Abstract
Previous observations in normal subjects have suggested that when 5-g glucose pulses (P) were given in the following sequence: before (P1) and 45 min after beginning a 300 mg/min glucose infusion (P2); during the 20th hr (P3) and 1 hr after the infusion was stopped (P4); the insulin responses were consistent with a simple two-pool model. One pool is a readily available small storage pool which is refilled by a second, larger, more slowly responding pool that controls basal and steady-state insulin output. The identical protocol was employed to evaluate the insulin responses in 13 nonobese diabetic subjects.
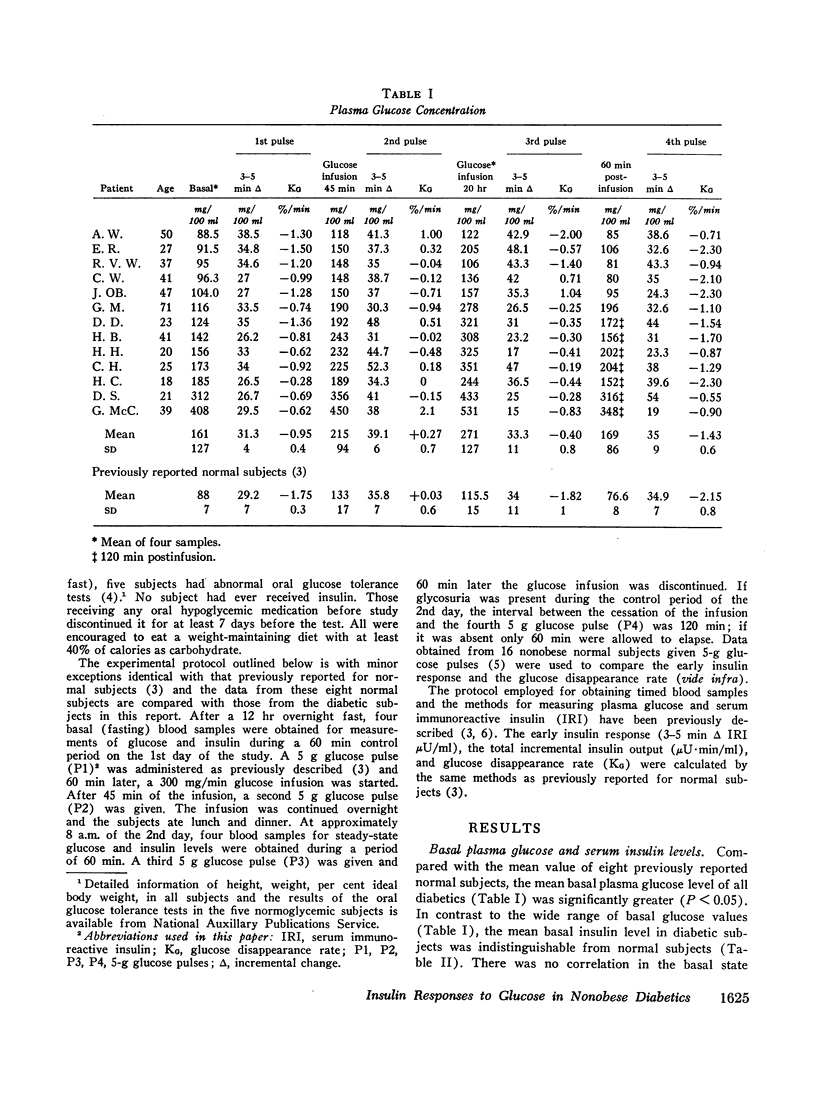
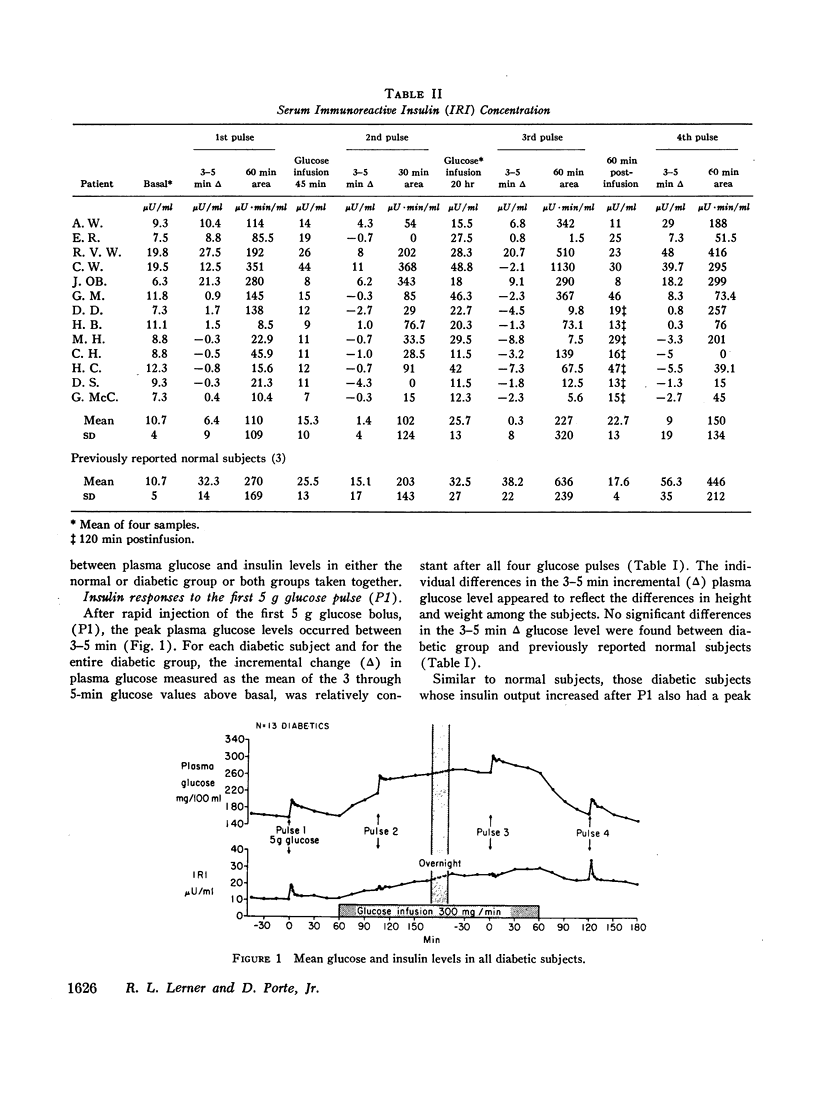
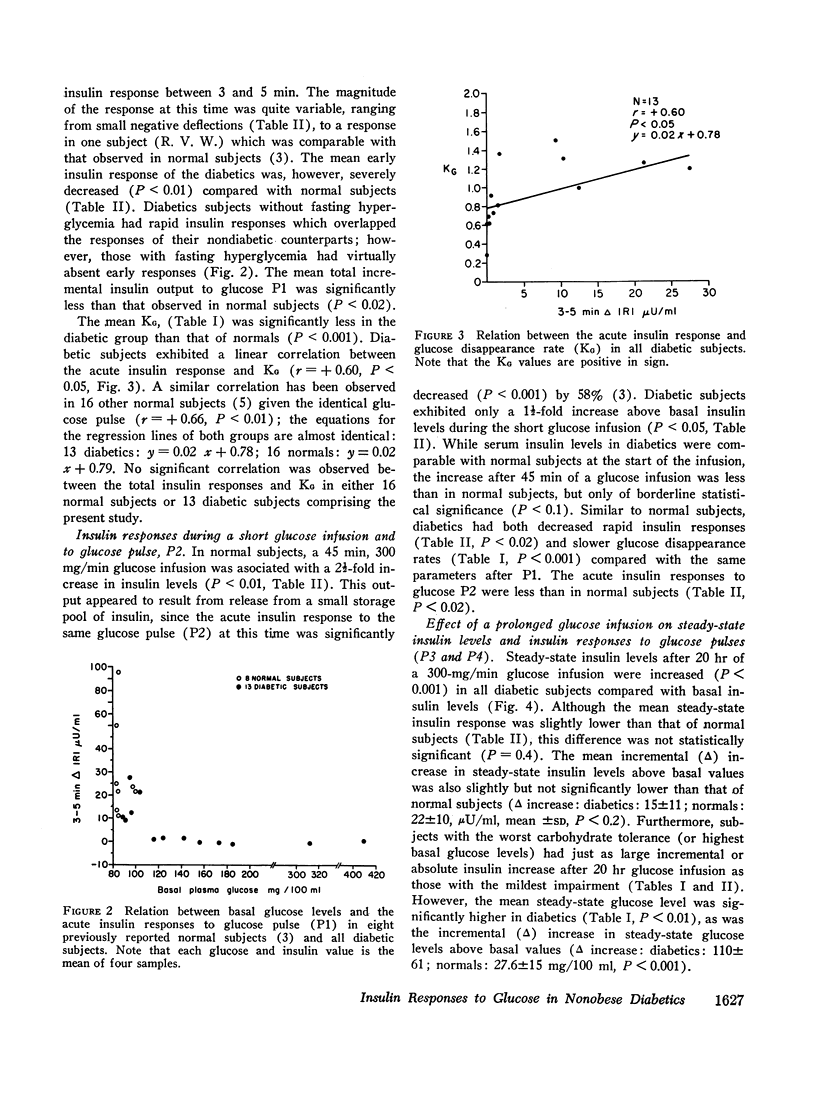
Diabetics had basal insulin levels indistinguishable from normals (diabetics: 10.7±4; normals: 10.7±5, mean ±SD, μU/ml), but had significantly elevated basal glucose levels (diabetics: 161±27; normals: 88±7, mg/100 ml, P < 0.05). The mean early insulin response (3-5 min Δ IRI) after a 5 g glucose pulse (P1) was significantly diminished in diabetics (diabetics 6.4±9; normals: 32.5±14, μU/ml, P < 0.01) consistent with a defective storage pool output. The glucose disappearance rate, KG, decreased in parallel with the early insulin response and the slope of the regression line between these two variables was virtually identical with that calculated from 16 normal subjects. Similar to normal subjects, during the short glucose infusion, the acute insulin response to P2 was diminished in diabetics (P < 0.02). In normal subjects after 20 hr of infusion, the rapid insulin responses to P3 are restored to the preinfusion P1 values, and 1 hr after the infusion was stopped, the responses to P4 are increased twofold (P < 0.001). Diabetics, however, demonstrated decreased early responses to P3 (P < 0.001) and no increased response to P4.
