Abstract
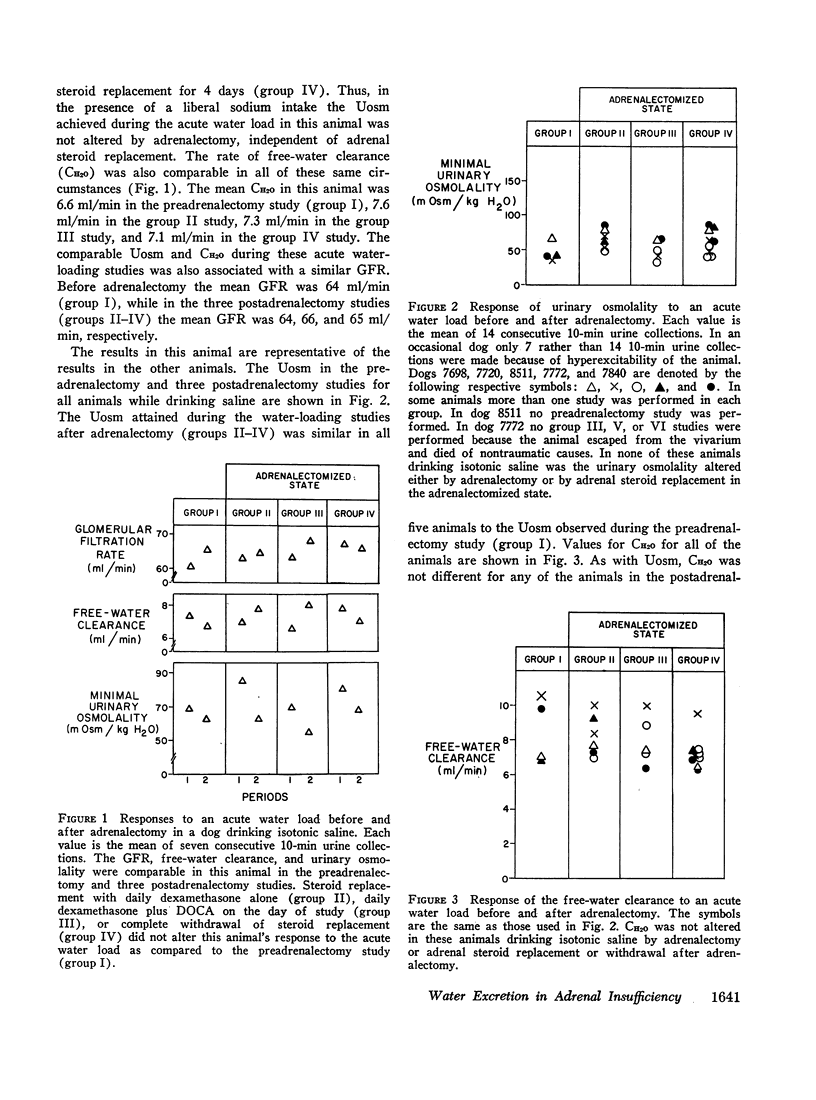
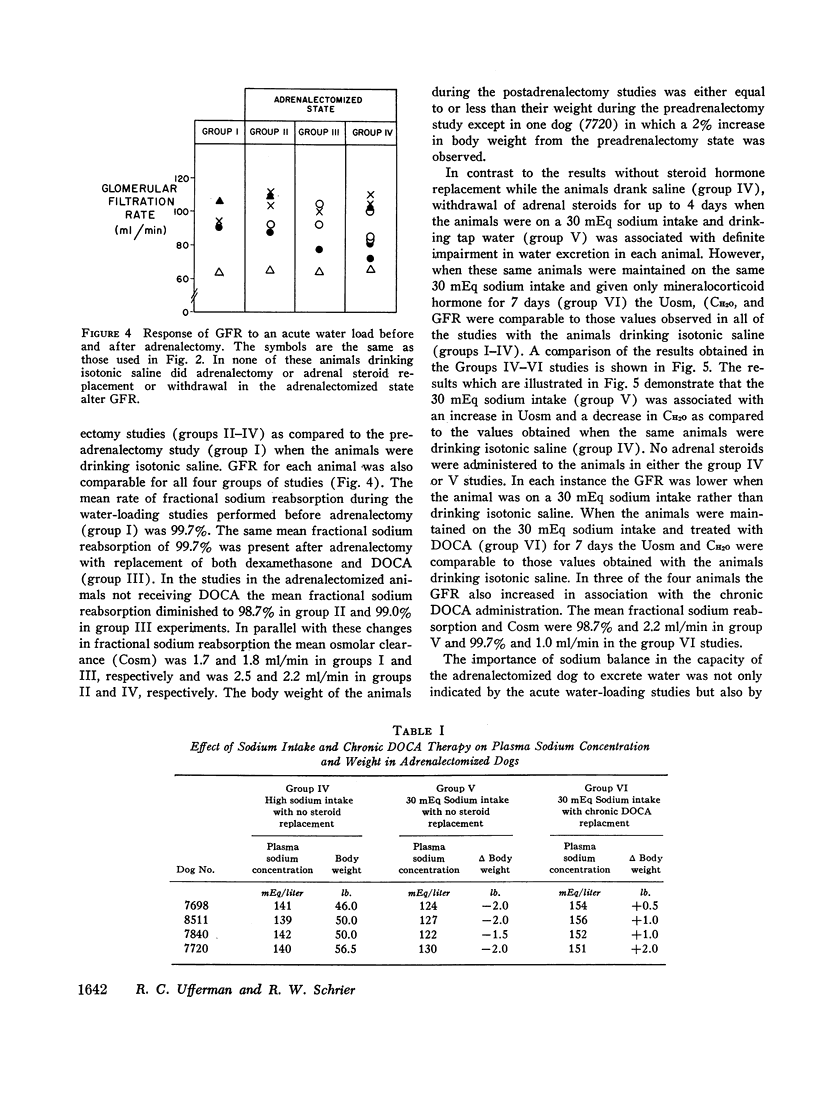
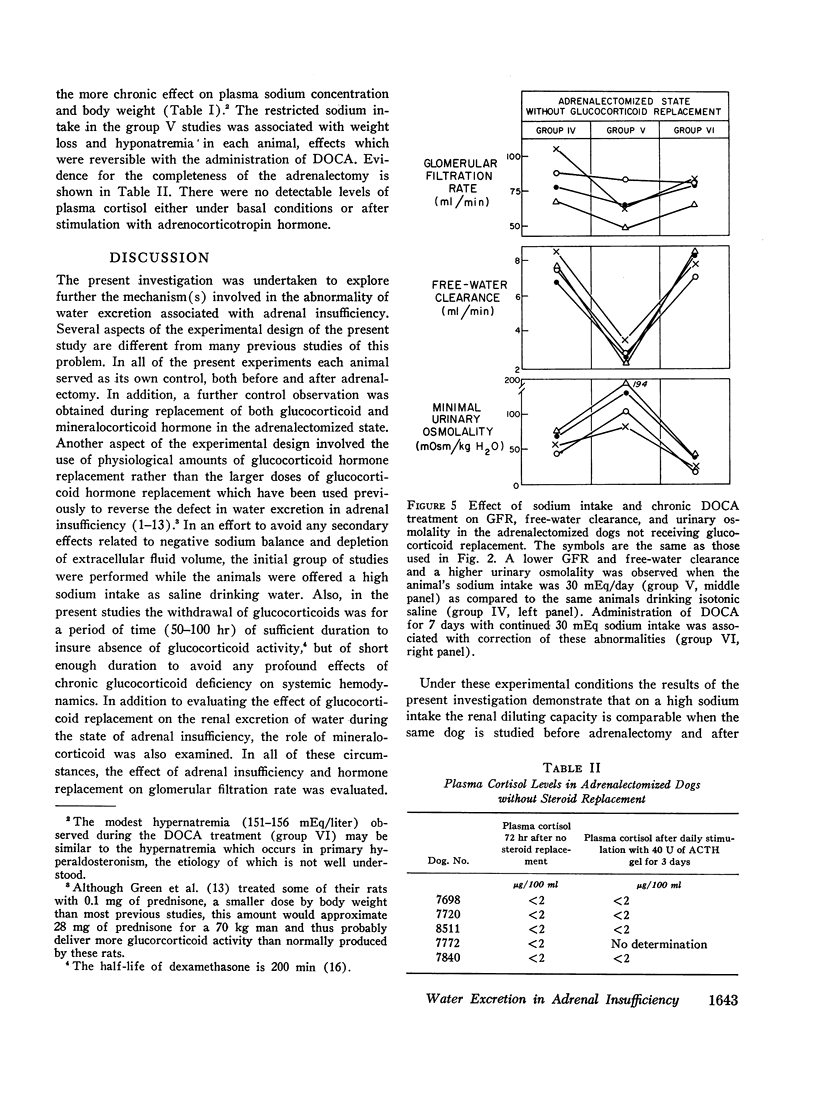
The response of trained, conscious dogs to an acute water load was studied before adrenalectomy and under five conditions of hormonal replacement and sodium intake after adrenalectomy. Before adrenalectomy, with the dogs drinking isotonic saline, the minimal urinary osmolality (Uosm) was 47±7 (SEM) mOsm and free-water clearance (CH2O) was 8.6±1 ml/min. These values were not different after adrenalectomy with or without deoxycorticosterone (DOCA) if the animals continued to drink saline and receive dexamethasone. Moreover, after adrenalectomy in the presence of saline drinking both dexamethasone and DOCA could be withdrawn for up to 4 days without impairment of diluting ability (Uosm, 54±7 mOsm and CH2O, 7.3±1 ml/min). In contrast, when the dogs drank tap water (Na intake 30 mEq/day), water loading in the absence of dexamethasone and DOCA was associated with a significantly higher Uosm (127±28 mOsm) and lower CH2O (2.7±0.3 ml/min). Replacing DOCA alone in the presence of this limited Na intake returned diluting ability to normal (Uosm 31±7 mOsm, CH2O 7.7±0.5 ml/min). Glomerular filtration rate for each animal was the same under each condition except for a significant diminution which occurred when dexamethasone and DOCA were withdrawn while the animals were on a 30 mEq sodium intake. In contrast to previous conclusions, the present results indicate that in the absence of adrenal hormones normal renal diluting ability may occur, indicating both maximal suppression of vasopressin release and maximal distal tubular impermeability to water. In the present study the diluting defect observed after adrenalectomy related to negative sodium balance and could be overcome by either replacement with DOCA or a high intake of sodium alone.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman G. L., Miller C. L. Role of hypovolemia in the impaired water diuresis of adrenal insufficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Feb;30(2):252–258. doi: 10.1210/jcem-30-2-252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agus Z. S., Goldberg M. Role of antidiuretic hormone in the abnormal water diuresis of anterior hypopituitarism in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1478–1489. doi: 10.1172/JCI106633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed A. B., George B. C., Gonzalez-Auvert C., Dingman J. F. Increased plasma arginine vasopressin in clinical adrenocortical insufficeincy and its inhibition by glucosteroids. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):111–123. doi: 10.1172/JCI105504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERLINER R. W., DAVIDSON D. G. Production of hypertonic urine in the absence of pituitary antidiuretic hormone. J Clin Invest. 1957 Oct;36(10):1416–1427. doi: 10.1172/JCI103541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUNIM J. J., BLACK R. L., LUTWAK L., PETERSON R. E., WHEDON G. D. Studies on dexamethasone, a new synthetic steroid, in rheurheumatoid arthritis: a preliminary report; adrenal cortical, metabolic and early clinical effects. Arthritis Rheum. 1958 Aug;1(4):313–331. doi: 10.1002/art.1780010404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUTLER R. E., KLEEMAN C. R., KOPLOWITZ J., MAXWELL M. H., DOWLING J. T. Mechanisms of impaired water excretion in adrenal and pituitary insufficiency. III. The effect of extracellular or plasma volume expansion, or both, on the impaired diuresis. J Clin Invest. 1962 Jul;41:1524–1530. doi: 10.1172/JCI104608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. W., Cleghorn R. A., Ferguson J. K., Fowler J. L. FACTORS CONCERNED IN THE CIRCULATORY FAILURE OF ADRENAL INSUFFICIENCY. J Clin Invest. 1947 May;26(3):359–363. doi: 10.1172/JCI101817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL GRECO F., DE WARDENER H. E. The effect on urine osmolarity of a transient reduction in glomerular filtration rate and solute output during a water diuresis. J Physiol. 1956 Feb 28;131(2):307–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINGMAN J. F., DESPOINTES R. H. Adrenal steroid inhibition of vasopressin release from the neurohypophysis of normal subjects and patients with Addison's disease. J Clin Invest. 1960 Dec;39:1851–1863. doi: 10.1172/JCI104209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD O., BURSTON R. A. The diuretic response to ingested water in Addison's disease and panhypopituitarism and the effect of cortisone thereon. Clin Sci. 1952 May;11(2):113–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD O., DAVIES S. A., CAHILL G., Jr The action of cortisone and desoxycorticosterone acetate on glomerular filtration rate and sodium and water exchange in the adrenalectomized dog. