Abstract
Urea transport in proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and descending limb of Henle (DLH) was studied in perfused segments of rabbit nephrons in vitro.
Active transport of urea was ruled out in a series of experiments in which net transport of fluid was zero. Under these conditions the collected urea concentration neither increased nor decreased when compared to the mean urea concentration in the perfusion fluid and the bath.
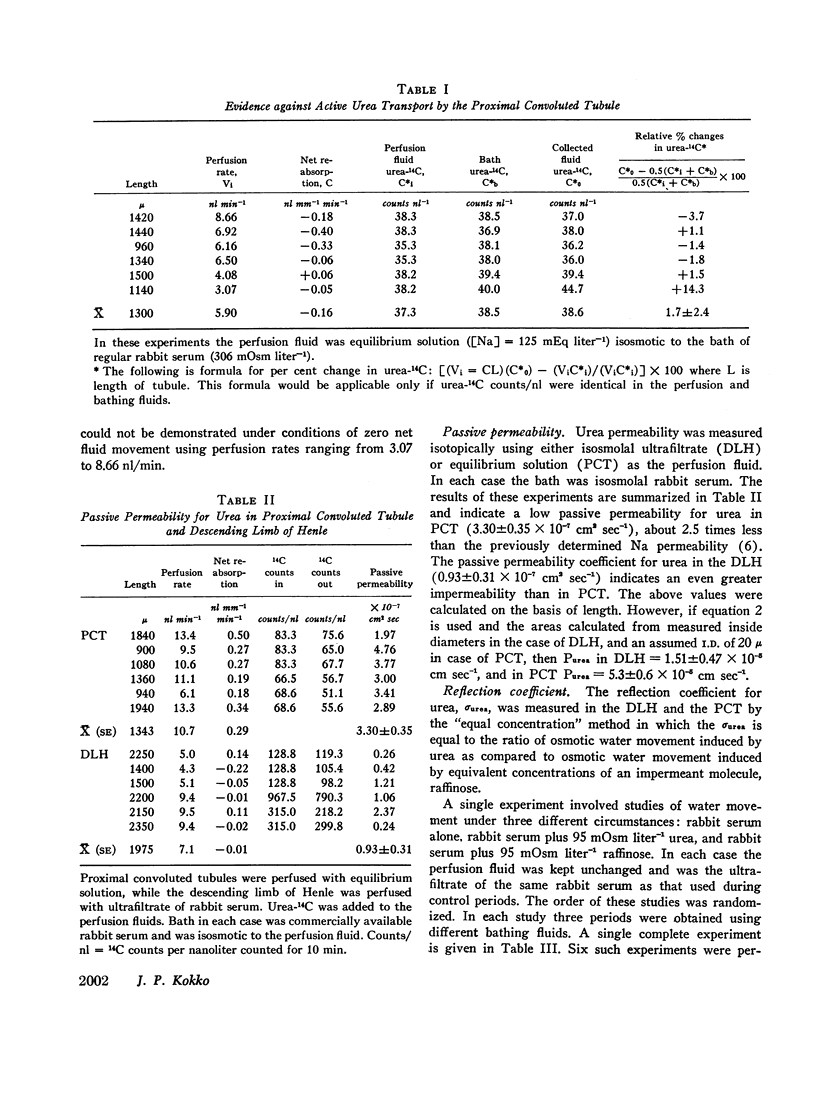
Permeability coefficient for urea (Purea) was calculated from the disappearance of urea-14C added to perfusion fluid. Measurements were obtained under conditions of zero net fluid movement: DLH was perfused with isosmolal ultrafiltrate (UF) of the same rabbit serum as the bath, while PCT was perfused with equilibrium solution (UF diluted with raffinose solution for fluid [Na] = 127 mEq/liter). Under these conditions Purea per unit length was 3.3±0.4 × 10-7 cm2/sec (5.3±0.6 × 10-5 cm/sec assuming I.D. = 20μ) in PCT and 0.93±0.4 × 10-7 cm2/sec (1.5±0.5 × 10-5 cm/sec) in DLH. When compared to previously published results, these values show that the PCT is 2.5 times less permeable to urea than to Na, while the DLH is as impermeable to urea as to Na. These results further indicate that the DLH is less permeable to both Na and urea than the PCT.