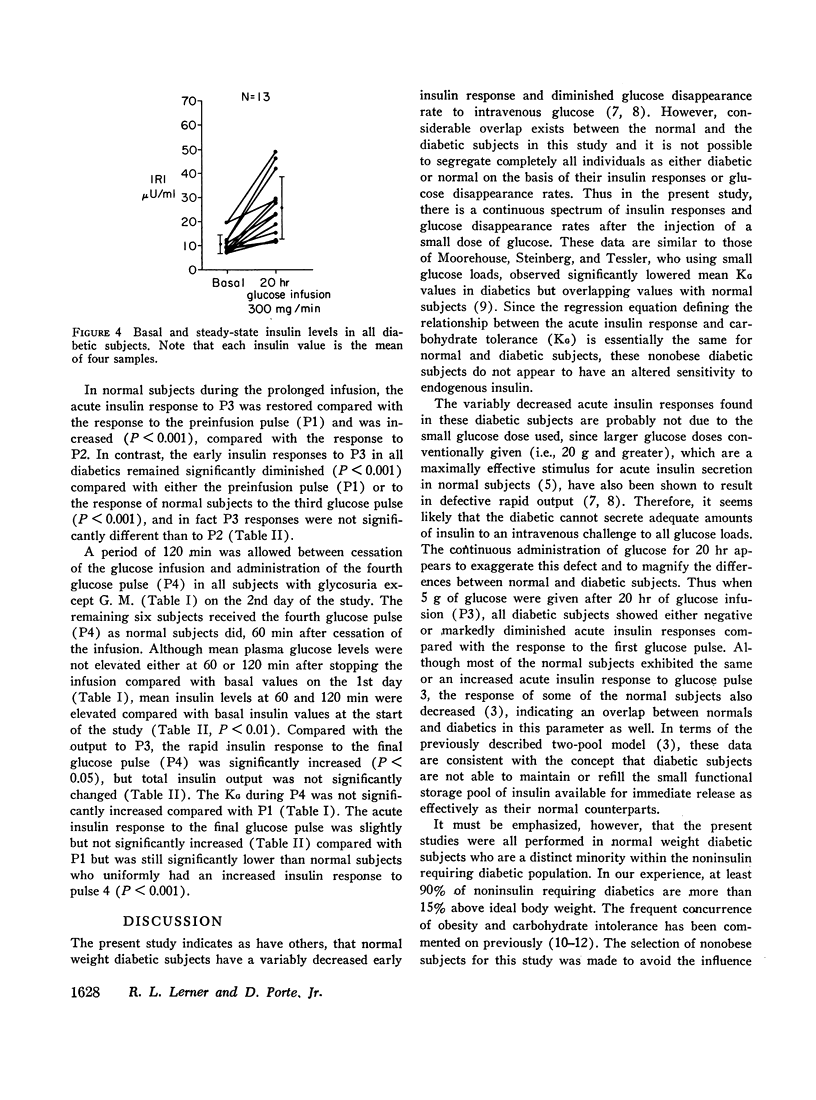
In contrast to the diminished acute insulin responses to glucose pulses, diabetics have steady-state insulin levels after 20 hr of glucose infusion similar to those of normal subjects (diabetics: 25.7±13; normals: 32.5±14, μU/ml). Thus both basal and steady-state insulin levels of diabetics were comparable with those of normal subjects, which suggest that although the rapid insulin response from the storage pool output is defective in diabetics, the more slowly responding pool is intact.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagdade J. D., Bierman E. L., Porte D., Jr Counter-regulation of basal insulin secretion during alcohol hypoglycemia in diabetic and normal subjects. Diabetes. 1972 Feb;21(2):65–70. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade J. D., Bierman E. L., Porte D., Jr The significance of basal insulin levels in the evaluation of the insulin response to glucose in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1549–1557. doi: 10.1172/JCI105646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Nelson N. C. Portal and peripheral vein immunoreactive insulin concentrations before and after glucose infusion. Diabetes. 1970 May;19(5):302–306. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.5.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Nelson N. C. Portal vein insulin concentrations in diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1971 May;20(5):286–288. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.5.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R. "What is inherited--what is added" hypothesis for the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1967 Sep;16(9):615–627. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.9.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J., Orskov H. The relationship between endogenous serum insulin concentration and glucose uptake in the forearm muscles of nondiabetics. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jun;47(6):1262–1268. doi: 10.1172/JCI105818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crockford P. M., Hazzard W. R., Williams R. H. Insulin response to glucagon. The opposing effects of diabetes and obesity. Diabetes. 1969 Apr;18(4):216–224. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.4.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Grodsky G. M. Dynamics of insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1968 Sep;83(3):572–584. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-3-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J. Influence of endogenous insulin secretion on splanchnic glucose and amino acid metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1702–1711. doi: 10.1172/JCI106659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbath N., Hetenyi G., Jr Glucose dynamics in normal subjects and diabetic patients before and after a glucose load. Diabetes. 1966 Nov;15(11):778–789. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.11.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Roth J. Plasma insulin: fluctuations in the "big" insulin component in man after glucose and other stimuli. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2225–2234. doi: 10.1172/JCI106188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Sherman B., Roth J. Proinsulin-like component of circulating insulin in the basal state and in patients and hamsters with islet cell tumors. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2113–2122. doi: 10.1172/JCI106705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARAM J. H., GRODSKY G. M., FORSHAM P. H. Excessive insulin response to glucose in obese subjects as measured by immunochemical assay. Diabetes. 1963 May-Jun;12:197–204. doi: 10.2337/diab.12.3.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. L., Porte D., Jr Relationship between intravenous glucose loads, insulin responses and glucose disappearance rate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Sep;33(3):409–417. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORHOUSE J. A., STEINBERG J., TESSLER B. B. EFFECT OF GLUCOSE DOSE UPON INTRAVENOUS GLUCOSE TOLERANCE IN HEALTH AND IN DIABETES. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1963 Nov;23:1074–1079. doi: 10.1210/jcem-23-11-1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to glucose and tolbutamide of normal weight and obese diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):867–874. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Pupo A. A. Insulin responses to glucose: evidence for a two pool system in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2309–2319. doi: 10.1172/JCI106197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer H. S., Allen E. W., Herron A. L., Jr, Brennan M. T. Insulin secretion in response to glycemic stimulus: relation of delayed initial release to carbohydrate intolerance in mild diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Mar;46(3):323–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI105534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. G., Benedetti A., Grodsky G. M., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Early phase of insulin release. Diabetes. 1968 Nov;17(11):684–692. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.11.684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKERSON H. L., HYMAN H., KAUFMAN M., McCUISTION A. C., FRANCIS J. O. Diagnostic evaluation of oral glucose tolerance tests in nondiabetic subjects after various levels of carbohydrate intake. N Engl J Med. 1960 May 26;262:1047–1053. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196005262622101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