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jun;34(6):761–776. doi: 10.1172/JCI103131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAUNT R., BIRNIE J. H., EVERSOLE W. J. Adrenal cortex and water metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1949 Oct;29(4):281–310. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1949.29.4.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILL J. R., Jr, GANN D. S., BARTTER F. C. Restoration of water diuresis in addisonian patients by expansion of the volume of extracellular fluid. J Clin Invest. 1962 May;41:1078–1085. doi: 10.1172/JCI104558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H. H., Harrington A. R., Valtin H. On the role of antidiuretic hormone in the inhibition of acute water diuresis in adrenal insufficiency and the effects of gluco- and mineralocorticoids in reversing the inhibition. J Clin Invest. 1970 Sep;49(9):1724–1736. doi: 10.1172/JCI106390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler J. S., Preston A. S., Orloff J. Effect of adrenal steroid hormones on the response of the toad's urinary bladder to vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):823–833. doi: 10.1172/JCI106040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEEMAN C. R., CZACZKES J. W., CUTLER R. MECHANISMS OF IMPAIRED WATER EXCRETION IN ADRENAL AND PITUITARY INSUFFICIENCY. IV. ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE IN PRIMARY AND SECONDARY ADRENAL INSUFFICIENCY. J Clin Invest. 1964 Aug;43:1641–1648. doi: 10.1172/JCI105039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEEMAN C. R., KOPLOWITZ J., MAXWELL M. H., CUTLER R., DOWLING J. T. Mechanisms of impaired water excretion in adrenal and pituitary insufficiency. II. Interrelationships of adrenal cortical steroids and antidiuretic hormone in normal subjects and in diabetes insipidus. J Clin Invest. 1960 Sep;39:1472–1480. doi: 10.1172/JCI104166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEEMAN C. R., MAXWELL M. H., ROCKNEY R. E. Mechanisms of impaired water excretion in adrenal and pituitary insufficiency. I. The role of altered glomerular filtration rate and solute excretion. J Clin Invest. 1958 Dec;37(12):1799–1808. doi: 10.1172/JCI103773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDEMAN R. D., VAN BUREN H. C., RAISZ L. G. Effects of steroids on water diuresis and vasopressin sensitivity. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jan;40:152–158. doi: 10.1172/JCI104229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefer A. M., Verrier R. L., Carson W. W. Cardiac performance in experimental adrenal insufficiency in cats. Circ Res. 1968 Jun;22(6):817–827. doi: 10.1161/01.res.22.6.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTINGLY D. A simple fluorimetric method for the estimation of free 11-hydroxycorticoids in human plasma. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Jul;15:374–379. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.4.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLEESKY S. A specific water diuresis test for adrenocortical insufficiency. Lancet. 1953 Apr 18;1(6764):769–770. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)91895-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOFF J., WAGNER H. N., Jr, DAVIDSON D. G. The effect of variations in solute excretion and vasopressin dosage on the excretion of water in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1958 Mar;37(3):458–464. doi: 10.1172/JCI103625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REIDENBERG M. M., OHLER E. A., SEVY R. W., HARAKAL C. Hemodynamic changes in adrenalectomized dogs. Endocrinology. 1963 Jun;72:918–923. doi: 10.1210/endo-72-6-918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROEMMELT J. C., SARTORIUS O. W., PITTS R. F. Excretion and reabsorption of sodium and water in the adrenalectomized dog. Am J Physiol. 1949 Oct;159(1):124–136. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1949.159.1.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. W., Earley L. E. Effects of hematocrit on renal hemodynamics and sodium excretion in hydropenic and volume-expanded dogs. J Clin Invest. 1970 Sep;49(9):1656–1667. doi: 10.1172/JCI106383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Share L., Travis R. H. Plasma vasopressin concentration in the adrenally insufficient dog. Endocrinology. 1970 Feb;86(2):196–201. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-2-196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolte H., Brecht J. P., Wiederholt M., Hierholzer K. Einfluss von Adrenalektomie und Glucocorticoiden auf die Wasserpermeabilität corticaler Nephronabschnitte der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;299(2):99–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


