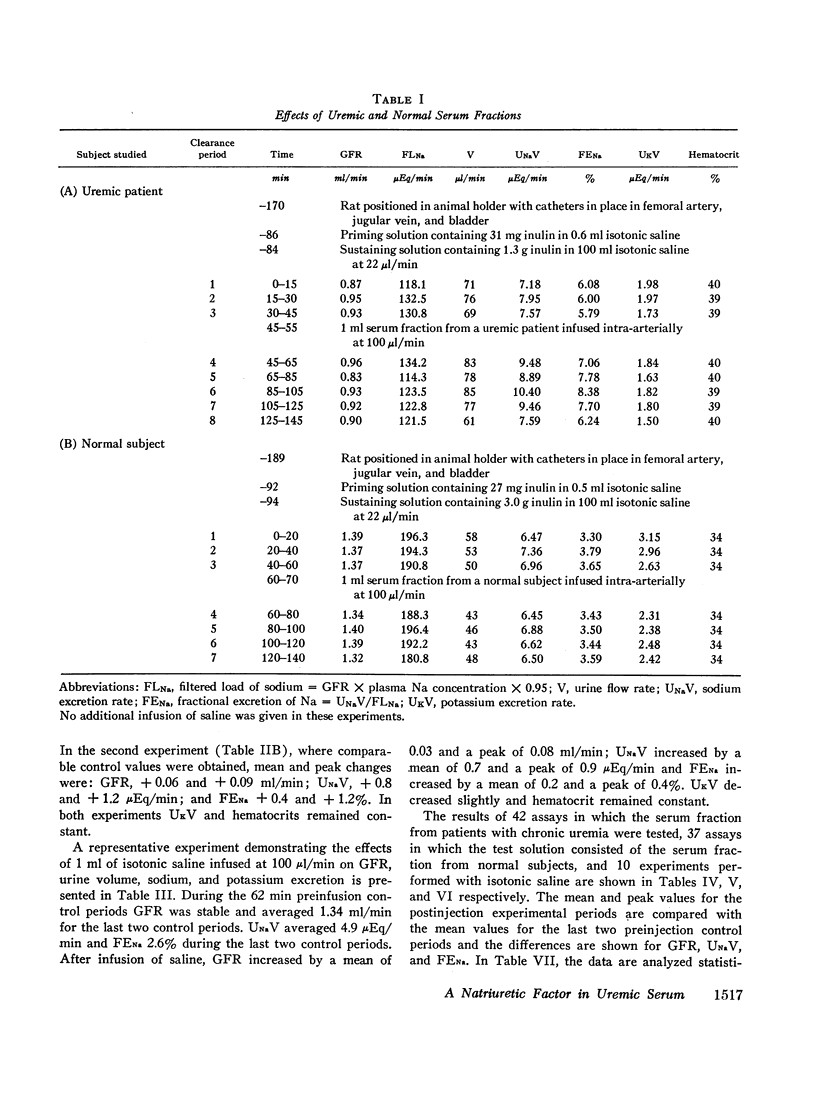
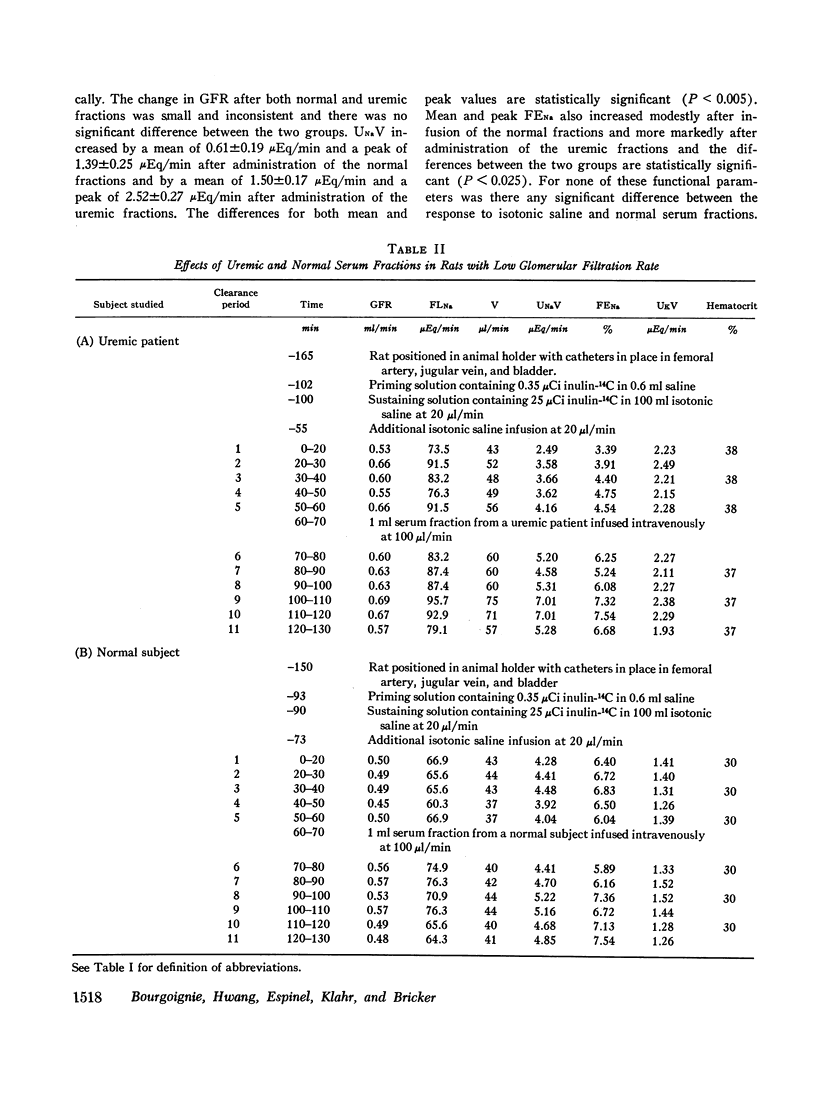
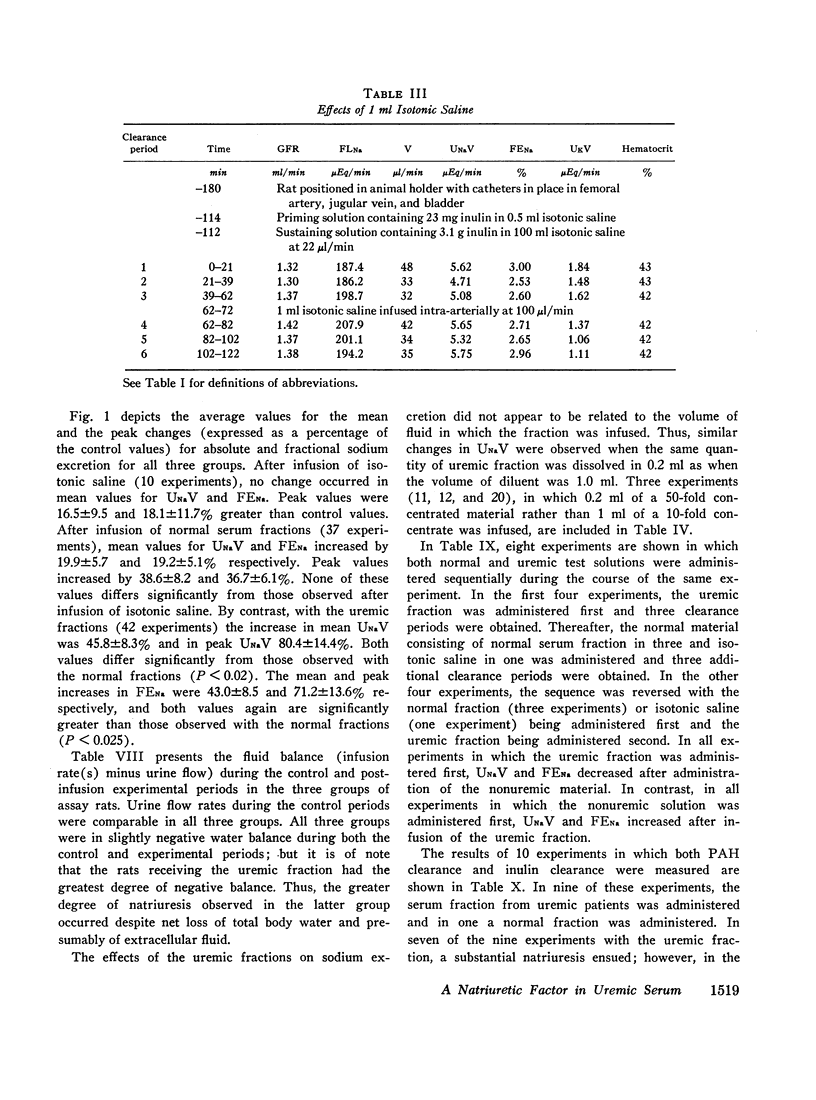
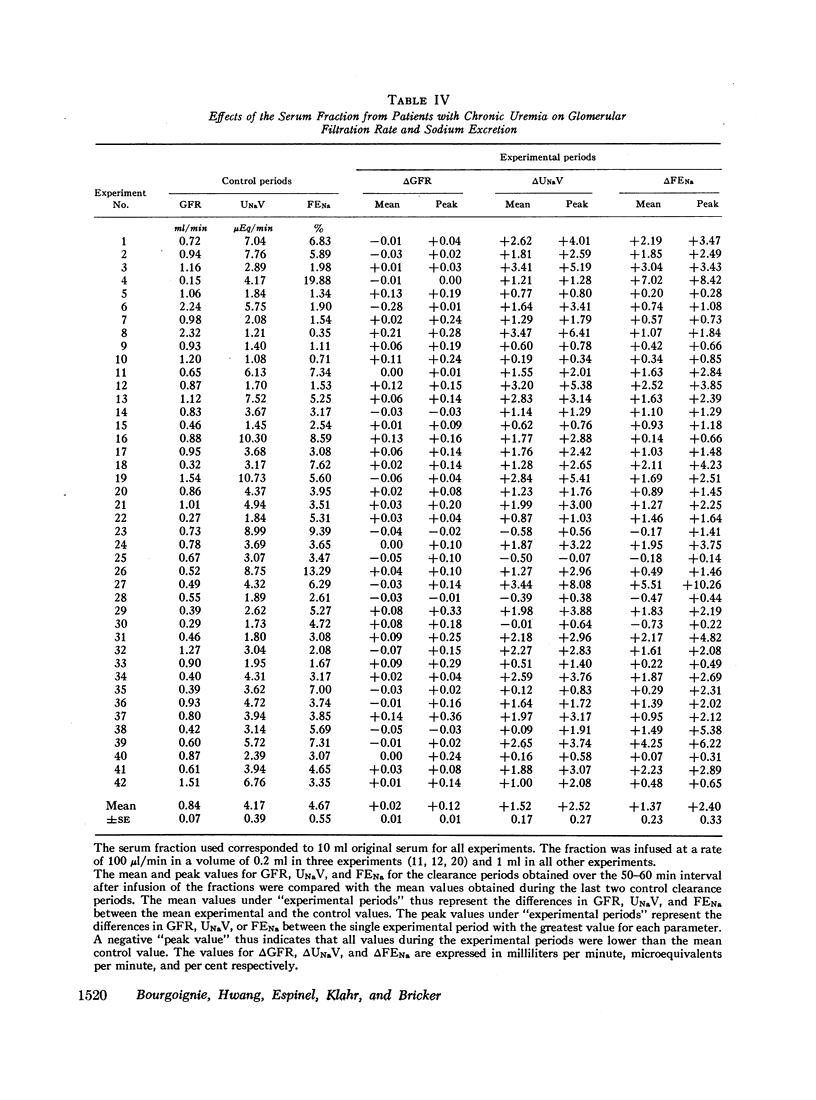
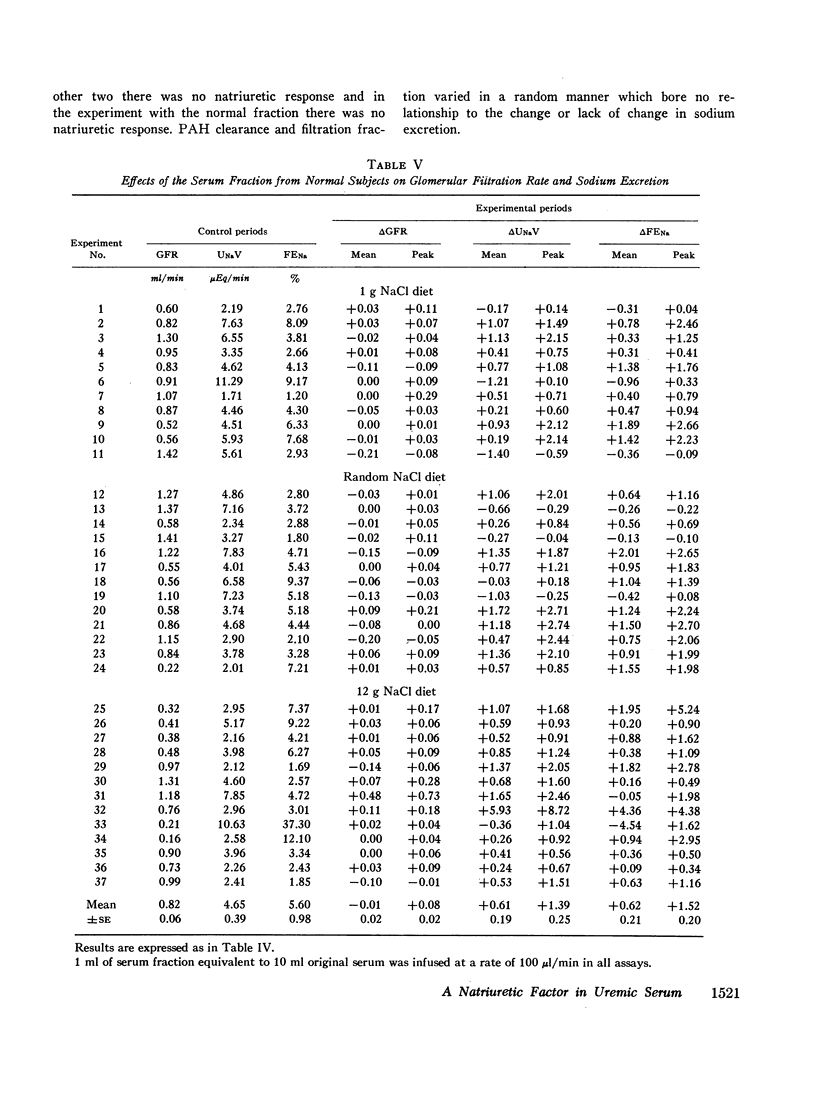
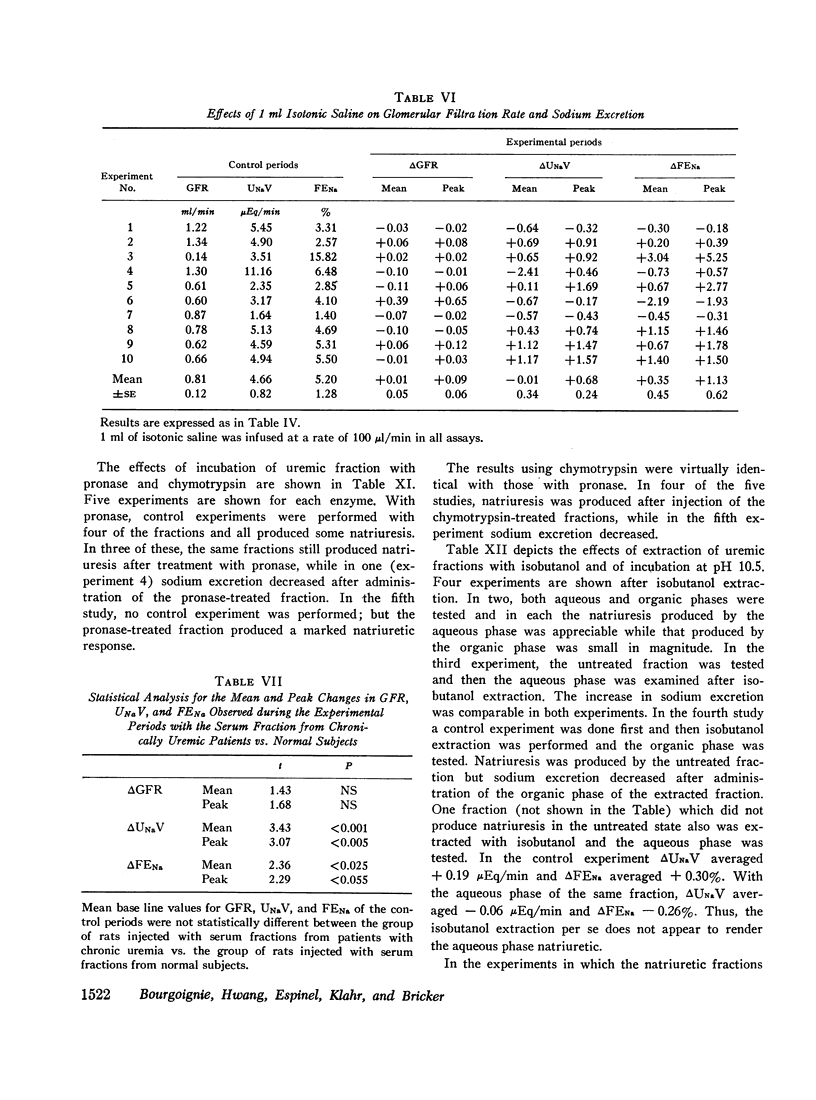
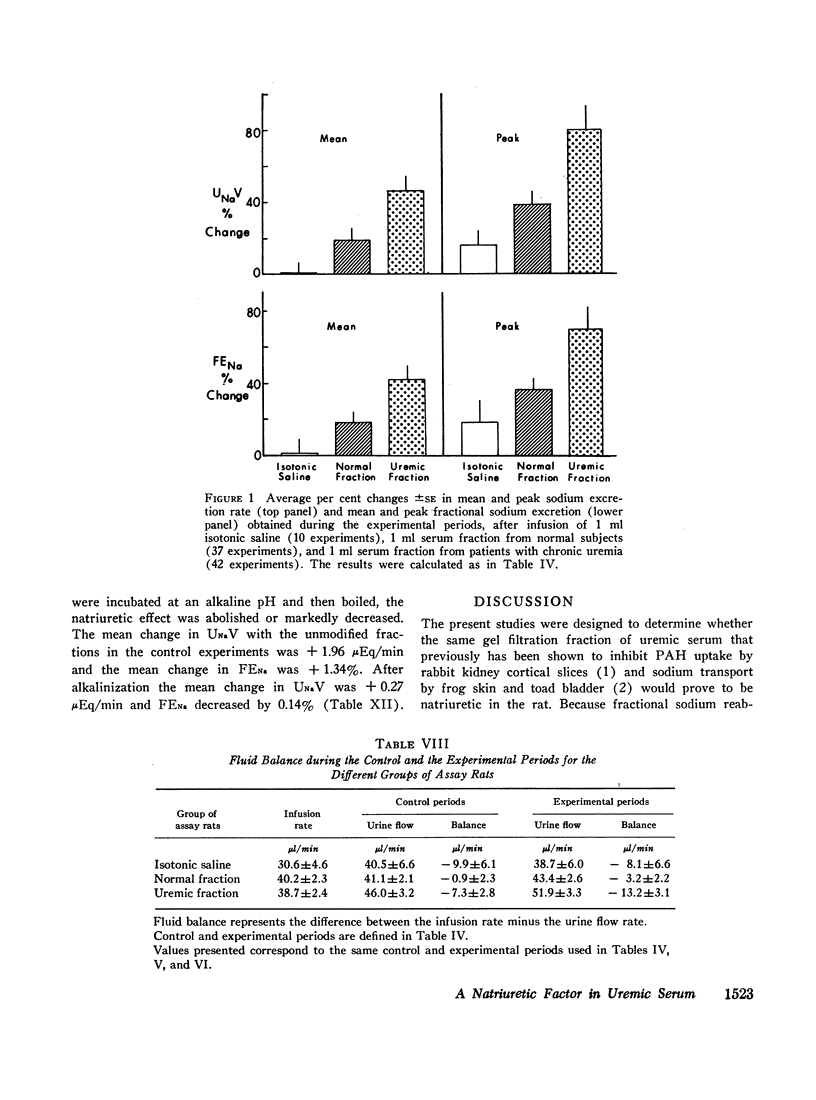
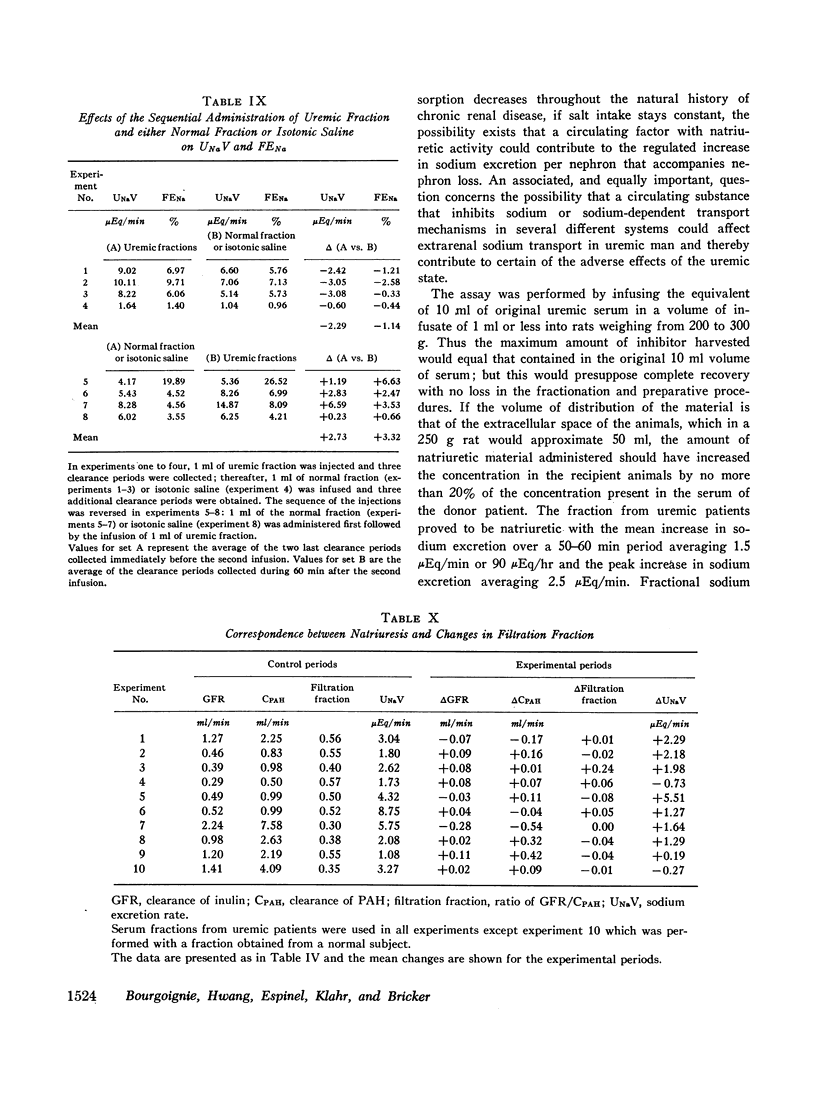
Abstract
Sera from chronically uremic and normal individuals were subjected to gel filtration with Sephadex G-25 and the same fraction of both was infused into rats with a decreased nephron population to determine the effects on sodium excretion. Sodium excretion rate and fractional sodium excretion increased slightly with the normal fractions; but