Abstract
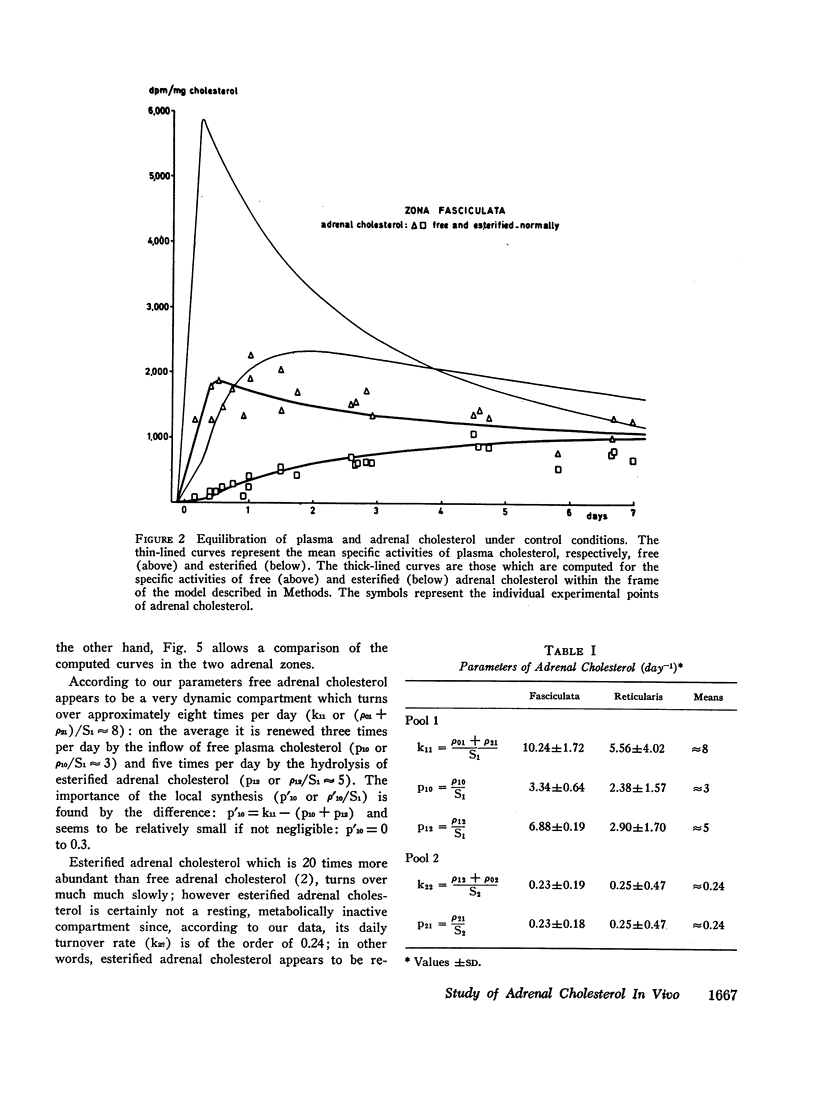
The kinetics of plasma and adrenal cholesteral equilibration were analyzed in patients undergoing bilateral adrenalectomy for generalized mammary carcinoma. A biological model is proposed to help in the understanding of adrenal cholesterol physiology. It comprises two intracellular compartments: (1) A compartment of free adrenal cholesterol which is small (of the order of 17 mg) but turns over very fast; it is renewed approximately 8 times per day: 3 times by the inflow of free plasma cholesterol, and 5 times by the hydrolysis of esterified adrenal cholesterol, the contribution of adrenal cholesterol synthesis appearing to be relatively small. (2) A compartment of esterified adrenal cholesterol which is 20 times larger; it is constantly renewed by in situ esterification and hydrolysis with a daily fractional turnover rate of the order of 0.25. The direct and selective accumulation of plasma cholesteryl esters is practically absent. Only free adrenal cholesterol returns to plasma, mostly after conversion into steroid “hormones.”
However small the synthesis of adrenal cholesterol may be, it seems more important in the zona “reticularis.” On the other hand, the inflow of plasma cholesterol and the turnover of the free adrenal compartment tend to be faster in the zona “fasciculata.” The equilibration of plasma and adrenal cholesterol can proceed unmodified under conditions of ACTH suppression.
