON A. K. Determination of the effective hydrodynamic radii of small molecules by viscometry. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Jul;44:1189–1199. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.6.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer J. A., Andreoli T. E. Cellular constraints to diffusion. The effect of antidiuretic hormone on water flows in isolated mammalian collecting tubules. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1264–1278. doi: 10.1172/JCI106921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