the increase in both functional parameters produced by the uremic fractions was substantially and significantly greater. The natriuresis could not be explained by associated changes in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), para-aminohippurate (PAH) clearance, filtration fraction, hematocrit, or blood pressure. The possibility thus exists that the inhibitor affected some component part of the transepithelial sodium transport system. The elution characteristics of the fraction plus certain of its physicochemical properties suggest that the inhibitor of sodium reabsorption by the rat nephron may be identical with the inhibitor of PAH uptake by kidney slices and the inhibitor of transepithelial sodium transport by the frog skin and toad bladder previously found in the serum of chronically uremic patients.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourgoignie J., Klahr S., Bricker N. S. Inhibition of transepithelial sodium transport in the frog skin by a low molecular weight fraction of uremic serum. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):303–311. doi: 10.1172/JCI106495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Falchuk K. H., Keimowitz R. I., Berliner R. W. The relationship between peritubular capillary protein concentration and fluid reabsorption by the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1519–1531. doi: 10.1172/JCI106118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bricker N. S., Klahr S., Purkerson M., Schultze R. G., Avioli L. V., Birge S. J. In vitro assay for a humoral substance present during volume expansion and uraemia. Nature. 1968 Sep 7;219(5158):1058–1059. doi: 10.1038/2191058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke T. J., Robinson R. R., Clapp J. R. Effect of arterial hematocrit on sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1971 May;220(5):1536–1541. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.5.1536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty T. M., Belleau L. J., Martino J. A., Earley