Abstract
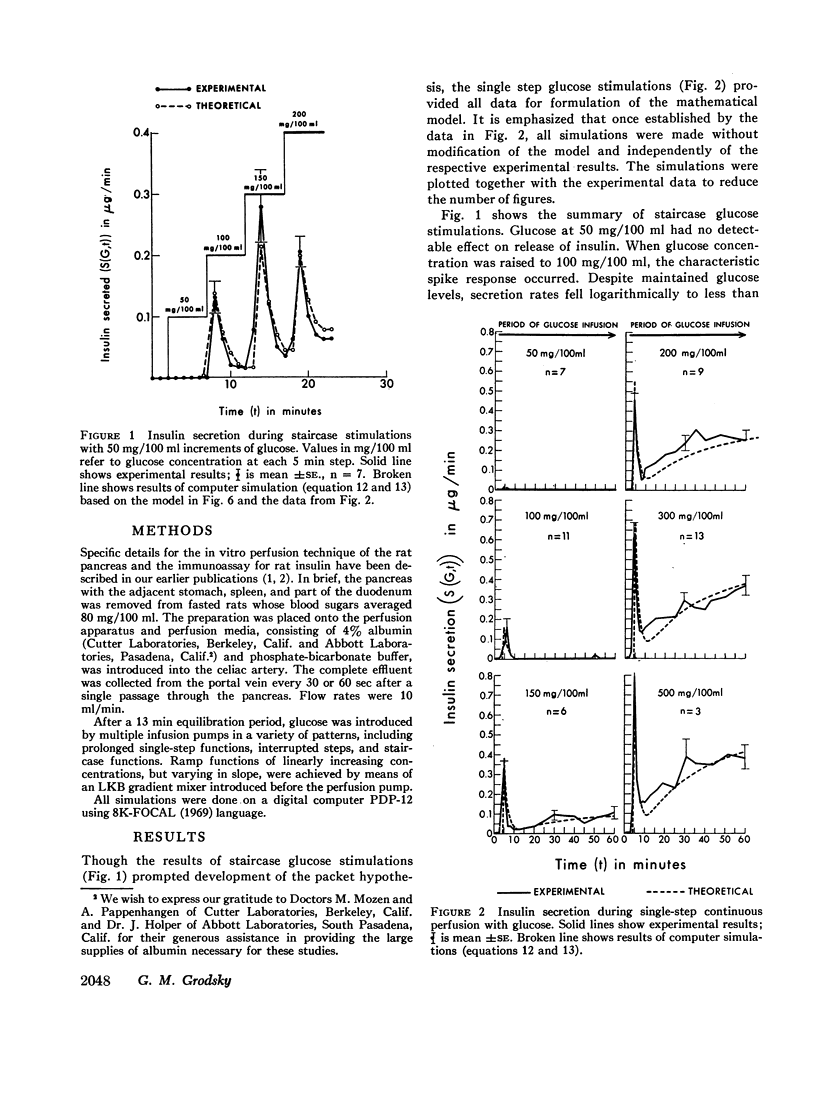
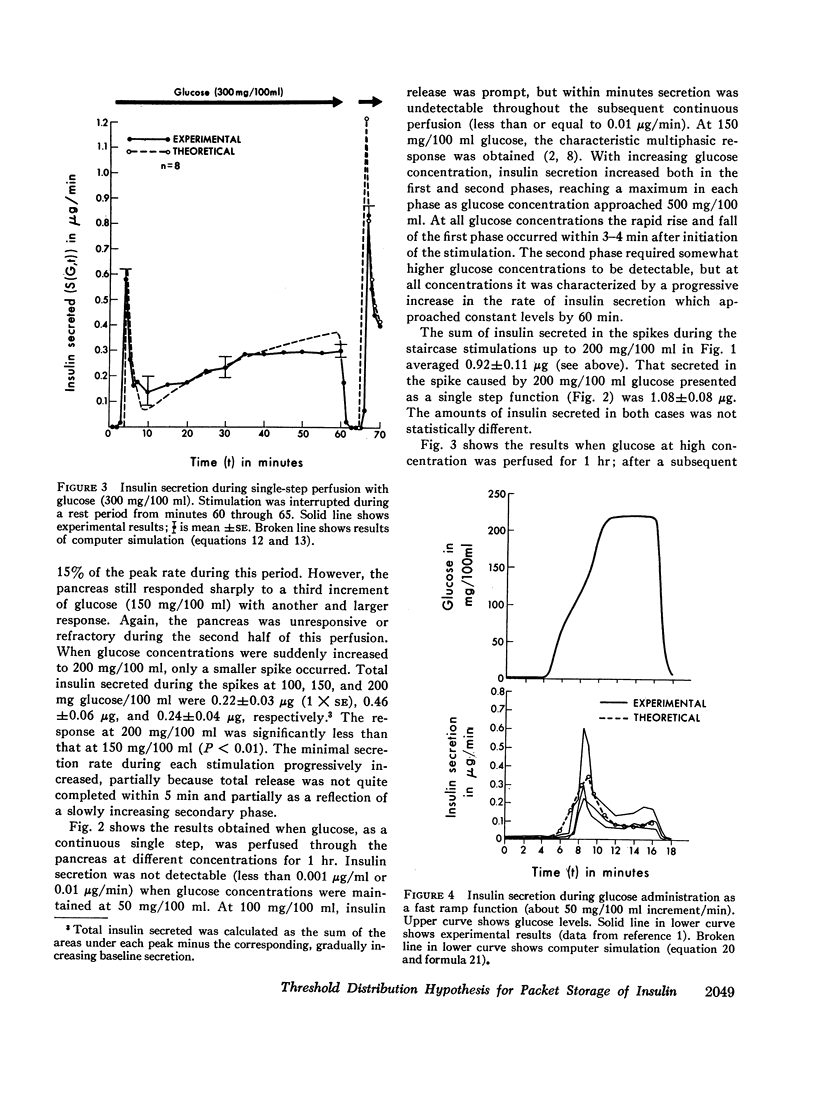
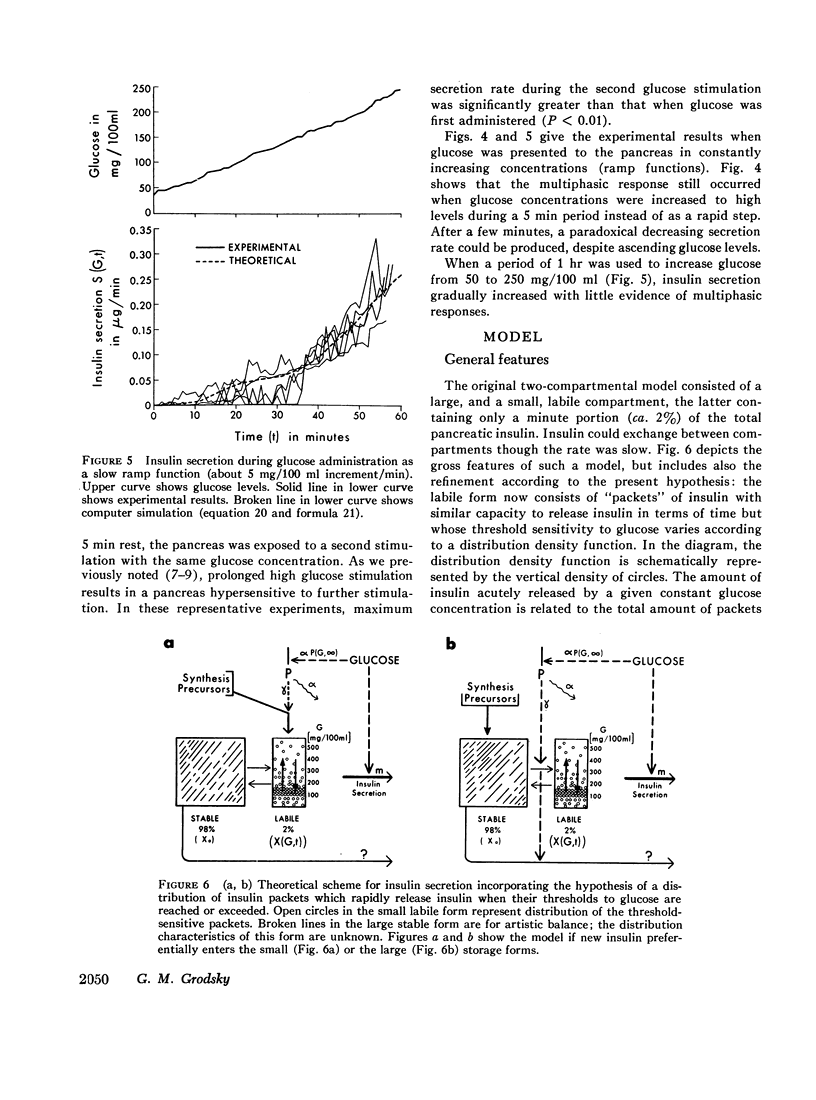
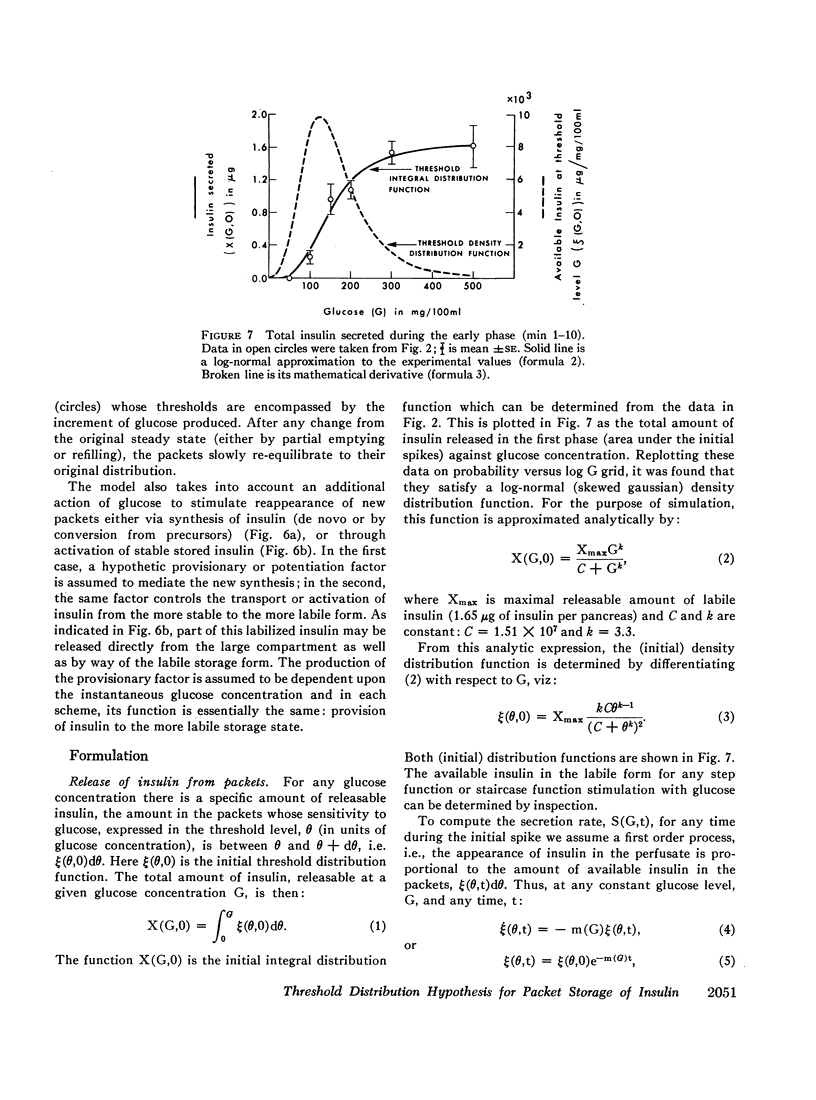
Phases of insulin release were studied in the perfused pancreas during a variety of glucose stimulation patterns. Patterns included staircase stimulations, constant prolonged single steps, restimulations, and ramp functions. Except at low concentrations, prolonged single steps of glucose elicited early spikes of insulin and a slowly rising second phase. Total insulin in the initial spikes increased with higher glucose concentrations. However, the time-related pattern of these spikes was similar in all cases; ratios of initial secretion rate to total insulin released were constant. Total insulin released in this early phase approximated a sigmoidal function of glucose concentration; mathematical differentiation of this function gave a skewed bell-shaped distribution curve. Staircase stimulations caused insulin to be released as a series of transient spikes which did not correlate with the increment of glucose but rather to the available insulin for a given glucose concentration minus that released in previous steps. The sum of total insulin released as spikes in a staircase series leading to a given glucose concentration was the same as when that concentration was used as a single step. Interrupted prolonged glucose infusions indicated the second phase of insulin release could prime the pancreas and that the first and second phases were interrelated. When glucose was perfused as ramp functions of slow, increasing, concentration, phasic response disappeared.
