Abstract
The role of augmented aldosterone production in pregnancy is poorly understood. Whereas some consider aldosterone secretion in pregnancy excessive, others suggest that this is a compensatory phenomenon. According to yet another view, mechanisms other than the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system control sodium homeostasis in pregnancy.
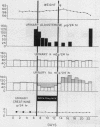
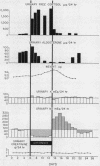
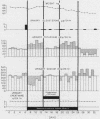
Metabolic balance studies were performed on 14 3rd trimester women. Mineralocorticoid activity was experimentally increased by administering desoxycorticosterone acetate, 9α-fluorocortisol acetate, or ACTH for 4-12 days. Administration of mineralocorticoid or ACTH consistently caused sodium retention. During this mineralocorticoid-induced volume expansion, aldosterone excretion decreased markedly. Natriuresis, which followed discontinuance of the drug, continued while aldosterone excretion, although greatly diminished compared to control values, was greater than that found in normal, nonpregnant individuals. This saline diuresis did not subside until aldosterone excretion returned to its previously high control values. These observations support the concept of the physiological role of increased aldosterone production in pregnancy.
Results further revealed a marked dissociation between antinatriuretic and kaliuretic effects of corticoids. Potassium balance was virtually unaltered during continued mineralocorticoid or ACTH administration, despite initially high or abruptly increased sodium intakes. Finally, mineralocorticoid escape was induced by continued desoxycorticosterone acetate therapy in two male volunteers. Kaliuresis occurred which was subsequently abolished when progresterone was administered. Sodium excretion, however, was virtually unaltered. These data, mimicking results observed in gravidas, suggest that progesterone is an important determinant of potassium homeostasis in pregnant women.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASSALI N. S., CLARK L. C., Jr, SOBEL E. H. Studies on toxemia of pregnancy: Effect of desoxycorticosterone acetate on hemodynamics and electrolyte balance of normal pregnant women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1953 Sep;13(9):1030–1042. doi: 10.1210/jcem-13-9-1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASSALI N. S., SUYEMOTO R. Studies on toxemia of pregnancy; effects of corticotropic hormone (ACTH) on the hemodynamics and the excretion of electrolytes of normal pregnant women. Metabolism. 1954 Jul;3(4):303–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AUGUST J. T., NELSON D. H., THORN G. W. Response of normal subjects to large amounts of aldosterone. J Clin Invest. 1958 Nov;37(11):1549–1555. doi: 10.1172/JCI103747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTTER F. C., DUNCAN L. E., Jr, LIDDLE G. W. Dual mechanism regulating adrenocortical function in man. Am J Med. 1956 Sep;21(3):380–386. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(56)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balikian H. M., Brodie A. H., Dale S. L., Melby J. C., Tait J. F. Effect of posture on the metabolic clearance rate, plasma concentration and blood production rate of aldosterone in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Nov;28(11):1630–1640. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-11-1630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biglieri E. G., Slaton P. E., Jr Pregnancy and primary aldosteronism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Nov;27(11):1628–1632. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-11-1628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHOBANIAN A. V., BURROWS B. A., HOLLANDER W. Body fluid and electrolyte composition in arterial hypertension. II. Studies in mineralocorticoid hypertension. J Clin Invest. 1961 Feb;40:416–422. doi: 10.1172/JCI104269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRABBE J. The role of aldosterone in the renal concentration mechanism, in man. Clin Sci. 1962 Aug;23:39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EHRLICH E. N., LAVES M., LUGIBIHL K., LANDAU R. L. Progesterone-aldosterone interrelationships in pregnancy. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Apr;59:588–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich E. N. Heparinoid-induced inhibition of aldosterone secretion in pregnant women. The role of augmented aldosterone secretion in sodium conservation during normal pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1971 Apr 1;109(7):963–970. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(71)90274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich E. N. Reciprocal variations in urinary cortisol and aldosterone in response to increased salt intake in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Oct;26(10):1160–1169. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-10-1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich E. N. Reciprocal variations in urinary cortisol and aldosterone in response to the sodium-depleting influence of hydrochlorothiazide and ethacrynic acid in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Jun;27(6):836–842. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-6-836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIEBISCH G., WINDHAGER E. E. RENAL TUBULAR TRANSFER OF SODIUM, CHLORIDE AND POTASSIUM. Am J Med. 1964 May;36:643–669. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebisch G. Functional organization of proximal and distal tubular electrolyte transport. Nephron. 1969;6(3):260–281. doi: 10.1159/000179733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H. H., Harrington A. R., Valtin H. On the role of antidiuretic hormone in the inhibition of acute water diuresis in adrenal insufficiency and the effects of gluco- and mineralocorticoids in reversing the inhibition. J Clin Invest. 1970 Sep;49(9):1724–1736. doi: 10.1172/JCI106390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer K., Stolte H. The proximal and distal tubular action of adrenal steroids on Na reabsorption. Nephron. 1969;6(3):188–204. doi: 10.1159/000179728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES K. M., LLOYD-JONES R., RIONDEL A., TAIT J. F., TAIT S. A., BULBROOK R. D., GREENWOOD F. C. Aldosterone secretion and metabolism in normal men and women and in pregnancy. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1959 Mar;30(3):321–342. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0300321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLIMAN B., PETERSON R. E. Double isotope derivative assay of aldosterone in biological extracts. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1639–1648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAIDLAW J. C., RUSE J. L., GORNALL A. G. The influence of estrogen and progesterone on aldosterone excretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Feb;22:161–171. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-2-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDAU R. L., LUGIBIHL K. Inhibition of the sodium-retaining influence of aldosterone by progesterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Nov;18(11):1237–1245. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-11-1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDAU R. L., LUGIBIHL K. The catabolic and natriuretic effects of progesterone in man. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1961;17:249–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton M. A., Laragh J. H. Effect of corticotropin on aldosterone excretion and plasma renin in normal subjects, in essential hypertension and in primary aldosteronism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Jul;28(7):1006–1013. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-7-1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RELMAN A. S., SCHWARTZ W. B. The effect of DOCA on electrolyte balance in normal man and its relation to sodium chloride intake. Yale J Biol Med. 1952 Jun;24(6):540–558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROVNER D. R., CONN J. W., KNOPF R. F., COHEN E. L., HSUEH M. T. NATURE OF RENAL ESCAPE FROM THE SODIUM-RETAINING EFFECT OF ALDOSTERONE IN PRIMARY ALDOSTERONISM AND IN NORMAL SUBJECTS. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Jan;25:53–64. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb C. A., Davis J. O., Johnson J. A., Blaine E. H., Schneider E. G., Baumber J. S. Mechanisms regulating the renal excretion of sodium during pregnancy. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):871–880. doi: 10.1172/JCI106306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMS E. A. KIDNEY DISEASE IN PREGNANCY. Annu Rev Med. 1965;16:221–238. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.16.020165.001253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G., Derra M. Der Einfluss hoher Aldosteron-Gaben auf die Elektrolyt-Ausscheidung bei gesunden Schwangeren. Arch Gynakol. 1965;200(7):715–734. doi: 10.1007/BF00668450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORN G. W., SHEPPARD R. H., MORSE W. I., REDDY W. J., BEIGELMAN P. M., RENOLD A. E. Comparative action of aldosterone and 9-alpha-fluorohydrocortisone in man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 May 27;61(2):609–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb42514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucci J. R., Espiner E. A., Jagger P. I., Pauk G. L., Lauler D. P. ACTH stimulation of aldosterone secretion in normal subjects and in patients with chronic adrenocortical insufficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Apr;27(4):568–575. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-4-568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE M., MEEKER C. I., GRAY M. J., SIMS E. A., SOLOMON S. SECRETION RATE OF ALDOSTERONE IN NORMAL PREGNANCY. J Clin Invest. 1963 Oct;42:1619–1631. doi: 10.1172/JCI104847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]