L. E. Interrelationship of physical factors affecting sodium reabsorption in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1968 Dec;215(6):1442–1447. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.6.1442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUHR J., KACZMARCZYK J., KRUTTGEN C. D. Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr. 1955 Aug 1;33(29-30):729–730. doi: 10.1007/BF01473295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. M., Aynedjian H. S., Bank N. Effect of acute hypertension on sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jul;47(7):1696–1709. doi: 10.1172/JCI105860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewy J. E., Windhager E. E. Peritubular control of proximal tubular fluid reabsorption in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1968 May;214(5):943–954. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.5.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. W., Earley L. E. Effects of hematocrit on renal hemodynamics and sodium excretion in hydropenic and volume-expanded dogs. J Clin Invest. 1970 Sep;49(9):1656–1667. doi: 10.1172/JCI106383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultze R. G., Shapiro H. S., Bricker N. S. Studies on the control of sodium excretion in experimental uremia. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):869–877. doi: 10.1172/JCI106045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankel S. W., Robson A. M., Bricker N. S. On the mechanism of the splay in the glucose titration curve in advanced experimental renal disease in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1967 Feb;46(2):164–172. doi: 10.1172/JCI105519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slatopolsky E., Elkan I. O., Weerts C., Bricker N. S. Studies on the characteristics of the control system governing sodium excretion in uremic man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Mar;47(3):521–530. doi: 10.1172/JCI105748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