The reflection coefficient for urea, σurea, was calculated as the ratio of induced solution efflux when 95 mOsm/liter of urea was added to the bath, as compared to net fluid movement induced by addition to the bath of equivalent amount of raffinose, σurea in DLH is 0.95±0.4 as compared to 0.91±0.05 in PCT. σurea in DLH is approximately equal to σNa; however, σurea in PCT is higher than σNa (0.68).
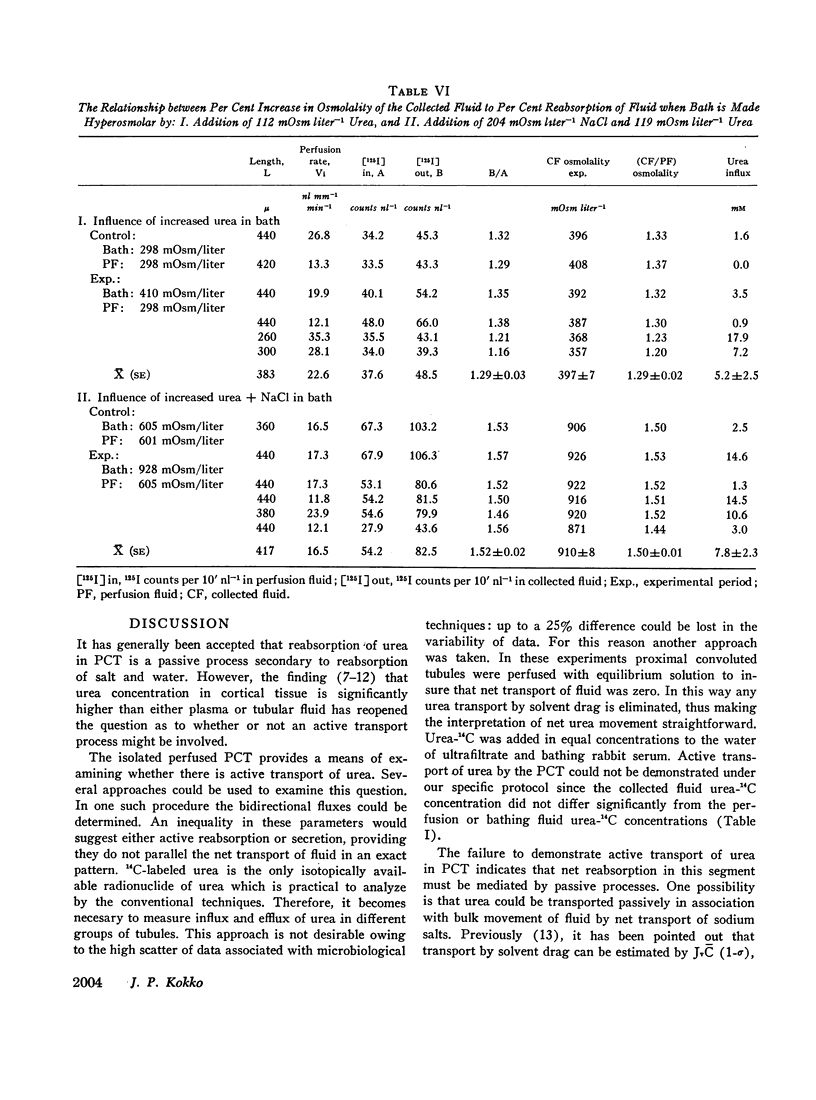
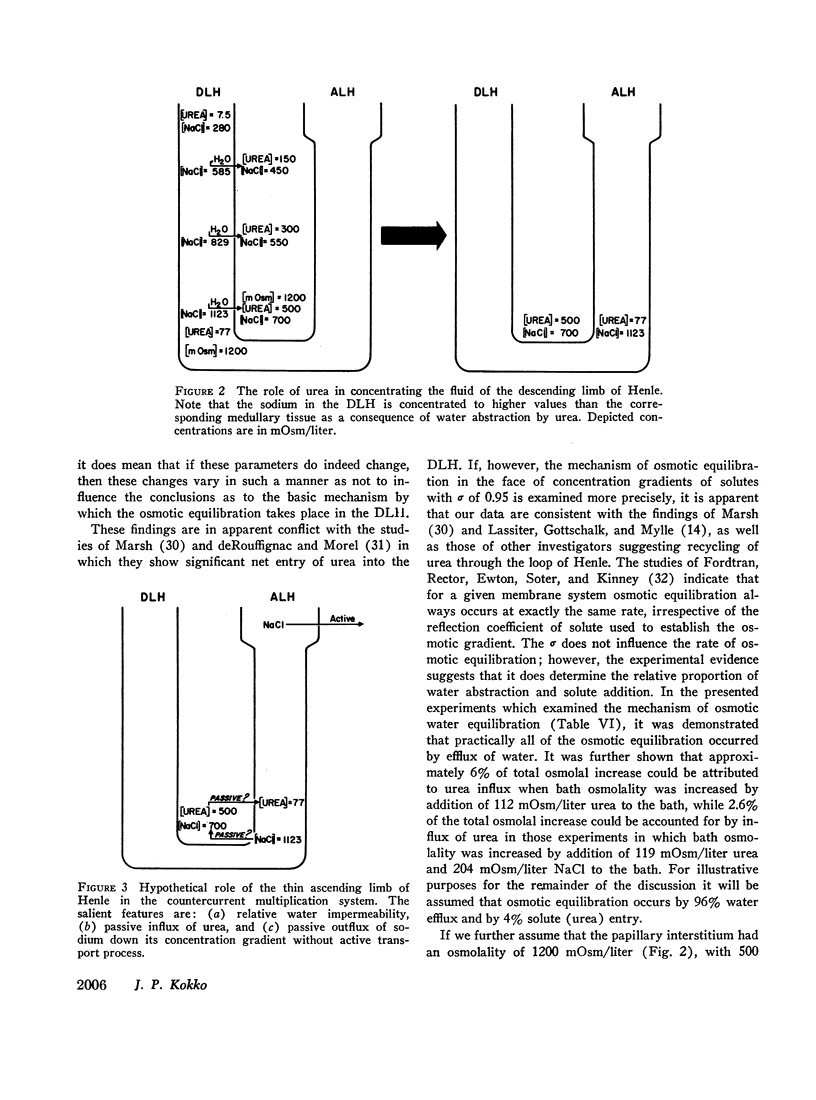
Several types of studies were conducted to examine the role of urea and urea plus sodium chloride in concentrating the fluid in the DLH. From the obtained results it was concluded that the intraluminal fluid of DLH is primarily concentrated by abstraction of water without significant net entry of solute. These results are discussed with respect to possible significance in the overall operation of the countercurrent system.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAY G. A., PRESTON A. S. Effect of urea on urine concentration in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:1952–1960. doi: 10.1172/JCI104420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODSKY W. A., SCHILB T. P. OSMOTIC PROPERTIES OF ISOLATED TURTLE BLADDER. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jan;208:46–57. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Grantham J., Abramow M., Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapp J. R. Renal tubular reabsorption of urea in normal and protein-depleted rats. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1304–1308. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAINTY J., GINZBURG B. Z. THE MEASUREMENT OF HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY (OSMOTIC PERMEABILITY TO WATER) OF INTERNODAL CHARACEAN CELLS BY MEANS OF TRANSCELLULAR OSMOSIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jan 27;79:102–111. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Ewton M. F., Soter N., Kinney J. Permeability characteristics of the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1965 Dec;44(12):1935–1944. doi: 10.1172/JCI105299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK C. W. OSMOTIC CONCENTRATION AND DILUTION OF THE URINE. Am J Med. 1964 May;36:670–685. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M., Wojtczak A. M., Ramirez M. A. Uphill transport of urea in the dog kidney: effects of certain inhibitors. J Clin Invest. 1967 Mar;46(3):388–399. doi: 10.1172/JCI105540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Burg M. B. Effect of vasopressin and cyclic AMP on permeability of isolated collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):255–259. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEDEM O., KATCHALSKY A. Thermodynamic analysis of the permeability of biological membranes to non-electrolytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Feb;27(2):229–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90330-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauker M. L., Lassiter W. E., Gottschalk C. W. Micropuncture study of net transtubular movement of urea and water in rats expanded with isotonic saline. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jan;133(1):216–221. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P., Burg M. B., Orloff J. Characteristics of NaCl and water transport in the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):69–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI106485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P. Sodium chloride and water transport in the descending limb of Henle. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1838–1846. doi: 10.1172/JCI106401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSITER W. E., GOTTSCHALK C. W., MYLLE M. Micropuncture study of net transtubular movement of water and urea in nondiuretic mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jun;200:1139–1147. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.6.1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSITER W. E., MYLLE M., GOTTSCHALK C. W. NET TRANSTUBULAR MOVEMENT OF WATER AND UREA IN SALINE DIURESIS. Am J Physiol. 1964 Apr;206:669–673. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.4.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassiter W. E., Mylle M., Gottschalk C. W. Micropuncture study of urea transport in rat renal medulla. Am J Physiol. 1966 May;210(5):965–970. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.5.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH D. J., SOLOMON S. ANALYSIS OF ELECTROLYTE MOVEMENT IN THIN HENLE'S LOOPS OF HAMSTER PAPILLA. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jun;208:1119–1128. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.6.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. J. Solute and water flows in thin limbs of Henle's loop in the hamster kidney. Am J Physiol. 1970 Mar;218(3):824–831. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.3.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T., Berliner R. W. Permeability of the loop of Henle, vasa recta, and collecting duct to water, urea, and sodium. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):108–115. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz L. Enhancement of renal concentrating ability in the rat by acetamide and methylurea. Am J Physiol. 