A previous two-compartmental model was expanded to include a threshold or sensitivity distribution hypothesis. This hypothesis proposes that labile insulin is not stored in a homogeneous form but as packets with a bell-shaped distribution of thresholds to glucose. These packets respond quickly when their threshold levels to glucose are reached or exceeded. Data from single step stimulations were utilized for constructing a mathematical model which simulated satisfactorily the various stimulation patterns.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basabe J., Lopez N., Viktora J., Wolff F. Studies of insulin secretion in the perfused rat pancreas. Effect of diazoxide and A025. Diabetes. 1970 Apr;19(4):271–281. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.4.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bencosme S. A., Tsutsumi V., Martin J. M., Akerblom H. K. Ultrastructural changes in B cells of pancreatic islets from rats with elevated levels of circulating growth hormone secreted by MtT-W15 tumor. Diabetes. 1971 Jan;20(1):15–26. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. L., Feldberg W. The acetyloholine metabolism of a sympathetic ganglion. J Physiol. 1936 Dec 11;88(3):265–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1936.sp003439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Balant L., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E., Grodsky G. Dynamic aspects of proinsulin release from perifused rat pancreas. Lancet. 1969 Oct 25;2(7626):882–883. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Balant L., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. Perifusion of rat pancreatic tissue in vitro: substrate modification of theophylline-induced biphasic insulin release. J Clin Invest. 1970 Nov;49(11):2097–2105. doi: 10.1172/JCI106427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Chowers I., Luft R., Widström A. The significance of the blood glucose level for plasma insulin response to intravenously administered tolbutamide in healthy subjects. Diabetologia. 1969 Oct;5(5):343–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00452910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R., Efendic S. Decreased sensitivity of the pancreatic beta cells to glucose in prediabetic and diabetic subjects. A glucose dose-response study. Diabetes. 1972 Apr;21(4):224–234. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.4.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R. The plasma insulin response to glucose infusion in healthy subjects and in diabetes mellitus. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 Jun;55(2):278–304. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0550278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
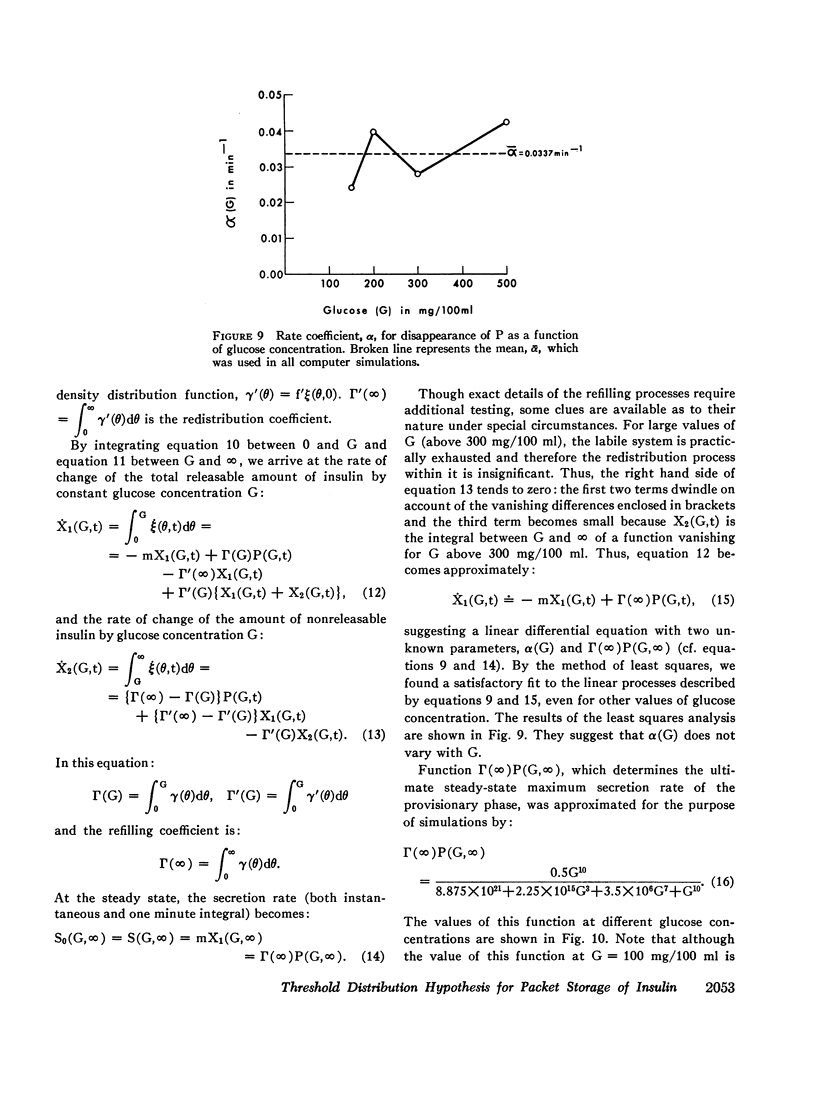
