Abstract
Factor VIII (antihemophilic globulin) has been prepared from Hyland method IV AHG and cryoprecipitate using limited chymotryptic digestion followed by Sepharose gel filtration. The activity of factor VIII is unaffected by the digestion procedure, while fibrinogen in converted to large noncoagulable fragments.
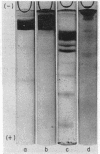
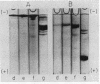
The purified factor VIII has been found to be a macromolecular glycoprotein with a major subunit of 240,000, as shown by sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Carbohydrate analysis of factor VIII gave values of 1% sialic acid, 2.8% hexosamine, and 1-2% hexose (mannose, galactose, and fucose). The lipid content was found to be less than 5% of the protein content, and included no detectable phospholipid. The amino acid content is also reported. Immunoelectrophoretic analysis using rabbit antibody to purified factor VIII produced a single precipitin line.
The chymotrypsin digestion step facilitates the preparation of factor VIII by reducing the viscosity of fibrinogen in the crude starting material, thereby increasing fivefold the quantity of material which can be processed at one time. It also improves markedly the resolution between factor VIII and fibrinogen on gel filtration.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIGGS R., MACFARLANE R. G., DENSON K. W., ASH B. J. THROMBIN AND THE INTERACTION OF FACTORS 8 AND 9. Br J Haematol. 1965 May;11:276–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb06588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck M., Blombäck B. Fractions rich in factor VIII. Bibl Haematol. 1968;29:1116–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eylar E. H. On the biological role of glycoproteins. J Theor Biol. 1966 Jan;10(1):89–113. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Abrell E., Eagley J. Immunological studies of factor VIII (antihaemophiliac globulin) in haemophilia A. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 3;230(1):16–17. doi: 10.1038/newbio230016a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. A simple method for the purification of factor VIII (antihemophilic factor) employing snake venom. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jan;77(1):153–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershgold E. J., Davison A. M., Janszen M. E. Human factor VIII (antihemophilic factor): activa- tion and inactivation by phospholipases. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Feb;77(2):206–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershgold E. J., Davison A. M., Janszen M. E. Isolation and some chemical properties of human factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Feb;77(2):185–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershgold E. J., Pool J. G., Pappenhagen A. R. The potent antihemophilic globulin concentrate derived from a cold insoluble fraction of human plasma: characterization and further data on preparation and clinical trial. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Jan;67(1):23–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt J. P., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Human antihemophilic factor (AHF) purification: A comparison of two procedures. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 May 15;15(3):327–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass L., Ratnoff O. D., Leon M. A. Studies on the purification of antihemophilic factor (factor 8. I. Precipitation of antihemophilic factor by concanavalin A. J Clin Invest. 1969 Feb;48(2):351–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI105991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laico M. T., Ruoslahti E. I., Papermaster D. S., Dreyer W. J. Isolation of the fundamental polypeptide subunits of biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):120–127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSESSON M. W., FINLAYSON J. S. SUBFRACTIONS OF HUMAN FIBRINOGEN; PREPARATION AND ANALYSIS. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Oct;62:663–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Alkjaersig N., Sweet B., Sherry S. Human fibrinogen of relatively high solubility. Comparative biophysical, biochemical, and biological studies with fibrinogen of lower solubility. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3279–3287. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemetz J., Nossel H. L. Activated coagulation factors: in-vivo and in-vitro studies. Br J Haematol. 1969 Apr;16(4):337–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POOL J. G., ROBINSON J. Assay of plasma antihaemophilic globulin (AHG). Br J Haematol. 1959 Jan;5(1):17–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1959.tb04009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPAPORT S. I., SCHIFFMAN S., PATCH M. J., AMES S. B. The importance of activation of antihemophilic globulin and proaccelerin by traces of thrombin in the generation of intrinsic prothrombinase activity. Blood. 1963 Feb;21:221–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Kass L., Lang P. D. Studies on the purification of antihemophilic factor (factor VIII). II. Separation of partially purified antihemophilic factor by gel filtration of plasma. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):957–962. doi: 10.1172/JCI106055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simone J. V., Vanderheiden J., Abildgaard C. F. A semiautomatic one-stage factor 8 assay with a commercially prepared standard. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Apr;69(4):706–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trayer H. R., Nozaki Y., Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. Polypeptide chains from human red blood cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4485–4488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER B. H., MCLESTER W. D., SMITH M., BRINKHOUS K. M. PURIFICATION OF ANTIHEMOPHILIC FACTOR (FACTOR VIII) BY AMINO ACID PRECIPITATION. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Apr 15;11:64–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Kochwa S. Molecular forms of antihaemophilic globulin in plasma, cryoprecipitate and after thrombin activation. Br J Haematol. 1970 Jan;18(1):89–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Ratnoff O. D., Powell A. E. Immunologic differentiation of classic hemophilia (factor 8 deficiency) and von Willebrand's dissase, with observations on combined deficiencies of antihemophilic factor and proaccelerin (factor V) and on an acquired circulating anticoagulant against antihemophilic factor. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):244–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI106480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Mourik J. A., Mochtar I. A. Purification of human antihemophilic factor (factor VIII) by gel chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 22;221(3):677–679. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90247-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]