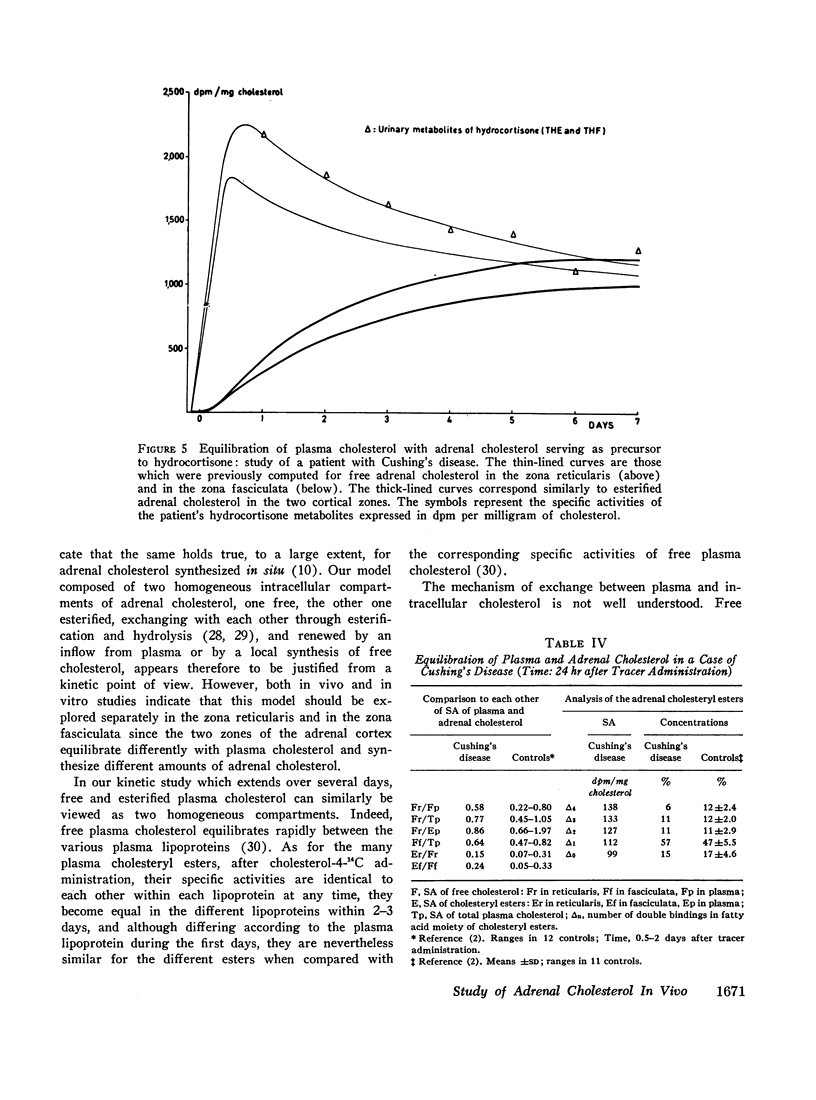
In one patient with Cushing's disease the size of the two adrenal compartments was clearly increased but their equilibration with plasma cholesterol proceeded normally. In another patient the kinetics of hydrocortisone corresponded to those of free adrenal cholesterol in the control studies.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., CANN M. C., HEARD R. D., JELLINCK P. H., O'DONNELL V. J., RAO B. G., WEBB J. L. Biogenesis of the sterols and steroid hormones; steroid biogenesis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1956;12:45-71; discussion, 71-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROT N., LOSSOW W. J., CHAIKOFF I. L. IN VITRO UPTAKE AND HYDROLYSIS, BY RAT TISSUES, OF CHOLESTEROL ESTERS OF A VERY LOW DENSITY, CHYLE LIPOPROTEIN FRACTION. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:63–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON R. B., ZAFFARONI, KEUTMANN E. H. Paper chromatography of steroids. II. Corticosteroids and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1951 Feb;188(2):763–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSH I. E. Methods of paper chromatography of steroids applicable to the study of steroids in mammalian blood and tissues. Biochem J. 1952 Jan;50(3):370–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0500370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird D. T., Horton R., Longcope C., Tait J. F. Steroid dynamics under steady-state conditions. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:611–664. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571125-8.50017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkowski A. J., Levin S., Delcroix C., Klastersky J. Equilibration of plasma and adrenal cholesterol in man. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Jan;28(1):42–49. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell G. L., Berman M., Robertson J. S. Nomenclature for tracer kinetics. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1968 Mar;19(3):249–262. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(68)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHOBANIAN A. V., HOLLANDER W. Body cholesterol metabolism in man. I. The equilibration of serum and tissue cholesterol. J Clin Invest. 1962 Sep;41:1732–1737. doi: 10.1172/JCI104631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christophe A., Matthijs F. New method for the determination of the fatty acid pattern of serum lipid classes. Clin Chim Acta. 1967 Apr;16(1):39–43. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(67)90267-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAILEY R. E., SWELL L., FIELD H., Jr, TREADWELL C. R. Adrenal cholesterol ester fatty acid composition of different species. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Oct;105:4–6. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-25990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAILEY R. E., SWELL L., TREADWELL C. R. Hydrolysis and utilization of cholesterol esters for steroid synthesis by canine adrenal homogenates. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Mar;100:360–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRUCKER W. D., SFIKAKIS A., BORKOWSKI A. J., CHRISTY N. P. ON THE RATE OF FORMATION OF STERIDAL GLUCURONOSIDES IN PATIENTS WITH FAMILIAL AND ACQUIRED JAUNDICE. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:1952–1967. doi: 10.1172/JCI105069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. W., Garren L. D. Evidence for the stimulation by adenocorticotropic hormone of the conversion of cholesterol esters to cholesterol in the adrenal, in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 8;24(5):805–810. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90398-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. W., Garren L. D. On the mechanism of action of adrenocorticotropic hormone. The inhibitory site of cycloheximide in the pathway of steroid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 10;243(19):5153–5157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter R. N., Fishman L. M., Ney R. L., Liddle G. W. An effect of adrenocorticotrophic hormone on adrenal cholesterol accumulation. Endocrinology. 1967 Nov;81(5):1185–1187. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-5-1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbie J. W., Symington T. The human adrenal gland with special reference to the vasculature. J Endocrinol. 1966 Apr;34(4):479–489. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0340479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EBERLEIN W. R., BONGIOVANNI A. M. New solvent systems for the resolution of corticosteroids by paper chromatography. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Nov;59(1):90–96. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90465-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W., Long J. A., Jones A. L. The ultrastructure of endocrine glands. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:315–380. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571125-8.50010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. S. THE IN VIVO TURNOVER OF INDIVIDUAL CHOLESTEROL ESTERS IN HUMAN PLASMA LIPOPROTEINS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Nov;43:2026–2036. doi: 10.1172/JCI105077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIFFITHS K., GRANT J. K., SYMINGTON T. A BIOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FUNCTIONAL ZONATION OF THE ADRENAL CORTEX IN MAN. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1963 Aug;23:776–785. doi: 10.1210/jcem-23-8-776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A. The plasma lecithins:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S. Cholesterol ester metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1965 Oct;45(4):747–839. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.4.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECHTER O., SOLOMON M. M., ZAFFARONI A., PINCUS G. Transformation of cholesterol and acetate to adrenal cortical hormones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Sep;46(1):201–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. E. Parametric sensitivity of physiological systems--prognostic analysis. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1967 Oct;14(4):209–215. doi: 10.1109/tbme.1967.4502507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang P. D., Insull W., Jr Lipid droplets in atherosclerotic fatty streaks of human aorta. J Clin Invest. 1970 Aug;49(8):1479–1488. doi: 10.1172/JCI106365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ney R. L., Dexter R. N., Davis W. W., Garren L. D. A study of mechanisms by which adrenocorticotropic hormone maintains adrenal steroidogenic responsiveness. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1916–1924. doi: 10.1172/JCI105681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RILEY C. Lipids of human adrenals. Biochem J. 1963 Jun;87:500–507. doi: 10.1042/bj0870500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAVARD K., MARSH J. M., RICE B. F. GONADOTROPINS AND OVARIAN STEROIDOGENESIS. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1965;21:285–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHYAMALA G., LOSSOW W. J., CHAIKOFF I. L. ESTERIFICATION OF CHOLESTEROL AND HYDROLYSIS OF CHOLESTEROL OLEATE BY HOMOGENATES OF BOVINE ADRENAL GLANDS AND THEIR SUBCELLULAR COMPONENTS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jan;118:138–142. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPERRY W. M., WEBB M. A revision of the Schoenheimer-Sperry method for cholesterol determination. J Biol Chem. 1950 Nov;187(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker V. N., Adams G. H. Circulating lipoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:113–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyamala G., Lossow W. J., Chaikoff I. L. Esterification of cholesterol by rat adrenal gland homogenates and subcellular components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 1;116(3):543–554. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart J. Adrenal blood flow and the adrenocortical response to corticotropin. Am J Physiol. 1965 Dec;209(6):1162–1168. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.6.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. G., Hall P. F. The side-chain cleavage of cholesterol and cholesterol sulfate by enzymes from bovine adrenocortical mitochondria. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2987–2997. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZILVERSMIT D. B. The design and analysis of isotope experiments. Am J Med. 1960 Nov;29:832–848. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilversmit D. B. Cholesterol flux in the atherosclerotic plaque. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Nov 21;149(2):710–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb53830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