- Clark J. L., Steiner D. F. Insulin biosynthesis in the rat: demonstration of two proinsulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):278–285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Grodsky G. M. Dynamics of insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1968 Sep;83(3):572–584. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-3-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRERICHS H., REICH U., CREUTZFELDT W. INSULINSEKRETION IN VITRO. I. HEMMUNG DER GLUCOSEINDUZIERTEN INSULINABGABE DURCH INSULIN. Klin Wochenschr. 1965 Feb 1;43:136–140. doi: 10.1007/BF01484504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Curry D., Landahl H., Bennett L. [Further studies on the dynamic aspects of insulin release in vitro with evidence for a two-compartmental storage system]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1969 Sep;6 (Suppl 1):554–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M. Insulin and the pancreas. Vitam Horm. 1970;28:37–101. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60888-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
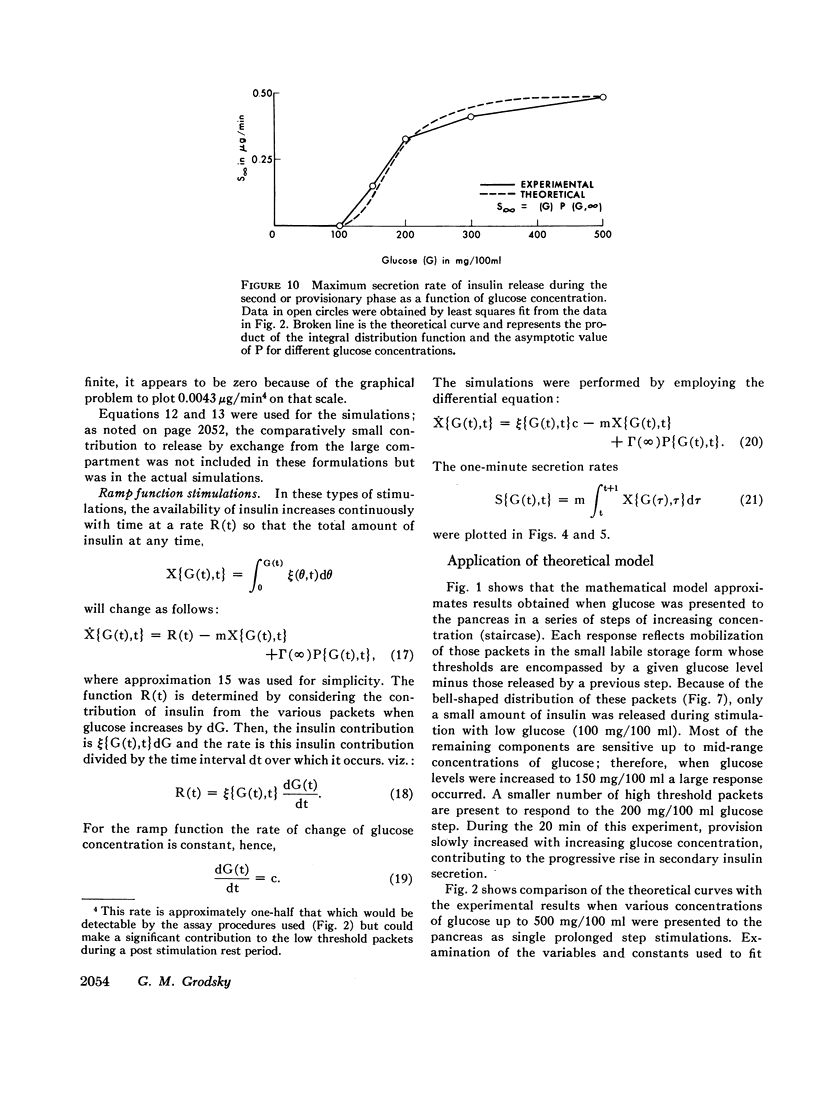
- Iversen J., Miles D. W. Evidence for a feedback inhibition of insulin on insulin secretion in the isolated, perfused canine pancreas. Diabetes. 1971 Jan;20(1):1–9. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen J. Secretion of glucagon from the isolated, perfused canine pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2123–2136. doi: 10.1172/JCI106706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. D., Palade G. E. Role of the Golgi complex in the intracellular transport of secretory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):424–431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Howell S. L., Young D. A., Fink C. J. New hypothesis of insulin secretion. Nature. 1968 Sep 14;219(5159):1177–1179. doi: 10.1038/2191177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Grodsky G. M., Bennett L. L., Smith-Kyle D. F., Craw L. Ultrastructure of beta-cells during the dynamic response to glucose and tolbutamide in vitro. Diabetologia. 1970 Dec;6(6):542–543. doi: 10.1007/BF00418219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Chick W. L. Studies in the diabetic mutant mouse. I. Light microscopy and radioautography of pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1970 Jun;6(3):207–215. doi: 10.1007/BF01212231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loubatières A. [Stimulators and inhibitors of insulin secretion. Physiological and pharmacological interferences. Synergisms and antagonisms]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1968 Oct;5 (Suppl 1):220–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Lacy P. E., Wright P. H. Insulin secretion by isolated islets in presence of glucose, insulin and anti-insulin serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Feb;124(2):497–500. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W., Malaisse-Lagae F., Wright P. H. A new method for the measurement in vitro of pancreatic insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1967 Jan;80(1):99–108. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W., Malaisse-Lagae F. [A possible role for calcium in the stimulus-secretion coupling for glucose-induced insulin secretion]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1970 Sep;7 (Suppl 1):264–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melani F., Rubenstein A. H., Steiner D. F. Human serum proinsulin. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):497–507. doi: 10.1172/JCI106259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E., Beaven D., Lambert A., Rouiller C. [Ultrastructural events associated with the action of tolbutamide and glybenclamide on pancreatic B-cells in vivo and in vitro]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1969 Sep;6 (Suppl 1):271–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Pupo A. A. Insulin responses to glucose: evidence for a two pool system in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2309–2319. doi: 10.1172/JCI106197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs H., Haller E. W. Further studies on the capacity of the neurohypophysis to release vasopressin. Endocrinology. 1968 Aug;83(2):251–262. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood L. M., Mayer G. P., Ramberg C. F., Jr, Kronfeld D. S., Aurbach G. D., Potts J. T., Jr Regulation of parathyroid hormone secretion: proportional control by calcium, lack of effect of phosphate. Endocrinology. 1968 Nov;83(5):1043–1051. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-5-1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F. Proinsulin and the biosynthesis of insulin. N Engl J Med. 1969 May 15;280(20):1106–1113. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196905152802008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese T., Lazarus N. R., Devrim S., Recant L. Synthesis and release of proinsulin and insulin by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jul;49(7):1394–1404. doi: 10.1172/JCI106357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart J., Li C. C. The dynamics of adrenocortical secretion. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jan;214(1):73–85. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Hoyos-Guevara E. The pancreatic islet system of the mouse (Mus musculus). Ultrastructural report of six new cell types. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969 Oct 1;101(1):28–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00335584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