1968 Apr;214(4):737–744. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.4.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roch-Ramel F., Chomety F., Peters G. Urea concentrations in tubular fluid and in renal tissue of nondiuretic rats. Am J Physiol. 1968 Aug;215(2):429–438. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.2.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roch-Ramel F., Diézi J., Chométy F., Michoud P., Peters G. Disposal of large urea overloads by the rat kidney: a micropuncture study. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jun;218(6):1524–1532. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.6.1524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roch-Ramel F., Peters G. Intrarenal urea and electrolyte concentrations as influenced by water diuresis and by hydrochlorothiazide. Eur J Pharmacol. 1967 Mar;1(2):124–139. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(67)90049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT-NIELSEN B., O'DELL R. Effect of diet on distribution of urea and electrolytes in kidneys of sheep. Am J Physiol. 1959 Oct;197:856–860. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.197.4.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUNIGER B., SCHMIDT-NIELSEN B. INTRARENAL DISTRIBUTION OF UREA AND RELATED COMPOUNDS: EFFECTS OF NITROGEN INTAKE. Am J Physiol. 1964 Nov;207:971–978. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.5.971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUNIGER B., SCHMIDT-NIELSEN B. INTRARENAL DISTRIBUTION OF UREA AND RELATED COMPOUNDS: EFFECTS OF NITROGEN INTAKE. Am J Physiol. 1964 Nov;207:971–978. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.5.971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULLRICH K. J., SCHMIDT-NIELSON B., O'DELL R., PEHLING G., GOTTSCHALK C. W., LASSITER W. E., MYLLE M. Micropuncture study of composition of proximal and distal tubular fluid in rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1963 Apr;204:527–531. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Rumrich G., Schmidt-Nielsen B. Urea transport in the collecting duct of rats on normal and low protein diet. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1967;295(2):147–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00362746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rouffignac C., Morel F. Micropuncture study of water, electrolytes, and urea movements along the loops of henle in psammomys. J Clin Invest. 1969 Mar;48(3):474–486. doi: 10.1172/JCI106005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


